Raft’s ten thousand character research report Decentralized lending protocol, the second largest LSD stablecoin $R issuer.
Raft's research report on decentralized lending protocol, the second largest issuer of the LSD stablecoin $R.Project Introduction
Raft is an immutable and decentralized lending protocol that allows users to obtain stablecoin loans by efficiently collateralizing their capital. It is a way to maximize capital utilization while maintaining your staking rewards.
$R is an Ethereum-based stablecoin fully backed by stETH (Lido Staked Ether). $R provides the most efficient capital utilization for borrowing using your stETH. The goal of $R is to become the preferred stablecoin in the decentralized ecosystem, with deep liquidity in many trading pairs and a stable anchor exchange rate.
Table of Contents
1. Research Highlights
1.1 Core Investment Logic
- Be vigilant of hidden Rug Pulls, as well as exit scams caused by contract storage.
- LianGuairadigm proposes ten potential trends, and intent-centric ranks first. What is intent-centric?
- Web3 Mobile Review Can the encryption industry usher in an iPhone moment?
1.2 Valuation
2. Project Overview
2.1 Project Scope
2.2 Past Development and Roadmap
2.3 Team Information
2.3.1 Overall Situation
2.3.2 Founders
2.3.3 Core Members
2.4 Financing Situation
3. Business Analysis
3.1 Target Users
3.2 Business Categories
3.3 Business Details
3.4 Industry Space and Potential
3.4.1 Categories
3.4.2 Market Size
3.5 Business Data
3.6 Project Competitive Landscape
3.6.1 Project Introduction
3.6.2 Project Comparison
3.7 Token Model Analysis
3.7.1 Stablecoin R
3.7.2 Value Capture of Stablecoin
3.7.3 Core Demand for Stablecoin
4. Preliminary Valuation
4.1 Core Issues
4.2 Valuation Level
4.3 Risk Analysis
5. References
1. Research Highlights
1.1 Core Investment Logic
Raft is an LSDfi (LSDFinance) protocol designed to provide users with capital-efficient lending tools. By collateralizing liquidity tokens, users can generate R as collateral and utilize their staking rewards in the best way to obtain loans.
In terms of product, R is an Ethereum-based USD stablecoin that supports collateralization of liquidity tokens (such as stETH, rETH, wstETH) and aims to become the preferred stablecoin in the decentralized ecosystem. R has deep liquidity and is closely and stably linked to the US dollar through a combination of hard peg and soft peg mechanisms.
Compared to traditional lending platforms, Raft has the following advantages: 0% interest rate and no issuance fees, borrowers do not have to worry about accumulating debts; high capital efficiency, minimum collateralization ratio of 120% (as of 2023.7.24 is 180%), allowing for more efficient utilization of deposited stETH; decentralized, key parts of the contract have no admin keys and are hosted by different frontend operators through multiple interfaces, increasing resistance to censorship.
However, there are also risks in investing in the Raft project. Firstly, the DeFi market itself is highly uncertain, and the innovative technologies and complex financial instruments involved may bring potential risks. In particular, in the Raft project, there are price fluctuations in the Liquid Staked Dollar (LSD), which may lead to price instability and potential liquidation risks for users.
In terms of future development, as the DeFi market continues to evolve, Raft is expected to bring more innovative and capital-efficient solutions to users. Overall, as a capital-efficient LSDfi protocol, Raft has innovative lending mechanisms and decentralized characteristics, and is expected to be widely used and developed in the DeFi market. However, investors should be aware of the risks in this field and make reasonable investment decisions based on their own circumstances.
1.2 Valuation
The valuation range of Raft is between 2.94 million and 32.32 million, please refer to section 4.2 for details.

2. Project Overview
2.1 Project Scope
The Raft project is a lending and stablecoin issuance platform for cryptocurrency holders. By allowing users to generate R tokens by pledging liquidity tokens as collateral, it provides an efficient way of borrowing capital and pegs it to the US dollar. The project focuses on providing deep liquidity and stable pegged R tokens to meet the stablecoin demand in the decentralized ecosystem. At the same time, it improves capital efficiency and fee flexibility, optimizes liquidation and incentive mechanisms, and is committed to providing a better user experience and incentive mechanism. Overall, the business scope of the Raft project covers aspects such as lending, stablecoin issuance, liquidity provision, and improvement mechanisms, aiming to bring more financial opportunities and benefits to cryptocurrency holders.
2.2 Past Development and Roadmap
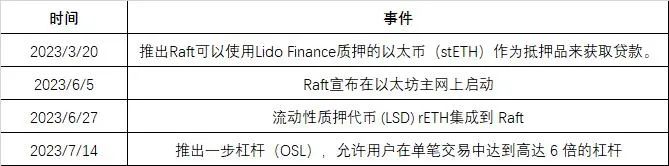
2.3 Team Overview
2.3.1 Overall Situation
Raft is a project created by the TempusLabs team, which is a service provider elected by the governance process of TempusDAO to lead product development. TempusDAO is a risk DAO supported by companies such as Lemniscap, Jump, Tomahawk.VC, GSR, and Winintermute, and is managed by TEMP token holders. The team is led by two founders, including departments such as product development, marketing and business development, and operations. Team members have rich industry experience and have worked in leading institutions such as BANKOF AMERICA, GoldmanSachs, NOAURA, BNPLianGuaiRIBAS, UBS, ethereumfoundation, ALLEN& OVERY, KIRKLAND&ELLIS, Barclaycard, Lendinvest, Microsoft, and IBM. Product developers account for 60% of the total team members, including 6 frontend engineers, 1 product and business developer, 1 research director, 1 quality inspector, 1 quantitative analyst, 1 graphic designer, and 1 product manager.
2.3.2 Founder
- David Garai – Founder

The founder graduated from the University of Manchester and founded Tempus, Nostra, and Raft. He served in strategic, financial, and operational leadership roles at Tempus. Previously worked as a structured finance lawyer in London and Tokyo, and co-founded Tempus with Dorde.
- Dorde Mijovic – Founder

He is a co-founder and chief technology officer of Tempus Finance, responsible for overseeing the technology aspects of Tempus. He has worked as a software engineer at Ethereum and Microsoft, and graduated from the University of Belgrade. He has 9 years of professional experience in various projects such as computer vision, web applications, and recently compilers. Currently, he is developing a Solidity compiler for Ethereum.
2.3.3 Core Members
- Daniele – Front-end Lead

Daniele is one of the front-end engineers at Raft. He has extensive work experience in various industries, including gaming, insurance, fintech, banking, and the current DeFi field.
- Connor – Business Development Manager

Connor is responsible for developing new partnerships at Raft. Connor has been a supporter of cryptocurrencies since 2013. Prior to joining Raft, Connor has worked in derivative brokerage and early-stage DeFi and fintech venture capital.
2.4 Financing Situation
According to the official website, Raft’s investment institutions include EmnisCap, Jump, Launchub, Tomahawk.vc, Wintermute, GSR, Koji, DistributedGlobal, and Supernova. However, disclosure of financing information is currently not available on the official website.

3. Business Analysis
3.1 Target Audience
The following are the business service objects of the Raft project:
1) Borrower Category:
Those who want to borrow R tokens by depositing liquidity collateral tokens on the Raft platform.
They need to meet certain requirements, such as maintaining a collateralization ratio greater than a specific value and meeting minimum debt requirements.
2) Investor Category:
Investors can use the Raft platform to redeem and receive collateral from other borrowers as a reward.
Debt can be redeemed by providing R tokens.
3) Liquidator Category:
Liquidators can obtain collateral and liquidation rewards by liquidating borrowers whose debt falls below the minimum collateral ratio.
4) Flash Minting Participant Category:
Flash Minting participants can use the Flash Minting function to obtain R tokens.
A certain proportion of the total $R supply can be minted at once.
5) Trader Category:
Traders can trade R tokens and other currency pairs against R tokens.
3.2 Business Categories
The Raft project covers borrowing, repayment, flash minting, one-step leverage, oracles, and Positions.
Borrowing: Users can borrow $R by depositing LSD and create a Position. Borrowing requires maintaining a collateral ratio of over 120% and a debt of at least 3,000R. The borrowing rate consists of a base rate and a borrowing spread, with a maximum limit of 5%.
Repayment: There are three methods to repay R, including repayment, redemption, and liquidation. Borrowers can use R tokens to repay debt and retrieve collateral. R holders can redeem R tokens to receive collateral from other borrowers. Liquidators can liquidate borrowers whose debt falls below the minimum collateral ratio and receive collateral and liquidation rewards.
Flash Minting: Users can use the Flash Minting function to mint 10% of the total R supply at once and obtain R tokens. Flash Minting has security measures such as returning and destroying the minted amount in the same transaction.
One-Step Leverage: Allows users to leverage on stETH using Flash Minting.
Oracles: Ensures the reliability of price data through two oracle systems.
Positions: Each wallet address is only allowed to have one Position and one LSD collateral. Supports depositing Non-Rebase LSD and wrapped Rebase LSD.
3.3 Detailed Business Description
1) Borrowing
Definition:
Borrowing $R requires users to deposit their LSD and maintain a collateral ratio of at least 120% for each borrowed $R, creating a Position.
- Minimum Debt
Users must have a minimum debt of 3,000 $R. This is the minimum amount of $R that can be borrowed.
Each wallet address can only have one type of LSD collateral.
- Borrowing Spread
The borrowing spread is a part of the borrowing rate. Each type of LSD collateral has a different borrowing spread.
- Borrowing Rate
The borrowing rate (BorrowingRate) is the sum of the base rate (BaseRate) and the borrowing spread (BorrowingSpread), with a maximum limit of 5%.
The base rate is based on the borrowing and redemption frequency of R.

Borrowing Fee
The Borrowing Fee is the Borrowed Amount multiplied by the Borrowing Rate, and the fee is paid in $R.

Calculating Borrowing Fee
To calculate the Borrowing Fee, multiply the rate by the borrowed amount in $R. For example, if the rate is 0.05% and the user borrows 10,000 $R, they will be charged a fee of 5 $R. After adding the Borrowing Fee, the total debt will be 10,005 ($R).
2) Repayment
There are three ways to generate $R:
- Repayment: Borrowers use $R to repay their debt and retrieve their LSD collateral.
- Redemption: $R holders purchase $R on the open market, redeem $R, and receive LSD collateral from other borrowers as a return.
- Liquidation: Liquidators pay off the R debt of borrowers with a collateral ratio below the Minimum Collateralization Ratio (MCR) and receive LSD collateral and liquidation rewards as a return.
When R is repaid, it is immediately destroyed through its fully decentralized smart contract.
- Repayment
When a user opens a position and borrows $R tokens, they can choose to partially or fully repay their debt. For partial repayment, it should be noted that the remaining debt balance after repayment cannot be less than 3000 $R.
A successful repayment will immediately destroy the repaid $R tokens through a smart contract. This process not only increases the collateral ratio of the position but also increases the amount of collateral available for withdrawal.
- Redemption – Ensuring Stability through Redemption
The redemption feature allows holders of $R stablecoins purchased on the open market to redeem them at any time, receiving LSD collateral from other borrowers equivalent to the value of the dollar. This mechanism ensures that $R always has support that can be redeemed for its face value, with the value of each $R’s LSD collateral being one dollar.
When a user redeems $R, the protocol uses it to partially repay the debt of each existing position and withdraws the corresponding LSD collateral, which is then sent to the redeemer. The amount of debt to be repaid will be proportionally allocated based on the relative share of collateral and debt of other positions. This mechanism ensures that the protocol increases its level of overcollateralization and the distribution of the withdrawn LSD collateral is fair among all borrowers.
- Redemption Spread
The redemption spread is a component of the redemption rate that sets a baseline for users who redeem their R. When redemption occurs, borrowers will lose a portion of their LSD collateral, and the benchmark rate will increase due to redemption. Therefore, a non-zero redemption spread can prevent potential market manipulation that may disrupt Raft’s normal borrowing activities and represents a component of the reward earned by the redeemed borrowers.
Note: Each LSD collateral token has a specific redemption spread, which has a hardcoded range with specific limits: the minimum redemption spread is set to 0.25%.
The maximum redemption spread is set to 100%, effectively disabling redemption. In this case, anyone who redeems will not receive any yield.
- Oracle Price Deviation
To prevent Raft users from being exploited when the oracle price deviates from the true market price but is still below the price deviation threshold, the redemption rate will take into account the price deviation threshold of the oracle being operated.
Since different oracles may have different price deviation thresholds, the corresponding price deviation will be applied based on whether the primary oracle or secondary oracle is currently being used by the protocol.
This measure ensures that price differences in the oracle system do not unfairly affect Raft users.
- Redemption Rate
The redemption rate is the sum of the base rate, redemption spread, and oracle price deviation. This rate is only charged when redeeming R if the price of R is below $1, reducing the attractiveness of redeeming R with stETH.
The base rate is based on the borrowing and redemption frequency of R.

Redemption Fee
The redemption fee is simply the redemption amount multiplied by the redemption rate, paid in R.

Redemption Return
If a Position is redeemed, the borrower is entitled to a redemption return, which is a percentage of the redemption fee (redemption return rate).
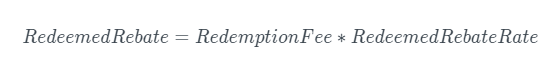
Liquidation – Ensuring Collateral Support
Note: Liquidation ensures that each R is always backed by LSD worth at least $1.
When the collateral of a Position is between the minimum collateral ratio and 120% collateral ratio (i.e., 100% < Position's collateral < 120%), the account is eligible for liquidation.
Note: When the collateral of a position is lower than or equal to 100% (i.e., the collateral of the position <= 100%), the account is eligible for reallocation.
The liquidation process is initiated when the liquidator calls the smart contract to execute the liquidation.
Then, the liquidator starts repaying the borrower’s total debt. In return, the liquidator receives the corresponding collateral and a liquidator reward.
Corresponding Collateral
The corresponding collateral is the LSD equivalent value of the total debt repaid by the liquidator.
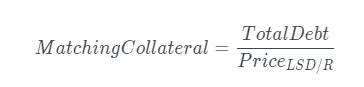
Excess Collateral
Excess collateral refers to the difference between the total collateral and the corresponding collateral, which is divided between the liquidator (liquidator reward) and the protocol (liquidation protocol fee).

The provision of liquidator rewards and liquidation protocol fees is to encourage users to support the protocol and prevent borrowers from leaving their positions and exposing the protocol to liquidation risk.
No liquidation penalty will be charged if the borrower voluntarily repays or replenishes their collateral.
Liquidator Reward
The liquidator reward is compensation for the risk taken by the liquidator in the liquidation process.
The liquidator reward rate is based on the percentage of excess collateral to the total debt. Currently, the liquidator reward rate is set at 100%, allowing liquidators to collect all excess collateral.
The actual liquidator reward is the excess collateral multiplied by the aforementioned liquidator reward rate.
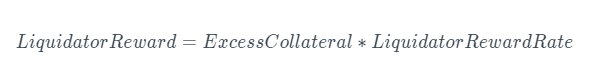
Liquidation Protocol Fee
If there is excess collateral remaining, it will be transferred to the protocol.
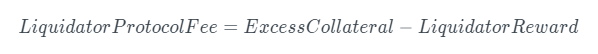
Example:
Assume that the borrower has a debt of 10,000 R and collateral of 5wstETH.
wstETH is trading at 2,180 R.
Calculation:
This position has a collateral ratio of 2,180 * 5 / 10,000 = 109%, which is below the liquidation threshold of 110%.
The liquidator can come in and repay 10,000 R.
In return, the liquidator will receive the following wstETH:
Corresponding wstETH = 10,000 / 2180 = 4.587
Liquidator reward rate = 100.0%
Liquidator reward = (5 – 4.587) * 100.0% = 0.413
Total = 4.587 + 0.413 = 5
Total collateral received in R: 5 * 2180 R = 10,900 R
Total debt repaid in R: 10,000 R
Net profit %: (10,900 – 10,000) / 10,000 = 9%
- Redistribution
When the collateral of a position falls to or below 100% (i.e., collateral <= 100%), the account is eligible for redistribution.
Redistribution is a key mechanism in decentralized finance protocols that ensures the stability and security of lending platforms.
In the highly unlikely event that the liquidator fails to liquidate all under-collateralized and high-risk positions, it serves as the last line of defense. This mechanism acts as a critical safeguard, protecting users with higher collateral levels.
In the reallocation process, the losses incurred by an under-collateralized position will be fairly distributed among all positions, reducing the risk of systemic failure. This mechanism helps maintain users’ trust and confidence in the protocol, making it an integral part of DeFi lending.
- Mechanism
If a borrower’s collateral ratio falls to 100% or below, reallocation can be initiated by a reallocator, who will receive a reallocation reward.
The remaining collateral and debt of the affected position will be proportionally allocated based on the collateral amounts of other positions, with positions having higher collateral amounts receiving a larger share.
Once reallocation is completed, the under-collateralized position will be closed.
- Reallocation Reward
The sole responsibility of the reallocator is to call the contract to initiate the reallocation process. Incentives are provided to reallocators due to the potential high gas fees involved.
The reallocation reward rate is a dynamic percentage of the total collateral. The rates are set according to the following table.
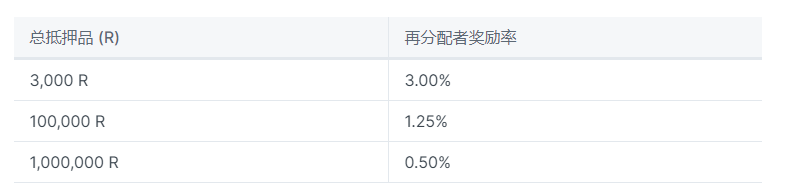
For values between the listed critical total collateral amounts, the reallocation reward rate is linearly interpolated between the corresponding reallocation reward rates.
For total collateral <3,000 $R, it will be a fixed rate of 3.00%.
For total collateral >1,000,000 $R, it will be a fixed rate of 0.50%.
The actual reallocation reward is simply the total collateral multiplied by the aforementioned reallocation reward rate.

Example:
When total collateral = 10,000
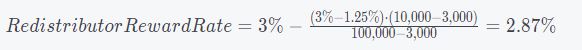
This means the liquidator will receive 2.87% of the total collateral, which is 287 $R.
- Reallocation Example
Position A has a debt of 10,000 $R and collateral of 5 wstETH. The current price of wstETH-USD is 2,000.
Its collateral ratio is below 100% (5 * 2,000 / 10,000), making it eligible for reallocation.
The reallocator calls the contract to initiate reallocation and collects 0.14 (5 * 2.87%) wstETH, which is equivalent to 287 $R.
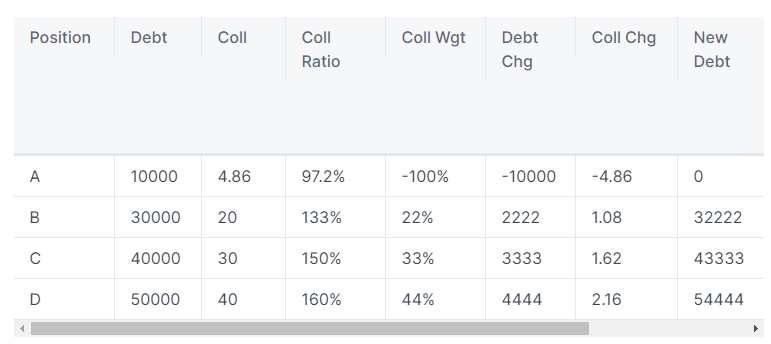
The remaining debt of 10,000 $R and collateral of 4.86 (5 * 97.13%) wstETH are distributed to Positions B/C/D at proportions of 22%/33%/44%. The calculation for 22% is 20 / (20 + 30 + 40).
After redistribution, the debt and collateral of all remaining positions have increased. Their collateral ratio decreases because they accept positions with a lower collateral ratio.
Note: All debts are represented in $R, and all collaterals (Coll) are represented in wstETH.
3) Flash Minting – a powerful and secure tool in the Raft ecosystem
The Flash Minting module is a powerful tool that allows users to mint 10% of the total supply of R tokens in one transaction, provided that they pay back at a Flash Mint rate of 0.01% in the same transaction.
Note: The Flash Mint rate is a value between 0% and 5%. This rate is initially set at 0.01% but may be adjusted as the R market becomes more efficient.
- Emphasis on Security
The Flash Minting feature of the R token is designed with a focus on security and incorporates various measures to protect the R token. The core feature is that the minted amount must be returned and destroyed in the same transaction, preventing malicious behavior or exploitation of the R token.
- Flash Minting vs. Flash Borrowing
Note: Flash Minting is Flash Borrowing directly provided by the Raft protocol.
Compared to Flash Borrowing, the Flash Minting module runs directly in the Raft smart contract, eliminating the need to borrow R from separate money markets or liquidity pools. Additionally, Flash Minting transactions require lower gas fees. This makes Flash Minting a more efficient alternative to Flash Borrowing, especially in cases of liquidity scarcity or high gas costs.
- Flash Minting for Leveraging
Similar to Flash Borrowing, Flash Minting allows users to mint R, convert it into LSD, and obtain a leveraged collateral position in one step.
- Application of Flash Minting in Liquidation
Flash Minting can play an important role in the liquidation process. Liquidators can use Flash Minting to acquire the required R tokens to repay the borrower’s debt. They can then convert the received collateral back to R and repay the Flash Minting, all in one transaction. This process allows liquidators to engage in risk-free arbitrage in the market.
- Flash Minting Calculator
We have created a Google Sheet to assist you in understanding. To customize input values, you just need to make a copy of this sheet.
4) One-Step Leverage – Flash Minting for leveraging
Raft allows users to obtain one-step leverage on stETH. With one-step leverage, users can open, close, and adjust their leverage on stETH.
The steps to generate LSD leverage through FlashMint are as follows:
A) Users
Select the amount of LSD collateral they wish to deposit, defined as InitialCollateral
Select the desired leverage multiplier (e.g., 3x), defined as Leverage
Select the desired slippage tolerance, defined as SlipLianGuaige, for the contract to execute the exchange between $R and LSD
B) The smart contract executes the following operations:
Flash issues a certain amount of R tokens, defined as FlashMintDebt, which is the sum of FlashMintAmount and FlashMintFee.
Exchange FlashMintAmount of R in the liquidity pool for LSD. This operation requires users to pay an exchange fee, defined as SwapFee. The expected value of R in wstLSDETH obtained through the exchange is defined as addCollateral, which equals: the contract deposits addCollateral in the user’s Position to increase the collateral base.
The final amount of wstETH collateral after the exchange will be equal to the amount of R borrowed by the contract, which is equivalent to repaying the amount borrowed from FlashMint and closing the transaction.
The steps to generate unleveraged LSD through FlashMint to close all debts are as follows:
Users select the desired slippage tolerance, defined as SlipLianGuaige, for the contract to execute the exchange between LSD and $R
Click ‘Close all Debts’
The smart contract executes the following operations:
1. Flash issues $R amount equal to totalDebt
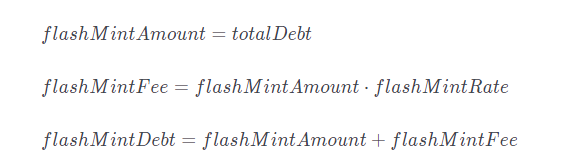
Use FlashMint’s R to repay the totalDebt of all Positions
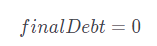
In the liquidity pool, exchange reduceCollateral amount of LSD for flashMintDebt amount of R. This operation requires users to pay an exchange fee, defined as swapFee
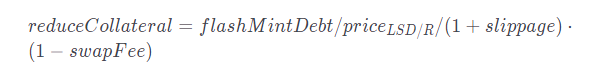
Reduce reduceCollateral in the user’s Position to decrease the collateral base. The final amount of LSD collateral after the exchange will be:
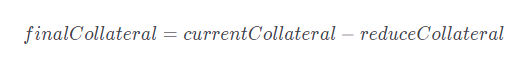
5. Repay the borrowed amount from FlashMint and close the transaction
6. The Position is now fully deleveraged
It should be noted that changes in the price of $R in USD may affect the amount of funds required to close the Position. In particular, if the price of $R in USD has increased since the Position was opened, more collateral will be required to repay the loan.
- Adjustments
Adjusting leverage allows users to change their Position to any other leverage (within limits) through Raft’s FlashMint mechanism.
The steps to generate LSD leverage through FlashMint are as follows:
1. Users
Select the desired leverage multiplier (e.g., 3x), defined as leverage
Users can choose the desired slippage tolerance, defined as slipLianGuaige, to execute the exchange between R and LSD in the contract.
2. The smart contract performs the following operations at once:
1) FlashMint an amount equal to the difference between the target and current debt amounts, and calculate the corresponding flashMintFee:
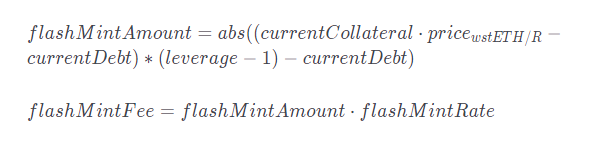
2) If the adjustment is to increase leverage:
Convert the flashMintAmount of R mentioned above into LSD in the liquidity pool and add it to finalCollateral:

Borrow the R amount of flashMintAmount+flashMintFee using the newly obtained collateral, resulting in an increase in finalDebt of R by the same amount:
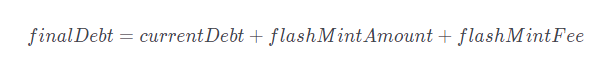
Repay the flashMint using the borrowed R
3. Otherwise, if the adjustment is to decrease leverage:
1) Repay the currentDebt using the flashMintAmount of R mentioned above
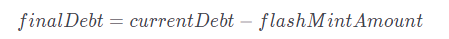
Exchange the mortgaged LSD into R of flashMintAmount+flashMintFee and calculate the fee. As a result, finalCollateral decreases by the exchanged amount
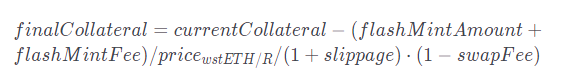
Repay the flashMint using the exchanged R
5) Oracle
To ensure that there is no single point of failure, Raft adopts two oracles: a primary oracle and a secondary oracle.
The oracle system consists of two encapsulated contracts designed to be adaptable and maintainable through a 3/5 multisignature configuration. This structure allows multisignature participants to perform necessary updates, such as replacing underperforming oracle services or swapping the roles of the primary and secondary oracles, ensuring the stability and reliability of the system.
Each LSD oracle’s price data source will be different. Specific details can be found here.
When an exception is detected in the primary oracle, the secondary oracle or the last good price will be used as a backup.
- Exception Detection
The primary oracle is considered to be exceptional under the following conditions:
1) Freeze: The price of the primary oracle has not been updated for X hours.
2) Malfunction: The call response of the primary oracle recovers, returning an invalid price or invalid timestamp.
3) Significant price change: The price change between two consecutive primary price updates exceeds Y%.
- Backup Mechanism
If the primary oracle is broken or frozen:
If the secondary oracle is functioning normally, use the price of the secondary oracle.
Otherwise, use the last good price.
When the main oracle has a significant price change:
If the secondary oracle is functioning normally:
If the price difference between the main and secondary oracle is within 5% (adjustable), use the price from the main oracle.
Otherwise, use the last good price.
6) Position
Here are some key points that will help you understand how Raft works:
To use it, each wallet address needs to open a new Position.
Each wallet address is only allowed one Position and LSD collateral.
In each Position, LSD must be deposited as collateral for borrowing.
Raft uses Non-Rebase LSD at the underlying level, supports depositing Rebase LSD, and wraps it during the transaction process, such as stETH.
Note: wstETH is a wrapped version of stETH that is compatible with DeFi. wstETH can still receive staking rewards; however, the rewards are not updated daily but realized when stETH is unwrapped.
- Deposit and Withdrawal Guide
Some LSD is created as Rebase, and some are Non-Rebase.
To provide users with the most convenient user experience, Raft automatically supports Rebase and Non-Rebase tokens as much as possible.
- Non-Rebase Tokens
Deposit: Transfer directly to the Position
Withdrawal: Transfer directly to the user’s wallet address. Supports Rebase tokens (such as stETH)
Deposit: Automatically wrapped into Non-Rebase and then transferred to the Position.
Withdrawal: Automatically unwrapped into Rebase tokens and then transferred to the user’s wallet address.
7) Benchmark Interest Rate
- Benchmark Interest Rate
In Raft, the benchmark interest rate is used to adjust the attractiveness of new borrowing and redemption and reduce the volatility of these events. When the benchmark interest rate increases, both events become more expensive.
For example, if $R depreciates and redemptions are expected, it indicates an oversupply in the market, which will increase the benchmark interest rate. This growth will further deter new borrowing and reduce supply.
- Calculation of Benchmark Interest Rate
For the calculation of borrowing and redemption fees, the benchmark interest rate first decreases based on the last fee event.
Only in redemption events, the benchmark interest rate is further added by the percentage of R redemption amount to the total supply.
The benchmark interest rate is set to decay with a half-life of 720 minutes (12 hours). This means that every 12 hours, if no redemption events occur, the benchmark interest rate will be halved.
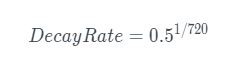
Then the benchmark interest rate is calculated as follows:

where
Δt\DeltatΔt
is the number of minutes since the last fee event.
3.4 Industry Space and Potential
LSD, which stands for Liquid Staking Derivatives, refers to liquidity staking derivatives.
3.4.1 Classification
LST is equivalent to Ethereum’s staking certificate. Users can exchange LST for Ethereum by holding LST, or use LST as collateral for more advanced financial activities. Currently, there are roughly two or three subdivisions in the LSDfi (LSTDeFi, referring to LST-based decentralized finance) field:
1. Lending: Mainstream lending platforms already support using LST as collateral. This means that users no longer need to collateralize Ethereum, but only need to collateralize LST certificates, such as Raft, Gravita, and other platforms.
2. Stablecoins: LST can be used as collateral to create new stablecoins on platforms, such as projects launched by Lybra Finance and Curve, like Prisma. According to market data, stablecoins account for the largest proportion of Total Value Locked (TVL).
3. Yield strategies: Pendle is an example, and it is essentially a traditional discount market. Users can separate funds into interest rights and principal, and still earn 15% interest income per year for three years, with 5% interest per year. However, they can discount the principal slightly to gain immediate use of the principal. In addition, Pendle also offers structured products that allow users to purchase Ethereum at a discount, but they need to wait for a period of time. In fact, the interest earned from staking is used as a discount subsidy for users.
3.4.2 Market Size
In April 2023, after the Shanghai upgrade of Ethereum, staked ETH became redeemable, making the LSD track complete.
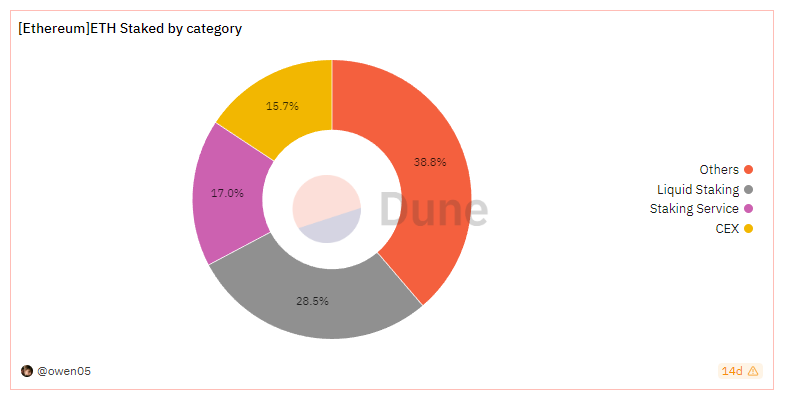
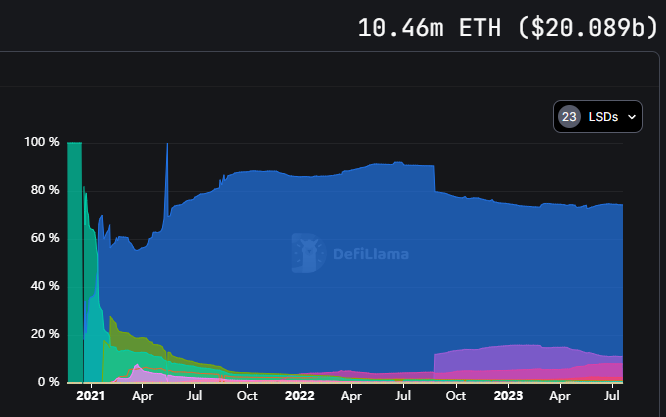
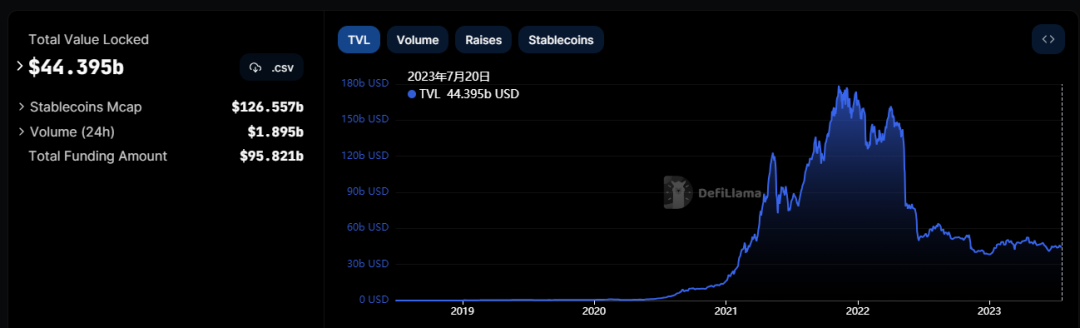
According to Defillama data, as of July 20th, the staking scale of Ethereum exceeded 20 billion US dollars (over 10.46 million ETH), with a staking rate of about 17%. The total locked value in the DeFi market reached 44.3 billion US dollars, and the staking market scale accounted for 45% of the DeFi market. The LSD track is worth long-term attention.
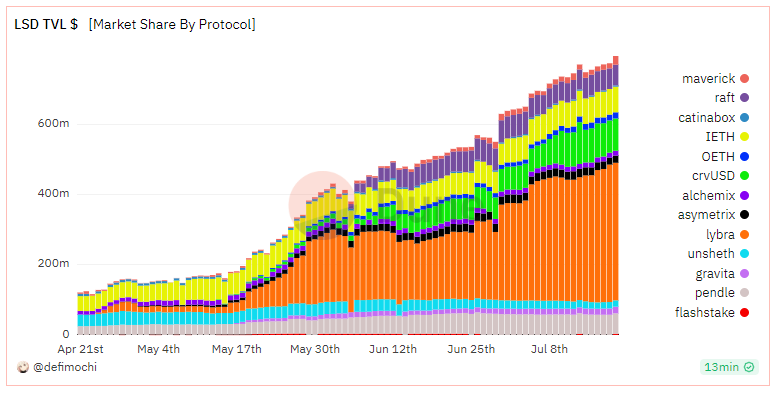
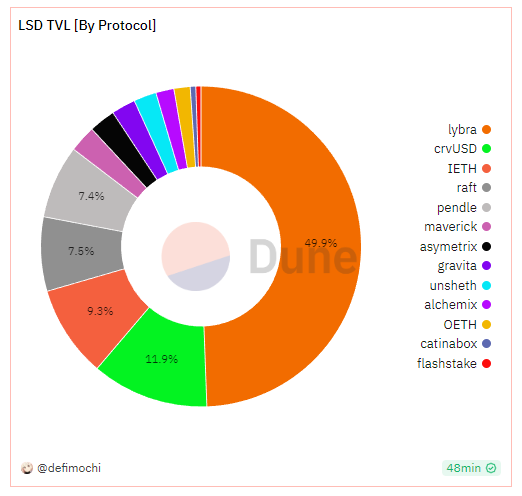
Thanks to the adoption of LSD, the TVL of the LSDfi protocol has grown rapidly in the past few months, with a cumulative TVL exceeding 794 million US dollars, more than doubling since May. However, the penetration rate of the LSDfi protocol is still relatively low, with a total TVL accounting for only 3.97% of the LSDTVL.
Based on the above data, we can see:
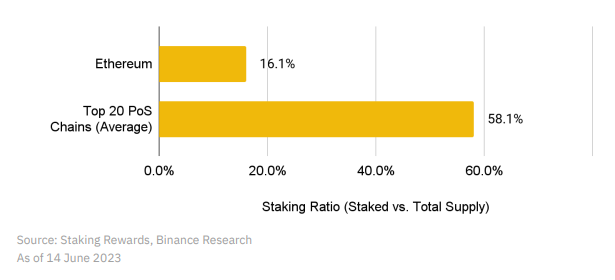
1. The current total staking rate of Ethereum is not high, leaving a huge room for growth (the average level of the top 20 POS chains is 58%). As a high-quality way to earn interest, it is believed that more and more people will participate over time;
2. With the increase in ETH staking participation, a considerable proportion of funds will enter LSD;
3. The funds entering LSD will also include a considerable proportion of funds seeking additional income, which will enter LSDfi;
4. Apart from the three points mentioned above, just looking at the current ratio of LSD entering LSDfi is less than 4%. As long as LSDfi is fully verified to be feasible and secure, the ratio will greatly increase.
ETH itself is a highly consensus-driven value encrypted asset, and ETH staking has been proven to be a feasible way to earn passive income. As the bear market approaches its end, LSD, as a high-quality income asset, will undoubtedly attract more conservative investors with its stable annualized rate of return.
In the future, the total staking rate of Ethereum is highly likely to reach the average level of 58%. Viewing LSD as a market size of hundreds of billions is not an exaggeration as Ethereum’s price rises with the bull market.
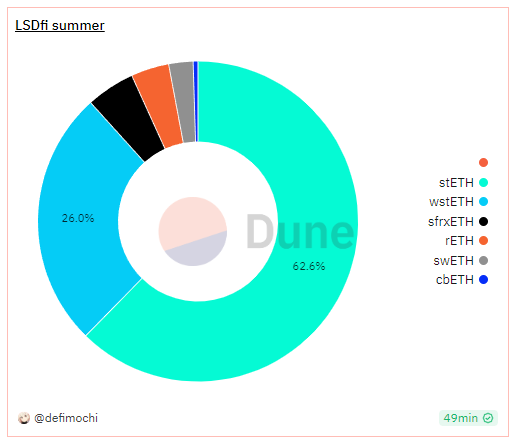
Just based on the ratio of Ethereum’s total locked value in the DeFi market at 45%, the market size of LSDfi can reach 45 billion US dollars. However, the current cumulative TVL of the LSDfi protocol is only 794 million US dollars, with a growth potential of up to 98.24%. It can be seen that LSDfi will be one of the explosive tracks in the future.
3.5 Business Data
TVL
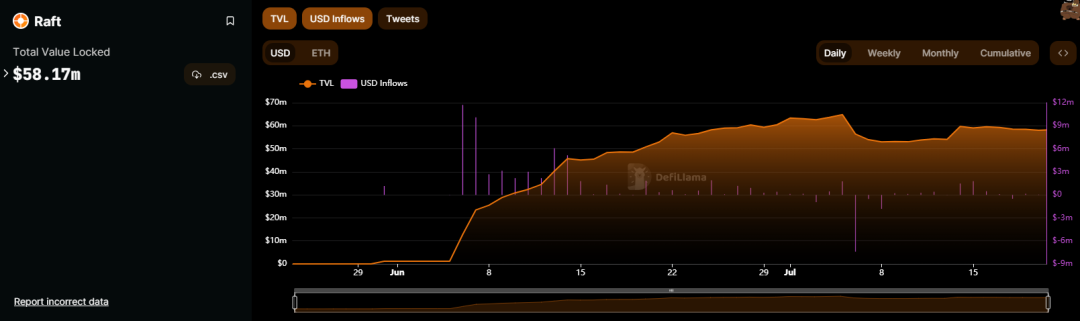
LSDfi is one of the popular tracks this year, so newly launched projects are highly sought after. Within just one month, the TVL of the Raft project has exceeded 58.17 million US dollars, which is quite impressive. This figure shows the influx of funds and user participation, especially when the project was just launched, with daily capital inflows reaching around 10 million US dollars. However, as time goes on, the inflow of funds gradually decreases. In July, the daily capital inflow is only about 100-200 thousand US dollars, and even a net outflow of up to 7.4 million US dollars has occurred.
This changing trend shows that investor interest in the project is gradually declining. Perhaps the initial hype of the project brought in a large amount of capital, but the subsequent development and operation failed to maintain continuous attractiveness. This may require the project team to take further measures to enhance user trust and participation to ensure the long-term sustainability of the project.
Distribution of Stablecoin
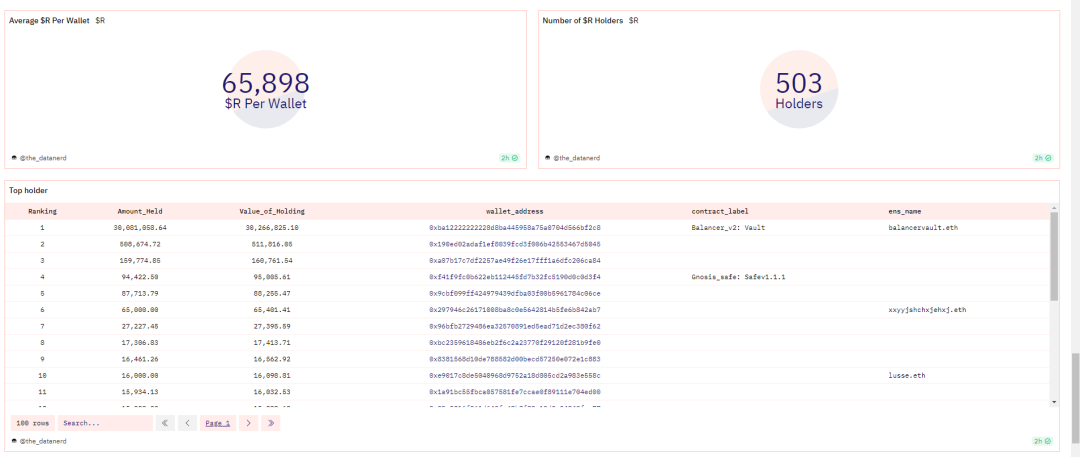
According to data from Dune, the number of stablecoin R holders is 503, indicating that the market for this stablecoin is relatively small. Each wallet holds approximately 65,898 stablecoin R, which is a relatively large amount. This may indicate that some individuals or institutions hold a large amount of stablecoin R, allowing them to participate in more trading activities and potentially exert greater influence on the price and market of stablecoin R. Furthermore, there is a significant difference in the amount of R stablecoin held among the top 10 addresses, indicating the presence of large holders or a concentration of funds in the stablecoin R market.
Quantity of Stablecoin
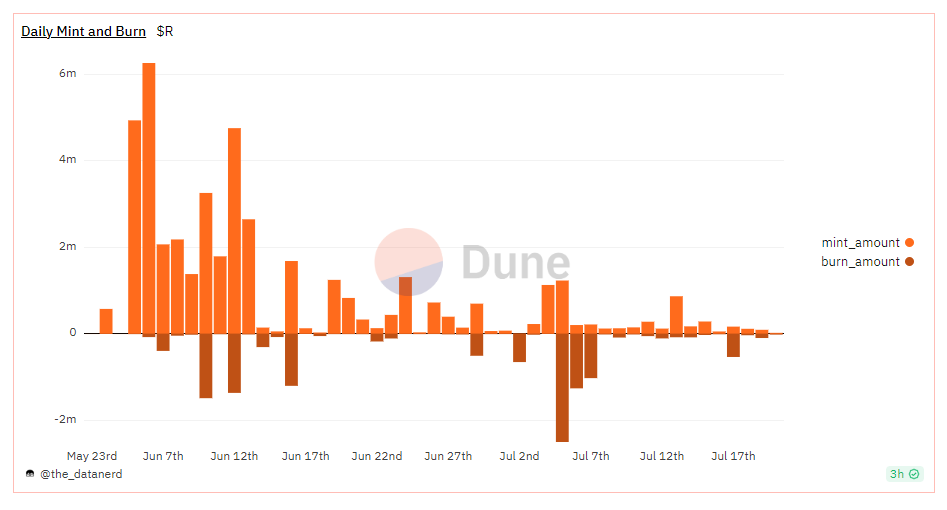
When first launched, the issuance of stablecoin R was relatively large, and the ratio to burned tokens was approximately 3-4 times. This situation indicates that in the initial stage, the supply of stablecoin R is likely to experience significant expansion.
Starting from mid-late June, the quantity of issuance significantly decreased, suggesting a decline in market demand for stablecoin R or an adjustment in supply strategy by reducing the amount of issuance to maintain stability or adjust market supply. Subsequently, the amount of burned tokens increased, with the highest daily burn exceeding 2 million R. This indicates that stablecoin R holders may selectively exchange or destroy stablecoin R to achieve other purposes, such as exchanging it back for corresponding assets or currencies, thereby maintaining its fixed proportional relationship with the represented assets or currencies.
Total Collateralization Ratio
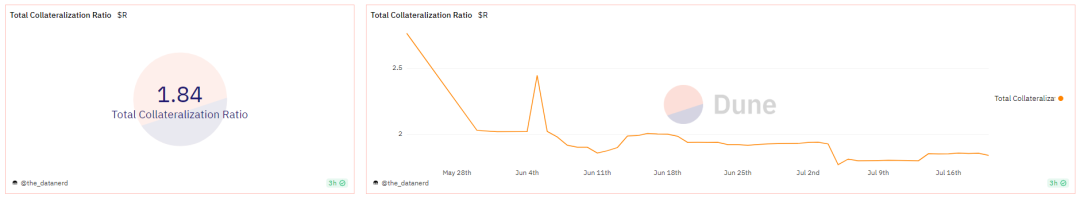
Total Collateralization Ratio is the ratio between the value of all loans and the value of all collateral in a cryptocurrency lending protocol or platform. This ratio is used to measure the health and security of the lending protocol.
Stablecoin R is an Ethereum-based stablecoin collateralized by stETH (Lido Staked Ether). Its current total collateralization ratio is 1.84. When this stablecoin was first launched, the total collateralization ratio was 2.5, but it has since decreased and stabilized at around 1.8.
The value of the total collateralization ratio reflects the value of collateral relative to the value of assets lent out in the lending protocol. Generally, the total collateralization ratio of stablecoins usually ranges between 100% and 150% to ensure that the stablecoins lent out have sufficient collateral support to maintain stable value. A higher total collateralization ratio typically indicates a safer protocol, as the value of collateral is relatively high and can support larger-scale lending. On the other hand, a lower total collateralization ratio may indicate that the assets lent out exceed the value of collateral, which could increase the protocol’s risk, especially when the value of collateral declines. Currently, the collateralization ratio of R is above 150%, ensuring sufficient collateral support and mitigating liquidation risks.
3.6 Project Competitive Landscape
Currently, the top three players in the LSD are Lido, Frax, and Rocket Pool.
3.6.1 Project Introduction
- Lido
Lido is a leading staking provider that aims to provide a solution for the Ethereum community to build liquidity staking services. Through Lido, users can stake assets such as ETH and receive stETH tokens in a 1:1 ratio. As a liquidity staking token, stETH can be transferred, sold, and used in DeFi protocols. Unlike ETH locked on the ETH2.0 network, stETH allows users to earn staking rewards without locking their assets or maintaining staking infrastructure. It can be exchanged for unstaked ETH and accumulated staking rewards once the ETH2.0 transaction functionality is enabled. Lido’s business model allows users to flexibly use staked assets for other DeFi activities after earning staking rewards. In addition, Lido’s services have expanded to support staking of assets on networks such as Terra, Solana, Kusama, and Polygon.
- Frax
The Frax protocol is an innovative stablecoin protocol that has gone through three stages: 100% collateral stage, partially collateralized stage, and algorithmic adjustment stage. In the initial stage, the stablecoin FRAX can be minted by simply depositing collateral into the smart contract. In the partially collateralized stage, minting FRAX requires placing collateral and FRAX (FXS) into the system in the appropriate ratio. Although the protocol accepts any type of cryptocurrency as collateral, it primarily accepts on-chain stablecoins to smooth the volatility of underlying assets and enable FRAX to transition to the algorithmic stage smoothly. Frax Finance provides a highly scalable, trustless, and stable solution through its unique collateral and algorithmic model. Its dual-token system includes Frax and FraxShares, and it also offers innovative features such as Frax price index, FraxLend, and FraxEther.
- RocketPool
RocketPool is a groundbreaking ETH2Stake staking pool protocol designed to provide a decentralized and trustless staking solution compatible with the Ethereum 2.0 staking mechanism. The project was first conceptualized in late 2016 and has undergone over 5 successful public tests, with extensive development and continuous improvement.
RocketPool aims to meet the needs of two main user groups: the first group consists of users who want to unlock their staked ETH and participate in DeFi using rETH. These users only need to stake a minimum of 0.01 ETH to earn rewards. The second group consists of users who want to stake ETH and run nodes on the network to achieve higher investment returns than staking outside the underlying ETHPOS protocol. These users can increase their earnings through additional RPL commissions.
RocketPool offers a flexible, secure, and efficient staking solution that allows users to participate in staking with low barriers and provides higher returns for their stakes. The goal of this protocol is to promote the development and security of the Ethereum 2.0 network, provide users with more diversified ways of participation, and drive innovation and development in the entire DeFi ecosystem.
3.6.2 Project Comparison
Lido:
Operation: Users deposit money in Lido and receive stETH, which is equivalent to participating in Ethereum staking. Lido, as a platform, has recruited 29 white-label node operators globally through public bidding, entrusting users’ funds to these operators. Recently, they have expanded by 5-10 new operators globally. This model has certain centralization drawbacks, but Lido is still striving for decentralization, for example, by considering geographical dispersion for suppliers. The Lido model is similar to a bank- when users deposit ETH, it is equivalent to a deposit, and the bank must use the deposit to generate interest, such as by lending to other businesses to seek higher interest rates. In this case, the node operators are the lenders, and the interest difference between the two parties is the profit for Lido.
LST interest payment model: Users naturally receive interest from participating in Ethereum staking, and Lido’s interest payment model is to pay more stETH to users. In other words, if you hold one stETH today, you will receive more stETH as interest tomorrow.
RocketPool:
Operation: Emphasizes the decentralization of underlying node operations. In the RocketPool ecosystem, there are two different roles: depositors and node operators. Therefore, RocketPool plays a role more like a matching platform, matching depositors’ funds with node operators. Because the security of depositors’ funds needs to be guaranteed, RocketPool has certain requirements for node operators. They require applicants to have at least 16 ETH to apply as node operators, and RocketPool will match 16 ETH in the staking pool to them, forming a node. Recently, they have lowered the threshold to 8 ETH. Therefore, RocketPool’s network can also be seen as a permissionless network.
LST interest payment model: Its interest payment model can be seen as an exchange rate model, where users are not paid more LST as interest, but the interest is added to the total pool, making the individual LST held by users more valuable. Therefore, the exchange rate of RETH to ETH has been continuously rising above 1.
Frax:
Operation: Frax also has a banking model similar to Lido, but instead of delegating to third-party operations, Frax tends to operate its own nodes.
LST interest payment model: Similar to RocketPool, it is an exchange rate model.
LST yield: Currently, users can mint frxETH at a 1:1 ratio on the Frax protocol official website using ETH, but this is one-way and Frax cannot be redeemed back to ETH. After obtaining frxETH, users have two choices: participate in staking to become sfrxETH and enjoy Ethereum staking rewards, or deposit it into the Curve frxETH/ETH pool to provide liquidity for Curve and earn Curve LP rewards. Users who provide liquidity for Curve no longer enjoy Ethereum staking rewards and transfer this portion of rewards to sfrxETH users. In simple terms, Frax diverts users who participate in dividends, allowing individual users to receive more dividends.
3.7 Token Model Analysis
There is no specific mention of tokens in the Raft protocol. The Raft protocol is an LSDfi protocol used for lending and staking, but it does not explicitly state that Raft has tokens as its core token issuance.
3.7.1 Stablecoin R
R is the most capital-efficient Ethereum stablecoin, backed by liquid staking tokens such as stETH (Lido staked Ethereum) and LidorETH (Rocket staking pool Ethereum). It provides the best way to borrow against stETHLSD collateral. The goal of $R is to become the preferred stablecoin in the decentralized ecosystem, with deep liquidity and stable anchoring across many trading pairs.
Each $R is designed to maintain a value of $1. It maintains its anchoring value of $1 through a combination of hard anchoring and soft anchoring mechanisms.
3.7.2 Stablecoin Value Capture
1. Hard Anchoring: Creating Hard Price Floor and Ceiling for R
The concept of “hard anchoring” relies on arbitrage opportunities to keep the stablecoin price consistent with its backing assets and always within the price range of $1 to $1.10. In the case of $R, it is backed by LSD and uses two mechanisms to achieve hard anchoring: redemption and overcollateralization.
Redemption (when the value of $R is below $1)
Redemption allows $R stablecoin holders to redeem it for an equivalent value of LSD collateral.
How does this help maintain tight anchoring?
Whenever users redeem their $R tokens, these tokens are destroyed by a smart contract, reducing the circulating supply of R and increasing its price. This means that only when the trading price of $R is below $1, can $R be redeemed with LSD. When the price deviates downward from the equilibrium, $R can be purchased at a price below $1 on the open market and redeemed for $1 worth of LSD per $R to maintain the anchoring of $R.
What happens to borrowing fees when the price of $R is below $1?
By maintaining anchoring through limiting the circulating supply of $R, the protocol raises the base interest rate, making borrowing $R (an action that increases the circulating supply of $R) less attractive. Redemption triggers an increase in the base interest rate: the more redemptions, the greater the increase in the base interest rate. Because we can reasonably assume that redemptions will continue as long as it is economically profitable, once redemptions cease, the base interest rate will approach zero, which will occur when the anchoring of $R is restored.
Overcollateralization (when the value of $R is above $1.10)
The redemption process creates an abstract lower limit for the price of $R, as there is an arbitrage opportunity for market participants whenever it falls below $1. On the other hand, overcollateralization of $R sets an upper limit on the price, which is $1.10.
Users can deposit LSD worth $1.2 and mint 1 $R. When the price of $R exceeds this level, users can sell it on the open market for more than $1.2, locking in risk-free profits. The minimum over-collateralization ratio represents a trade-off between solvency and price stability: a higher ratio provides better protection against bad debts and increases the deviation space of the stablecoin price from the anchor.
2. Soft Anchoring – Incentivizing Stability through Market Dynamics
Introduction
Compared to hard anchoring, the concept of “soft anchoring” relies on the stablecoin design’s ability to incentivize actions that are expected to maintain the anchoring in the future.
Soft anchoring can be seen as a Schelling point that the system tends to return to after temporary deviations. For example, when the trading price of R is above $1, existing borrowers are not incentivized to repay their positions. Instead, potential users can borrow and sell R on the open market to make a profit. The same reasoning applies when the trading price of R is below $1: borrowers are incentivized to repay their debts, and potential R holders can buy R on the open market and redeem it.
Having advance knowledge of the expected behavior of the economic system can create a self-fulfilling mechanism that enhances trust in the system’s expected future operation. The soft anchoring mechanism also emphasizes that deviations from the Schelling point are temporary, thereby creating competition among market participants who desire to benefit from it. This, in turn, reduces the duration of deviations.
Strengthening Soft Anchoring through Deep Liquidity
Raft aims to establish deep liquidity across multiple market venues to enhance the soft anchoring of $R to $1. By leveraging a combination of decentralized automated market makers (AMMs) and centralized exchange market-making strategies, the protocol aims to create a robust liquidity foundation. To incentivize users to contribute to the liquidity of $R, they can deposit $R into various liquidity pools and receive other assets as rewards. This simultaneously incentivizes user participation and enhances liquidity.
The Liquidity Committee plays a crucial role in achieving this goal by managing and deploying incentives across different pools. This dedicated committee ensures that the protocol can adapt to changing market conditions and optimize incentives to promote liquidity and maintain the stability of R.
3.7.3 Core Demand for Stablecoins
1. Investors and traders: Stablecoin $R, as a stable currency directly linked to the value of anchoring assets such as the US dollar or gold, enables them to use stablecoin $R as a medium for trading and investment, enjoying relatively stable value reserves.
2. Borrowers: Borrowers hope to use stablecoin $R as collateral for loans and obtain funds through borrowing. For borrowers, the price stability of stablecoin $R is crucial to ensure that their loans are not lost due to price fluctuations.
3. Liquidity Providers: The liquidity of stablecoin $R is an important factor in attracting liquidity providers. They want to provide funds to the market of stablecoin $R and earn returns through market-making activities. Price stability and market depth of stablecoin $R are crucial for liquidity providers.
4. Regulatory Agencies and Governments: Regulatory agencies and governments are highly concerned about the stability and compliance of stablecoin $R. They expect stablecoin $R to comply with relevant regulations, ensure sufficient reserve assets behind it, and withstand external market shocks.

4. Preliminary Valuation
4.1 Which stage of the business cycle is the project in? Is it in the mature stage or the early to mid-stage of development?
1. Development Stage: A project that has been launched for only one month is typically in the early stage of development. During this stage, the project may still be trying to build a user base, increase awareness, and promote itself.
2. Business Model: During the early launch stage, the Raft project may still be adjusting and optimizing its business model to ensure its sustainability and profitability. The stability of the business model may still need to be validated over time.
3. User Base: One month may not be enough time to establish a large-scale user base. Typically, in mature projects, the user base is relatively large, and the project has accumulated a certain level of user trust and loyalty.
What are the main variable factors in the project’s operations? Are these factors easily quantifiable and measurable?
The main variable factors in the operations of the Raft project may include the following:
1. Liquidity Collateral: Quantifying and measuring liquidity collateral is relatively easy and can be done by tracking the amount of tokens being collateralized.
2. Lending Activities: Variable factors in lending activities may include the number of lending transactions, loan amounts, lending rates, etc. These indicators can be quantified and measured by tracking the number and amount of lending transactions.
3. Circulation and Trading Activities of R Tokens: This includes the circulation volume, trading volume, and trading price of R tokens. These indicators can be quantified and measured through blockchain data statistics.
4. User Engagement and Activity: This includes indicators such as the frequency of user participation in the project, usage frequency, average transaction amount, etc. These indicators can be quantified and measured through user behavior data, the number of active users, etc.
4.2 Valuation Level
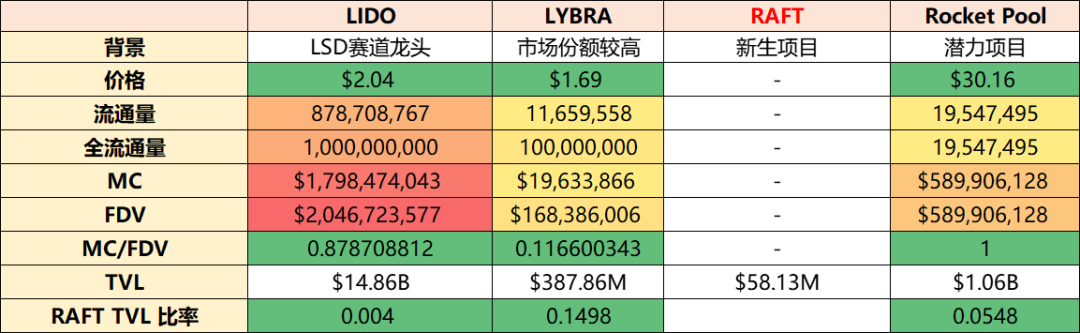
(Data extracted on July 21, 2023) By comparing the current Total Value Locked (TVL) of the project, we can calculate the ratio of Raft to other projects. Among them, the ratio of Raft to Lido is 0.004, the ratio of Raft to Lybra is 0.1498, and the ratio of Raft to RocketPool is 0.0548. Based on these ratios, the valuation range of Raft is estimated to be between 2.94 million and 32.32 million, and the specific valuation may fall within this range. It should be noted that these valuations are based solely on TVL ratios and the actual valuation may be influenced by other factors such as the project’s actual value and market demand. Therefore, this valuation range is for reference only, and the specific valuation needs to consider more factors for comprehensive evaluation.
4.3 Risk Analysis
1. Counterparty Risk: The operation of LSDfi stablecoin usually relies on interactions with other projects or protocols. For example, LSDfi stablecoin may collaborate with certain projects to use the stablecoin funds for specific yield strategies such as liquidity mining or lending. If these projects have security vulnerabilities, improper management, or other risk issues, users may suffer financial losses.
2. Price Fluctuation Risk: Due to market forces, the price fluctuations of the collateralized token (LSD) associated with the Raft project may differ from the price fluctuations of its underlying token. This may result in users facing price instability and potential liquidation risks, especially when LSD is used as collateral.
3. High Fee Risk: Users have mentioned that the fees of the Raft project are too high, referring to the one-time fees required in lending operations. If calculated based on the prevailing 4% lending interest rate in the market, users may need to borrow for more than a month to benefit from the lending operation. This brings a risk that the fee costs are high for short-term borrowing or frequent lending, which may not be attractive.
5. References
https://raft.fi/Raft Official Website
https://dune.com/the_datanerd/raftDune Data
https://defillama.com/protocol/raft?usdInflows=true&twitter=false&denomination=USDDefillama Data
https://mirror.xyz/0xa486d3a7679D56D545dd5d357469Dd5ed4259340
https://twitter.com/raft_fi/status/1637827396576645120Twitter
https://mirror.xyz/0xa486d3a7679D56D545dd5d357469Dd5ed4259340/IqVMOJp2gKKD7chQGGIx5AbV2_D54gjwwvHCw7FMZbQIntroducingrETH: A New Liquid Staking Token Joins Raft
https://www.linkedin.com/comLianGuainy/tempusfinance/LinkedIn
https://www.crunchbase.com/organization/tempus-finance?utm_source=linkedin&utm_medium=referral&utm_camLianGuaiign=linkedin_comLianGuainies&utm_content=profile_ctaCrunchbase Data
https://tempus.finance/teamTempus Official Website
https://dune.com/owen05/lsd-datacheckDune Data
https://dune.com/defimochi/LSDfi-summerDune Data
https://research.binance.com/static/pdf/LSDfi-when-liquid-staking-meets-defi.pdfLSD Study Research
https://defillama.com/lsdDefillama Data
https://www.coinonpro.com/news/toutiao/263379.htmlLSDfi, Research on a New Stablecoin
— Investment Risk and Disclaimer —
The content analysis provided in this report is for reference information only and does not constitute any form of investment advice or decision-making basis. We strongly recommend that you do not engage in any investment activities based on this report to avoid potential risks. WJB and the report authors are not responsible for any investment results made by users based on this report.
The preparation time of this report is as shown on the date, and due to changes in subsequent market or economic conditions, the content may be subject to changes. Therefore, the report cannot fully reflect these changes. The graphics, charts, and other visual aids in the report are for reference only and should not be used as a basis for making investment decisions. Any graphics, charts, or other visual aids in the report cannot cover all factors and variables required to make such decisions. Please note that WJB does not assist anyone in making specific investment decisions.
Some of the discussions mentioned in this report may be WJB’s assumptions about future expectations and other forward-looking views. However, these assumptions and views are subject to known and unknown risks and uncertainties that may result in significant differences between actual results, performance, or events and the stated views and assumptions.
All speculations, forecasts, and estimates included in this report are based on certain assumptions and are speculative in nature. These forward-looking statements may prove to be incorrect and may be affected by incorrect assumptions or known or unknown risks, uncertainties, and other factors, most of which are beyond control. It is expected that some or all of these forward-looking assumptions will not be realized or will have significant differences from actual results.
We will continue to update Blocking; if you have any questions or suggestions, please contact us!
Was this article helpful?
93 out of 132 found this helpful
Related articles
- Another example of a flash loan attack, analysis of the LianGuailmswap security incident
- Comparative Study Differences and Similarities between ANS and ENS
- No worries about secure cross-chain transactions? Understanding the xERC20 cross-chain token standard in one article.
- UniswapX Opening the Gateway to Uniswap V4 DeFi Experimental Base
- Twitter renamed X, Musk ignites the X universe! From AI to exploring space, the prototype of a universal app emerges.
- Tokyo and Kyoto, the rising encrypted ‘twin stars
- a16z In-Depth Analysis What New Gameplays Will AI Create?






