Stick to the Right Path and Surprise Everyone A Rational Choice for ETH Staking’s Security and Returns
Stay on the right path with ETH staking for security and returnsThe development of Ethereum’s liquidity staking derivative track (LSD) is booming. For ordinary cryptocurrency players, participating in LSD is sufficient. However, they do not have a deep understanding of the underlying logic and secure implementation of staking. The large number of users choosing LSD has caused a centralization risk in Ethereum, which is a significant threat to the entire Ethereum ecosystem.
Decentralization is not a team effort, but a rational choice made by each user based on their own interests. And I want to say that Staking as a Service is an Ethereum staking method that balances security and profits in accordance with your own interests.
Staking as a Service (SAAS) is suitable for users with medium to large funds. However, there is very little information available on SAAS in both Chinese and English news sources, which has caused a loss of a large number of users who could have participated in SAAS under certain conditions. The biggest advantage of this method compared to LSD is higher security, lower trust in third parties, lower costs, and potentially higher returns. Cryptocurrency players holding more than 32 ETH should seriously consider this method.
In my own experience, when researching the staking track of Ethereum, I kept asking myself what I considered the most important thing. After asking myself countless times, I still believe that as an investment decision with a time span of several years, and even possibly as passive income for a lifetime, the security of assets is unquestionably the top priority. From this perspective, LSD does not give me enough security.
- Unraveling the Rise and Fall of Open Edition NFTs
- Three Reasons to Be Bullish on Pendle Earn
- Introduction to Zero Knowledge Proofs
According to @0xtodd’s classic article “Starting with Staking: 4 Ways to Control the Ethereum Network”
There are only two staking methods that meet this demand.
-
solo home staking
-
staking as a service
For most ordinary people, they do not have the technical knowledge or energy to run their own nodes, so although solo staking is the most decentralized and relatively has no intermediate costs or commissions, it is too difficult. This article will not discuss it further.
This article will mainly focus on the staking as a service method. In plain language, SAAS means you provide funds – 32 ETH, and the node operator provides technology (software and hardware), and both of you cooperate in staking.
SAAS is not a familiar concept for most Ethereum users, and even for experienced defi degens, because almost all Ethereum staked liquidity tokens (LST) in defi are derivatives of the other two staking methods, pooled staking and staking on centralized exchanges. The former includes well-known tokens such as lido’s stETH, rocketpool’s rETH, FRAX’s sfrxETH, etc., which have a large trading volume and TVL in various DEXs. The latter is represented by Coinbase’s cbETH and Binance’s BETH.
Although the degree of decentralization varies between the latter two staking methods, one thing is the same, and that is the staker cannot personally control the two keys for Ethereum POS validation and withdrawal. Therefore, you have to choose to trust that the third party will not do anything malicious. Whether your faith will collapse, you will only know on the day something goes wrong. After all, I have been in the cryptocurrency circle for 10 years and have seen all kinds of ridiculous things.
If we look at the cycle of the next few decades, there will definitely be bigger black swan events happening, so there is nothing more important than taking control of our own destiny.
“
Investment decisions based on wishful thinking often lead to complete failure, and this level of failure can destroy your life with just one instance.
If you agree with the above viewpoint, then you might as well follow me to learn more about the SAAS pledge method. To truly take control of your assets.
The Ethereum official website evaluates the SAAS pledge method from the following aspects:
1. Open source
The key code is 100% open source and available to the public for free forking and use.
2. Audit
The key code has undergone formal audits, and the audit results have been publicly released and open to the public.
3. Bug Bounty
A public bug bounty program has been conducted for the key code to reward users for reporting or fixing bugs securely.
4. Real-world testing
The service has been open to the public and put into use within a specified time period. It’s better if it has been running for more than a year.
5. Permissionless
Users can participate in the service without any special permission, registration, or KYC verification.
6. Diversified client
The service provider should not use a majority of validator clients running over 50% of the total validators. It’s better if the percentage is less than 50%.
7. Self-custody
Users keep all validator credentials, including signing and withdrawal keys.
On the other hand, we can also judge which node operator is more stable and secure from the data on Ethereum staking dashboard rated.network.
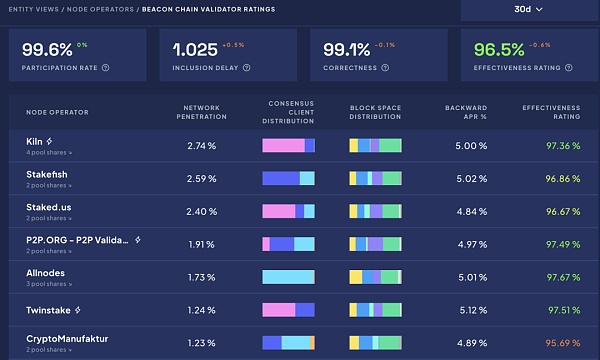
From the perspective of the website’s node operators, we can see that the market share of mainstream large node operators is not too high, with no operator surpassing 3%. This makes pooled staking relatively decentralized compared to lido’s dominance.
Here, I have listed the performance of several major node operators in the six dimensions.
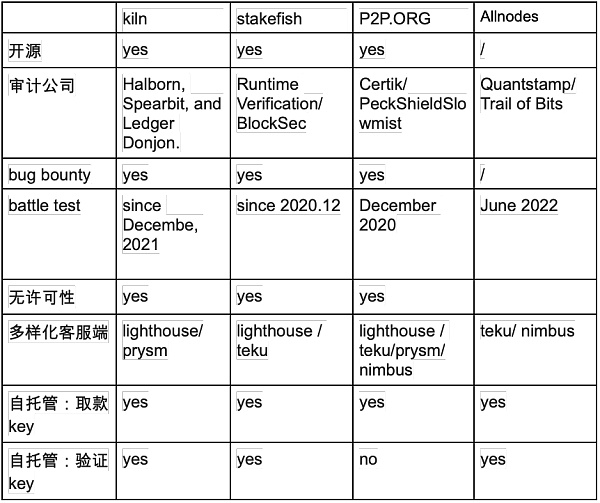
However, these six dimensions are too general and do not provide much guidance for users’ choices. For example, it is difficult to determine whether a protocol is completely open source. It may only put some components of the protocol on GitHub, and it is hard to know if the core code is fully open source.
There are also differences among node operators in how they handle the two keys, especially the verification keys that the protocol side needs to keep. This actually tests their understanding and implementation capabilities of security. Lido’s data in an article can show this difference from one perspective.
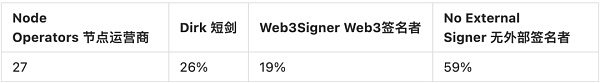
Dirk and Web3 Signer are two different ways to protect validator keys. They are both designed to provide secure key management to protect validators’ private keys from unauthorized access and malicious attacks. Unfortunately, most node operators do not adopt the basic practice of using external signatures to protect validator keys.
So I think a more reasonable evaluation of node operators should be based on the following aspects:
1. Security
For SAAS, the custody of the withdrawal key is entirely your own responsibility. As long as you ensure that your withdrawal address’s private key is not leaked, no one can take away your staked Ethereum. This is completely different from LSD, where node operators are not involved at all, which is why it is called self-custody.
The other key, the verification key, is where node operators can demonstrate their security concepts and execution methods.
In this regard, Attestant, a node operator, has a very detailed discussion on the technical means of protecting the verification key in an article. The original article is:
https://www.attestant.io/posts/protecting-validator-keys.
In simple terms, the verification key is in a dilemma. Although the verification key itself cannot access funds, if it is obtained by an attacker, indirect attacks such as blackmail or direct destructive attacks that result in penalties and loss of funds can occur. Therefore, security is very important.
At the same time, the verification key needs to be constantly accessible: the validator needs to sign multiple messages in each epoch (about 6.5 minutes). Therefore, the accessibility requirements for the verification key are also very high.
Generally speaking, we can have security or accessibility, but not both. This is the dilemma that node operators need to solve with the verification key.

In addition, the entire security system is highly asymmetric. Attackers only need to sign any message to achieve their destructive goals, while users have ongoing goals. In other words, attackers only need to win once, but users need to win every time.
So one way to protect validator keys is to layer multiple layers of security on top of the original plaintext storage of the keys, achieving a balance between cost and benefit. The technologies involved include remote LianGuaissphrase, remote signer, threshold signing, distributed key generation, etc. The layered security technologies mentioned above are quite impressive. If you are interested, you can learn more about the article mentioned above.
The ultimate result is to refuse single-point server failure and use DKG technology for threshold signing. If one of the servers is compromised, there will be no permanent weaknesses. By re-entering the key, the stolen key held by the attacker will be rendered useless.
Another article that I think all SAAS users should be aware of is:
https://www.stakingrewards.com/journal/choosing-the-best-using-metrics-and-data-to-choose-the-right-ethereum-validator/. It mentions several node operators who use threshold remote signing technology.
-
Attestant
-
Cryptomanufaktur
-
Certus one
-
P2P.org
-
Stakely
-
Staking facilities
Some of these node operators can be found on rated.network, and their performance is indeed very good. Their effectiveness ratings are relatively high, and there has never been a slash in history.
2/ Earnings
Once the security issue is resolved, the issue of earnings is largely resolved as well. Because when node operators can ensure the security of the validation key and have mechanisms to ensure the timely and effective issuance of correct messages, your earnings are naturally guaranteed. In addition, I believe there are three key indicators to help you choose the node operator with the best earnings.
1. Effectiveness Rating
Usually, users choose node operators based on the APR. You will check the APR earnings of each operator over a period of time. However, due to Ethereum’s complex reward structure (the APR for each month or even quarter highly depends on many random variables, such as the number of blocks created or the MEV extracted, and it cannot reflect the true performance of the operator), it is better to compare staking providers based on the validator’s effectiveness rating rather than APR.
I have explained this indicator in detail in my previous article “Complete Guide to Ethereum Staking Metrics – A Guide to Understanding Ethereum Staking Dashboard rated.network”.
https://mirror.xyz/darkforest.eth/lYp2RDybbioSns0TyIXe5y9w9AlbDraRkTX3q7diygc
In the long run, the validator’s effectiveness rating is a good predictor of APR because it measures how well the validator fulfills its duties. If the validator does not miss any attestations, it has 100% effectiveness and receives 100% of all possible rewards.
Among the top market-share players, the highest and lowest effectiveness ratings over a longer time period can differ by one percentage point. But apparently, the contribution to APR under random earnings interference is not significant. However, you should still choose node operators with higher effectiveness ratings, and you can’t go wrong with that.
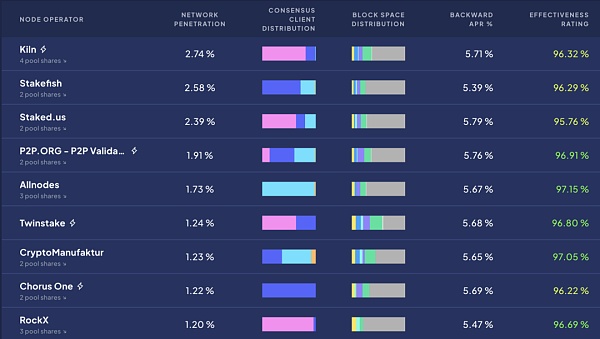
By comparison, during the same time period, the effectiveness ratings of LSD-like projects are generally not as ideal.
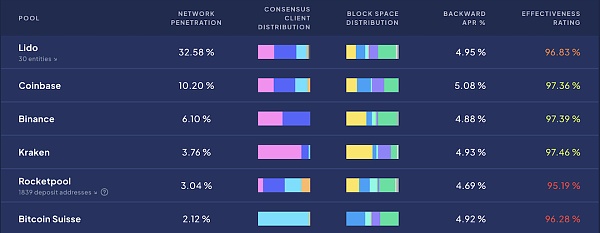
Another interesting point is that stakefish, allnodes, P2P.ORG, kiln, and other large node operators are also node operators participating in Lido or Rocketpool. Therefore, if you don’t care much about the liquidity of staking Ethereum and the composability of DeFi, or if you just want to prevent yourself from being impulsive and playing away your chips, you can choose the same node operator as the LSD protocol under the premise of controlling your private key, so you don’t need to share 5% or even 10% of your earnings with the LSD protocol, thereby increasing your earnings benchmark and extending the time horizon, which can result in significant earnings difference.
In summary, using reliable node operators can reduce risks and increase returns.
2. MEV Extraction Income
The number of MEV relays that a node operator connects to will affect the amount of MEV income you can earn. Currently, there are ten active MEV relays. If a validator connects to each relay, it will receive more bids and can choose the most valuable bid to earn higher MEV rewards. On Rated, we can see that the largest node operators in terms of BLOCK SLianGuaiCE DISTRIBUTION have almost the same graph, and almost all blocks are relayed through MEV-boost, maximizing the value extraction of MEV and increasing APR returns.
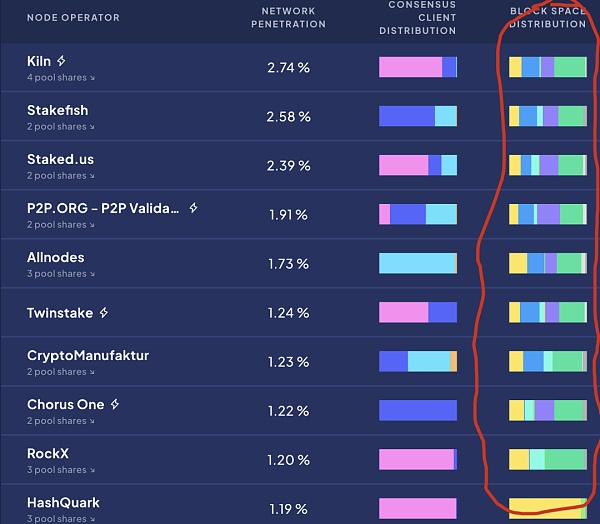
From the relay landscape interface on Rated, we can see the importance of increasing returns through MEV relays.
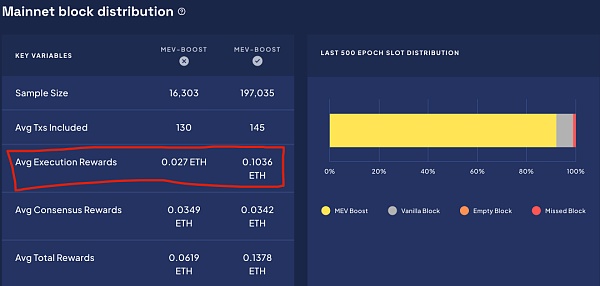
In the past 30 days, the rewards at the consensus layer are not significant for those who do not use MEV-BOOST, with almost no difference. However, at the execution layer, using MEV-BOOST can increase the rewards by nearly 4 times. This difference is not significant in the current low gas fee market, but in April, using MEV-BOOST even increased the execution layer rewards by more than 10 times. This is the role of MEV in increasing APR staking returns.
Of course, a higher percentage of MEV blocks is not necessarily better because when the time it takes to propose a block through MEV relays is too long, there is a high risk of missing that block. Therefore, when creating blocks, node operators do not achieve a 100% success rate.
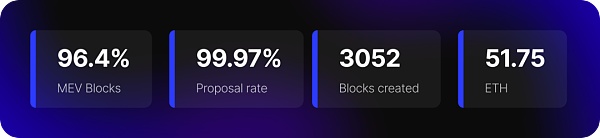
By the way, let’s take a look at the projects in the top ten active MEV RELAY tracks. Some of them have issued coins, but most of them have not. However… it seems that not many projects in this track are profitable, and the situation is quite challenging.

3. Slashing
Ordinary small-scale slashing does not have a significant impact or loss on individual stakers and the entire Ethereum ecosystem. If within 36 days, only 1, 100, or even 1,000 validators are slashed, the penalty will be equal to 0 ETH. However, if the number of slashed validators increases to about 1.1% of all validators (currently 6.4k), the penalty becomes 1 ETH and an additional 1 ETH is slashed for each additional 1.1% of validators. Therefore, if 1/3 of the network is slashed, the penalty will offset all equity (32 ETH). This mechanism is designed to prevent attacks on the network and should never be accidentally triggered.
We can compare the data on slashing events between the top node operators in the SAAS sector and the top projects in the LSD sector. Most SAAS operators have been running for a long time, while the coinbase and rocketpool in LSD have not been running for too long. However, based on the slashing data, SAAS, except for stake.us, is overall superior.
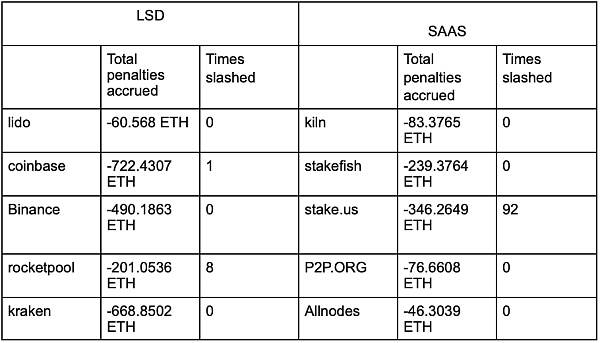
Comparison of LSD and SAAS Forfeiture Data
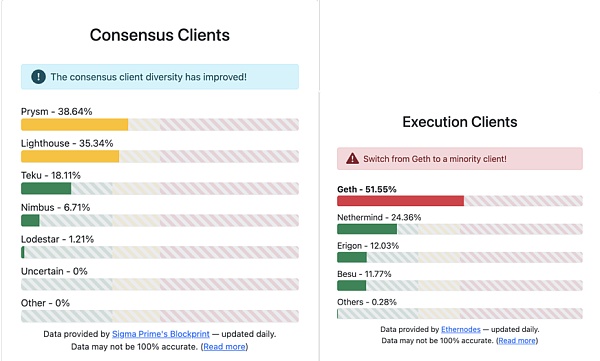
For Ethereum stakers, the potential for large-scale forfeiture is an absolute disaster, which is why the Ethereum community is very much pursuing client diversity. Currently, there are basically two dominant clients at the consensus layer, Prysm and Lighthouse, which together account for 74% of the market share. As for the execution layer, there is only one dominant client. It can be said that any serious bug in any of these clients could potentially lead to a severe forfeiture event in Ethereum POS. Therefore, for individual stakers, it is crucial to choose a node operator with client diversity, especially one that has minority clients, as this could potentially save their assets in critical moments.
3. Cost
If Ethereum staking is a long-term investment for you, choosing a staking method with lower fees is of great importance in terms of increasing your earnings over a long period of time. This is similar to choosing between actively managed funds and passive index funds in your investments. I believe mature investors can understand this.
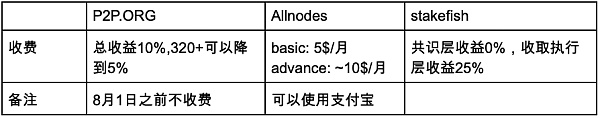
Since most SAAS node operators target institutional clients or directly connect to the LSD project, I have only found a few node operators that individual participants can join. Some node operators are open to negotiating fees, such as P2P.ORG, which offers a fee as low as 5% for large clients with more than 10 validators. Compared to Coinbase’s 25% fee for cbETH, this is quite attractive.
stakefish has a unique fee structure. They don’t take any fees from the consensus layer rewards, but only charge 25% of the execution layer rewards. In my opinion, this fee structure is quite savvy because as the number of stakers increases, the consensus layer rewards will continue to decrease, but once a bull market starts, the increase in priority fees and MEV income in gas fees will significantly increase the execution layer rewards, allowing stakefish to earn more.
I’m not sure about the specific fees and staking methods for kiln as I currently do not use Ledger Live.
Overall, Allnodes has the lowest fees. Based on the current Ethereum price of $1900, the annual fee for their premium plan is only 4% of the earnings. One thing I really like is that the fees are calculated in US dollars, so if the Ethereum price increases significantly in the future, other operators that charge fees based on the proportion of Ethereum will become expensive.
4. Operability
When participating in staking with most staking service providers, you need to generate your own validator mnemonic. They usually provide two options: the official Ethereum tool and their own tool. You need to properly store the mnemonic and generate two .json files: keystore and deposit. Note that you need to carefully safeguard the mnemonic because if you lose it, you will not be able to initiate withdrawal requests and your Ethereum will be permanently staked.
From a certain perspective, this doesn’t seem to be a big deal for lifelong stakers. After all, your interest is automatically deposited into the withdrawal address every few days, as long as you have the wallet private key for the withdrawal address, you won’t have to worry about not having money to spend. But, it’s still one less option.
The above operation may bring some psychological pressure to new stakers, although it is not complicated, it is recommended to practice more before actually doing it, and you can also try it on the Goerli test network. Some staking service providers have also prepared simpler staking methods, such as stakefish’s NFT staking method, and P2P.ORG’s staking can also be done almost with one click, without much operation. However, convenience comes with a certain cost. The withdrawal address for stakefish’s NFT staking is not your own address, but a whitelist contract address. P2P.ORG generates and manages validator keys for you, and you need to make your own choice in balancing security and ease of use.
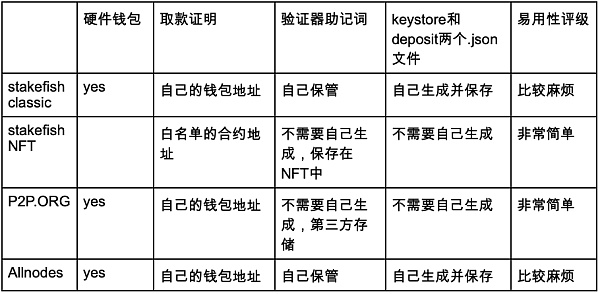
5/Overall Evaluation
Staking Rewards (https://www.stakingrewards.com/verified-staking-provider) is a website that provides information and tools related to cryptocurrency staking. You can learn about the staking rewards, expected yield, and guides and resources for participating in staking from this website. It also compares and ranks different staking projects and has its own rating system. It divides certified node operators into three levels: AAA, AA, and A. I have listed some AAA-level node operators, and interested friends can continue to delve into it.
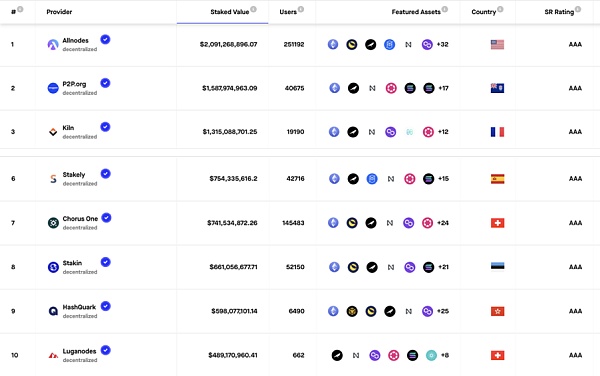
Summary
This is an investment research I wrote for myself. Although SAAS is also Ethereum POS staking like LSD, the popularity can be said to be polar opposites, with few people paying attention to SAAS and almost no in-depth Chinese content in this field. Most of the English content is written by the project teams themselves. After all, the threshold of 32 ETH to create a node is not low, but I believe there will still be people with this demand. At least for those who participate in LSD, if they can have a clear understanding of the operating indicators and security management methods of the underlying node operators of the LSD project, it will be of great help to their investment in the LSD project.
In my opinion, every staker participating in Ethereum needs to make choices that align with their own values based on their actual situation, and understand what is most important to themselves. As the saying goes, decentralization is not just the team’s responsibility, but a rational choice made by each user based on their own interests and independent thinking.
Sun Tzu’s “The Art of War” says, “In war, the victorious strategist only seeks battle after the victory is won.”
In my opinion, SOLO and SAAS are undoubtedly the “victory” that medium Ethereum stakers must hold on to. Only by securing your funds can you have the capital to “surprise” and go all out in the LSD race track. This can be called the way of investment – hold on to victory and surprise.
We will continue to update Blocking; if you have any questions or suggestions, please contact us!
Was this article helpful?
93 out of 132 found this helpful
Related articles
- What happened with the price surge of over 400% in the community tokens of multiple subreddits in just two days?
- Comprehensive Analysis of Opportunities and Challenges in the RWA Track
- Vitalik EthCC Speech Summary Account Abstraction Will Completely Change Wallet Interaction Methods
- A SNARK player actually announced that they will follow STARK?
- CME Executive Why Are People Interested in Our Cryptocurrency Products
- Hubei police crack the first nationwide ‘virtual currency case’, with a transaction volume of 400 billion.
- LianGuaiWeb3.0 Daily | Chainlink Launches Cross-Chain Interoperability Protocol on Ethereum and other Networks






