Future Development History of NFT Derivatives: From Commodity Speculation to Financial Speculation, Gradually Abstracted Asset Symbols
3. Hedging: People want to hedge the risks of holding non-financial products. (Short demand)
4. Portfolio diversification: People want to diversify the risk of their portfolio into new asset classes (both long and short demand).
Additionally, NFT derivatives also have a strong upward trend in the foreseeable future.
The trading volume of the FT derivatives market is about three times that of spot trading. Assuming similar momentum, the short-term best case for NFT derivatives could be at least three times that of blue-chip NFT spot trading volume (Est. $8B). Even if the NFT derivatives market does not become as large as the FT market, its growth momentum can still be expected.
- Why did Ethereum have two brief outages in a row? An analysis of the causes of the incident.
- After the explosion, searching for the past of BRC-20
- Facebook’s issue of stable currency is likely to fail
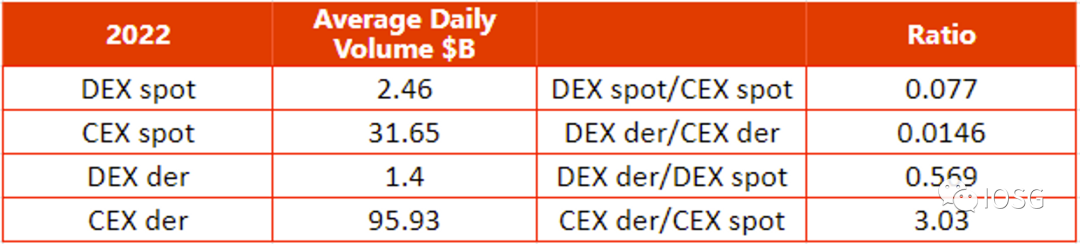
Because it shares the characteristics of illiquidity and difficult valuation, the financial evolution of real estate is also a good reference for the development of NFTs. Property derivatives: derivatives related to real estate debt, such as mortgage-backed securities (MBS) and credit default swaps (CDS), represent a huge market, with an estimated nominal value of over $100 trillion. The nominal value will exceed $100 trillion.
Next, we will analyze the two tracks of NFT futures and options respectively.
Futures (Perpetuals)
Like FT futures trading, NFT futures trading is also a lucrative business. NFTperp has successfully earned impressive trading fees from their testnet mainnet in three months. In addition, OpenSea’s profitability comes from its high fee (2.5%), although its trading volume is smaller than Uniswap’s. If the perpetual trading market of NFT can gain the favor of high-frequency and proprietary traders, even if the trading volume cannot reach the same level as FT perpetual trading, the future fee deduction is enough to make it have a decent return on investment.
Trader Feedback
In order to further clarify the value and potential user market of NFT perpetual trading, we collected the following feedback after interviewing dozens of traders:
- Mechanism issue: it should be a fair game (most important).
- Incentives and leverage are important: join for huge returns.
- Not concerned about manipulation in the spot market.
- No loyalty to the platform. Early adopters are not important to them.
- Small features like social communication will increase appeal.
Project Comparison
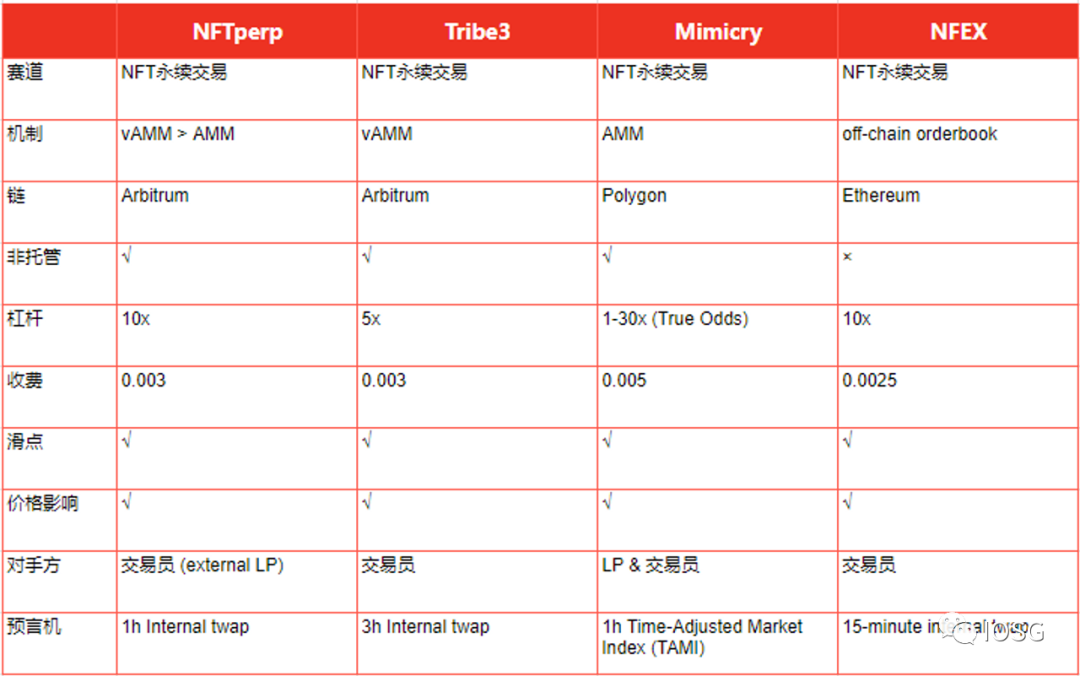
Case Analysis: NFTperp vs Tribe3
A. Similarities
NFTperp and Tribe3 both use vAMM design:
-
No need for real LP, no need for order book
-
The trader is the counterparty, and one trader’s profit is another trader’s loss.
-
Both traders will take slippage (usually with a 0.5% tolerance) when opening a position.
-
By adjusting the K value, the depth of the virtual pool can be dynamically adjusted to avoid the price fluctuations caused by excessive slippage (the larger the K value, the lower the slippage).
-
All profits and losses are settled in the insurance fund.
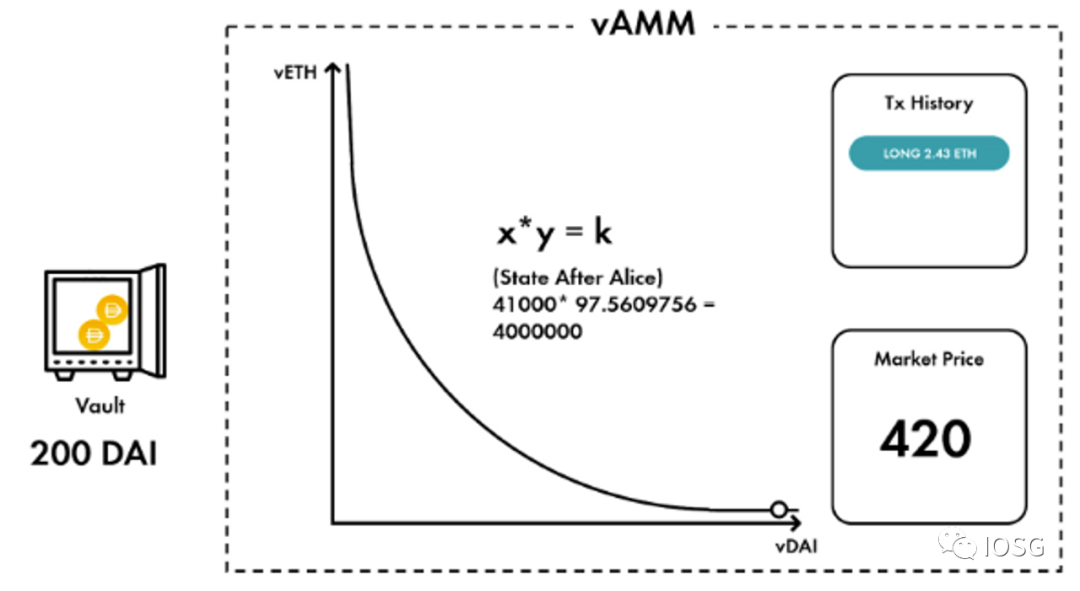
A Deep Dive into our Virtual AMM(vAMM)| by PerpetualProtocol
For a simple analysis of the advantages and disadvantages of the Orderbook, AMM, and vAMM mechanisms, see the following figure:
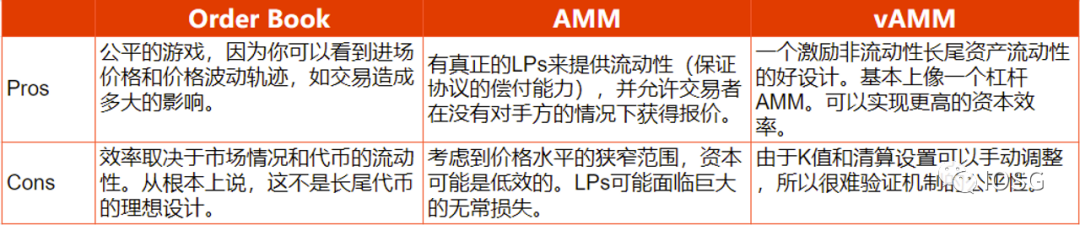
B. Differences
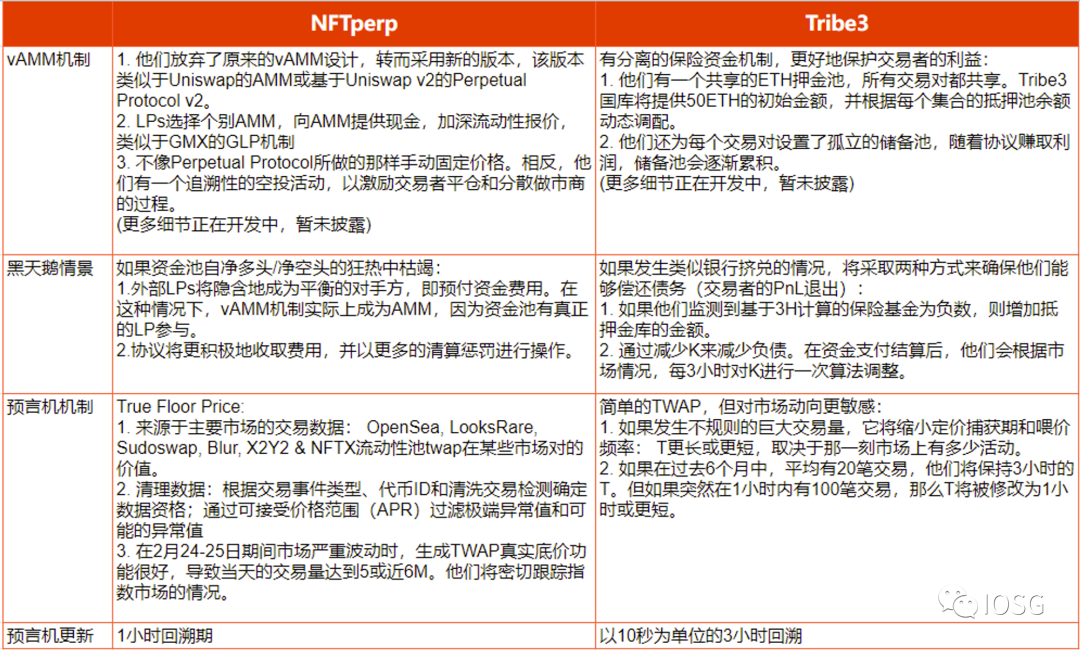
The main differences between NFTperp and Tribe3 are reflected in the vAMM mechanism design details, black swan scenario handling, oracle feeding and updating, among other aspects (see the figure below). However, it is still difficult to determine which mechanism can find PMF first, as success may depend heavily on whales’ acquisition capabilities and ecosystem development.
Potential Risks
1. Adoption Risk
Although there are opportunities for speculation with leverage, the speculation scope is limited. The derivative market has indeed lowered the threshold for speculation, but people’s mentality is still to treat NFTs as FTs. I doubt whether it is necessary to create a market that is infinitely similar to the token derivative market, even considering the existence of certain risk diversification needs.
Furthermore, there are no fundamentals (most FTs have some fundamentals, excluding meme coins) to help traders analyze strategies. In the case of NFTs, we can only rely on community activity/emotion and pure technical analysis to help make decisions, so professional traders without altcoin trading experience may be worried about getting burned in the game (the best estimate is that 1-2 proprietary traders have a risk position of up to $50 million in this business).
However, most NFTs can still be traded as altcoins, so from this point of view, derivatives of floor prices make sense. If one day NFTs can obtain more value, we can use the real estate market as an analogy. For people, speculating on the bottom price of New York real estate may still be interesting. But large-scale adoption definitely cannot be achieved in the short term, so the return theory will mainly focus on profitability.
2. Oracle Risk
The biggest technical risk should be the oracle attack and different types of oracle manipulation, such as MEV robots/front-running arbitrage.
The oracle mechanism is very critical in the construction of the entire perpetual exchange. I do think that the current market NFT oracle mechanism has flaws and some are centralized. They have not been attacked simply because they have not reached a high trading volume (limited arbitrage income) compared to FT perpetual exchanges.
The solution I think should be:
-
Integrate multiple oracles to avoid single node failures like perpetual protocol. It can reduce manipulation risks when different oracle reporters use different data processing mechanisms to send deterministic data to the blockchain.
-
Input source prices from multiple data providers. The calculation of the determined price of an NFT collection can be cross-checked by collecting sales data from Dune Analytics, Reservoir, OpenSea API, or custom subgraphs that monitor OpenSea smart contract events.
But according to my conversation with traders, they are not really concerned about manipulation in the spot market. And we have a consensus that the cost of attack would be very high, and it is unlikely to happen unless the NFT derivative market is ten times larger than the spot market (which is unlikely). Therefore, it will be extremely important to filter out NFT collections with low manipulation potential. As long as the filtering system makes sense (similar to the theory of NFT loans), inherent manipulation risks cannot prevent people from speculating.
Options
FT vs NFT
The price of each NFT is different at different times, just like investors in stock index futures will see differences in prices for different months. Like upstream trading in commodities, NFTs themselves have a high purchase threshold, large price steps, poor liquidity, and ordinary consumers or retail investors cannot buy and sell NFTs like they do with altcoins or immediately execute trades based on a spot price they see.
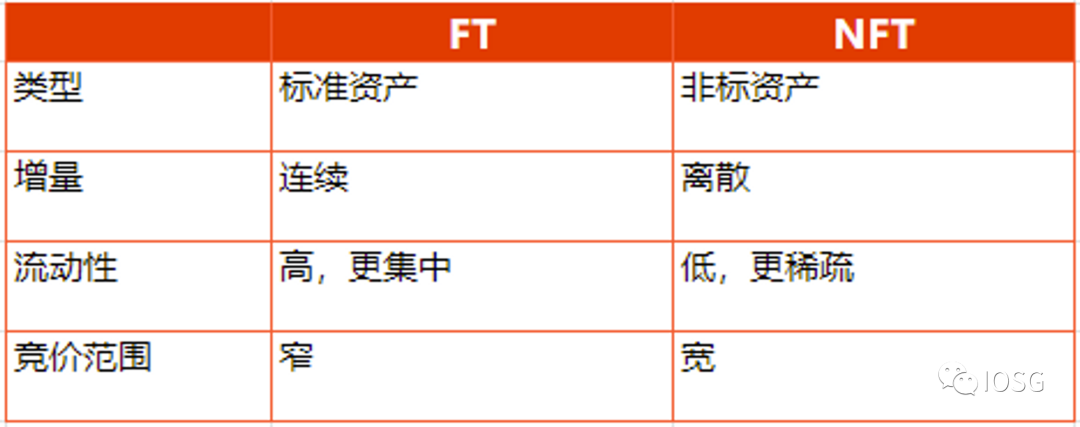
Therefore, NFT traders naturally have a certain demand for more flexible and diverse contracts and trading methods. In the current situation where liquidity is good and their own funds are sufficient, traders can choose to directly purchase spot products. When funds are short and confidence in the current market is low, traders can sign contracts for forward delivery to better arbitrage and hedge risks. For example, NFT traders can now sign spot contracts that will be executed within a few days, futures contracts that will be executed in one month, and futures contracts that will be executed in three months. Because market supply and demand expectations are different, the execution prices of these contracts are generally different.
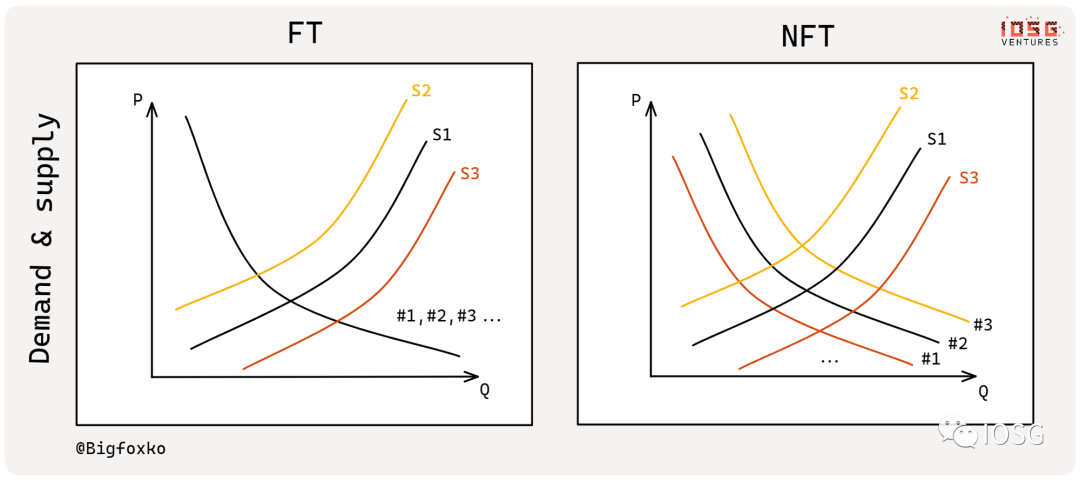
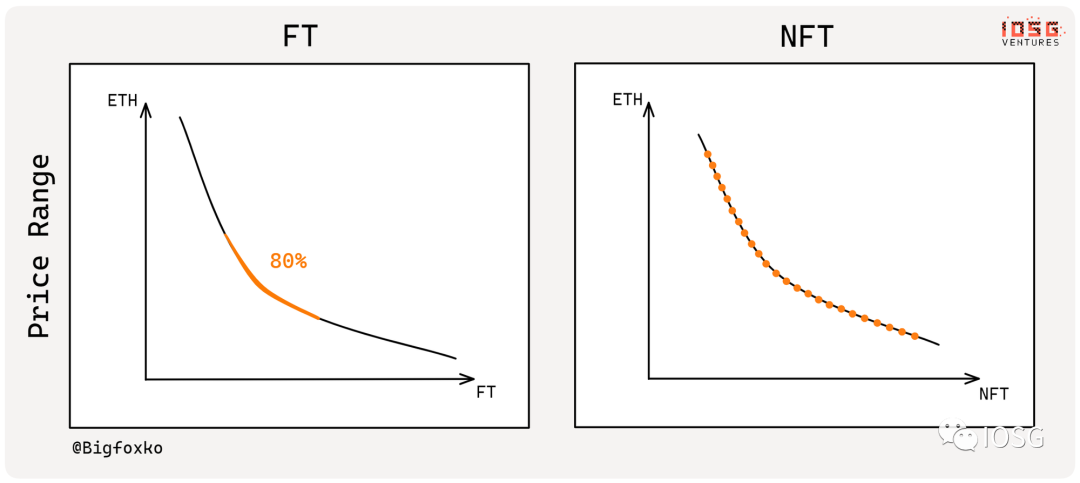
NFT futures vs options vs forward
Futures contracts actually represent standardized (securitized) forward contracts traded on public exchanges (OTC >> Floor). In traditional commodity trading, the trading volume of spot contracts is gradually decreasing, while the trading volume of forward contracts and futures contracts is increasing .
The difference between an options contract and a futures contract is that the buyer of an options contract has the right to refuse contract execution, and will pay an insurance fee for this right if the price drops.
For example, assuming that the option fee for a BAYC option position executed three months later is 3 eth/BAYC, the buyer needs to compare the expiration purchase price of the spot price and the current contract price to decide whether to sign. For example, if the current spot price is 50 eth/BAYC, it is only advantageous to sign the contract when the expiration spot price rises to more than 53 eth/BAYC. As a comparison, as long as the expiration spot price is higher than 50 eth, the futures contract will be cost-effective.
However, if the spot price of BAYC falls below 47 eth three months later, the options contract is better than the futures contract because you can refuse to execute the contract and directly buy the spot. In this case, the money you save by buying the spot is more than the options fee you pay. The buyer of an options contract can also transfer the contract to another person at a different price, which means that the option position/contract can be used or aggregated into financial instruments such as ETFs, or developed into more complex meta-markets (releasing more imagination for NFT structured products) .
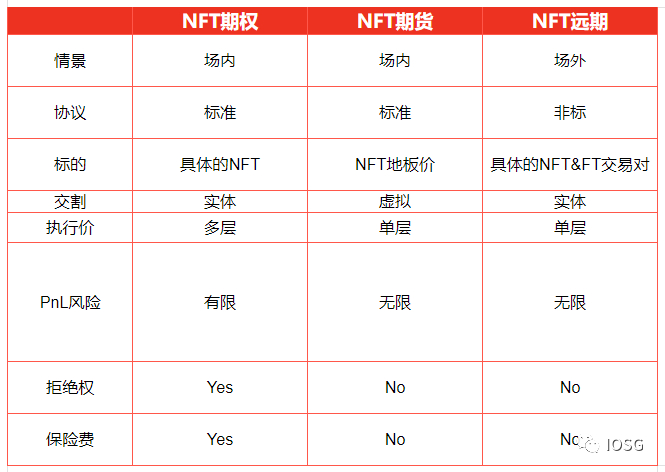
Comparison of Projects
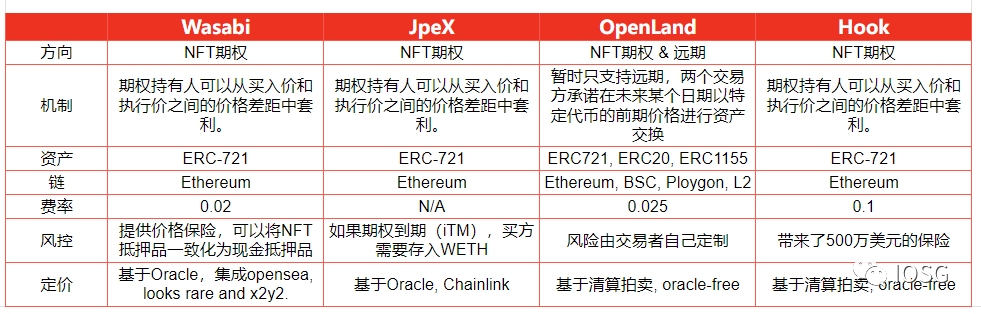
Potential Risks
The main risk is the adoption risk, which requires educating non-expert users. The appeal is likely to be provided primarily by market makers and professional traders in the early stages.
Conclusion
Finally, let’s talk about some financial philosophy.
The exploration of virtual item commercialization by Internet companies began as early as 20 years ago. The new generation of O2O is not online to offline, but on-chain to off-chain. NFTs in the art and gaming categories are just a small attempt of this non-standard protocol on the chain. As more and more off-chain assets are written into the chain in the form of NFTs, we may see the arrival of a new decade of NFT turbulence.
Ultimately, gold is valuable because people think it is valuable. The US dollar itself is just a symbol of a symbol. The disintegration of the gold standard has made value a fluctuating signal, and virtual capital does not have to follow the laws of value like the real economy. The market’s volatility depends more on the faith of symbol holders and subjective expectations of the future. The abstraction of this transaction itself is caused by the symbolization of underlying assets. Therefore, whether the underlying asset represented by this symbol is fiat currency, securities, tokens, or meaningless small pictures, it is no longer important. They are like history, not real, but chosen to believe .

The bold prediction is that eventually, what will be widely circulated on the market will no longer be value, but pure symbols, meaning, or faith. Everything is cycling back and forth with hedging, speculation, and side-stepping intertwined with the Minsky cycle.
It’s just money, it’s made up 🙂
We will continue to update Blocking; if you have any questions or suggestions, please contact us!
Was this article helpful?
93 out of 132 found this helpful
Related articles




