Ethereum brings ‘bad news’ Futures ETF falls short of expectations, on-chain data at a low point
Ethereum's Futures ETF disappoints, on-chain data hits a low point.Ethereum’s Institutional Interest Limited in Bear Market
In the context of the crypto bear market, six different Ethereum futures financial instruments officially began trading on October 2, but they have not reignited institutional investors’ enthusiasm for ETH. The total trading volume of the first day of ETH futures ETF was less than $1.5 million, compared to the Bloomberg data which showed that the first day trading volume of the first BTC futures ETF (BITO) in 2021 exceeded $1 billion. In other words, the net inflow of funds on the first day of ETH futures ETF was less than 2% of BITO.
Duong, the head of Coinbase Research, believes that the above differences are due to the following main reasons:
Firstly, the timing of the ETF launch is different. Proshares’ BTC futures ETF was launched during the bull market cycle in 2021, with ample market liquidity, while ETH futures ETF was launched during the current bear market cycle with severe funding shortages.
Secondly, the familiarity of investment advisors is different. Investment advisors are usually more familiar with BTC, which is easier to integrate into their clients’ portfolios. ETH is generally considered a more complex investment product and has not been well understood and accepted in the traditional investment world.
- South China Morning Post Article Why can’t the JPEX incident shake Hong Kong’s cryptocurrency vision?
- Forbes Binance’s Golden Touch, how did they turn failed ICO tokens into unexpected fortunes worth billions of dollars?
- Web3 Legal Popularization丨Can GameFi Go Online Without a Game License and Constitute Illegal Operations?
Thirdly, the change in expectations at the legal level. In a recent court ruling in Risely vs Uniswap, Judge Katherine Polk Failla classified ETH as a commodity. This may have raised market expectations for ETH spot ETFs, but resulted in a lackluster market response to ETH futures ETFs.
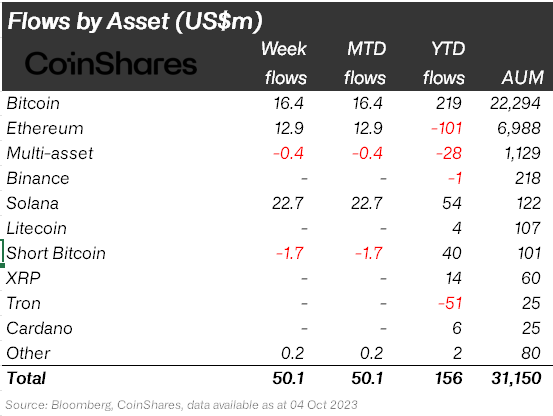
In terms of fund flows, the crypto bear market continues to have a significant impact on institutional capital. According to statistics from Coinshares, there were 24 weeks of net outflows of funds within the 39 weeks since 2022, accounting for 61.5% of the entire period. The changes in institutional interest in crypto assets can also be seen from the fund flow data: as of October 4, the net outflow of funds for ETH this year reached $101 million, while BTC had a net inflow of $219 million during the same period. However, the recent weekly net inflows for BTC and ETH are similar, at $16.4 million and $12.9 million respectively.
Overall, although ETH futures ETF has received a lukewarm response, its trading volume is still within normal levels for new ETFs, and it has played a positive role in attracting institutional investment interest. However, due to factors such as the bear market background, it will require an overall warming of the crypto market to attract more institutional capital inflows.
Potential Risks of Ethereum Staking
On October 5, JP Morgan released a research report pointing out the centralization issue of the Ethereum network and stating that the ETH staking yield has dropped from 7.3% before the Shanghai upgrade to 5.5%. Compared to the rising yields in traditional financial markets, the attractiveness of ETH as an investment target has declined.
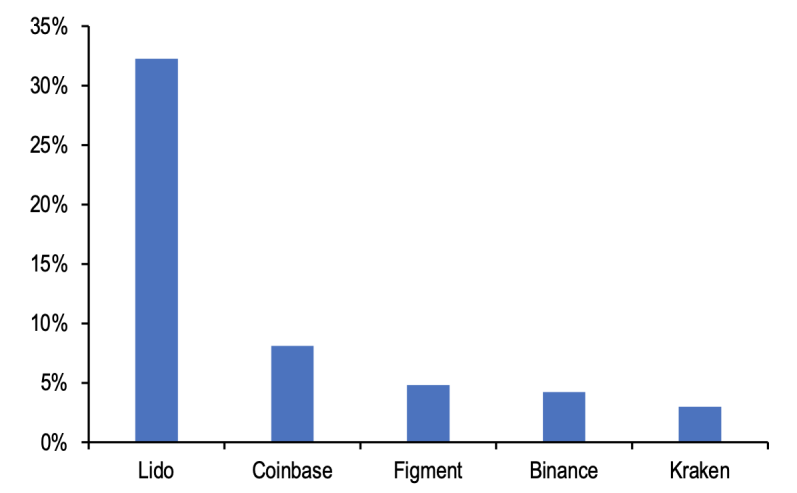
This report points out that the top five liquidity providers, Lido, Coinbase, Figment, Binance, and Kraken, control 50% of the ETH staked, with Lido accounting for almost one-third of the total ETH staked.
The liquidity staking platform Lido is seen by the cryptocurrency community as a superior alternative to centralized exchange staking platforms. Currently, in order to mitigate centralized risks, Lido has been expanding its list of node operators, aiming to prevent any single entity from controlling the majority of staked ETH.
In addition, in order to counter the centralization risks of the Ethereum blockchain, the Ethereum community has begun promoting Distributed Validator Technology (DVT), such as SSV and Obol. DVT allows multiple node operators to run a validator. This is done to reduce validator-related risks without affecting the blockchain.
Another concern raised by JP Morgan is the practice of rehypothecating liquidity staking assets. This involves the issue of reusing liquidity tokens as collateral in various DeFi protocols. This practice could trigger a chain reaction of liquidations if the value of the staked assets suddenly plummets or is compromised due to malicious attacks or protocol vulnerabilities.
Ethereum gas fees hit bottom
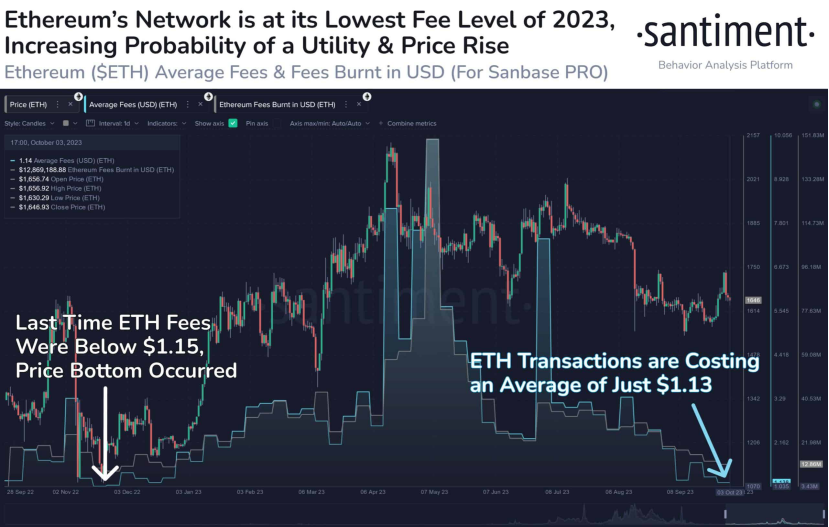
According to statistics from on-chain analytics platform Santiment, Ethereum gas fees have dropped to the lowest level in nearly a year. The average cost of Ethereum on-chain transactions in the past week is only $1.13, significantly lower compared to early May. It is worth noting that the last time gas fees were below $1.15, the price of ETH was at the bottom.
L2 paving the way for Ethereum scalability
The significant decrease in Ethereum gas fees is related to the adoption of L2 scalability solutions. Due to the cost and efficiency advantages, a large number of users have flocked to L2, resulting in a significant increase in the block space demand of L2.
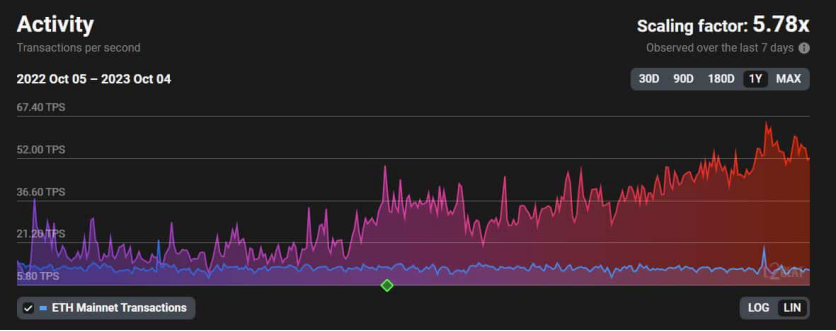
According to data from L2Beat, transaction activity on L2 scalability solutions has seen a significant increase in 2023. Based on recent data, the TPS (transactions per second) of L2 has reached 5.78 times that of the Ethereum blockchain.
Essentially, L2 is fulfilling its original intention of alleviating the transaction burden on the Ethereum main chain and assisting in its scalability. Santiment believes that lower gas fees can promote the utilization of the Ethereum network, attracting more decentralized applications and smart contracts. In the long run, as the Ethereum network is more widely adopted, the price of ETH will also increase.
Recently, a Grayscale report also pointed out that L2 is paving the way for Ethereum scalability. Functionally, L2 can enhance the scalability of Ethereum, reducing network costs for users by 100 times. In August of this year, Coinbase launched BASE (Ethereum’s L2 blockchain), which also marks a strong endorsement of the Ethereum ecosystem and opens its decentralized applications to 100 million Coinbase users.
Coinbase is trying to pave the way for the widespread adoption of DApps on its own Ethereum L2 solution, BASE. If alternative L1 solutions are not attractive due to low security budgets and lack of liquidity, integrating with Ethereum L2 may be a more appealing choice.
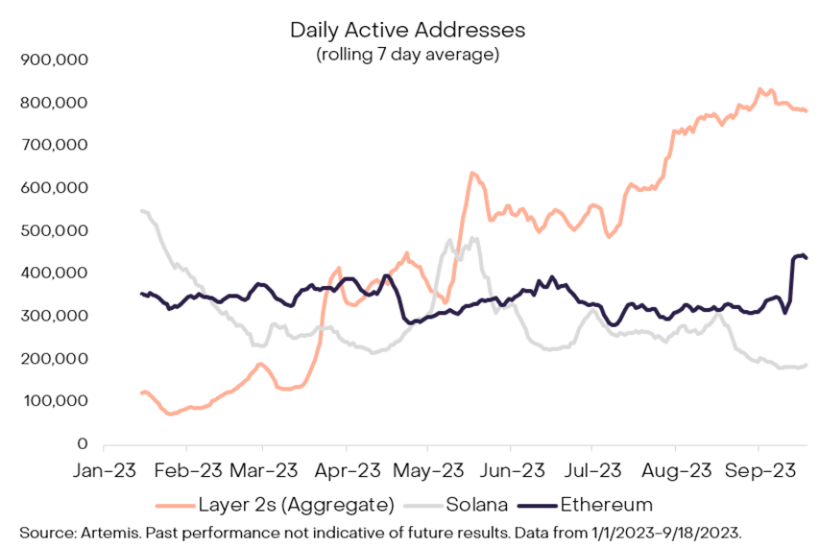
The usage of Ethereum L2 scaling solutions has been growing over the past year, with the total daily active addresses on L2 surpassing those on leading L1.
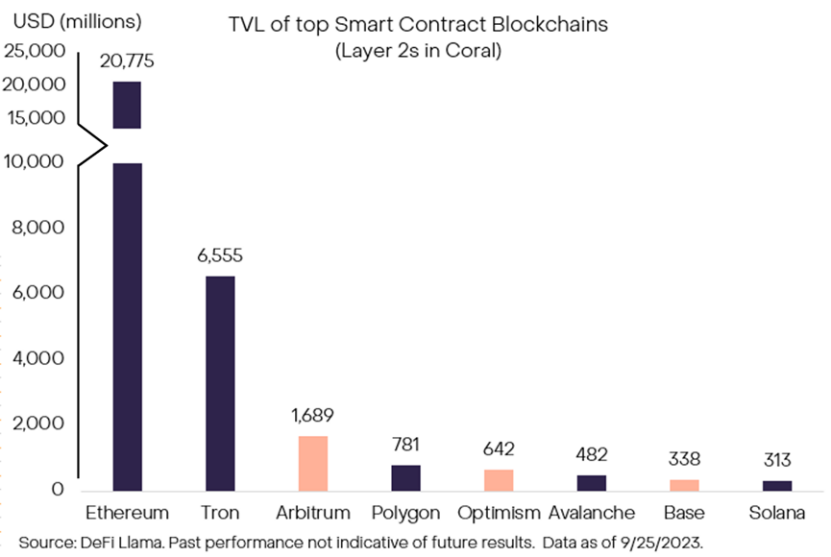
In addition to active addresses, the Total Value Locked (TVL) is also important as it reflects the level of trust users place in a particular blockchain by locking their funds. The TVL of the top-performing L2 solutions (including Arbitrum and Optimism) has exceeded that of Ethereum’s competitors on L1 (Solana and Avalanche), indicating the overall market trust in the Ethereum ecosystem and the attractiveness of scaling solutions.
As the network scales, more activity will shift to cheaper L2 solutions. In return, L2 directly accrues value back to Ethereum. Specifically, for every transaction on L2, users pay transaction fees. L2 retains a portion of the fees (currently with an average profit margin of about 1/4), while Ethereum network validators capture the remaining approximately 3/4.
For every transaction sent on L2, a small portion of the total Ethereum supply is burned. Therefore, the incremental activity on Ethereum L2 directly accumulates value for ETH. If Ethereum’s L2 solutions continue on a positive development trajectory, they will solidify Ethereum’s position as the leading L1 blockchain.
ETH Balance on Centralized Platforms Hits a 5-Year Low
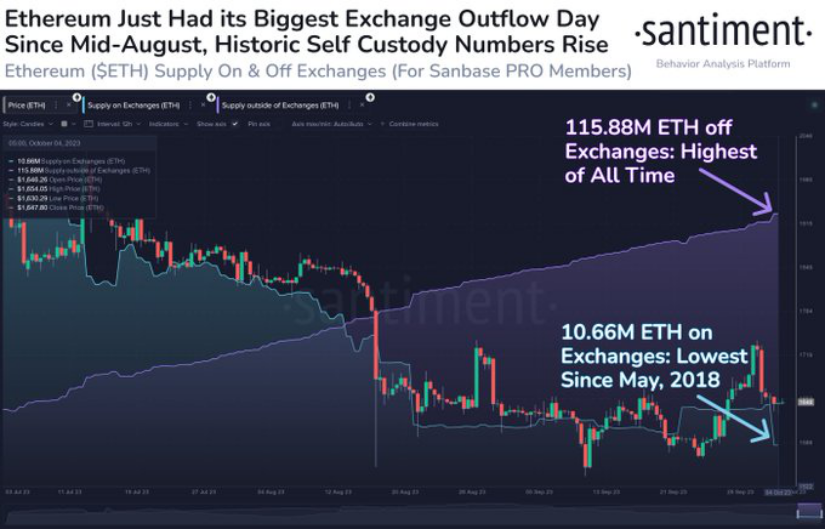
According to Santiment data on October 5th, the amount of ETH held on cryptocurrency exchanges has dropped to 10.66 million, reaching its lowest level since May 2018. In contrast, there is a record high of 115.88 million ETH stored outside of centralized exchanges.
On October 4th, approximately 110,000 ETH (worth over $180 million) was withdrawn from centralized exchanges, marking the largest single-day outflow of ETH from centralized exchanges since August 21st. These phenomena are often seen as long-term bullish signals for the valuation of ETH assets, showcasing investors’ long-term confidence.
We will continue to update Blocking; if you have any questions or suggestions, please contact us!
Was this article helpful?
93 out of 132 found this helpful
Related articles
- Crypto Race Weekly Report [10/9/2023] Decrease in ETH Staking Rewards, POW Track on the Rise
- Polkadot Q3 Development Summary Native USDC will enter the ecosystem, staking and independent account data continue to grow.
- Financing Weekly Report | 14 public financing events; Web3 restaurant loyalty application Blackbird completes $24 million Series A financing, led by a16z Crypto.
- In the past month, about 270,000 RNDR tokens have been destroyed. How big is the future space for the distributed rendering network Render Network?
- Q3 Crypto Dapp Report Daily active wallet count increased by 15% compared to the previous quarter, NFT transaction volume hits a new low in the past year.
- LayerZero’s Full-Chain Narrative Security Prospects and Ecological Opportunities
- What happened during the first week of the SBF case in a comprehensive article?




