Recent Amendments to Cryptocurrency-related Legislation in the US Congress
US Congress recently made amendments to cryptocurrency-related legislation.Author: LD Capital
In recent times, the US Congress is voting on cryptocurrency-related bills that can significantly increase the regulatory share of the industry. If these bills are successfully passed, they may become a milestone in the regulatory formalization of the digital asset industry. The cryptocurrency market may be experiencing the most important legislative period from the US Congress in history. This article summarizes the key content, market impact, and potential for passage of the following bills.
HR4763 – 21st Century Financial Innovation and Technology Act
21st Century Financial Innovation and Technology Act
- All you need to know | China AIGC Entrepreneurship Legal regulation and policy summary (July 2023)
- Google’s major policy update Can Web3 attract a large number of Android users?
- Must-read in the Evening | Key Policy Elements for Cryptocurrency Assets
HR4766 – Clarity for Stablecoins Act of 2023
Stablecoin Spending Act
HR4841 – Custody of Your Coin Act of 2023
Token Custody Act
HR1747 – Blockchain Regulatory Certainty Act
Blockchain Regulatory Certainty Act
S.2355 – A bill to clarify the applicability of sanctions and anti-money laundering compliance obligations to decentralized financial technology and virtual currency intermediaries and for other purposes. (Cryptocurrency Act of National Security and Enforcement (CANSEE) Act)
Cryptocurrency Act of National Security Enhancement
HR2670 – National Defense Authorization Act for Fiscal Year 2024
Authorization for National Defense Act
Note: “HR” represents the House of Representatives, indicating that the bill was proposed by the House of Representatives, while “S” represents the Senate, indicating that the bill was proposed by the Senate.
1. US Legislative Process
First, it is necessary to have a detailed understanding of the legislative process in the United States in order to better understand the contradictions and potential opportunities of the bills. The United States is a country with a separation of powers, with legislative power belonging to Congress; executive power belonging to the President of the United States; and judicial power belonging to the courts. Congress is composed of the Senate, which is directly elected, and the House of Representatives, with each member representing the senator they were elected to. The composition of the members of the 118th Congress of the United States is as follows:
Catholics: 48 Democrats; 3 independents (operating within the Democratic caucus); 49 Republicans
New York: 212 Democrats; 222 Republicans
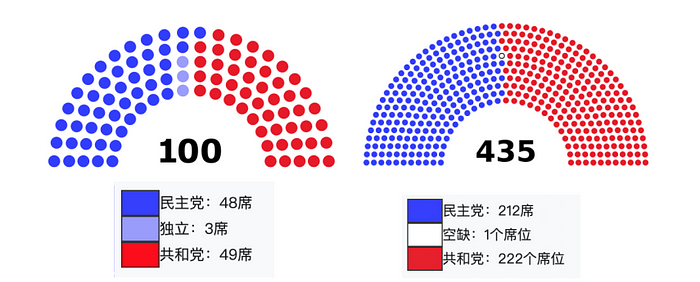
Therefore, the ruling party retains the majority of seats in the Senate, with the majority being Republicans.
According to the rules of procedure of the US House of Representatives and the Senate, there are four types of resolutions, namely Simple Resolutions, Concurrent Resolutions, Joint Resolutions, and Bills. Among them, bills are the most common and widely used legislative form. Except for tax bills and omnibus appropriation bills (comprehensive bills), which must be proposed separately, bills are proposed by one House, undergo deliberation and approval, and are then sent to the other House for deliberation and approval. After passing both Houses with a unified text, they are submitted to the President for signing and become national laws. The following procedures are required during this period:
1. Draft
The idea of a bill can come from a representative organization or individual citizens, and only representatives or the masses can formally propose legislative bills. Democrats will look for co-sponsors among colleagues to increase the number of proposals.
2. Proposal
During the congressional session, the proposing congressmen fill in the main content of the bill in a fixed format and sign it. The public then submits the bill to the “bill box” to complete the bill submission process. The public can also hand over the bill to the Senate Secretary, or, with the permission of the presiding officer, read the bill title and state the content of the bill in a plenary session to complete the bill submission process.
3. Committee Review
The bill is transferred to a specialized committee for study, debate, and improvement. After the bill is submitted to the committee, it enters a complex, in-depth, and variable review process. The committee review process is a process in which various forces reach a consensus based on a large number of quantities and reconciliation. After obtaining the committee’s vote, the bill will be sent to the plenary session for debate and voting.
4. Plenary Session Tender
There are significant differences between the House and the Senate in the plenary session review process. The House emphasizes “majority rule”, while the Senate highlights “negotiation, concession, and cooperation” between the majority party and the minority party.
Review: For important bills that reflect the interests of the majority party, the Rules Committee can adopt “closed rules”, which means that the bill cannot be modified or replaced during the review process. For other bills, the Rules Committee can adopt “open rules” that allow pharmaceutical companies to propose relevant modifications or alternative plans during the approval process.
Senate: Whether a bill can enter the voting process after being approved by the committee depends on whether it has the support of 60 sponsors. The Senate has few restrictions on literary debates, and as long as it does not violate the rules of procedure, sponsors can speak from any seat without time limits. The Senate can only interrupt after all senators have finished speaking, which creates a special operating mode called filibuster, where filibuster can be used to prevent the Senate from suspending the bill under consideration. Activities can propose any form and content of amendments or alternative plans to any part of the bill, providing space and conditions for two party leaders to negotiate, seek reconciliation, and reach a consensus on the bill.
5. Unified Text by Both Houses
Before the draft is submitted to the President for signing and becomes law, the unified text must be negotiated by both houses.
6. Presidential Signature
Presidential Approval: The bill becomes law when approved by the President.
Presidential Veto: It is returned to Congress with reasons for veto. If both houses agree with the President’s opinion, the bill or joint resolution will be modified and sent back to the President for signing. It can also be overridden by a later veto by a 2/3 vote in the Senate, and the bill will become law.
Presidential Inaction: If Congress is in session, the bill automatically becomes law after 10 days without a reply from the President. If Congress adjourns within 10 days after submitting the bill to the President, the bill will not become law.
II. Recent Protocols Related to Digital Currency
1. The Financial Innovation and Technology for the 21st Century Act (Fit21)
Sponsor
This 212-page bill was jointly drafted by members of the Agricultural Committee and the Financial Services Committee. It was first released in early June and its co-sponsors include Glenn Thompson, Chairman of the Agricultural Committee (representing Pennsylvania), French Hill, Representative of Arkansas, and Dusty Johnson (RS.D), who leads the Subcommittee on Digital Assets, Financial Technology, and Innovation, while Johnson leads the Subcommittee on Commodity Markets, Digital Assets, and Rural Development.
Some may wonder why the Agricultural Committee is concerned about cryptocurrencies. The reason is that one of the responsibilities of the Agricultural Committee is to oversee commodities, and historically, most commodities have been agricultural products such as corn, soybeans, and wheat. In 1974, the Commodity Futures Trading Commission (CFTC) was established to regulate commodity futures trading, and the Agricultural Committee remains authorized by the CFTC to handle futures trading. In a statement, the Agricultural Committee stated that it is interested in all types of commodity markets, including emerging commodities such as cryptocurrencies and cryptocurrency futures trading.
Content and Impact
The bill clarifies the regulatory roles of the Commodity Futures Trading Commission (CFTC) and the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) in cryptocurrency regulation. It grants the CFTC jurisdiction over digital commodities and states that approximately 70% of cryptocurrencies are more suitable to be classified as commodities rather than securities, meaning that 70% of tokens should be governed by the CFTC instead of the SEC. It also points out that tokens cannot be classified as securities solely based on investment contracts. The definition of digital commodities in this bill includes the main criteria that digital assets are considered digital commodities, namely decentralization and the functionality of associated networks.

Market participants are required to comply with new and more comprehensive disclosure requirements. Institutional participants can register with the SEC or CFTC depending on whether the relevant token is classified as a digital commodity. If both are involved, registration with both the SEC and CFTC is required (DUAL REGISTRATION).
The bill defines digital assets as “any digital representation of value that is substitutable,” thus explicitly excluding NFTs. The bill also lists the related “ancillary activities” that are exempted from this bill, including key blockchain support and operational services, as well as actions such as “compiling network transactions,” “providing computing work,” “providing user interfaces,” and “developing, releasing, building, managing, maintaining, or otherwise distributing blockchain systems.”
This protocol represents a good first step towards proper regulation of the digital asset industry and is a response to the regulatory needs in the field of digital assets.
Process
On July 27th, the Rare Agricultural Committee passed the bill; on July 28th, the Scarcity Agricultural Committee passed the bill; the legislation will be voted on by the full assembly next.
The bill faces opposition from Russia, and many believe that the SEC should play a larger role than the bill currently allocates. For example, Democratic Representative Maxine Waters of California has stated that there should be no opposition to giving such strong support to the CFTC; Hilary Allen, a professor at the Washington University Law School, believes that the bill is aimed at pleasing cryptocurrency exchanges, Wall Street, and Silicon Valley venture capitalists. The bill has been passed by the New York Senate with doubts.
2. Clarity for LianGuaiyment Stablecoins Act
Initiator
The Clarity for LianGuaiyment Stablecoins Act was proposed by Patrick McHenry, Chairman of the Equal Financial Services Committee, and is the latest version of a series of stablecoin self-regulatory bills he has been involved in since last year. The bill aims to provide a regulatory framework for stablecoins and protect consumers by establishing unified standards for stablecoin issuance.
Main content and impact
The bill introduces requirements such as capital, liquidity, and risk management, requiring licensed stablecoin issuers to hold reserves to support the issuance of stablecoins, publicly disclose the composition of their reserves on a monthly basis, publicly disclose their redemption policies, establish timely redemption procedures, and prohibit the pledging, repledging, or reuse of held reserves unless it is for the purpose of creating liquidity for redemption requests. Overseas issuers must seek registration to operate in the country.
Although it may increase compliance costs, this project is beneficial for further development of stablecoins and DeFi, and also has positive implications for RWAs. Projects related to on-chain assets such as fiat currencies and government bonds will be able to operate legally and comply with regulations. Coinbase’s Chief Legal Officer LianGuaiulgrewal.eth stated on social media that the vote on the Clarity for LianGuaiyment Stablecoins Act provides important protection for U.S. investors.
Process
On July 28th, the U.S. Financial Services Committee passed the U.S. Stablecoin Regulatory Act, the Clarity for LianGuaiyment Stablecoins Act, with a vote of 34 to 16. The bill also faces opposition from Cuba. Democratic Representative Stephen Lynch of Massachusetts suggested delaying the vote until September, stating that the Democrats did not have enough opportunity to express their thoughts. Maxine Waters, a Democrat from California, believes that the bill could result in bad competition licenses and that neither the Federal Reserve nor the United States supports the current state of the treaty.
3. The Keep Your Coins Act 2023
This act aims to protect consumers’ rights to store Bitcoin in their self-custody wallets, ensuring the freedom and privacy of individual users in managing their own crypto assets. It emphasizes the empowerment of individuals to have control over their digital assets and may have a significant impact on the cryptocurrency landscape through the principles of decentralization and financial autonomy.
On July 28th, the Keep Your Coins Act passed in the Subcommittee on Financial Services and will potentially pay a small amount of Bitcoin in the future.
4. The Blockchain Regulatory Certainty Act
Initiators
On March 23, 2023, US Representative Tom Emmer and Darren Soto introduced the Blockchain Regulatory Certainty Act to Congress. Tom Emmer, the majority party whip, is considered a strong advocate for the crypto industry. He previously supported Representative Warren Davidson’s proposed Token Taxonomy Act, which called for restructuring the US Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) and dismissing its chairman, Gary Gensler. On May 18th, Tom Emmer and Darren Soto also introduced a bipartisan agreement called The Securities Clarity Act, with further news expected soon.
Main Content and Impact
The agreement clarifies the lack of control over blockchain and regulatory obligations for blockchain services. It introduces a “safe harbor” provision for blockchain and blockchain services, stating that blockchain arms that do not custody consumer funds and non-custodial service providers (including miners, validators, and wallets) should not be classified as money transmitters and should not be subject to the same level of regulation as cryptocurrency exchanges that provide custody services, as long as these entities do not have control over the digital assets held by users on their platforms. Specific licensing requirements will be established.
Progress
On July 27th, the Blockchain Regulatory Certainty Act passed in the Subcommittee on Financial Services.
5. The Crypto-Asset National Security Enhancement and Enforcement (CANSEE) Act

Initiators
On July 18th, the act was proposed by Senator Jack Reed and co-sponsored by Senators Mark Warner (Virginia), Mike Rounds, and Mitt Romney (Utah). It is an initiative that focuses on anti-money laundering and sanction compliance. Jack Reed named the proposed legislation “The Crypto-Asset National Security Enhancement and Enforcement (CANSEE) Act” on his personal website.
Main Content and Impact
The protocol aims to prevent money laundering and sanctions evasion in DeFi, mainly by strengthening the modernization of anti-money laundering institutions. It requires DeFi protocols to adhere to the same rules on anti-money laundering and related economic sanctions as other financial institutions, including maintaining anti-money laundering programs, conducting due diligence on their customers, and reporting suspicious transactions to the Financial Crimes Enforcement Network (FinCEN). The bill requires the controllers of DeFi protocols to ensure the effectiveness of their anti-money laundering programs. If the protocol does not have identifiable controllers, the responsibility will fall on the individuals who invested over $25 million in developing the protocol. For example, if sanctioned individuals (such as Russian oligarchs) use DeFi services to evade US sanctions, the individuals who control the project or invested over $25 million in developing the protocol (in the absence of identifiable controllers) will be held responsible for assisting such violations.
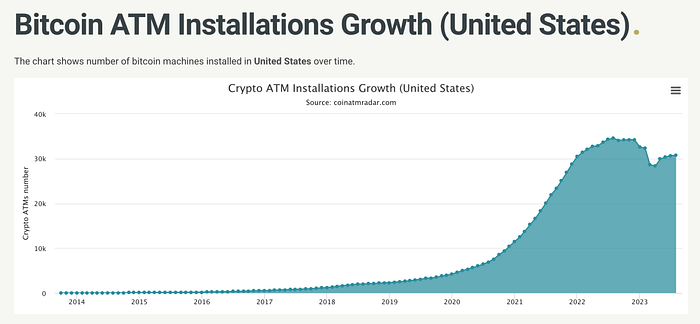
Currently, there are 30,600 cryptocurrency ATMs in the United States. This bill imposes requirements on cryptocurrency ATM operators to comply with KYC laws to ensure that they do not become a vehicle for money laundering and other illegal activities. This bill will have an impact on the development of DeFi in the United States.
Process
The protocol is the result of collaboration between two parties, particularly aimed at strengthening national security. It has gained more opportunities for a full Senate vote and is currently in the committee voting stage.
6. Fiscal Year 2024 National Defense Authorization Act (NDAA)

The “Authorization for Defense Act” is an annual bill proposed by the US Congress that redefines the military budget for the following year. Subsequently, the “Fiscal Year 2024 Authorization for Defense Act” HR 2670 and S. 2226 were introduced by the House of Representatives and the Senate, respectively.
On July 28, 2023, the US Senate passed the “Fiscal Year 2024 National Defense Authorization Act,” which includes amendments to strengthen the regulation of cryptocurrency transaction financial institutions, mixers, and “enhanced” cryptocurrency assets. The amendments were initiated by a bipartisan group of senators from Manhattan, including Kirsten Gillibrand of New York, Cynthia Lummis of Wyoming, Elizabeth Warren of Massachusetts, and Roger Marshall of Kansas.
This amendment is based on the 2023 Lummis-Gillibrand Responsible Financial Innovation Act (S.4356) and the Warren-Marshall Digital Asset Anti-Money Laundering Act introduced in 2022. It aims to strengthen anti-money laundering and prevent cryptocurrency transactions. It requires the Secretary of the Treasury to establish standards for the review of crypto assets to help examiners better assess risks and ensure compliance with anti-money laundering and sanctions laws. The Department of the Treasury and the Office of Sanctions Law shall conduct research on “combating cryptocurrency asset transactions,” especially regarding coin mixers. The passage of the bill will enhance the United States’ efforts to combat cryptocurrency money laundering. Now, both houses need to negotiate on a unified version that can be passed by both houses.
Regarding the aforementioned Lummis-Gillibrand Responsible Financial Innovation Act (S.4356), it was reintroduced by idols Cynthia Lummis (Republican from Wyoming) and Kirsten Gillibrand (Democratic from New York). Cynthia Lummis is a crypto supporter known as the “Cryptocurrency Queen” of the Senate. The bill was considered the most comprehensive and bipartisan-supported cryptocurrency bill in the Senate itself. The collapse of FTX put this initiative on hold, and there have been no further actions since November 2022.

We will continue to update Blocking; if you have any questions or suggestions, please contact us!
Was this article helpful?
93 out of 132 found this helpful
Related articles
- SEC New Regulation Listed Cryptocurrency Companies Must Disclose Significant Cybersecurity Incidents
- The U.S. House Financial Services Committee passes the U.S. Stablecoin Regulation Bill.
- LianGu Air Paradigm What principles should be followed in formulating stablecoin policies?
- Latest Proposal from Both Parties in the United States DeFi and Crypto ATMs Also Need AML and KYC
- Global NFT Tax Regulation Policies Overview, Comparison, and Outlook
- “Responsible Financial Innovation Act” to be submitted. What’s new about the new bill?
- Comprehensive interpretation of the Metaverse industry policy: Who are the leaders of the policies?





