HyperCycle: An innovative blockchain architecture for AI algorithm data
HyperCycle: A new blockchain for AI algorithm data.The effect of quantitative change leading to qualitative change has been repeatedly verified in AI algorithm models. The iterative process from GPT1 to GPT4 is mainly due to changes in the number of parameters, which makes GPT4 possess intelligence that researchers find difficult to explain. If our ambitions are even greater and we bring together large and small models such as GPT, BingChat, midjourney, and Wenxin Yiyi, it is not an exaggeration to say that AI intelligence will rise to a new level in a short period of time.
This ambitious idea is called collective AI, where each AI model in the system will work together to solve complex problems. In simple terms, we can understand it as the difference between individual efforts and team collaboration – individuals in individual efforts need to be responsible for everything, while individuals in team collaboration only need to be responsible for part of it.
- Project Research | Canvas: Focused on DeFi, Layer2 Protocol Based on StareWare ZK Rollups
- Neutron: A new cross-chain DeFi blockchain on Cosmos
- Standing at the forefront of the Meme trend, how did Ben become a cryptocurrency legend from an unknown person?
Ideals are always full, and reality is always skinny. It is unrealistic to want these technology companies to turn their swords into plowshares and make common contributions to human development by voluntarily sharing their core algorithms and databases.
But what if we use blockchain technology to break this chain of suspicion?
Introduction to HyperCycle
It is not realistic to coordinate these AI technology giants through the assistance of organizations or other third-party institutions. We need a truly fair and just “supervisor” to maintain order in the game, and HyperCycle is such a role.
As early as 1995, Ben Goertzel, the core founder of HyperCycle and the chief AI scientist of SingularityAI, envisioned building a decentralized basic platform architecture for the global artificial intelligence network by leveraging the development bonus of the global Internet. However, due to objective conditions such as network hardware limitations, working in a safe and decentralized manner is very expensive, so this idea has always been just an idea.
When the time fast forwards to 2015, Ethereum proposed the concept of smart contracts. Although strictly speaking, smart contracts are neither intelligent nor contracts, the idea of using a decentralized method to verify and maintain the overall network security by continuously setting validation scripts in network nodes in advance allowed the founder to see a new idea for verifying this AI innovation experiment—making nodes intelligent.
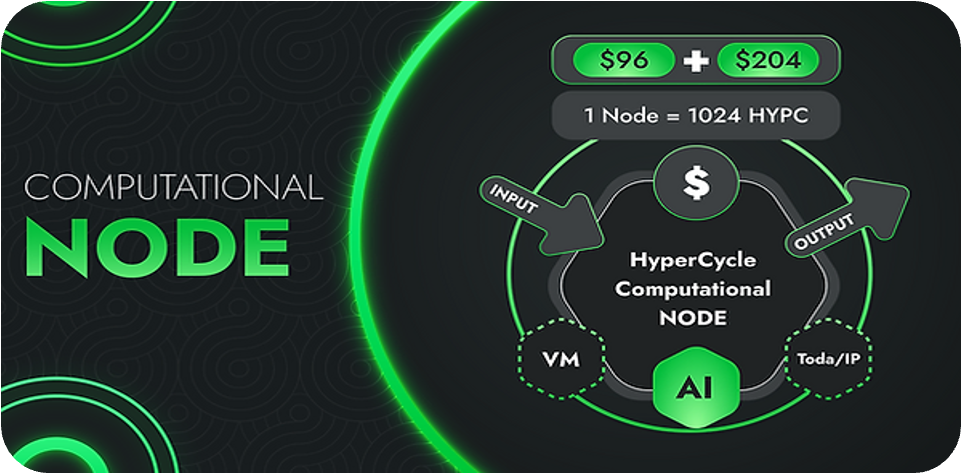
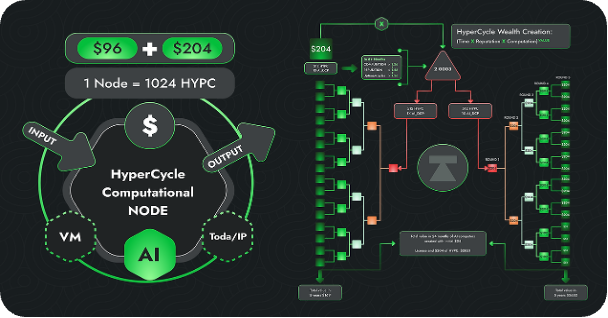
If we describe HyperCycle in concrete terms, it can be understood as a blockchain architecture that allows AI algorithms and data to be put on the chain. It uses decentralized organizational design and more efficient data transmission and security technology to enable not only AI computing power sharing between different projects, but also to ensure that each AI algorithm can receive the rewards it deserves after algorithmic calculations.
From a technical perspective, HyperCycle can be described as a brand new blockchain architecture, assembled from TODA/IP and TODA framework, consensus and reputation mechanisms, system supervision, smart contracts, MeTTa, etc. HyperCycle is able to handle fast and large-scale on-chain agents and interactions, such as on-chain deployment of AI algorithms trained based on population data volume and interaction media driven by token economics.
With HyperCycle, originally independent and functionally single AI algorithm models can cooperate with each other to execute complex intelligent algorithm processes internally, achieving a qualitative change effect.
TODA/IP ledgerless blockchain: making blockchain transmission efficiency applicable to AI
The most difficult problem in making blockchain technology applicable to AI is time cost and data transport cost. In traditional blockchain systems, whenever a transaction occurs, all nodes receive all transaction data, hash reference values and block headers, and this replicative ledger recording mode leads to linear increases in system recording efficiency and cost.
In past mode iterations, some projects have proposed the solution of shard management, dividing blockchain nodes into different fragments, each fragment only recording its own responsible transaction records. This sharding mode partially solves the efficiency problem, but also increases the complexity of the system, further increasing the operating cost of the system.
- TODA/IP is a secure and efficient point-to-point network protocol based on cryptographic principles, which allows each network data packet to have a unique global identifier and belong to a data structure that ensures that the data packet belongs to a single signing public key.
TODA/IP is similar to the underlying principles of shard management to some extent, but it maintains the lightweight operation and low overhead of the system through a more thorough decentralized approach – each local data block is responsible for managing its own historical information.
The core structure of TODA/IP is to connect personal records to their localized ledger, which makes these records a semi-autonomous agent in a sense. During transactions or data transmission, individual nodes only need to interact with transactions related to their own ledger, especially those involving disputes.
- Given a record R owned by wallet A, the record can be sent to wallet B by generating a transaction request, which is signed by wallet A, then by B, and finally distributed and signed by a group of validators. One cycle of TODA/IP includes a round of transaction requests and subsequent validation.
In such a transaction process, transaction validators replace the traditional mode of ledger and provide four important functions for the entire transaction:
-
Determine the validity of the transaction (structural rationality and proof correctness)
-
Prevent sending the same data packet twice in the same cycle
-
Help establish consensus proof of the transaction
-
Provide matching proof for A and B
To match the data architecture of TODA, the file format transmitted between nodes has also been iterated accordingly. “TODA files” are essentially digital data files attached to the ledger of each file as metadata. The combination of internal data of a file and its ledger allows a file to behave like a “unique digital object” (a type of NFT, which can be understood as a group of keys that jointly open a lock, or open part of the lock).
When a transaction occurs, each transaction involved will result in corresponding records attached to the relevant ledger of the file. These transaction records also contain other information, such as the addresses of other parties involved in the transaction.
With the TODA/IP mechanism, the originally cumbersome accounting data transmission process is optimized, and the transmission efficiency of the blockchain is matched with AI algorithms.
POR (Reputation Proof Mechanism): Secondary Lubrication of Efficiency and Fairness
Efficiency alone is not enough to support the operation of the entire swarm AI, and fairness is also a crucial part of the blockchain architecture. In HyperCycle, the system introduces a dynamic consensus mechanism that is more suitable for AI algorithm systems than the PoS and PoW mechanisms – Reputation Proof Mechanism (POR).
In the earliest blockchain systems, the PoW (Proof of Work) mechanism was used, and each node had to prove its participation by calculating work to obtain corresponding rights. However, the PoW mechanism consumes a lot of energy, so a lighter PoS mechanism has emerged: network nodes can obtain the right to confirm transactions by owning tokens without performing calculation work.
Although PoS avoids the energy waste issue of PoW, it continues the “rich get richer, poor get poorer” Matthew effect in PoW, where consensus can only be provided by nodes with a large amount of data processing power or tokens. This winner-takes-all situation is clearly unfavorable for nodes that want to truly win-win or provide computing power for the entire swarm AI, especially for small and medium-sized models. Therefore, the Proof of Reputation mechanism (PoR) was born.
- TODA had its own consensus mechanisms, which were also great, but layering a Proof of Reputation dynamic on top of them would increase efficiency and simplify things in many use-cases.
The core idea of PoR is to use liquidity-weighted reputation scores as the consensus mechanism of the blockchain network. The reputation of network nodes used by the PoR framework is determined over time and interaction.
The reputation score of a single node is calculated synthetically by mixing standardized ratings and the overall reputation value of the node, and will change dynamically over time. This is not a simple rating value given directly by other nodes. The behavior of a single node will also affect its overall reputation through a corresponding quantification formula.
Based on this, the PoR mechanism will determine a group responsible for maintaining the heat sharing state based on reputation, and the reputation value between nodes will be continuously updated with interaction over time. At the beginning of each round of the PoR consensus mechanism, the community needs to select consensus members and invite them to the corresponding consensus group, and the members of the consensus group will be selected from the nodes with the highest reputation value.
For example, when the collective reputation score exceeds 50% of the network’s total reputation value, a leader will be selected from the group, whose functions are:
-
Pack all valid transactions in the waiting transaction list into a block
-
Calculate the new reputation value generated by all network nodes using transaction data in the transaction list
-
Broadcast and submit information to the consensus group
The greatest value of the PoR mechanism in the AI innovation ecosystem is that regardless of whether the participant uses a large or small model, as long as its algorithm is sufficiently effective for the entire cluster, it will obtain higher reputation scores and returns. This will greatly attract various small and medium-sized AI model projects to actively participate, and also fully play the advantages of swarm AI.
Lightweight “Loop”: Mechanism innovation that adds the finishing touch
In the overall architecture of HyperCycle, the most ingenious design is the lightweight “loop” mechanism.
According to the definition in the HyperCycle whitepaper, the nodes in the TODA/IP network can be identified as “loops”, each of which is a specific set of records and is hierarchically connected. And a TODA/IP system can hold a collection of loops, which we can call a “loop set”. And the smallest node is called a “lightweight loop”.
The most ingenious part of the lightweight loop lies in the fact that it can both work with other loops to form a loop set to meet the needs of super-large computing power or data transactions, and it can also become an independent ecosystem. If one day GPT joins this bee AI, it can exist either as a world-class AI language generation chat system on its own, or it can be integrated into a cluster to become one of the language content generation modules in an AI virtual person.
MeTTa Contract Language: Making Contracts Truly Smart
Only one step remains in a brand-new AI blockchain architecture, namely, how to migrate various AI algorithm models onto the chain. The answer is: a native smart contract MeTTa. MeTTa (Meta Type Talk) language was developed in the context of the OpenCog Hyperon AGI project, and it has many excellent features that make it the core intelligent language of HyperCycle.
MeTTa has flexible underlying semantics, such as equivalent processing based on the configurational theory of the same type. AI project parties can directly call the system to process various transactions through API interfaces, which means that redundant script operations will not be performed when processing TODA/IP messages or TODA data, thus improving operational efficiency.
On the other hand, MeTTa is a language based on metagraph rewriting, which represents data and code in a unified way, and realizes higher-order functions and dynamic types. MeTTa supports multi-paradigm programming, including functional, logical, object-oriented, and concurrent programming. MeTTa also provides a powerful type system to ensure the correctness and safety of the code.
More importantly, by using the MeTTa compiler, project parties can compile MeTTa source code into the source code of rholang, which was originally developed in Rchain blockchain. This enables MeTTa to achieve true intelligence by leveraging the powerful concurrency features of rholang. Tokenomics can even be used within the MeTTa smart contract to manage the allocation of computing resources.
- With their new scheme, every validator in a network doesn’t need to verify that a smart contract is being run correctly, only a judiciously chosen random subset.
With MeTTa, both AI and other project parties can run relevant smart contracts on HyperCycle nodes, automatically managing resource allocation, outsourcing work to others, and proactively encouraging collaboration between nodes.
By completing this final step, our cluster AI will truly come to life.
Summary
The combination of blockchain and AI can bring new value to both business and society. Blockchain provides a secure and transparent database for storing encrypted data, while AI has the ability to simulate human thinking to solve problems. When used together, blockchain can increase the credibility and transparency of the data resources used by AI models, and improve the speed of AI operations by connecting the model to automated smart contracts.
In addition, the combination of blockchain and AI can also achieve a unified representation of data and code, enabling higher-order functions and dynamic types. This means that AI can quickly and comprehensively read, understand, and associate data, bringing new intelligence to blockchain-based business networks. By using blockchain to store and distribute AI models, audit tracking functions can also be provided, and tokenomics can be used to manage the allocation of computing resources.
In summary, the combination of blockchain and AI not only enhances the credibility and transparency of data and models, but also brings more efficient, secure, and intelligent solutions to business and society. This combination will bring more innovation opportunities to various industries and promote social progress.
References
-
https://wiki.opencog.org/w/File:A_Formalization_of_Hyperon_MeTTa_language_in_terms_of_metagraph_rewriting.pdf
-
https://wiki.opencog.org/wikihome/images/1/1e/Basic_Atomese_Features_required.pdf
-
https://medium.com/singularitynet/hypercycle-the-journey-to-a-fully-ai-capable-blockchain-9d2b7431cfa1
-
https://medium.com/singularitydao/singularitydao-launchpad-hypercycle-token-generation-event-9eeeea17f0ce
-
https://medium.com/singularitynet/hypercycle-a-convergence-of-radical-technologies-c59aeb83ab3
Disclaimer: This article is for research reference only and does not constitute any investment advice or recommendation. The project mechanism introduced in this article represents only the author’s personal opinion and has no interest or relationship with the author or this platform. Blockchain and digital currency investment carry extremely high market risks, policy risks, technical risks and other uncertain factors. The prices of tokens in the secondary market fluctuate sharply. Investors should make decisions prudently and independently assume investment risks. The author of this article or this platform shall not be liable for any loss caused to investors due to the use of the information provided in this article.
We will continue to update Blocking; if you have any questions or suggestions, please contact us!
Was this article helpful?
93 out of 132 found this helpful
Related articles
- 4.5BTC night market quote video analysis
- What is the problem with the current peak game of players less than 3 ‰ of Steam?
- Axie Infinity, a cute blockchain game
- Can 2020 games become a solution to the blockchain game?
- Blockchain + football: is grass or leeks on the green field?
- Not enough for 1000 years: a crypto art piece sold for 160,000
- Decentraland: Will it be the "Second Life" in the blockchain era?






