Age of Inscription 2.0: Can Recursive Inscription Enable Bitcoin On-Chain Smart Contracts?
Can Recursive Inscription enable Smart Contracts on the Bitcoin Blockchain? A closer look at Age of Inscription 2.0.Author: Wuhai, BlockingNews
Since the release of the Ordinals protocol on the Bitcoin chain and the subsequent brc20 concept proposed by developer domo, micro innovations based on the Ordinals protocol have emerged one after another, such as orc20, which aims to make brc20 more flexible, and GBRC721, which optimizes block space. However, apart from whether these protocols are pseudo-demands or hot topics for attention or speculation, they are optimizing the already existing protocols, that is to say, they have been discussing how to make a carriage run faster, rather than trying to invent a car.
However, the “recursive inscription” proposed recently by Casey Rodarmor, the creator of the Bitcoin protocol Ordinals, has surprised the community and opened up more imagination. On June 12, Raph, the newly appointed chief maintainer of the Bitcoin protocol Ordinals, merged the “recursive inscription” update No. 2167 to the Ordinals code on Github. This inscription can request the content of other inscriptions using special syntax “/-/content/:inscription_id”. This simple change has unlocked many powerful use cases.
- Full testimony of Avalanche founder: We are standing at the edge of a new era
- How is the NFT market performance of Azuki and Beanz? Let’s start from the borrowing and lending activities.
- Will the regulatory crackdown on Binance fall through? Analysis of recent market data changes in Binance
The era of Inscription 2.0 may have arrived
According to the interpretation of developer Leonidas.og, it is very expensive to engrave 10,000 JPEG files separately for a PFP collection inscription, but it is more efficient to engrave 200 features from the collection and then make 10,000 inscriptions, each of which requests features using a small amount of code and presents images through programming. This makes it possible to store art on the chain in a more efficient way.
In addition, in the previous inscription method, each inscription was independent and there was no correlation between inscriptions. However, this situation is about to change by introducing recursive inscriptions. It is possible to completely package many codes into inscriptions on the Bitcoin chain, and because the code (in text form) is called, the volume is very small, which can allow the size of inscriptions to break through the 4MB limit of the Bitcoin block size, and can completely put complex 3D video games on the chain.
This also makes the community believe that smart contracts similar to ERC20 may be able to run on the Bitcoin chain, making scalability and interoperability on the Bitcoin chain possible.
In addition, the reason why many people are willing to pay for NFTs on the Bitcoin chain, apart from speculation, is the story of permanent storage on the chain. Therefore, if recursive inscriptions make it possible for the metaverse of gaming, DeFi and other subdivisions to operate on the Bitcoin chain, the story will be even more attractive compared to other chains.
Perhaps, recursive inscriptions will lead the revolution of Bitcoin inscriptions on the chain, bringing Bitcoin inscriptions from the 1.0 era to the inscription 2.0 era.
After the birth of recursive inscriptions, multiple projects have been built based on its syntax by the community or individuals. Currently, there are already six collections and indexes on the trading platform MagicEden. Below, we will introduce the Recursive Punks series, which ranks high in daily trading volume and is very story-driven and dramatic.
Dramatic Opening of Recursive Punks
On June 13, the Recursive Punks official account announced the free casting of 10k Recursive ordinals series, and the community subsequently spread the news. Whether driven by the FOMO caused by the previous surge in the first project on the new protocol, or the desire to try out innovation, the 10K quantity was quickly engraved after being discovered by the Chinese community. When Twitter KOLs forwarded the news successively, it even caused the official website to be unable to open.
However, after the community finished engraving, users found that the official developer of Recursive Punks used old text, which means that the syntax that should be used for recursive inscriptions is “/content/”, but the official used “/-/content/:”, resulting in users who previously used the official SVG file to engrave getting a version without images. Subsequently, the community began to spread the correct method of using the modified version, which is to replace the “/-/content/:” in the original SVG file with “/content/”.
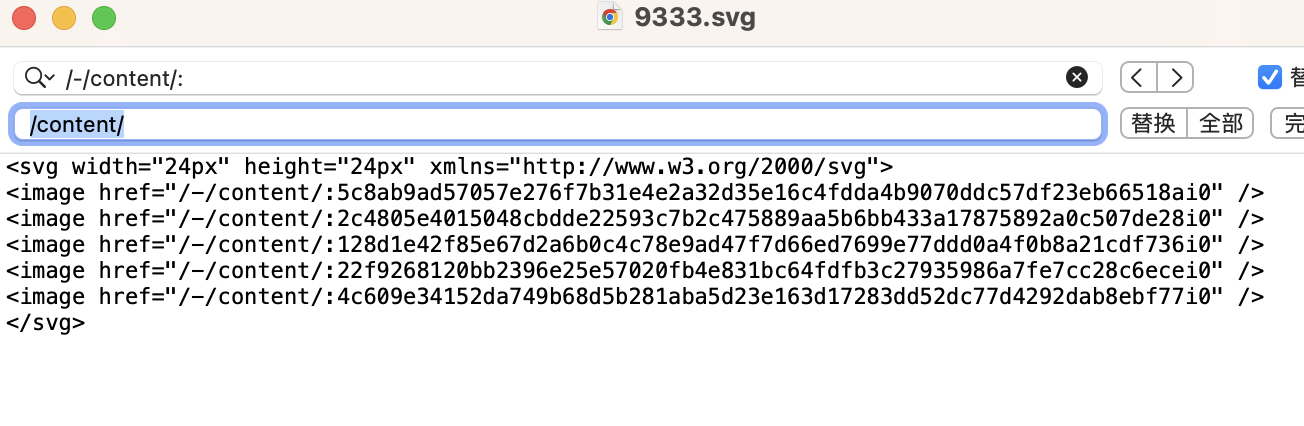
Compared to the imageless version officially released by Recursive Punks, the modified version with images was engraved relatively slowly because the community could not confirm which version would become the series with stronger consensus. After 24 hours, the modified version of Recursive Punks with images was engraved. In the meantime, the official of Recursive Punks also discovered their syntax error and sent out a tweet expressing their hope that the protocol developers and the community could recognize both the imageless and image versions at the same time, but they subsequently deleted the tweet and launched the imageless collection on MagicEden.
The surprising thing for the community was that the series without images was displayed with clear images on MagicEden. After analysis by technical personnel, it was found that the official of Recursive Punks submitted the collection to MagicEden and used front-end rendering to display images on the platform. In other words, they did not use the implementation method of recursive inscriptions to display, which is somewhat different from what the community expected.
According to MagicEden data, the total transaction volume of the Recursive Punks no-graph series encoded with old syntax reached 8.15 bitcoins on the day of launch, becoming the series with the highest transaction volume on the platform. The highest price rose to 0.002 bitcoins, with the highest increase of up to 30 times relative to the encoding cost. In addition, multiple punks with rare attributes were traded at a price of 0.05 bitcoins. The number of holders also grew by more than 2,000 overnight.
The community-encoded graph versions using corrected syntax are displayed as blurry images on the new NFT platform odyssey, displayed as recursive inscriptions. They were later listed on the MagicEden platform, but the platform currently does not support SVG format display, so the image cannot be displayed until it is further supported. The number of addresses holding the graph version of Recursive Punks encoded with corrected syntax is continuously increasing, and the total transaction volume is currently 1.3 bitcoins, ranking third in the daily trading volume.
It is reported that the community is continuing to follow up, so that the correct version of the graph version encoded with corrected syntax can further develop. As for whether the community-supported graph version that occupies the side of protocol justice or the official no-graph version can have a stronger and wider community consensus, it remains to be seen.
The emergence of recursive inscriptions has opened up possibilities and imaginativeness that were previously not interoperable, not programmable, and had poor scalability on the Bitcoin chain. For example, it enables NFTs to be combined with each other, and makes chain-based games possible; or disassembles inscriptions, similar to fragmentation, to generate more calls. Community members also imagine the possibility of decentralized websites.
From the protocol level, the future is boundless, with sufficient grand narratives waiting for developers and users to build and use. However, the front end is still in a highly controlled state, because whether an inscription or an NFT series can be listed and indexed on a platform determines the speed of its development and the consensus it is preached. As mentioned earlier, Recursive Punks is difficult for new users to identify due to indexing.
However, these problems will gradually be solved as the ecosystem develops. We cannot stop or stand idly by because of some minor issues or difficulties that arise. The era of Bitcoin Inscription 2.0 may be led by recursive inscription, which is full of opportunities and risks. Let us participate in this experiment, explore, discover, and research, and participate under the premise of controlling risks.
We will continue to update Blocking; if you have any questions or suggestions, please contact us!
Was this article helpful?
93 out of 132 found this helpful
Related articles
- Viewpoint: How to view the prospect of the cryptocurrency market?
- SEC has launched a comprehensive political battle over cryptocurrency.
- Delphi Digital: Analyzing the Five Types of Instances of LSDFi: Interest Rate Swaps, CDP Stablecoins, Multi-Asset LSD, Money Markets, and DEX. Author: Delphi Digital
- What happened to the cryptocurrency market with a 30% drop in altcoins due to the “610” attack?
- SEC Complaint Reveals the Truth: Major Players Have Stumbled in the Crypto World in Recent Years
- Is the collective waterfall of altcoins just the beginning of regulatory impact?
- On the Eve of GameFi Explosion, the Competition of Chain Games “Tribes” is Underway