Understanding the business model and product components of Centrifuge, one of the leading companies in RWA
Understanding Centrifuge's business model and product components, a top company in RWA.Author: Jiang Haibo, BlockingNews
Real-world assets (RWA) may be the next growth direction for the cryptocurrency market, but the connection between RWA and blockchain is not easy and requires compliance, a trusted asset issuance framework, and corresponding liquidity on the chain.
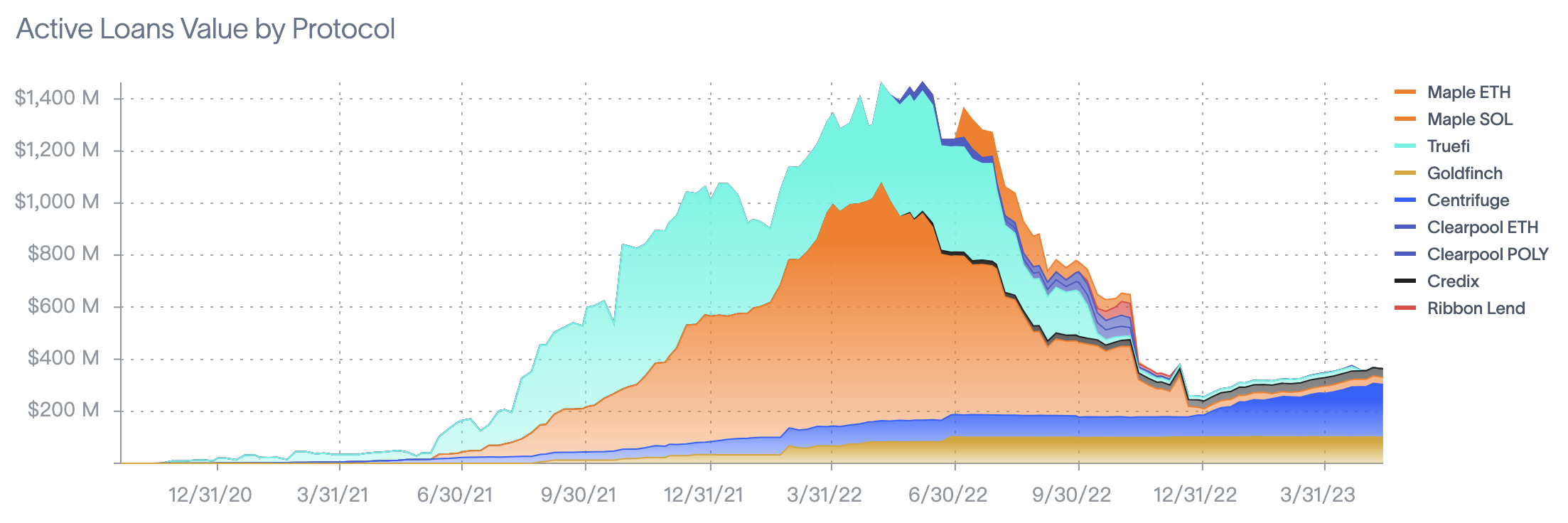
Centrifuge is currently one of the more comprehensive projects in the RWA field, establishing a framework that links on-chain and off-chain transactions, hoping to become a trustless consensus layer for RWA. According to rwa.xyz, Centrifuge is already the most active project in the private credit sector. In this article, BlockingNews will break down Centrifuge’s business model and product components.
- Deep Analysis: Exploring Hooked’s Ambitious Goals in Web3 Education through Collaboration with Animoca
- Is the ultimate goal of AI Web3? “Father of ChatGPT” launches encrypted wallet World App
- Why has Cosmos become the first choice for many developers in application chains?
Centrifuge Chain
First, Centrifuge has its own independent exclusive blockchain-Centrifuge Chain, which is developed based on the Substrate framework and can share the security of the Polkadot network. Centrifuge Chain won the eighth slot auction of Polkadot in January 2022.
Centrifuge believes that there are many advantages of a dedicated blockchain for RWA, including lower transaction fees and excellent scalability. Compared with general smart contract blockchains such as Ethereum, it has greater flexibility, can provide dedicated block space to process RWA transactions, and can define the order of transactions to ensure that RWA-related transactions can be carried out normally even in extreme situations such as network congestion.
As of May 17th, Centrifuge’s main product Tinlake was still deployed on the Ethereum mainnet, but it is being prepared to be deployed on the Centrifuge Chain, and related functions are being tested online.
Tinlake Financing Platform and Structured Products
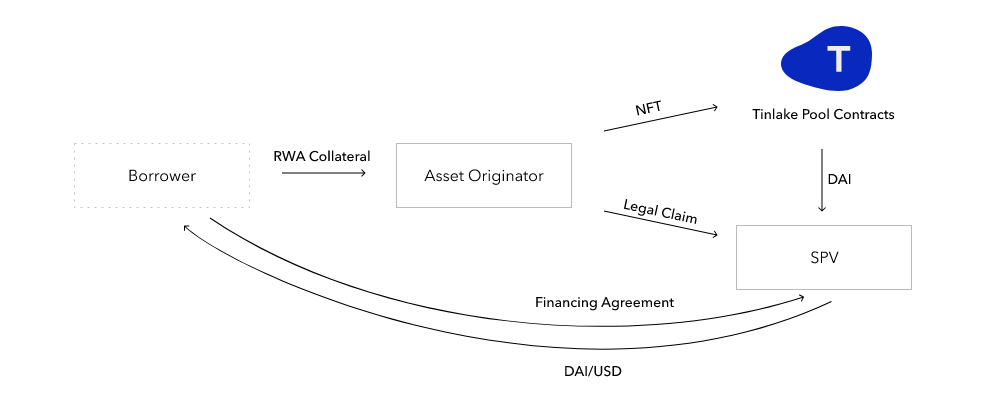
The interaction between real-world and encrypted assets in Centrifuge occurs on its open-source smart contract platform, Tinlake. In Tinlake, borrowers can tokenize assets through asset issuers and then invest these tokens into asset pools created by Tinlake. In this way, borrowers can obtain stablecoins invested by on-chain investors with physical assets as collateral. As of May 17th, Tinlake’s TVL (approximately equivalent to active loans) was 201 million US dollars.
Through structured products, Tinlake effectively divides the risk and return of physical collateral to meet the needs of different investors. Structured products consist of two ERC20 tokens: DROP and TIN.
- DROP Tokens: The DROP token is senior to the Tinlake pool and represents the fixed-rate portion of the pool. DROP token holders have priority in profit distribution from the asset pool but have a relatively lower exposure to risk (e.g. loan defaults). Therefore, DROP tokens typically have lower risk and lower returns.
- TIN Tokens: The TIN token is junior to the Tinlake pool and represents the floating-rate portion of the pool. Compared to DROP tokens, TIN token holders have lower priority in profit distribution from the asset pool, but have larger exposure to both returns and risks. Therefore, TIN tokens usually have higher risk and higher returns.
In Tinlake, investors can choose to purchase DROP or TIN tokens based on their own risk tolerance and expected returns. Among them, TIN tokens have a minimum subscription ratio. If the ratio of TIN is too low, DROP tokens cannot continue to be purchased.
Legal Structure
Centrifuge has done a considerable amount of work in compliance with the legal structure of US asset securitization. Its legal structure is completed based on Section 506(b) or 506(c) of the 1933 US Securities Act.
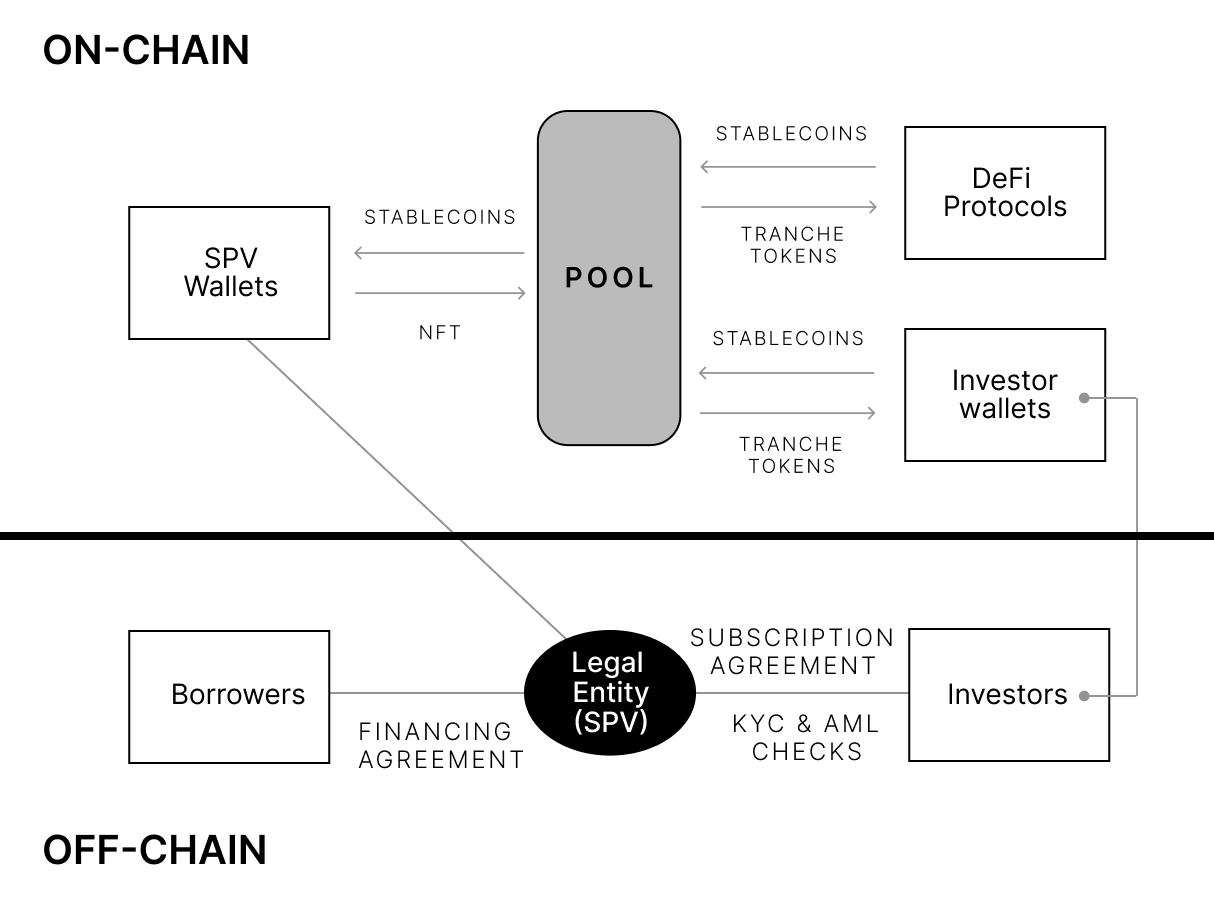
Every asset issuer on Centrifuge must establish an independent legal entity corresponding to the funding pool, namely a special purpose entity (SPV). SPVs can play a critical role in asset securitization, separating the asset issuer’s business from the financing activities in the pool. It only provides a channel and has no employees. Legally, these assets have been sold to the SPV, and even if the asset issuer goes bankrupt, it will not affect the assets held by the SPV, thus protecting the interests of investors. After completing KYC and other compliance operations, investors sign agreements with the SPV.
The current legal structure is developed for the issuance of asset securitization products in the United States. If you are a US citizen, you must meet the SEC’s requirements for “qualified investors” when investing in this product. Centrifuge is also working to introduce product structures for non-US jurisdictions, but currently, countries subject to US sanctions cannot invest in Centrifuge’s products.
Financing Process
The relationship between the asset initiator, issuer, investor, and Centrifuge in Centrifuge, as well as the specific financing and investment process, is as follows:
1. The borrower wants to finance on the chain with assets such as invoices or real estate as collateral.
2. The asset initiator (who has a business relationship with the borrower and executes underwriting, and also invests in the higher-risk TIN token) establishes a legal entity SPV for the fund pool, even if the parent company goes bankrupt, the SPV will bear responsibility. A fund pool may include multiple collateralized loans for the same type but corresponding to different borrowers.
3. The asset initiator initiates and verifies RWA, and for the collateralized assets, mints an NFT on the chain.
4. The borrower signs a financing agreement with the SPV and mortgages the NFT in the Tinlake pool, and the Tinlake pool mints DROP and TIN two tokens.
5. Centrifuge and Securitize cooperate to help investors complete the KYC and AML processes. Securitize is an SEC-licensed institution that provides qualified investor verification services.
6. Investors sign an investment agreement with the SPV corresponding to the Tinlake pool, which includes investment structure, risks, terms, etc., and then purchase DROP or TIN tokens with DAI.
7. When investors provide liquidity for the corresponding fund pool with DAI, the SPV exchanges DAI for US dollars and transfers them to the borrower’s bank account.
8. Investors can request to redeem their DROP or TIN tokens at any time, but must ensure that the DROP token is redeemed first and the TIN token cannot be lower than the set minimum ratio.
9. When the NFT expires, the borrower pays the financing amount and financing fees, and the NFT is returned to the asset initiator.
Relationship with MakerDAO and Aave
Among the main DeFi protocols, MakerDAO and Aave are actively carrying out RWA business, and the relevant business is carried out through Centrifuge.
There are multiple MakerDAO-related fund pools on Centrifuge, and these fund pools are integrated with MakerDAO’s Vault, which can directly extract funds from the Vault. The largest active fund pool with BlockTower as the initiator is BlockTower Series 3 and BlockTower Series 4, both of which are private pools. Priority capital is obtained from Maker Vault, and secondary capital is contributed by the initiator BlockTower. The funds in these two pools are US$37.33 million and US$97.17 million, respectively. In addition, there are two fund pools, BlockTower Series 1 and BlockTower Series 2, which are also initiated by BlockTower and will be launched soon. In addition, there are several fund pools integrated with Maker Vault on Centrifuge, including New Silver Series 2, ConsolFreight Series 4, Fortunafi Series 1, and Harbor Trade Credit Series 2. The corresponding values in the flow pool are US$12.05 million, US$3.61 million, US$8.43 million, and US$2.14 million. There is approximately US$161 million in funds related to MakerDAO in the fund pool, which accounts for 80% of the Centrifuge TVL.
One advantage of a fund pool integrated with Maker Vault is that each fund pool has a reserve pool. The funds in the reserve pool can be borrowed by issuers or redeemed by investors, but do not generate interest, and usually there are no funds left in the reserve pool. However, if integrated with Maker Vault, as long as the debt limit of the Vault is not reached, when a user needs to redeem, they can directly extract funds through Maker Vault and transfer their personal debt to Maker Vault.
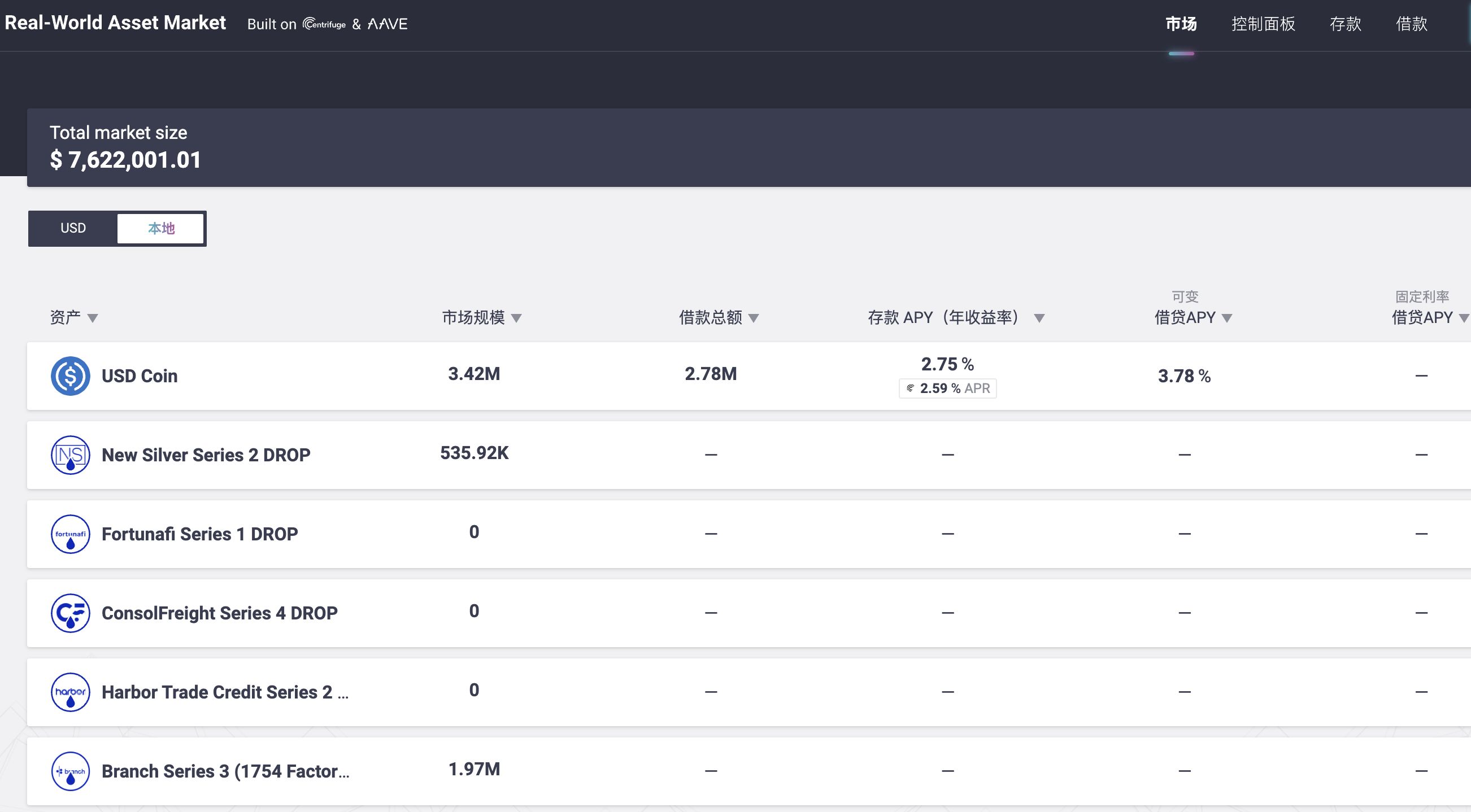
Aave and Centrifuge have jointly established a lending pool dedicated to RWA. Depositors can deposit USDC and not only receive interest income, but also receive mining rewards from Centrifuge. Borrowers use various DROP tokens as collateral to borrow USDC and increase fund utilization. The total deposit in the RWA market in Aave is currently 7.62 million U.S. dollars, of which the USDC deposit is 3.41 million U.S. dollars, and the total borrowing is 2.78 million U.S. dollars, which is not high compared to MakerDAO.
CFG Token
Centrifuge’s native token is CFG, which is mainly used to pay gas fees for on-chain transactions, participate in governance activities such as protocol upgrades and parameter adjustments, and maintain the security of the Centrifuge Chain.
It is worth noting that there are currently no protocol fees in Centrifuge, and the current lending is built on the Ethereum mainnet. Recently, there have been more and more discussions in the community about Centrifuge protocol fees. The vote to enable protocol fees has been conducted on OpenSquare and received 100% approval. However, before conducting on-chain voting, a fund pool needs to be deployed on the Centrifuge Chain, and this function is currently being tested in Centrifuge’s testnet.
Summary
According to rwa.xyz data, Centrifuge is currently the project with the highest active loan amount in the on-chain private lending field, with a TVL of 201 million U.S. dollars. According to official website data, about 80% of them are integrated with Maker Vault fund pools. Since the debts of these fund pools have not reached the limit and new fund pools are being established, the recent data growth of Centrifuge may mainly come from these fund pools and may continue to grow.
Centrifuge has its own chain, but its main financing platform Tinlake is still built on the Ethereum mainnet, and related functions have also been tested on Centrifuge Chain’s testnet. Currently, Centrifuge does not charge protocol fees. After the test is completed and deployed on the mainnet, protocol fees may be enabled through on-chain voting.
We will continue to update Blocking; if you have any questions or suggestions, please contact us!
Was this article helpful?
93 out of 132 found this helpful
Related articles
- Dark Side of NFT History: Reviewing the Darkest Moments of 5 Blue Chip Tokens
- Conversation with Coinbase Protocol Director: How is Base, as a highly anticipated new Layer2, building its ecosystem step by step?
- How does ERC-6551 change the game by turning NFTs into Ethereum accounts?
- Embark on the Opside Value Exploration Journey: Pre-Alpha Incentive Test Network Countdown officially launched
- Exploring the New Trends of the Three Pillars of DeFi: DEX, Lending, and Stablecoins
- Why is everyone choosing to create platforms instead of making games?
- The World Cup is targeted by Web3 on a global stage






