Another case of flash loan attack Analysis of the LianGuailmswap security incident
Flash loan attack LianGuailmswap security incident analysisOn July 24, 2023, LianGuailmswap suffered a flash loan attack, resulting in a loss of 901,455 USDT (approximately 901,000 USD). This attack was caused by a vulnerability in the project’s PlpManager contract, which led to an incorrect calculation of USDP and resulted in the attack.
Event Summary
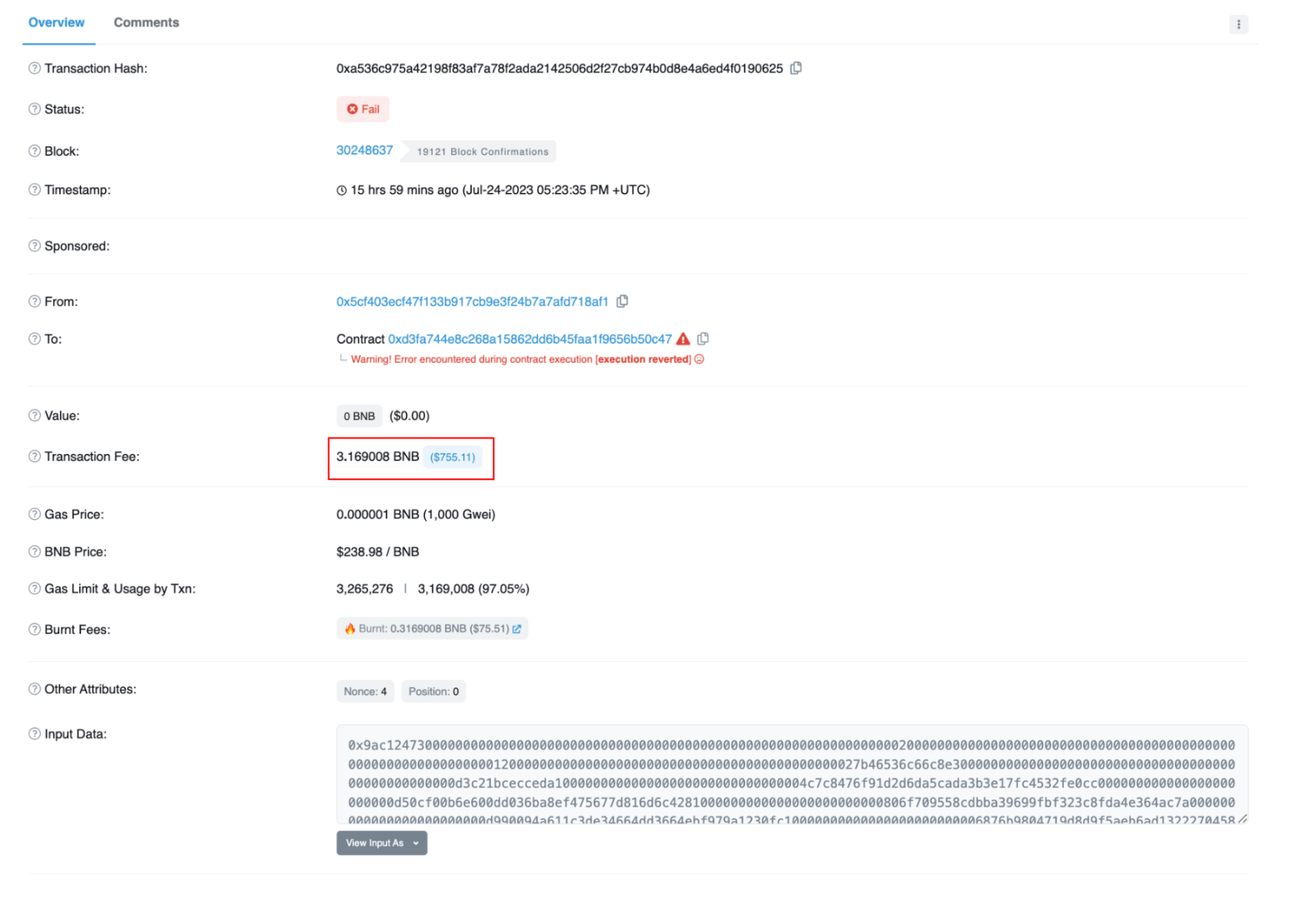
On July 24, 2023, LianGuailmswap suffered a flash loan attack, resulting in a loss of approximately 901,000 USD. The attack was initially attempted by an externally owned address (EOA) 0x5cf40 on block 30248637, but the attacker ran out of gas and failed.
Image: Failed transaction. Source: Bscscan
The original attacker extracted 1 ETH from the Ethereum network’s Tornado Cash. Then, they exchanged 1 ETH for USDT and transferred it to the Binance Smart Chain (BSC) through a cross-chain bridge. Subsequently, the USDT was exchanged for BNB and used to create the attack contract. However, unfortunately, the attacker did not have enough BNB to cover this attack.
- Why is Musk’s Twitter reform said to have a profound impact on cryptocurrencies?
- Google Play Store announces new rules allowing games and apps to offer NFTs.
- The Struggle between Ripple and SEC What Will Happen Next? Experts Evaluate Four Possible Outcomes.
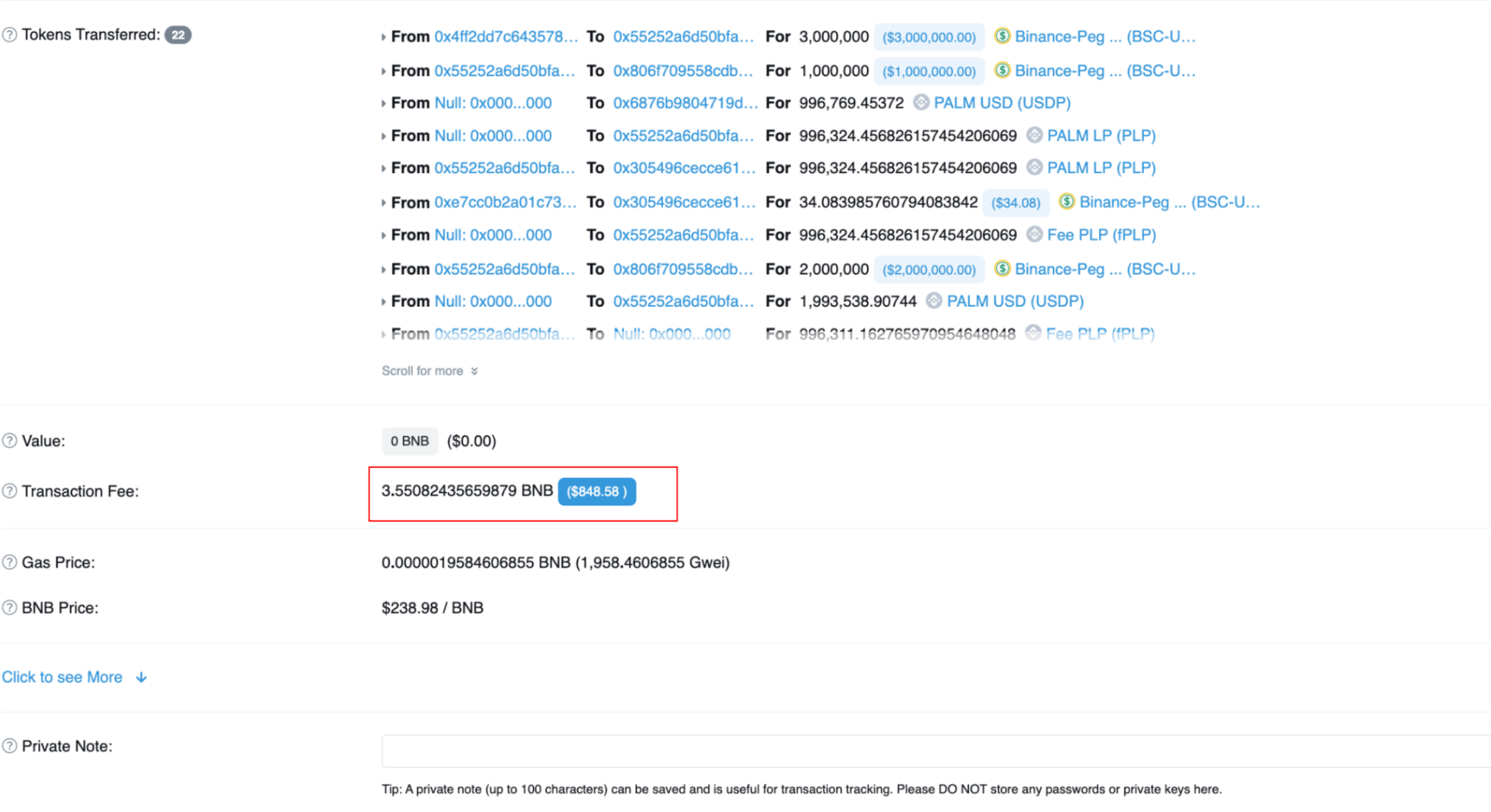
This enabled EOA 0xf84ef to discover the failed transaction, understand and replicate the transaction from block 30248638, and pay the correct amount of gas fees.
Image: Successful transaction. Source: Bscscan
It can be seen that the original attack failed because the attacker did not have an additional 0.4 BNB to pay the transaction fees.
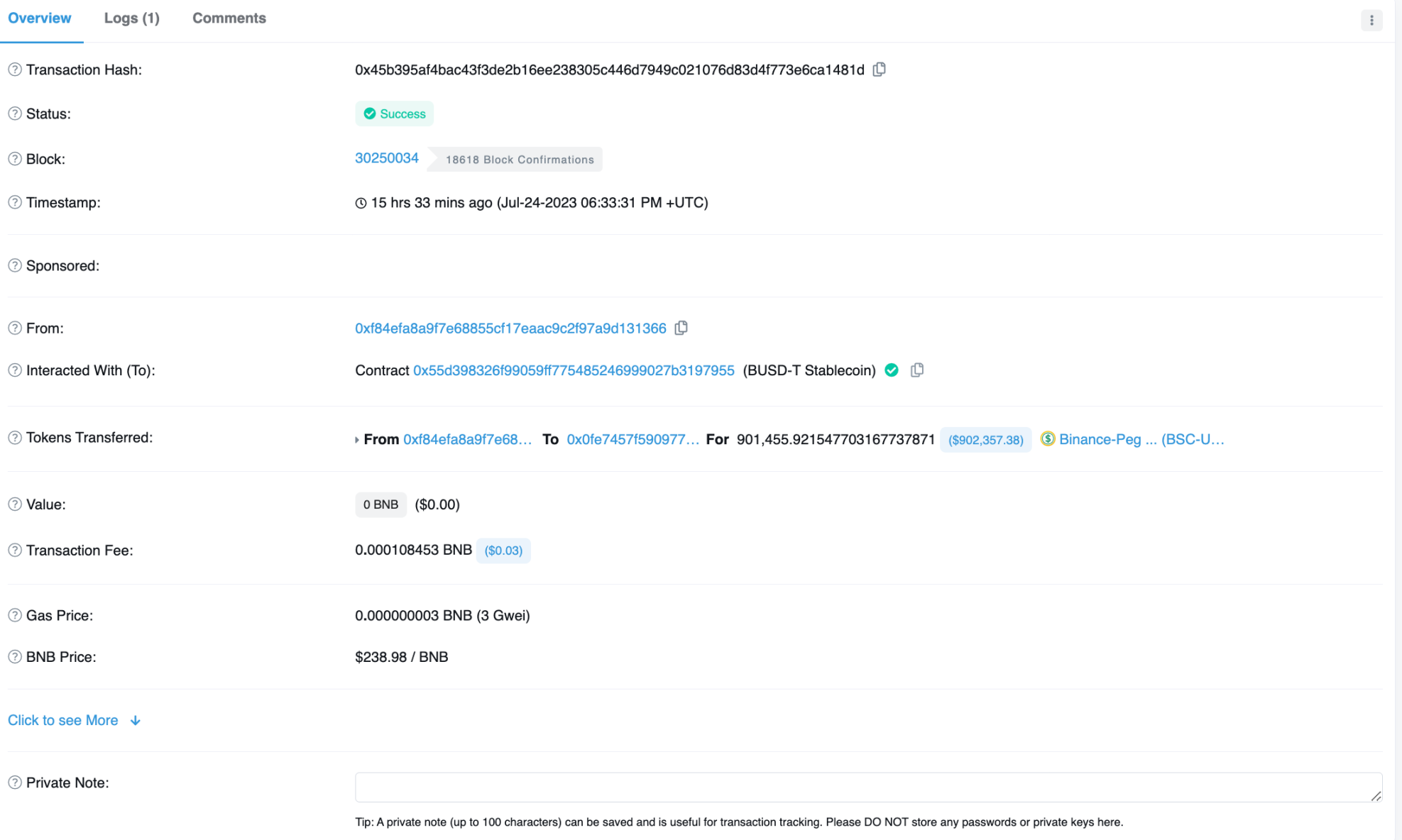
Once EOA 0xf84ef successfully exploited the vulnerability, the stolen funds were transferred to EOA 0x0Fe74, which is still in that address.
Image: Transfer of stolen funds. Source: Bscscan
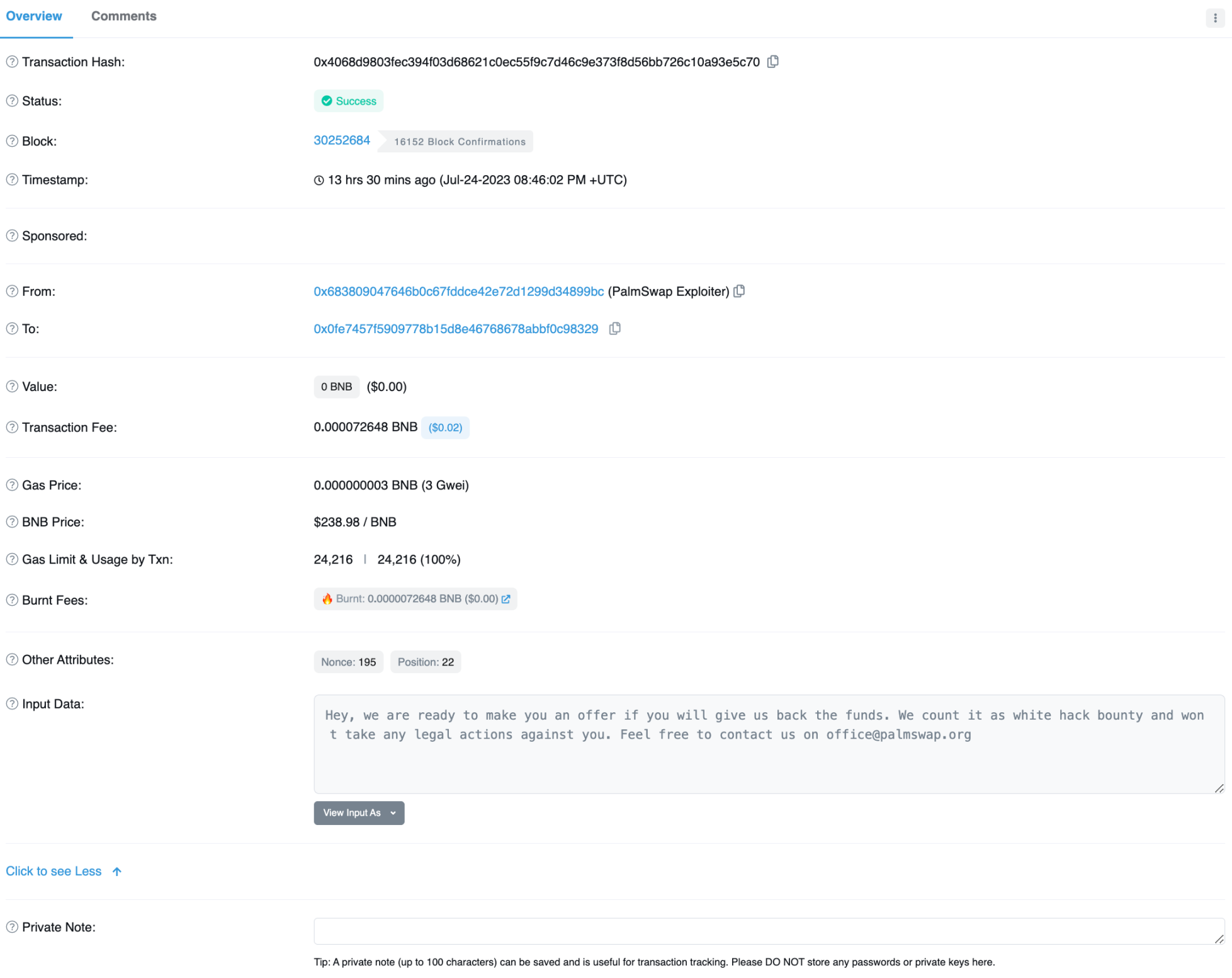
The LianGuailmswap team has contacted the wallet holding the stolen funds and attempted to negotiate a bounty. However, BSC scan seems to have mistakenly identified a wrong wallet as the attacker of LianGuailmswap:
Image: On-chain message offering bounty. Source: Bscscan
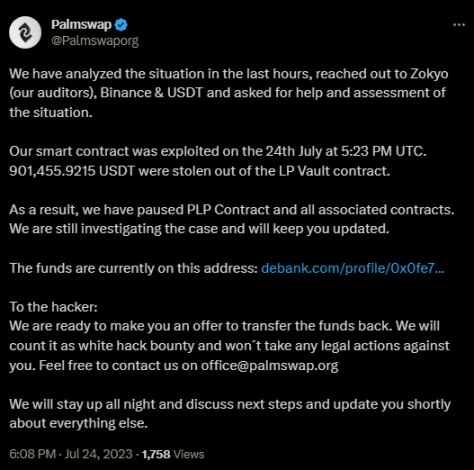
LianGuailmswap’s official X account has confirmed that negotiations with the hacker have begun.
Image: LianGuailmswap X official announcement (Source: @LianGuailmswaporg)
Attack Process
Exploiting transaction: 0x62dba55054fa628845fecded658ff5b1ec1c5823f1a5e0118601aa455a30eac9
Attacker: 0xf84efa8a9f7e68855cf17eaac9c2f97a9d131366
Affected contract: 0xa68f4b2c69c7f991c3237ba9b678d75368ccff8f
1. The attacker borrowed 3,000,000 USDT (worth 3,000,691.52 USD) using flash loans.
2. Through the buyUSDP() function, the attacker exchanged 1,000,000 USDT with Vault and obtained 996,769 LianGuailm USD (USDP) and 996,324 LianGuaiLM LP (PLP). Subsequently, the attacker obtained 996,324 fee LianGuaiLM LP (fPLP) by staking PLP.
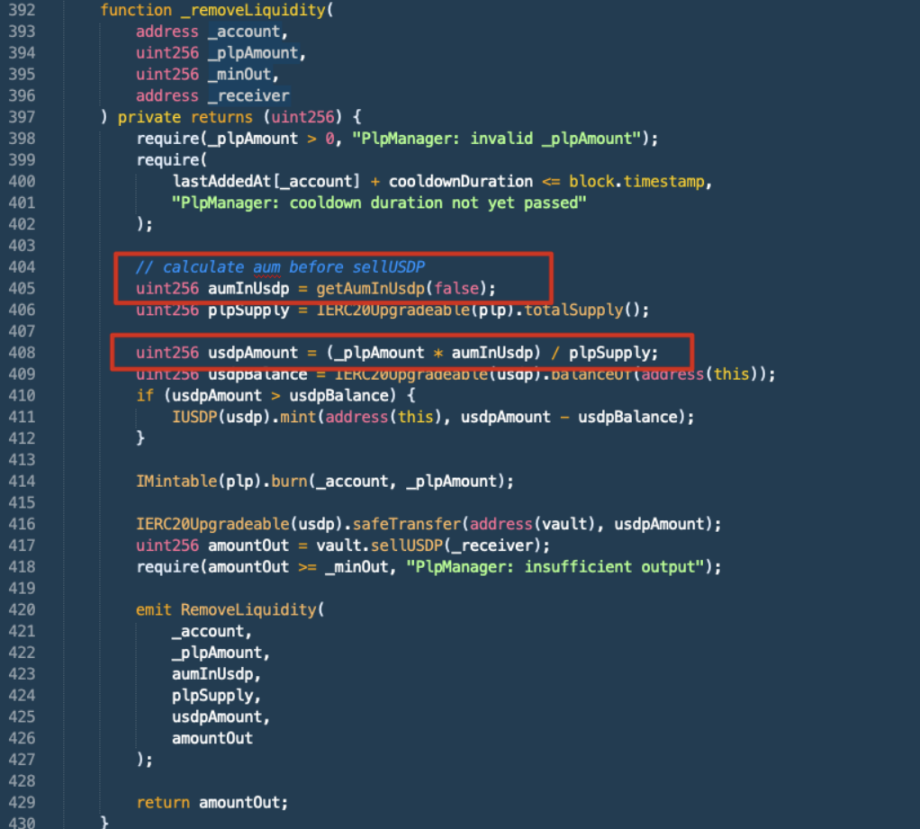
3. The attacker exchanged the remaining 2,000,000 USDT with Vault, obtaining 1,993,538 USDP. Then, the removeLiquidity() function was triggered, which exchanged the fPLP obtained in the previous step with Vault, resulting in 1,962,472 PLP. The PLP was further exchanged for 1,956,585 USDT (worth 1,957,036.45 USD). Due to a calculation error in the PlpManager contract, Vault mistakenly returned more USDT to the attacker.
Image: plpmanager.sol source code from BscScan
4. In step 3, 1,953,430 USDP was exchanged for 1,947,570 USDT (worth $1,948,019.41).
5. The attacker repaid the initially borrowed 3,000,000 USDT through the flash loan, leaving $901,445 in the attacker’s wallet.
Flash Loan Attacks in 2023
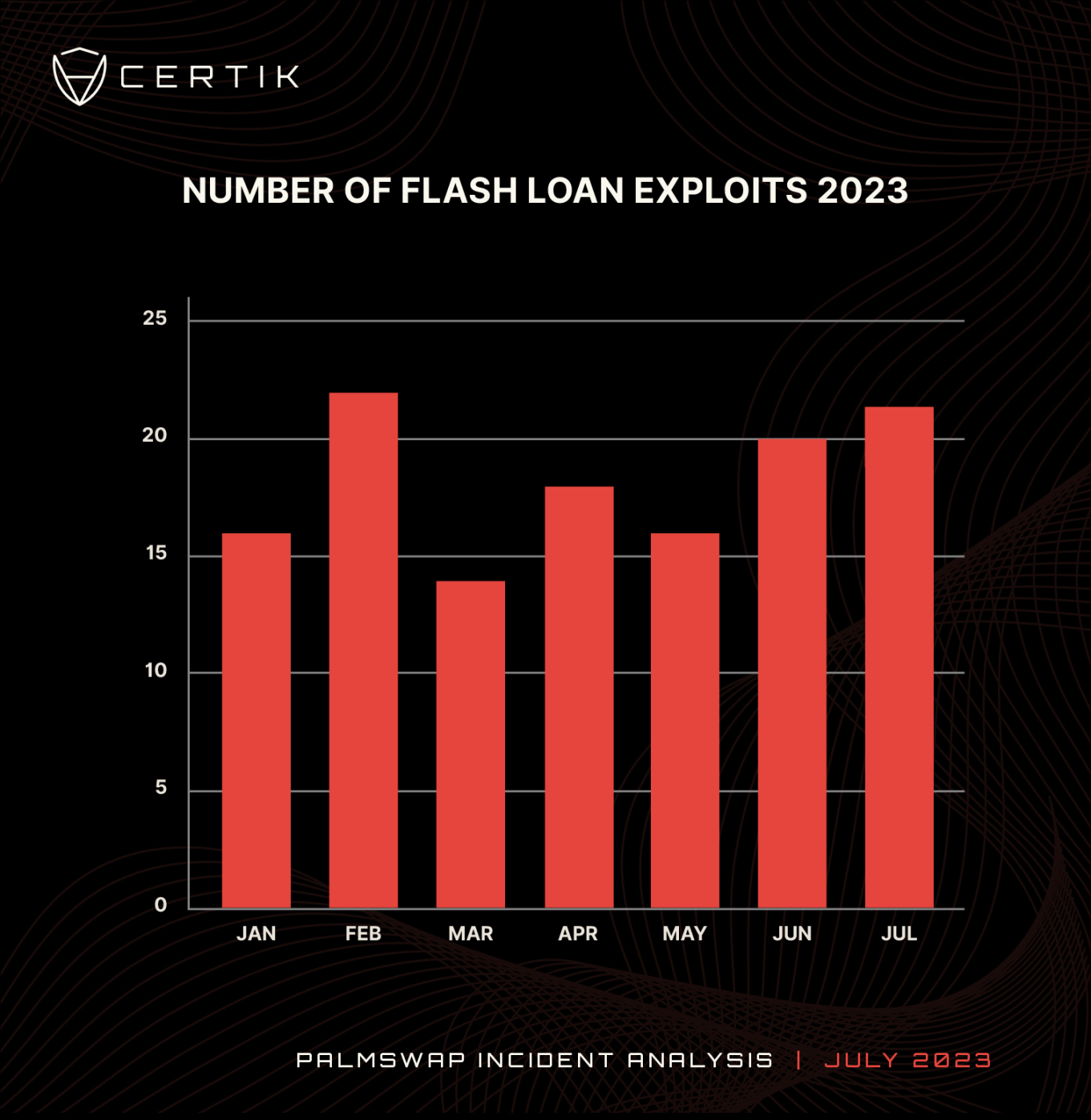
In 2023, there have been 128 flash loan attacks, compared to the 101 recorded in 2022. As attackers seek to maximize profits from smart contract vulnerabilities, flash loan attacks are becoming increasingly popular among hackers.
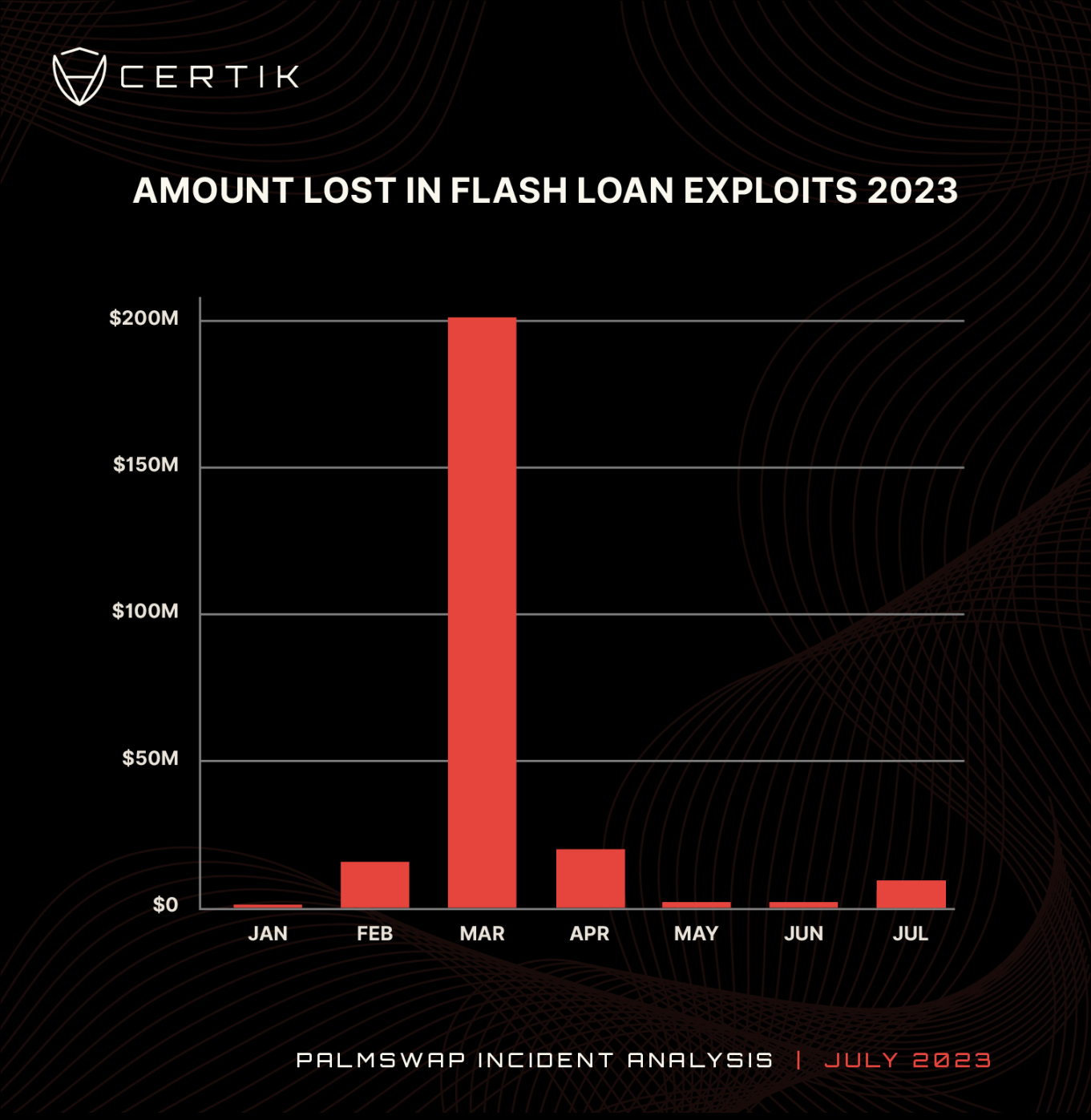
At the time of this event, flash loan attacks have already caused losses of 255 million USD, with an average loss of about 2 million USD per attack. In the first three weeks of July, we have recorded 22 flash loan attacks, resulting in a total loss of 8.5 million USD. The average number of flash loan attacks per month in 2023 is 18. Currently, the number of flash loan events in July is trending towards a record high. It is currently on par with February 2023, which also had 22 attack events.
Chart: Funds lost due to flash loan attacks in 2023. Data source: CertiK
Chart: Number of flash loan attacks each month in 2023. Data source: CertiK
Conclusion
The flash loan attack on LianGuailmswap was the second-largest malicious flash loan attack detected by CertiK in July, resulting in a total loss of $5.8 million. This attack ranks tenth among malicious flash loan attacks in 2023. Although the number of flash loan attacks in 2023 has not decreased, with 127 incidents occurring this year compared to 101 in 2022, the amount of funds currently being lost has significantly decreased. There may be several reasons for this. Firstly, market conditions in the first half of 2022 resulted in stolen assets having a higher value in USD. Secondly, as flash loans are a relatively new concept, security strategies to defend against such attacks are still being developed, making projects holding a large amount of funds a target. The number of flash loan attacks in 2023 demonstrates the need for strong security measures and third-party audits by project teams.
We will continue to update Blocking; if you have any questions or suggestions, please contact us!
Was this article helpful?
93 out of 132 found this helpful
Related articles
- Blockchain Criminal Case 3.0 How to Reduce Illegal Gains? How to Deduct Reasonable Expenses?
- Zonff LianGuairtners The Logic behind Investing in EigenLayer
- Clash of Perspectives Taking on-chain games as an example, is Optimistic Rollups more suitable for high throughput and low composability applications?
- Exploring the Decentralized Business Potential of XMTP from the Perspective of Coinbase Wallet’s New Features
- World Coin Hard to Talk About Fairness?
- Must-read in the evening | Understanding the ‘World Coin’ by OpenAI Founder in One Article
- Opinion Stack’s ability for generalized decentralization is worth paying more attention to, while the narrow decentralization between components such as L2 internal Sequencer and Verifier is more important.