What are long positions and short positions?
Long positions and short positions—what are they?Author: Guneet Kaur, Cointelegraph; Translation: Song Xue, LianGuai
1. Concept of Long and Short Positions
Long and short positions represent opposite strategies that investors and traders use to speculate on the price movements of the assets they are considering.
In the field of cryptocurrency, long and short still apply the concepts of traditional financial markets. To profit from the rise in cryptocurrency prices, going long (long position) means buying it and expecting its value to increase over time.
- Three Reasons Why Ethereum Price Cannot Break Through $2000
- The king of Web3 scams is leading Pudgy Penguin to its demise.
- LianGuaiWeb3.0 Daily | TRON Mainnet Will Soon Release Chiron Version
In contrast, going short in the cryptocurrency market means selling a cryptocurrency that is not actually owned in anticipation of a price decline, and then buying it back at a lower cost to close the position and profit from the price drop.
Cryptocurrency traders and investors use these strategies to deal with the high volatility and speculation of digital assets and seize opportunities in both bullish and bearish market conditions.
2. Basic Differences Between Long and Short Positions
In cryptocurrency trading, a long position is initiated by buying an asset with the hope that its price will rise, while a short position is initiated by disposing of an asset (usually borrowed) with the hope that its price will fall.
Closing a position means buying the asset at a lower price to gain profits, while exiting a long position means selling the asset at a higher price to lock in profits. Entry and exit points are crucial for the successful implementation of these strategies.
Understanding the differences between long and short positions in the cryptocurrency trading field is crucial for successfully navigating the volatile digital asset market. The following is a summary of the differences between the two:
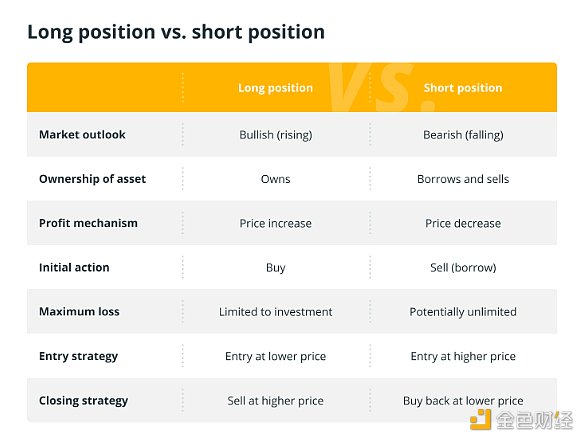
The content of the above table is summarized in Chinese as follows:
Long Positions and Short Positions
3. The Process of Going Long on Cryptocurrency
Going long on cryptocurrency involves a strategic process of profiting from an expected price increase.
The following is a step-by-step process:
Research and Analysis
Before making any investment, one must carefully investigate and analyze the chosen cryptocurrency. Consider factors such as technology, market trends, historical data, and acceptance possibilities.
Choose a Cryptocurrency Exchange
Next, the trader must choose a trusted cryptocurrency exchange or trading platform that offers the desired cryptocurrency. They should set up an account, perform the necessary checks, and use two-factor authentication to protect the account.
Deposit Funds
After creating an account, the next step is to deposit funds into it. Depending on the platform, users can typically deposit fiat currency or other cryptocurrencies to purchase the desired tokens.
Place a Buy Order
The next step is to place a “buy” order on the chosen cryptocurrency platform. Users can choose the current market price or a limit order with a specific purchase price.
Monitoring and Management
After executing the purchase order, individuals own the cryptocurrency. They should carefully monitor market developments and choose exit strategies, which may require determining price targets based on technical indicators or other requirements. When it is necessary to sell long positions and convert the cryptocurrency into their preferred currency, they can place a “sell” order.
IV. Risks and Potential Returns Associated with Long Positions
Long positions in cryptocurrencies have the potential to generate substantial profits through price appreciation, but they also come with significant risks of market volatility and potential losses.
Despite the existence of certain risks, long positions in cryptocurrencies have the potential to generate significant returns. The opportunity to profit from price increases is the primary advantage. For example, an investor purchased Bitcoin (BTC) at a discounted price and held it during a period of sharp value increase, resulting in substantial gains.
Long positions allow investors to participate in the evolving cryptocurrency ecosystem and potentially profit from the adoption of blockchain technology. However, the risks are equally prominent. It is well known that cryptocurrencies are highly volatile, with prices prone to sudden changes.
If the market turns bearish and the value held by investors decreases, they may incur losses. Prices can also be affected by regulatory uncertainty, security vulnerabilities, and market sentiment.
Due to the long-term instability and unfavorable trends that can affect the cryptocurrency market, maintaining long positions requires patience. Investors must conduct in-depth research, practice risk management, and continuously educate themselves to make wise decisions when buying long positions in cryptocurrencies.
V. The Process of Shorting Cryptocurrencies
In the world of cryptocurrencies, shorting involves betting on price declines and profiting from them.
The following is a step-by-step process:
Research and Analysis
Traders first thoroughly research and analyze the cryptocurrency they want to sell. They look for signs that the asset’s value may decline, such as unfavorable news, overvaluation, or technical indicators indicating a bearish trend.
Selecting a Trading Platform
Traders choose a reputable cryptocurrency exchange or trading platform that offers margin trading or alternative options for shorting the specific cryptocurrency they want to short.
Setting Up a Margin Account
Traders open a margin trading account on the selected platform, complete any necessary identity verification steps, and deposit fiat currency or cryptocurrency as collateral. This collateral is necessary to mitigate potential losses when holding short positions.
Borrowing Cryptocurrency
To short sell cryptocurrency, one must borrow it from an exchange or another platform user. The borrowed cryptocurrency is then sold on the open market.
Monitor and Set Limits
Traders carefully monitor the cryptocurrency market to observe price changes. They set target buyback prices and establish stop-loss orders to prevent further losses. They intend to repurchase the borrowed cryptocurrency to close the short position at this target price.
Closing the Position
When an expected price drop occurs in cryptocurrency, traders close their position by buying back the borrowed cryptocurrency at a lower price, returning it to the lender, and profiting from the price drop. This action marks the completion of the short position.
Risks and Potential Returns Associated with Short Positions
Short positions in cryptocurrency have the potential for high returns, but they also come with significant risks. The primary benefit is the opportunity to profit from the price drop of cryptocurrency. For example, if a trader accurately anticipates a bearish trend and shorts cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin, they may repurchase it at a lower price and profit from the price difference.
However, short-term investments often come with significant risks. The cryptocurrency market is notorious for its high volatility, and an unexpected price increase can result in substantial losses for short sellers.
Unlimited risks also need to be considered, as there is no upper limit to how much prices can rise. Legislative changes, unexpected shifts in market sentiment, or unexpected positive news can cause prices to surge.
Short selling cryptocurrency requires precise timing, meticulous risk management, and continuous market monitoring to successfully navigate its inherent volatility and maximize potential gains while limiting losses.
Tax Implications Related to Profits and Losses from Long and Short Positions
The tax implications of profits and losses from long and short cryptocurrency positions can be complex and vary by country/region.
In many countries, profits from long positions are typically treated as capital gains, and capital gains tax may be imposed when the asset is sold. Short-term gains are taxed higher than long-term gains, and tax rates often vary based on the holding period.
In contrast, short positions may entail special tax difficulties. In some countries, the act of borrowing and selling cryptocurrency short may not immediately generate tax obligations since the short position is not closed until the borrowed asset is repurchased. Traders may experience capital gains or losses when closing short positions, depending on the difference between the selling and buying prices.
In order to understand and comply with local tax laws, cryptocurrency traders should be aware of the cryptocurrency tax laws applicable in specific jurisdictions, as there may be significant differences in the tax treatment of cryptocurrency gains and losses in different locations. Additionally, proper record keeping and reporting are crucial for maintaining tax compliance in the cryptocurrency industry.
We will continue to update Blocking; if you have any questions or suggestions, please contact us!
Was this article helpful?
93 out of 132 found this helpful
Related articles
- Duties Embezzlement Crime in the Employee Risk Prevention of NFT Digital Collection Company
- The golden age of Web3 protocol unlocking the potential of the future economy
- Decentralization and protocolization of the whole-chain game
- Introducing zkUniswap The First zkAMM
- Exploring the Opportunities of Layer2
- A Quick Understanding of Zora Network, an NFT Application Chain Based on OP Stack
- Cryptocurrency Involved in Singapore’s Largest Money Laundering Case





