Solana Latest Research Report Resilient Ecosystem, Growth and Challenges Coexist
Solana Research Report Resilient Ecosystem, Growth, and ChallengesOriginal Title: “Solana: Past, Present, and Future”
Source: Nansen
Author: Sandra Leow
TL;DR
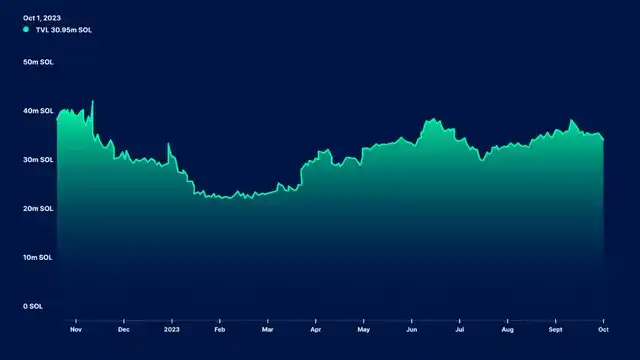
– Since the beginning of this year, the total locked value (TVL) of Solana has almost doubled, reaching 30.95 million SOL. Despite challenges such as network interruptions and the FTX/Alameda incident, Solana has achieved 100% uptime from the beginning of the year, demonstrating significant improvements and recovery capabilities of the network.
- Web3 Legal Education | How can GameFi games that make money while playing stay away from the gambling red line?
- Another re-entry vulnerability? Analysis of the Stars Arena attack incident
- Caroline Ellison testified in court Acting on the instructions of SBF, embezzlement of approximately $14 billion in FTX client funds.
– Solana has introduced solutions such as state compression and segregated fee markets to address prominent issues in its technical stack. For example, state compression technology has reduced the cost of NFT minting on Solana to 1/2000 of its original cost.
– The liquidity staking sector is rapidly growing, with Marinade Finance, Lido, and Jito leading the way. Only 3-4% of staked SOL is locked in Solana’s liquidity staking protocols, indicating significant growth opportunities.
– There is increasing interest in enterprise adoption and payment rails, especially with Visa integrating USDC settlement on Solana, the growth of liquidity staking on Solana, and collaborations with entities like Shopify.
– Other potential drivers for Solana include the successful implementation of the Firedancer vision and the continuous development of consumer-facing applications leveraging Solana’s advantages.
– However, potential challenges such as uncertainty surrounding FTX/Alameda’s holdings of SOL may temporarily impact its growth trajectory.
Solana’s Promising Outlook and Challenges
Promising Outlook
Increased adoption of Solana Virtual Machine (SVM) by more enterprises
If more institutional participants recognize Solana’s continuously improving technical stack (high TPS compared to peers, solving downtime issues, cost-effective on-chain storage) and decide to openly collaborate and leverage the Solana network, Solana’s reputation will further enhance. Some adoption cases of Solana include Visa introducing Solana as a settlement layer to facilitate cross-border USDC payments and the new payment system Solana LianGuaiy on Shopify (in collaboration with Mastercard). Compared to other chains in the market, Solana’s key value proposition lies in low transaction costs and high network speed (TPS of around 3,000, 30 times that of Ethereum and Layer 2).
Solana developers are actively advancing the Firedancer vision, and interest in SVM is growing.
Firedancer can be seen as one of the most exciting upgrades for Solana. It has the potential to bring significant optimizations for validator clients and should run more efficiently than the current Solana Labs client.
Currently, the cryptocurrency narrative is primarily dominated by 97% Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM) and 3% SVM. If SVM continues to gain market share from EVM, the Firedancer upgrade and improvements in hardware/bandwidth efficiency could contribute to accelerating the adoption of SVM.
Growth of JitoSOL and other liquid staking tokens
Jito Labs is the latest “success story” in the field of liquid staking on Solana. The growth of JitoSOL has staked over 2.4 million SOL within a year, which is an impressive feat for the Solana ecosystem and benefits many dApps. Ethereum has over 40% of staked ETH in liquidity staking protocols, whereas Solana only has about 3-4% of staked SOL. If the staked SOL on Solana can continue to grow in the form of LSD, even a small portion of it will contribute to the increase in Solana ecosystem’s total TVL. Solana’s staking yield is currently twice that of Ethereum’s yield, and historical risk statistics are also similar.
More consumer-oriented applications recognize the advantages of Solana
When building consumer-oriented applications, Solana has proven to be the most user-friendly chain. Blockchain provides a mature technology stack optimized for retail adoption. Solana’s cNFTs are suitable for minting NFTs on a large scale, optimized for low cost as much as possible, and the on-chain fee market aims to eliminate unnecessary congestion in the network, while the high TPS environment provides the speed required to drive these applications.
Launch native tokens for Solana-centric protocols
The crypto community often wonders why most Solana DeFi applications have not yet launched their own native tokens. The answer is simple: protocols usually want their user count and activity to reach a certain threshold before launching tokens. The token economics of DeFi protocols indicate that native tokens often suffer from excessive inflation and typically come with sell-off plans. However, the issuance of native tokens for DeFi protocols is often a necessary step in the lifecycle of the protocols.
Challenges
If Galaxy chooses to fully liquidate its SOL holdings in a short period of time, the SOL price will drop to the level after FTX’s collapse
If Galaxy sells all of its SOL positions in FTX/Alameda within a short period of time, the SOL price may experience a negative reaction due to selling on the open market (assuming that a portion of the SOL may be traded off-exchange). If the price of SOL retraces to the level after FTX’s collapse, it may cause market panic.
A recurrence of network downtime will damage Solana’s reputation
So far this year, Solana has maintained 100% uptime, which is a very positive record for the network. Any future network interruptions will have a negative impact on Solana’s reputation and confidence in its recent technical upgrades.
Lack of cross-chain bridge infrastructure and native assets
Despite the significant development in the Solana ecosystem, there is still a lack of on-chain liquidity, native asset support, and sufficient bridging infrastructure. In addition, the ecosystem still needs to break the record of bridge “vulnerabilities”.
Macro Data
TVL
The TVL of Solana is 30.95 million SOL, compared to 25.12 million SOL at the beginning of the year. Since the beginning of this year, Solana’s TVL (calculated in USD value) has almost doubled and has been continuously trending upward as shown in the chart.
Solana has previously dealt with some urgent issues such as the FTX/Alameda incident, network downtime causing outages, and network congestion due to spam transactions. However, most of these issues have been resolved through improvements in the technical stack, which will be further discussed in the later part of this report. It is worth noting that Solana has maintained 100% uptime since the beginning of the year.
DeFi Velocity
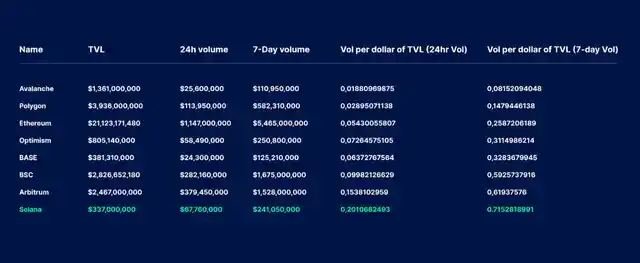
The transaction volume per $1 TVL can be used to measure chain activity and adoption rate, as TVL often fails to accurately reflect subtle differences in user behavior. In terms of “DeFi Velocity”, Solana is still one of the most active chains, with a transaction volume ratio of 0.71 per $1 TVL (in the past 7 days).
The “DeFi Velocity” metric refers to the “24-hour DEX trading volume / blockchain TVL” ratio. The higher the value, the more active the DeFi ecosystem. Taking Solana as an example, for every $1 of liquidity, the weekly transaction volume is approximately 0.71 times (as of October 2, 2023). Compared to networks such as Arbitrum, Binance, Base, Optimism, and Ethereum, Solana has also provided the highest DeFi Velocity in the past 24 hours and 7 days. Interestingly, some chains report higher TVL numbers, but their DeFi fund utilization is much lower than Solana, indicating lower on-chain economic activity.
Let’s narrow the scope and consider the DeFi Velocity for cross-chain transactions on a monthly basis.
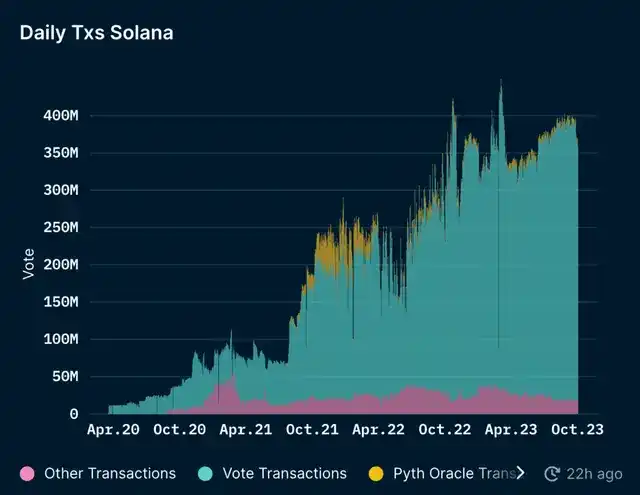
Daily Trading Volume
This year, Solana’s daily trading volume has remained relatively stable with an increase in voting transactions. The transactions on Solana are a combination of voting and non-voting transactions. Voting transactions are linked to vote accounts owned by validators, including configuration, registration, vote collection, and new vote signatures.
Decentralization
Customer Diversity
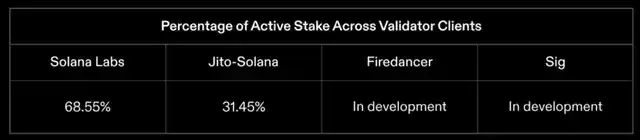
Having diverse clients is crucial in reducing any single point of failure in a given blockchain.
Solana is developing more than 4 validator clients for the Solana network. In addition to Solana Labs, the proportion of validators running through Jito-Solana Client is also increasing, accounting for almost one-third of the total validator token supply. Since the Solana Foundation last released the validator health report in March, the number of validators using Jito has almost doubled.
Currently, efforts are being made to create more full or lightweight validator clients on Solana, including Jito Labs, Firedancer, Sig, and Tinydancer. For more detailed information on validator clients, please refer to the latest report from the Solana Foundation on the health of network validators.
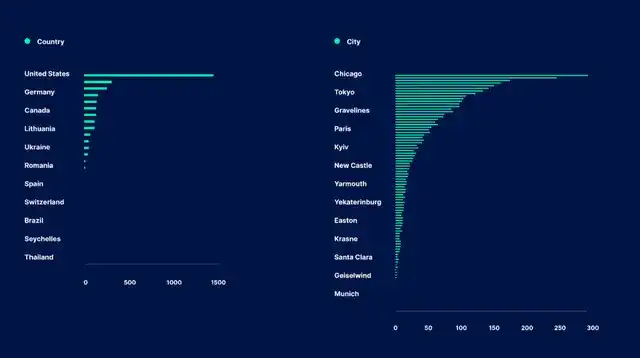
Regions
Solana currently has 2,919 nodes distributed across 31 countries and 211 cities worldwide. The United States ranks first in terms of the number of nodes, followed by Germany, Canada, and Lithuania. The United States has 1,370 nodes, accounting for almost half of the total nodes. While node concentration in the United States may bring slight risks, it is worth noting that nodes are distributed among validator clusters in different regions of the United States.
Nakamoto Coefficient
The Nakamoto Coefficient is an indicator that measures the minimum number of independent entities required to collude and shut down a blockchain. The higher the coefficient, the more decentralized the blockchain. In a typical proof-of-stake network (such as the one listed below on Nakaflow), the Nakamoto Coefficient is defined by the proportion of node operators who collectively control over one-third (33.33%) of all stakes on the network. Since its inception, Solana’s Nakamoto Coefficient has been steadily increasing and has remained relatively stable at 30-31% over the past year. However, it must be emphasized that the Solana Foundation controls about 20% of the stakes and delegates them to small and medium-sized validators.
When measuring decentralization, relying solely on the Nakamoto Coefficient is not enough. Other indicators such as geographic diversity, data center ownership, and validator client diversity should also be considered. The Firedancer upgrade and Jump Crypto’s “Firedancer” client are driving client diversity, which will be explored in the later part of the report.
Catalysts, Drivers, and Challenges
Alameda / FTX Selling SOL
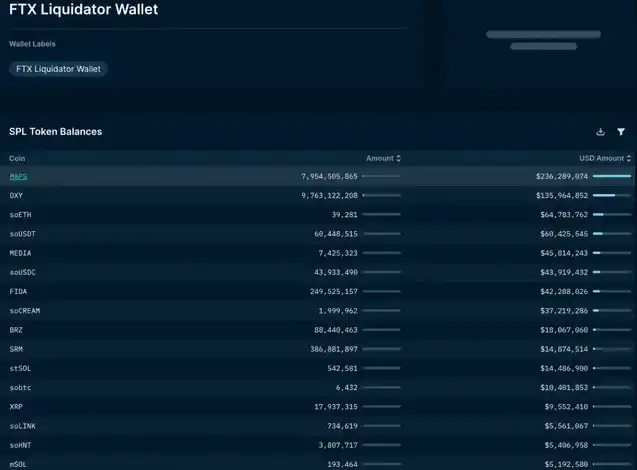
FTX is the largest holder of SOL, locking and holding over 71.8 million SOL (valued at approximately $1.16 billion). This accounts for 17% of the circulating supply of SOL (as of the time of writing) and approximately 13% of its total supply. Disclaimer: Not all holding accounts are public, and non-public accounts may impact certain data. Special thanks to SolanaFM for providing the data.
What we know is:
Alameda and FTX collectively hold about $1.3 billion worth of crypto assets, including SOL, BTC, ETH, and APT.
Their hot wallet addresses are:
· 9uyDy9VDBw4K7xoSkhmCAm8NAFCwu4pkF6JeHUCtVKcX
· 6wEMcwrcF5AP9jpHWQcPxHXciWA2g217Qq81CTWjbgBw
· 6b4aypBhH337qSzzkbeoHWzTLt4DjG2aG8GkrrTQJfQA
· The hot wallet addresses hold 6.98 million SOL.
They have a total of three staking wallets, holding a total of 65 million SOL.
Among them, the staking account holds 61 million SOL, including 52 million locked staked SOL;
In addition, 3.8 million SOL is in a locked state.
Galaxy Digital is pushing for the sale of Alameda and FTX’s shares, but it is unclear when this process will take place. The weekly limit for the sale of tokens is $100 million (including hedging) to limit price fluctuations.
What we are not sure about is:
The locked staked 52 million SOL will be unlocked in 2027, and one Alameda/FTX account will unlock 7.5 million SOL on March 1, 2025. Although these SOL are locked/staked, FTX’s liquidator has the right to fully liquidate all the SOL held by FTX/Alameda.
We cannot determine the impact of SOL liquidation or sale on the market, as Galaxy Digital may conduct as many over-the-counter transactions as possible. Galaxy Digital can also choose to sell in batches, fully liquidate SOL, or use other alternative methods that we may not be able to verify on-chain. Another point worth noting is that FTX/Alameda’s OTC trading of SOL may alleviate some buying pressure in the market.
Ecological Highlights
Solana’s ecosystem has been developing well recently:
September 2023: Visa introduced USDC settlement on Solana. This is noteworthy considering future payment architectures and other use cases involving interaction between public blockchains and private (or public) financial entities.
September 2023: The founder of MakerDAO is considering using Solana SVM as Maker’s new native chain. This is part of Maker’s “Endgame” upgrade plan, which is expected to take 2-3 years and be divided into 5 stages.
August 2023: Solana LianGuaiy integrated with Shopify.
June 2023: Tensor NFT launched a compressed NFT marketplace and occupies the majority of the NFT market share on Solana. Tensor and Magic Eden account for nearly 90% of the entire Solana NFT trading volume.
Since April 2023: With the adoption of BackLianGuaick Wallet on Solana, the interaction between users and wallet infrastructure has become more seamless. BackLianGuaick Wallet also comes with numerous plugins such as Jito Stake, Solend, and Drift Protocol, as well as games that users can interact with directly on the wallet interface.
Development and Collaboration
Solana’s State Compression
State compression is an on-chain solution that significantly reduces storage costs. It refers to storing a large amount of data off-chain (such as NFT data in this example) and using Merkle trees to keep its “footprint” on-chain. This compression-friendly data structure allows developers to store smaller data on-chain and update it directly in Solana’s ledger, reducing data storage while still retaining Solana’s underlying layer.
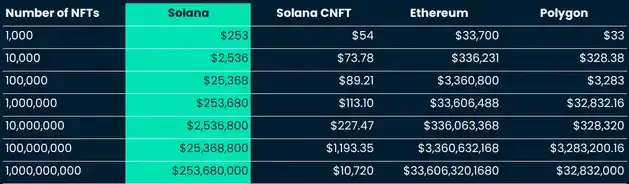
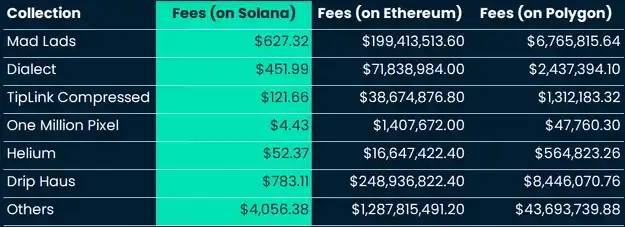
Comparing the cost of minting NFTs with and without state compression technology, the cost of minting 1 million NFTs on Solana was $2.53 million before the introduction of state compression, and only $113 after enabling state compression. In contrast, a similar scale of collection would cost $33.6 million on Ethereum and $32,800 on Polygon.
If there were no state compression upgrade, minting collections on Polygon would actually be much cheaper than on Solana. Clearly, Solana has gained a significant advantage in compression technology, greatly reducing the minting and transaction costs of NFTs.
Source: Flipside
For a more in-depth article on NFT compression and how it works, please refer to Helius’s article.
Solana’s state compression technology has been applied throughout the ecosystem, benefiting many projects. In summary, Drip Haus and Mad Lads have become two top collections in the compressed NFT space, with a total of 7.4 million and 5.9 million NFTs minted, respectively.
Source: Flipside
Note: The costs are estimated values and depend on the prices of each asset within a given time frame. The above costs are calculated based on the prices of Solana, Ethereum, and Polygon on October 2, 2023.
Here are some interesting use cases of Solana state compression so far:
DRiP
DRiP recently reached a milestone by minting its 1 millionth Solana NFT and is hailed as the largest NFT collection across all chains.
As background, DRiP offers free NFTs to its users on a weekly basis. The NFTs are created by the artist community on Solana, and the ability to mint NFTs at this scale is attributed to Solana’s state compression.
Mad Lads
Mad Lads is the first xNFT (executable NFT) collection, which is a new token standard that allows code tokenization.
In short, xNFT can be seen as a dApp that users can access directly from their wallets. It is similar to the functionality of plugins on Google Chrome. Additionally, xNFT is also a programmable dynamic asset and runs on the Solana blockchain using the React xNFT framework. In contrast, regular NFTs are static and non-programmable.
BackLianGuaick is a platform that supports the wallet of Mad Lads. BackLianGuaick is the place where Mad Lads NFT is first minted and managed, and it is also the execution environment for xNFT.
Crossmint
Crossmint is an NFT infrastructure that allows developers to seamlessly build NFT applications.
Dialect
Dialect is a messaging platform on Solana that is popular for its compression capabilities, allowing creators to mint NFTs and distribute them to users on the platform.
To understand the technical components of such large-scale in-app sticker production, refer to the case study of Solana on Dialect.
Essentially, the introduction of state compression reduces infrastructure costs (such as the provision and storage of “text” or NFTs in this case, as well as transaction costs) to almost negligible digits.
Dialect has released its first NFT collection and allows users to claim it for free. This is objectively impossible on Ethereum or any other L1/L2.
DePIN Narrative
The narrative of DePIN benefits from state compression technology. DePin stands for Decentralized Physical Infrastructure Networks. Over the years, we have seen explosive growth in DePIN networks, from graphics to energy to logistics, some of which are unique to Solana. Kuleen Nimkar, head of dePIN at the Solana Foundation, also stated that dePIN is reshaping traditional infrastructure models and providing opportunities similar to today’s gig economy. Over time, we can see that people can earn additional income by contributing hardware to the dePIN protocol.
Helium
Helium is a decentralized wireless network that supports hotspots in over 170 countries/regions and provides 5G services in some cities in the United States. Helium started by building its own hotspots during the initial stages of network development and then turned to open-source its hardware specifications.
Helium mints each hotspot as an NFT supported by Solana’s state compression technology. The cost of minting an NFT is only a fraction of a cent compared to uncompressed tokens. Helium is one of the earliest DePIN businesses. Hivemapper is an example, which is a decentralized mapping network that recently started using Helium to verify the location of each driver.
Hivemapper
Hivemapper is a decentralized mapping network that essentially builds and distributes its own hardware dashcams. Hivemapper also controls the entire manufacturing and distribution process, giving it complete autonomy over its supply chain.
Hivemapper provides tokens to drivers who install the “dashcam” and collects map data while they drive.
Render Network
Render Network allows individuals to contribute unused GPU capacity to help render dynamic graphics and visual effects for projects. It recently announced its expansion from Polygon to the Solana blockchain.
QUIC
QUIC replaces UDP (User Datagram Protocol), which was Solana’s previous transaction propagation protocol. Solana previously used a protocol based on raw UDP to handle transaction messages from client to main validator client. UDP was unable to handle certain transaction filtering within the network, which caused network downtime issues in the past.
QUIC is currently used as the default transaction ingestion protocol, which can better control data flow to avoid issues like spam attacks. QUIC is designed for fast asynchronous communication, similar to UDP, but with session and traffic control similar to TCP (Transmission Control Protocol). This upgrade provides more control over network traffic and is more optimized for data ingestion, solving Solana’s downtime issues. Since the deployment of QUIC, Solana has maintained 100% uptime.
Local Fee Market
Solana introduces priority fees on top of the existing base fees in its network. The local fee market allows any user to send priority fees to validators. Previously, users had to send spam transactions to the network to ensure their transactions were prioritized, resulting in network congestion. Additionally, the quantity of invalid or duplicate messages sent by users or algorithms could also increase overall costs. It is clear that priority fees are important for block inclusion and transaction queue ordering. Priority fees simply add to the cost of network spam attacks.
Priority fees can also serve as a proxy for measuring activity happening within the network. The increase in priority fees (as a percentage of total fees) can also be attributed to the growth of economic activity on the network, such as large-scale NFT minting, DeFi activities, etc.
Currently, priority fees are calculated based on the estimated computational resources required for the transaction. For example, simple transactions from DeFi activities require lower total priority fees compared to large-scale NFT minting happening simultaneously, so it will be dynamically adjusted based on the type of transactions occurring.
Liquidity Staking on Solana
Liquidity staking is one of the most important economic activities in DeFi, and it has even surpassed lending on several DeFi metrics, as seen on Ethereum, where nearly $202.2 billion worth of ETH is locked in liquidity staking protocols (such as Lido, RocketPool, etc.), accounting for around 40% of the total ETH liquidity staked (see Nansen’s article on Mapping the Ethereum landscape). However, on Solana, only about 3-4% of the total SOL supply is staked in Solana’s liquidity staking protocols. Solana has a huge opportunity to utilize its liquidity staking space to increase the capital efficiency of its tokens, thereby increasing the total TVL (Total Value Locked) and ecosystem.
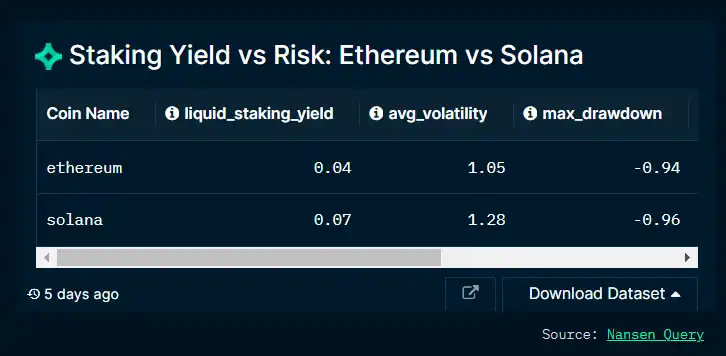
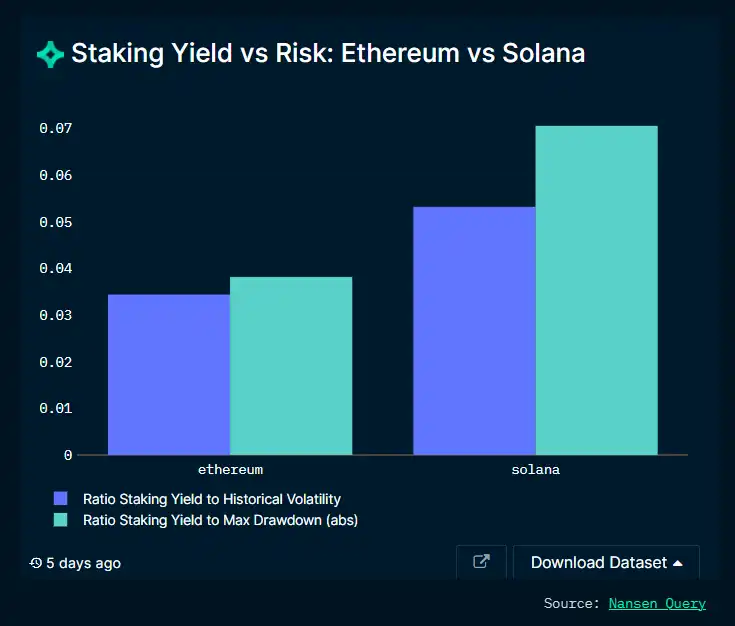
How does staking on Ethereum compare to staking on Solana? We have studied the liquidity staking on both chains for Lido, as well as historical average volatility, maximum drawdown, and risk-reward ratio. Currently, for a very similar risk profile, Solana’s investment returns are almost double that of Ethereum.
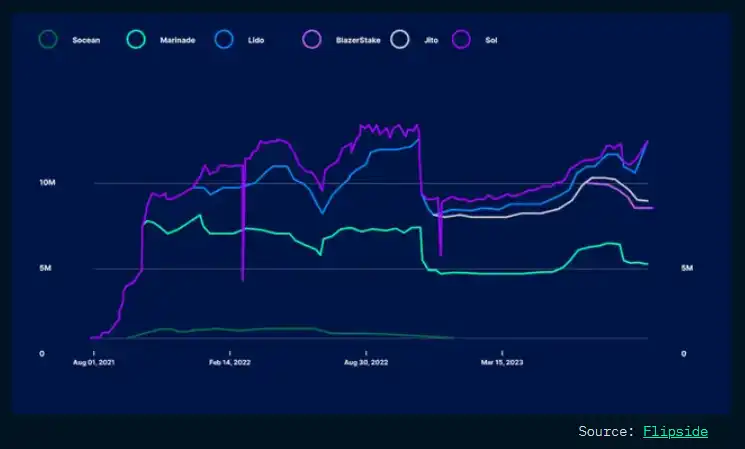
Currently, a total of 295.7 million SOL tokens have been staked on the Solana network, but the use of liquidity staking derivatives is still very limited. The area of liquidity staking on Solana has been impacted by FTX (a cryptocurrency trading platform), with the peak total value locked (TVL) of liquidity staking reaching 12.8 million SOL, but it dropped to 5 million SOL during the market crash. However, since then, liquidity staking activities have fully recovered and returned to levels prior to FTX, with over 12 million SOL staked.
We have also seen new participants in liquidity staking protocols, such as Jito, an equity delegation service provider, which has accumulated a TVL of over $44.86 million (2.3 million SOL) since its launch in late November last year. In addition, the growth of liquidity staking derivatives (LSD) and DeFi use cases has been significant, with certain DeFi protocols allowing users to deposit their SOL LSD tokens and use them as collateral for trading (in perpetual contracts) or for lending/borrowing activities on lending platforms.
Marinade Finance still holds the majority market share in the area of Solana liquidity staking, with over 5.47 million SOL tokens locked, followed by Lido and Jito. It is worth noting that more liquidity staking protocols such as Marinade, Socean, Lido, BlazeStake, and Jito are emerging and offering different reward programs to attract more users to stake SOL tokens.
Marinade’s new project, “Marinade Native,” allows users to delegate staking rights while retaining withdrawal rights. As part of their incentive program, Marinade has also announced the “Marinade Earn” program, which will run from October 1, 2023, to January 1, 2024. Users holding mSOL or Marinade Native tokens during this period will receive a reward of 1 MNDE/SOL (approximately 3 months). There is also a referral system where referrers can earn a reward of 1 MNDE/SOL through their unique referral links.
Speaking of “newcomers,” Jito reached an all-time high total value locked (ATH TVL) of $57.50 million on October 2, 2023, and currently has 2.4 million SOL tokens staked, showing a rising trend since its launch. In the third quarter, the total value locked (TVL) increased by 100%, from 0.74 million SOL to 1.62 million SOL.
Jito is Solana’s first staking product with MEV rewards. Users can stake their Solana tokens in exchange for LSD token JitoSOL.
JitoSOL has two main advantages:
– JitoSOL provides additional rewards for users conducting MEV transactions on Solana.
– Jito is staked on validators running specially designed software to improve network performance.
Based on the amount of JitoSOL deposits, the top-ranked projects have over 750,000 SOL with the following market shares:
· Marginfi – 250,000 SOL
· Drift Protocol – 225,000 SOL
· Squads Protocol – 146,000 SOL
· Orca – 51,000 SOL
· And 30 other projects
BlazeStake is another newly launched project that has experienced over 10x growth in Total Value Locked (TVL) from $631,000 to $10.68 million at the time of writing. SolBlaze has launched its native token BLZE and plans to introduce new features on its platform, including BLZE Gauges and incentive programs for staking. The estimated Annual Percentage Yield (APY) for staking on the SolBlaze platform is approximately 9.37% (with approximately 2.13% coming from BLZE).
Hyperledger Solang
Solana is known for its Rust or C programming languages for smart contracts. Recently, Hyperledger Solang has been introduced to allow developers from EVM chains to deploy their dApps on Solana without learning new languages. Hyperledger Solang lowers the barrier for developers, making Solana a more accessible blockchain to build on. However, it is currently unclear how this will impact developer activities on Solana.
Upcoming Catalysts
Emerging Solana DeFi Applications
Phoenix
Phoenix is a decentralized limit order book on Solana that supports spot asset markets. It is built by the Ellipsis Labs team, which recently raised $3.3 million in funding led by Electric Capital. Phoenix is primarily betting on the growth of native assets on Solana. The Phoenix project serves as an entry point to their decentralized trading platform, where the team believes market creation should be permissionless. All market events (order placements, order cancellations, trades, etc.) are recorded on-chain, allowing traders to easily query real-time and historical states of all Phoenix markets.
Drift Protocol
Drift Protocol is a derivatives trading platform on Solana. Drift v2 has recently surpassed $1 billion in cumulative trading volume with $4.9 million in open interest. The total value locked in Drift has grown by over 50% in the past month (measured in USD and SOL). Overall, Drift Protocol has shown strong growth across various metrics.
In addition to high-level statistics, Drift has also launched CONNECT, an open-source Metamask plugin that allows users of the Metamask wallet to bridge between EVM chains and Solana. Furthermore, Drift plans to support permissionless prediction markets in the future, which is still in the early discussion stage.
Squads Protocol
Squads Protocol has just launched its new platform, which is the exclusive comprehensive multi-signature platform of the Solana ecosystem. Squads Protocol has obtained $600 million in assets and has a total trading volume of $950 million.
Kamino Finance
Kamino is an automated liquidity solution that allows users to earn profits by providing liquidity to centralized liquidity market makers. In the third quarter, Kamino Finance facilitated over $1 billion in transactions and generated $1.25 million in fees for its depositors. Kamino Finance’s v2 is highly anticipated and is planned to be launched in the fourth quarter.
Points System for DeFi Protocols
The points system allows protocols to test different incentive mechanisms so that the protocol can evaluate what is effective and what is not. So far, the system has been extensively tested and experimented by the NFT protocols led by Tensor and Blur. We also need to see the adoption of these points systems by Solana DeFi applications.
MarginFi
MarginFi is a lending market that has introduced a points system in the Solana DeFi space, and other protocols have followed suit. The points system was inspired by the famous NFT platforms Blur and Tensor, but has been improved and applied in DeFi protocols. Following MarginFi, some Solana DeFi protocols have started to launch their own points programs, including Cypher, Solend, and Jito.
The system of MarginFi introduced a points system similar to Swell Network, where every dollar borrowed accumulates 1 point per day, and every dollar lent accumulates 4 points per day. Borrowing earns more points as it is the main driving factor for the success of the lending protocol.
Cypher
Cypher experienced explosive TVL growth before, but then encountered platform security vulnerabilities. Although there was a setback due to the exploitation of the vulnerabilities, Cypher later resolved most of the issues and restarted its operations.
Cypher’s points system is allocated to trades, borrowing, and lending on the platform. For the points allocation in spot and perpetual markets:
· Perpetual Market
Maker trades: Earn 20 points per $1 of trading volume
Taker trades: Earn 15 points per $1 of trading volume
· Spot Market
Maker trades: Earn 10 points per $1 of trading volume
· Lending Market
Borrowing: Earn 5 points per $1 borrowed per day
Lending: Earn 1 point per $1 lent per day
Solend
Solend takes a unique approach, where Solend Points have a minimum rewards pool and are divided by “seasons”. Season 1 will start with 100,000 SLND and will grow as more partners are attracted and transactions are made.
· Lending/Loan Market
10 million points are allocated daily, distributed according to the ratio of supply and borrowing. The borrowing volume is twice the supply volume.
· Leveraged Trading
10 points can be earned for every 1 USD of leveraged trading volume.
Jito
Jito launched Jito Points on September 28th, allowing users to compound their jitoSOL assets. The bonus/points distribution is as follows:
· 1.5x points for providing liquidity in any JitoSOL/xSOL trading pair
· 2.5x points for JitoSOL/SOL liquidity providers
· 3.5x points for JitoSOL/USDC and other volatile trading pair providers
Potential strategies (not financial advice):
Provide JitoSOL liquidity on these integrated protocols:
· Kamino Finance
· Meteora
· Orca
· Raydium Protocol
· Drift Protocol
Firedancer: When will it achieve over 1 million transactions per second?
Firedancer is a Solana validator client developed by Jump Crypto, aiming to further reduce latency and improve client diversity for Solana. To effectively achieve the goal of processing over 1 million transactions per second, the network needs to scale load balancing. Firedancer utilizes hardware and software upgrades to scale load balancing. In this report, we won’t delve into the details of Firedancer and its implementation.
Firedancer will release its components in stages.
The implementation of the QUIC Transaction Propagation Protocol marks the first step of Firedancer’s development. In performance testing, “fd_quic” demonstrated a propagation throughput of 1 million transactions per second.
The goal is to recreate each component of the Solana architecture to fully unleash the potential of Firedancer. QUIC marks the first step in recreating each validator component, and the release date for the comprehensive technology is currently unclear.
Conclusion
Solana has achieved a series of key technological milestones, addressing challenges and pioneering potential future directions for infrastructure, applications, and even partnerships with the traditional finance sector. Despite facing various technical and network challenges in the past, Solana’s strong technology stack and commitments to improvements, such as the implementation of QUIC, have greatly alleviated concerns.
The growing Total Value Locked (TVL) of Solana, leading DeFi transaction speed, and stable monthly transaction data highlight the chain’s potential to become a center of diverse economic activities. Decentralization metrics, such as the Nakamoto coefficient, reveal the chain’s dedication to creating a more distributed ecosystem.
The ecosystem is supported by various partnerships and technological advancements. From promising state compression technology (for significantly reducing NFT minting costs) to the expectations for Firedancer and its potential to further optimize the Solana experience, the chain continues to innovate. Integrations with Metamask Snaps and developments like Hyperledger Solang also suggest Solana’s efforts to become more EVM-friendly.
So far, Solana’s development represents a broader evolution of blockchain, filled with hope, occasional challenges, but continuous progress. Like any emerging technology, the road ahead is filled with uncertainty. The upcoming liquidation of FTX/Alameda SOL holdings by Galaxy may represent a potential inflection point on Solana’s timeline. However, Solana’s commitment to innovation, adaptability, and user-centric approach suggests promising prospects for this blockchain contender.
We will continue to update Blocking; if you have any questions or suggestions, please contact us!
Was this article helpful?
93 out of 132 found this helpful
Related articles
- New Organizational Paradigm An In-Depth Explanation of the Various Aspects of DAO
- Closing the ‘backdoor’ opened by the god mode, is a DEX without an administrator key the future?
- Ethereum brings ‘bad news’ Futures ETF falls short of expectations, on-chain data at a low point
- South China Morning Post Article Why can’t the JPEX incident shake Hong Kong’s cryptocurrency vision?
- Forbes Binance’s Golden Touch, how did they turn failed ICO tokens into unexpected fortunes worth billions of dollars?
- Web3 Legal Popularization丨Can GameFi Go Online Without a Game License and Constitute Illegal Operations?
- Crypto Race Weekly Report [10/9/2023] Decrease in ETH Staking Rewards, POW Track on the Rise