Project Research | Aptos In-Depth Study Report on MOVE’s New Public Chain
MOVE's new public chain: Aptos in-depth study report. 
Editor | [email protected]
Table of Contents
I. Project Overview
II. Project Vision
- MEV vs. Flashbots: A Story of Natural Rivals and the Delicate Balance of Building DeFi Systems
- From Wealth Effect to Organic Growth: Revealing the Secrets to the Success of High-Quality Cryptocurrency Projects
- HyperCycle: An innovative blockchain architecture for AI algorithm data
III. Features and Advantages
(1) Meta System
(2) Move Language
(3) Block-STM Technology
(4) More Secure Account Management
(5) Support Frequent Upgrades
(6) High-Performance Sparse Merkle Tree
(7) Comparison of Meta System Public Chains
IV. Development History
V. Team Background
VI. Financing Information
VII. Achievements
(1) Technical Progress
(2) Market Conditions
(3) Ecological Development
VIII. Economic Model
IX. Risks and Opportunities
I. Project Overview
Aptos is a brand-new independent public chain project established in 2021, a first-layer public chain that focuses on security and scalability. Its consensus mechanism adopts Proof of Stake, and it has attracted attention due to its Meta system background, Move language, high TPS, and other features.
II. Project Vision
Aptos aims to provide a blockchain that can bring mainstream applications to web3 and enhance the ecosystem of decentralized applications to solve real-world user problems. The team is committed to developing products and applications that “redefine the web3 user experience” on the Aptos blockchain.
The mission of Aptos is to improve the latest technology level in terms of blockchain reliability, security, and performance by providing a flexible modular blockchain architecture. The system architecture should support frequent upgrades, rapid adoption of the latest technological advances, and provide first-class support for emerging use cases.
III. Features and Advantages
(1) Meta System
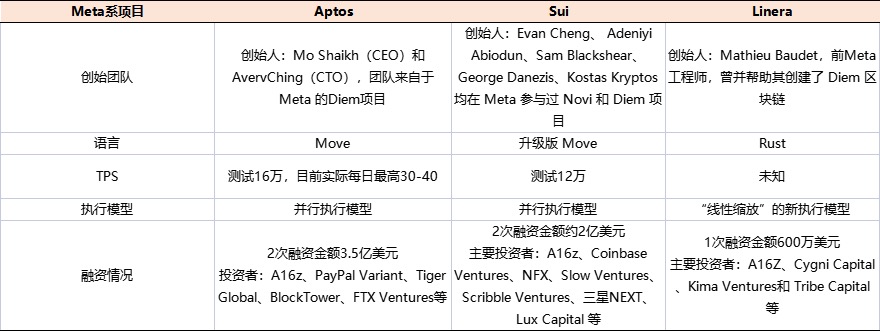
Aptos, Sui, and Linera are often discussed together because the co-founders of these three projects have experience working on projects at Meta.

The Aptos team is made up of Diem’s original creators, researchers, designers, and builders. Diem was a stablecoin project by Facebook (Meta), formerly known as Libra. Libra was a digital currency project that started in 2019 and aimed to facilitate payment transactions. Due to regulatory issues, it pivoted to being a stablecoin and was renamed Diem, but has yet to be successfully launched.
For Aptos, having a team background in Diem is one of the reasons why it is being watched closely.
(2) Move Language
In theory, using the Move language, Aptos can simultaneously have high transaction throughput and scalability without sacrificing security.
Move was inspired by Rust and was developed as a new programming language for Diem, different from the Solidity used by Ethereum.

Ethereum primarily addressed the difficulty of writing smart contracts on Bitcoin, so Solidity is a programming language for blockchain smart contracts. It treats tokens as value (numeric) variables, which makes it easy to have asset security issues, such as assets appearing or disappearing out of thin air.
Move is not a programming language for smart contracts, but for on-chain assets of blockchain. It treats tokens as resources, which are encapsulated at the underlying level and must be bound to an account. Each account can only have one type of resource at a time, and when it is removed from the account, it must be used. The Move module defines the validity period, storage and access modes of each resource and can be labeled, such as store for storage and key for indexing. Therefore, tokens can be safely stored and transferred, without appearing, disappearing, or being reused without proper credentials.
Currently, projects using the Move language include: Aptos, Sui, Starcoin, and 0L Network.
(3) Transaction parallelism: Block-STM technology brings high TPS
Currently, most blockchains use serial transaction execution, where transactions are added to blocks one by one and must wait for the previous transaction to complete before the next transaction can take place. This makes it easier to confirm transaction status, but scalability is limited.
Serial execution means that only one transaction can be executed at a time, and transactions are executed in sequence. Parallel execution, on the other hand, means that multiple transactions can be executed at once. The current state is usually snapshot, and multiple transactions are processed simultaneously. This clearly increases transaction throughput, but the difficulty is to ensure that different transactions do not affect each other.
Block-STM is a technology that accelerates smart contract execution and is derived from Diem. Block-STM increases throughput by parallel processing and is the core technology of Aptos. Aptos allows new nodes to participate in state synchronization through Block-STM to achieve high TPS.
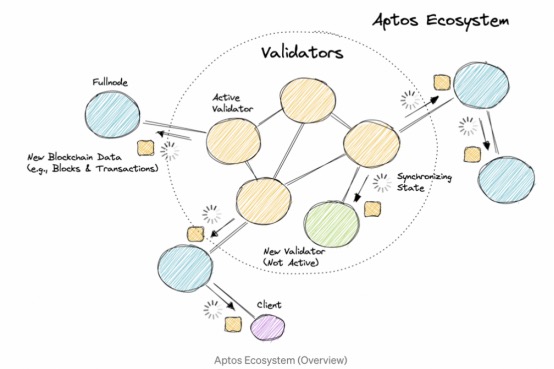
As shown in the figure, Aptos consists of a group of validation nodes, these validation nodes use Byzantine fault tolerance (BFT), equity proof consensus mechanism (PoS) to jointly receive and process transaction requests from users.
Unlike other blockchains, most blockchains are hierarchical structures, and the core of the network is a group of active validators responsible for transaction processing, block generation, and consensus. Aptos network allows active nodes to synchronize states with new validation nodes (non-active validation nodes). The goal is high throughput, low latency, fast synchronization time, resistance to faults and malicious behavior, tolerance for resource constraints and heterogeneity.
(4)Account management is more secure
Aptos’ data model supports flexible key management and hybrid custody options. Together with the transparency of transactions before signing and the practical lightweight client protocol, it provides a more secure and trustworthy user experience.
The method of decoupling accounts and keys allows Aptos to seamlessly add new digital signature algorithms to support public and private key types. The hybrid custody model supports advanced recovery solutions and account management to help bridge the gap between Web2 and Web3. To further enhance the user experience, the Aptos blockchain limits the feasibility of each transaction and protects the signer from unlimited validity through three protection areas-serial number, expiration time, and chain ID-to prevent errors and attacks.
(5)Support frequent upgrades
Aptos has a history of upgradability, and every area in the system is designed with modularity and flexibility in mind from the ground up. This makes the Aptos architecture able to support frequent upgrades, which in turn means that the blockchain can quickly adopt the latest technological advances and provide technical support for emerging use cases.
Aptos’ modular architecture design creates flexibility and is optimized for zero-downtime frequent upgrades – features that have been demonstrated in mainnet iterations, testnets, and many internal stress tests. The Aptos blockchain includes an embedded on-chain governance protocol that enables rapid deployment of new technology innovations and supports new Web3 use cases.
(6) High-performance sparse Merkle tree
Aptos uses Jellyfish Merkle Tree (JMT, sparse Merkle tree) design, which optimizes write scalability on the underlying storage engine based on LSM tree (log-structured merge tree) using a monotonic increasing version-based key pattern. JMT achieves a practical balance between CPU, I/O, and storage consumption, ensuring satisfactory performance without dealing with huge and hard-to-handle bloated state data on disks.
In addition to using JMT as the persistent format of the Aptos state, it also has another in-memory, lock-free sparse Merkle tree implementation. It is tailored for caching and parallelization and works with Block-STM to facilitate high-performance global state updates.
(7) Comparison of meta public chains
Four, development history
-
January 31, 2022 Meta (formerly Facebook) stablecoin project Diem acquired by Silvergate
-
February 24, 2022 Aptos publicly enters the market sight, with founding team members from Diem
-
March 15, 2022 Aptos completes $200 million financing
-
March 28, 2022 BinanceLabs announces strategic investment in Aptos
-
May 14, 2022 Aptos launches incentive testnet
-
June 29, 2022 Aptos launches ecosystem funding program
-
July 01, 2022 Aptos incentive testnet 2 opens registration
-
July 25, 2022 Aptos completes $150 million new round of financing
-
August 19, 2022 Aptos incentive testnet 3 opens registration
-
October 18, 2022 The public chain Aptos has officially launched the mainnet “Aptos Autumn”
-
October 18, 2022 Aptos announces token economics
-
October 19, 2022 Aptos official domain name service Aptos Name Service goes online
-
February 17, 2023 Aptos launches ambassador program Aptos Collective
-
March 11, 2023 Aptos on-chain transaction volume exceeds 100 million
-
April 13, 2023 Aptos launches $20 million grant program to encourage artists to create on its chain
-
April 21, 2023 Aptos launches delegation staking function
5. Team Background
Many key members of the Aptos team come from Meta, such as Aptos co-founder and CTO Avery Ching and Mo Shaikh, who were both key builders of Diem and Novi.
In addition, most of the developers and researchers in the development team, such as Alden Hu, participated in the development of Diem and Novi.
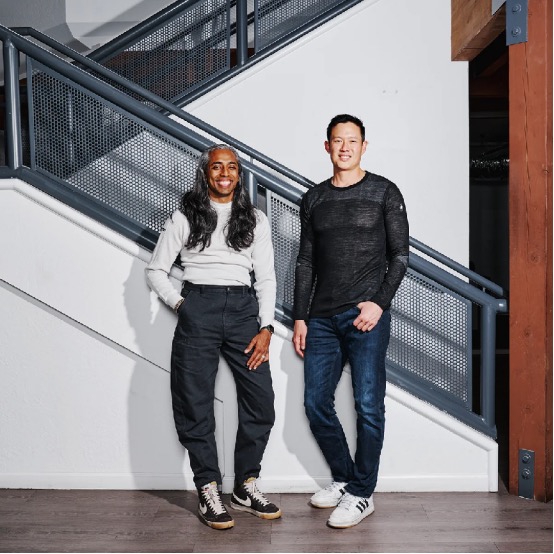

Mo Shaikh (left) and Avery Ching (right)
Mo Shaikh , Aptos co-founder and CEO, was responsible for strategic partnerships at Meta from May 2020 to December 2021. Prior to that, he was co-founder and CEO of Meridio from October 2017 to May 2020. Meridio is a blockchain-based platform for investing in and trading fractional real estate with liquidity.
Avery Ching , Aptos co-founder and CTO. Avery Ching worked as a chief software engineer at Facebook for over 10 years from September 2011 to December 2021. He was also the technical lead of the Novi team, a former crypto platform under Meta, focusing on the development of various aspects of blockchain technology and maintaining the Diem blockchain. From October 2007 to September 2011, he worked as a chief software engineer at Yahoo.
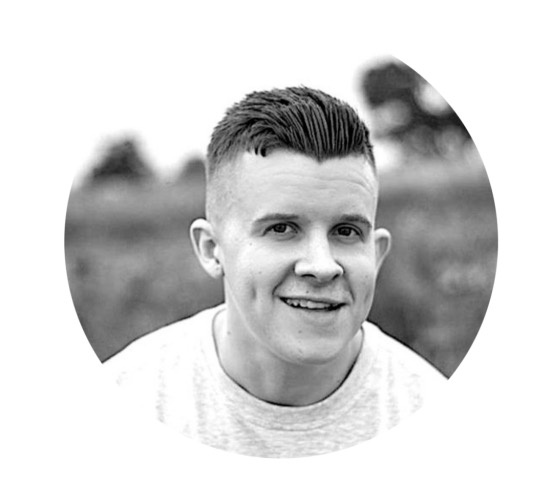

Josh Lind - Founding Engineer
Josh Lind , Aptos founding engineer, is involved in researching Layer 1 blockchain technology. Previously, he was a research scientist who worked on the Diem blockchain at Novi. He holds a Ph.D. degree in using trusted hardware to improve security and privacy in large-scale distributed systems from Imperial College London’s Large Scale Data and Systems (LSDS) group and the Cryptocurrency Research and Engineering Center (IC3RE).
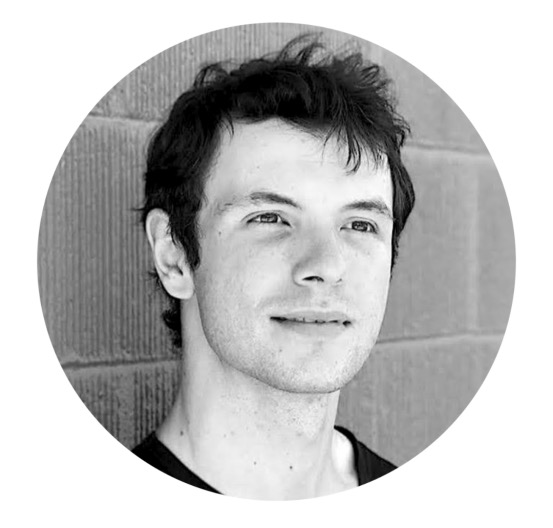

Alin Tomescu - Researcher
Alin Tomescu , a founding member and researcher of Aptos, holds a Master’s degree in Computer Science and a Ph.D. in Philosophy from MIT. He has over six years of research experience at MIT and specializes in cryptocurrency, public keys, authenticated data structures, secure communication, and secure web applications.

David Wolinsky--Software Engineer
David Wolinsky , a software engineer at Aptos, was previously the technical lead for Web3 at Meta, working on strategic technology and product plans for multiple organizations and teams. Prior to that, he worked on the Diem blockchain for almost two years, including designing governance and genesis programs, establishing security infrastructure plans and principles, and defining integrations with Diem. Before joining Novi, he was a technical lead/manager at Facebook, responsible for Facebook’s ad growth. Previously, he was a research scholar at Yale University.

Alden Hu--Software Engineer
Alden Hu , a software engineer at Aptos Labs, was a senior software engineer at Novi from February 2019 to February 2022, and previously worked at Instagram and Baidu.

Rati Gelashvili--Researcher
Rati Gelashvili , a founding team researcher at Aptos, has a PhD from MIT and extensive expertise in concurrency, parallel and distributed algorithms, and data structures. He was a senior research scientist at Novi from May 2020 to January 2022.
VI. Financing Information
On March 15, 2022, Aptos completed a $200 million financing round led by a16z, with participation from Multicoin Capital, Katie Haun, BlockingraFi Capital, IRONGREY, Hashed, Variant, Tiger Global, BlockTower, FTX Ventures, Blockingxos, Coinbase Ventures, and others.
On March 28, 2022, Binance Labs announced a strategic investment in Aptos Labs, the development team behind the public chain project Aptos, and will work closely with Aptos on development, code review, infrastructure construction, and hackathons.
On July 25, 2022, Aptos announced the completion of a new $150 million funding round led by FTX Ventures and Jump Crypto, with other investors including Griffin Gaming Partners, Franklin Templeton, Circle Ventures and Superscript, a16z crypto and Multicoin Capital.
On September 15, 2022, Binance Labs announced an increased strategic investment in Aptos Labs to expand its commitment to infrastructure construction.
7. Development Achievements
(1) Technological Progress
① Move Language: A next-generation programming language for secure, sandboxed, and formally verified programming. Its first use case is the Diem blockchain, for which Move provides the foundation. Move allows developers to write programs that flexibly manage and transfer assets while providing security and protection against attacks on those assets. Currently, blockchain projects using the Move language include Aptos, Sui, Starcoin, 0L Network, and others.
When the Move language was designed, it attempted to solve the problem of protecting digital assets from the perspective of programming languages. Aptos and Move language were developed simultaneously more than three years ago. Aptos’ accounts, transaction fees, standard libraries, validator node management, and configuration are all implemented using Move.
② Parallel Execution Engine
Aptos implemented Block-STM in its open-source code repository, relying on Rayon, Dashmap, and ArcSwap crates for concurrency.
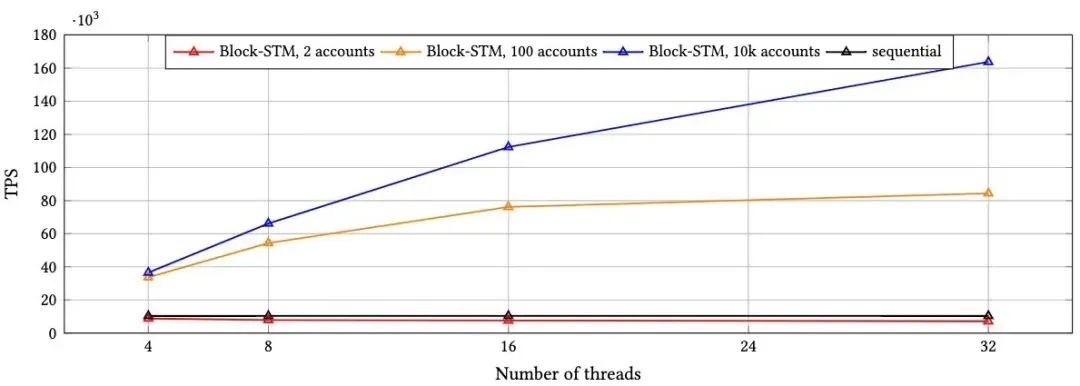
Aptos compared Block-STM with block sequential execution. Each block contains 10k transactions, and the number of accounts determines the degree of conflict and contention. In low contention, Block-STM archives are 16 times faster than sequential execution using 32 threads, while in high contention, Block-STM archives are more than eight times faster. Importantly, Block-STM incurs only a small overhead when the workload is essentially continuous. Overall, Block-STM can dynamically and transparently (without user prompting) extract inherent parallelism from workloads.
③ BFT Consensus Protocol
Aptos team developed a production-grade, low-latency Byzantine Fault Tolerant (BFT) engine. The protocol has been implemented four times in the past three years.
Aptos added an active pacer using timeouts to synchronize validators through the BFT protocol, which is much faster than waiting for the added timeouts. With the latest improvements to the protocol, blocks can be submitted in only two network round-trips, making sub-second finality a common occurrence.
④ Network
Aptos Incentive Testnet 1: Successfully launched nodes and achieved over 95% availability with liveness checks within 24 hours.
Aptos Incentive Testnet 2: Test coin support for staking and staking rewards, decentralized faucet support.
Aptos Testnet 3: Successfully launched nodes and passed activity checks within 12 hours of node startup, with availability exceeding 97%.
Aptos Mainnet “Aptos Autumn” is online.
(2) Market situation
On October 24th, 2022, Aptos reached a partnership with BlockingncakeSwap, and BlockingncakeSwap and CAKE tokens will be deployed on Aptos.
On November 11th, 2022, Aptos reached a partnership with Google Cloud and will launch an accelerator program.
On March 9th, 2023, Aptos reached a partnership with cross-chain bridge Wormhole, and users can bridge NFT assets to Aptos.
On April 26th, 2023, 11 Web3 companies have joined the Google Cloud Startup Support Program, including Aptos, Base, Flow, etc.
On May 11th, 2023, the long-term funding program Aptos Grant DAO has surpassed 300 projects.
(3) Ecological development
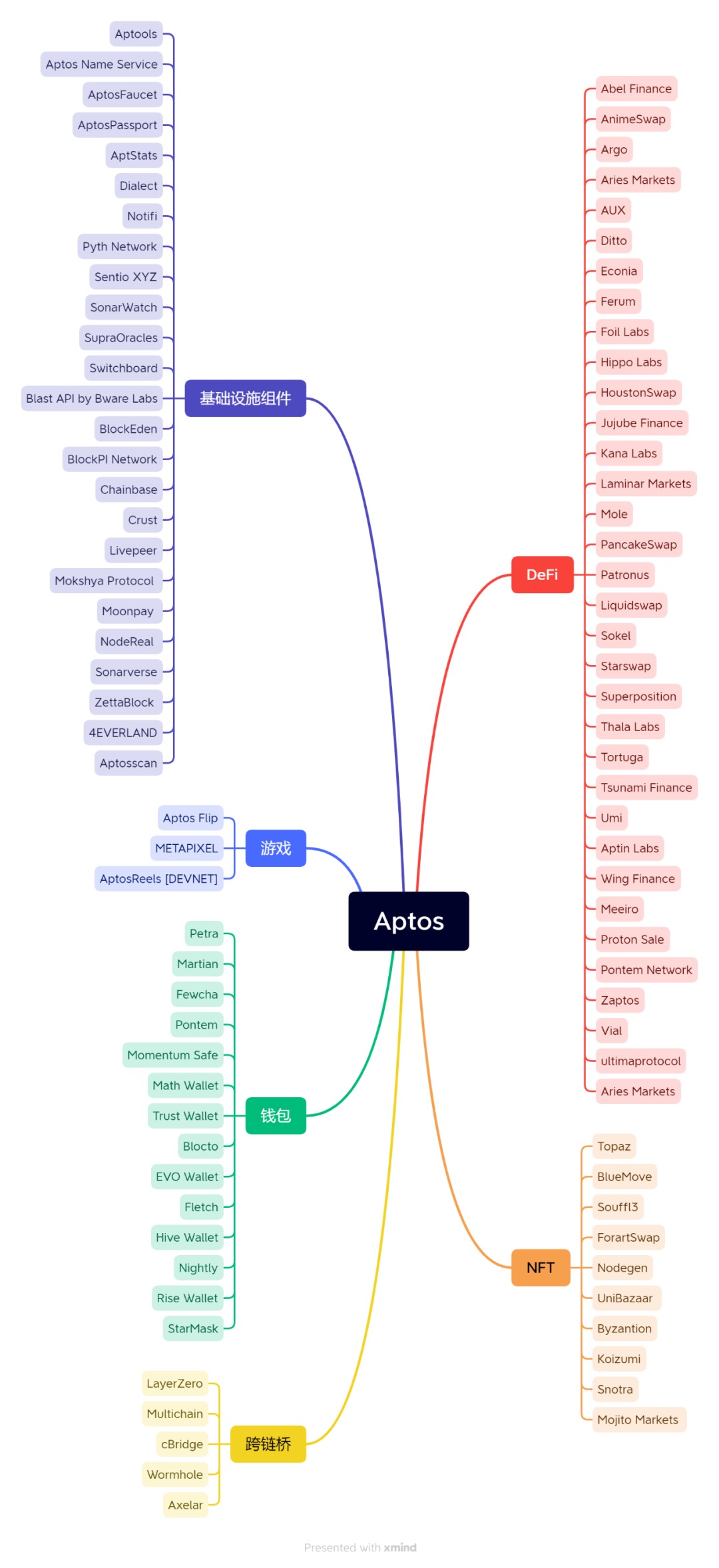
Currently, Aptos official website shows that there are nearly 150 ecological projects on the chain, including cross-chain bridges, DeFi, NFT, games, infrastructure and other fields.
Eight, Economic Model
(1) Token Overview
APT is the governance token of Aptos, with a total of 1 billion tokens, a precision of 8 digits, and the smallest unit is called Octa.
51.02% of the tokens will be allocated to the community, 16.5% will be allocated to the foundation, 19% will be allocated to core contributors, and 13.48% will be allocated to investors.
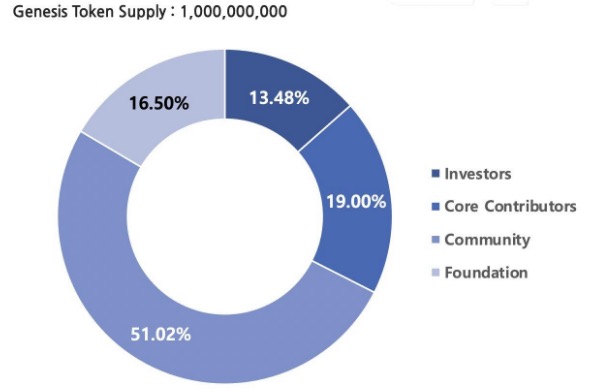
(2) Community and Foundation Distribution
The token pool is designated for ecosystem-related projects, such as grants, rewards, and other community development plans. The community and foundation hold a total of 410,217,359.767 tokens, of which 100,000,000 are held by Aptos Labs. It is expected to be unlocked within ten years. The specific distribution details are as follows:
· 125,000,000 APTs are used to support ecosystem projects, grants, and other community construction
· A preliminary plan is to provide 5,000,000 APTs to support the Aptos Foundation
· 1/120 of the remaining tokens in the community and foundation are expected to be unlocked every month in the next ten years
(3) Core contributors and investor distribution
Core contributors and investors: All investors and core contributors will be locked up for four years, with no APT distributed during the first 12 months. 3/48 of the APT will be unlocked in the 13th month after the mainnet is launched, and they will continue to be unlocked each month until they are completely unlocked in the 18th month. Starting in the 19th month after the mainnet is launched, 1/48 of the tokens will be unlocked each month until all such tokens are unlocked on the fourth anniversary of the mainnet’s launch.
(4) Token supply schedule
Over 82% of the tokens have been locked in the categories above and cannot be released at this time.
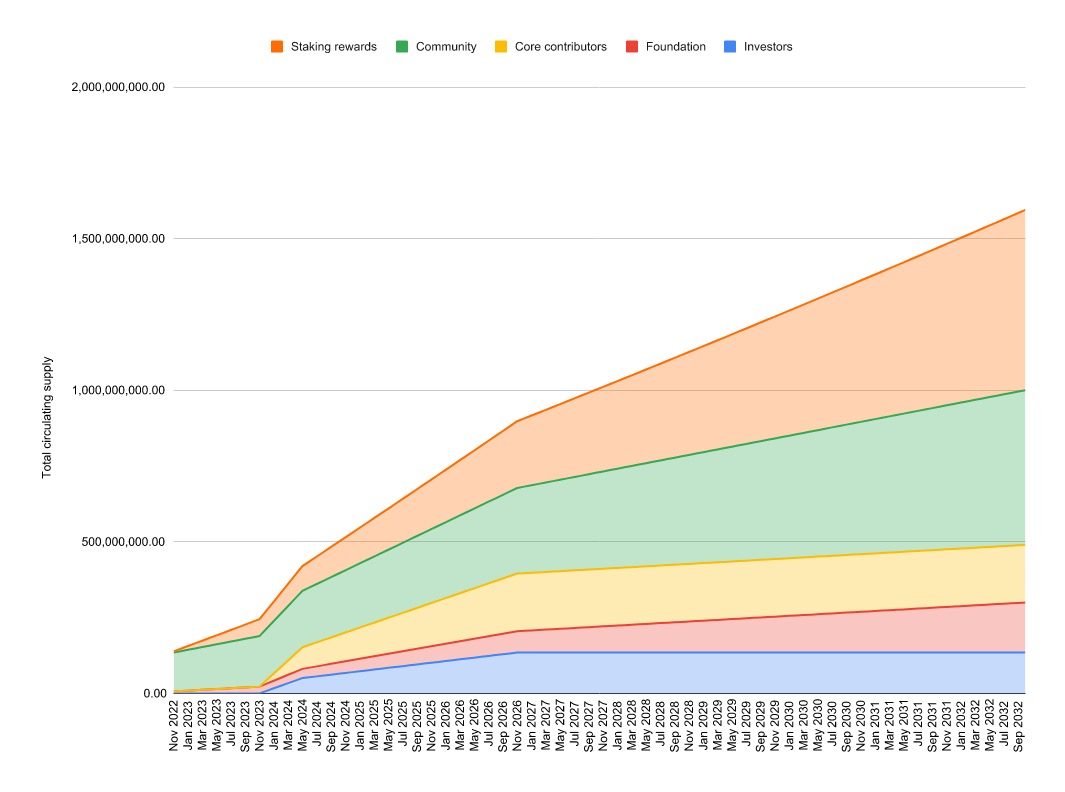
IX. Risks and Opportunities
(1) Opportunities
① Market environment:
The public chain track has always been the most challenging and the best place to carry value. With the rapid emergence of applications such as DeFi, NFTs, and Web3, the description and concept of public chains are still one of the main focus of the market. Of course, the competition in the public chain track has never stopped.
Counting the development of the public chain track, from BSC, Solana, Avalanche, Fantom, Near, Avalanche, to Terra, one public chain after another has not only shown good results in the secondary market prices, but also brought about a vigorous development in the ecology, driving a small climax of emerging public chains.
② Project progress:
Aptos has a total of 108 global verification nodes. The total supply of APT is 1,034,592,689, and the token amount in the staking pool is 877,583,198. Its market value is currently $1,681,095,144, ranking 33rd in the world.
The trading volume of APT is still at a low level. If there is no significant bearish pressure in the market, the bullish trend may continue.
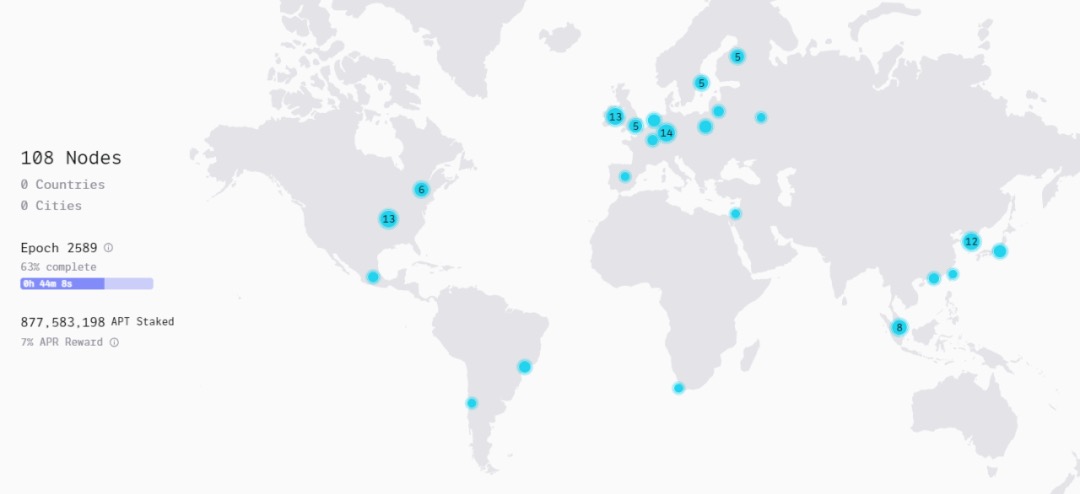
(2) Risks
① Results fall short of expectations
The performance of Aptos Autumn mainnet launched last October was not satisfactory. Aptos official data claimed that it can achieve 160,000 TPS, but according to browser data, the Aptos network throughput is only 30-40 TPS, far from the target.
② Lack of advantageous projects
Although Aptos also tries to develop on the path of a public chain with its own characteristics, for example, Vance Spencer, co-founder of Framework, questioned on Twitter: What has Aptos done that Solana hasn’t?
Due to the high degree of overlap with Solana in various aspects such as technology, capital, and ecosystem development, Aptos also needs to face competition pressure from Solana.
③ Overvaluation
As a star public chain, Aptos has been a darling of capital since its launch. In the financing in July 2022, Aptos was valued at US$2.75 billion, which is relatively high from the perspective of a bear market.
④ Potential risks brought by the Korean market
As one of the hottest cryptocurrency trading markets in the world, the cryptocurrency assets on the Korean market often have higher prices than in other countries, a phenomenon known as the “kimchi premium.” After Terra’s collapse, the Korean local cryptocurrency market was in a vacuum and urgently needed a new protagonist, so Aptos seized the opportunity to enter the Korean market. In the white paper released simultaneously on the Aptos official website, Korean is the only language besides English. The madness of the Korean market may pose potential risks to the project.
Reference:
Comprehensive interpretation | Dark horse star public chain Aptos: opportunities and challenges under the first-mover advantage
Aptos rises, what does it rely on?
We will continue to update Blocking; if you have any questions or suggestions, please contact us!
Was this article helpful?
93 out of 132 found this helpful
Related articles
- Project Research | Canvas: Focused on DeFi, Layer2 Protocol Based on StareWare ZK Rollups
- Neutron: A new cross-chain DeFi blockchain on Cosmos
- Standing at the forefront of the Meme trend, how did Ben become a cryptocurrency legend from an unknown person?
- 4.5BTC night market quote video analysis
- What is the problem with the current peak game of players less than 3 ‰ of Steam?
- Axie Infinity, a cute blockchain game
- Can 2020 games become a solution to the blockchain game?






