Can recursive inscriptions trigger the next bull market?
Can recursive inscriptions trigger the next bull market?2023 is undoubtedly an important milestone in the expansion of the Bitcoin blockchain ecosystem. From the introduction of concepts such as Ordinals and RGB protocol, to the emergence of Bitcoin Stamps and BRC20 standards, the call for supporting the development of the Bitcoin ecosystem is growing stronger.
In the past, few NFT players would have thought of the Bitcoin network. Most people use Ethereum or specially built NFT blockchains. It wasn’t until early 2023 that Casey Rodarmor introduced Ordinals and Inscriptions to the most purist Bitcoin network, introducing NFTs to this network. These NFT-like “inscriptions” gradually became rare and collectible, and began to be listed and traded on the secondary market. On January 21, 2023, the Ordinals protocol released version 0.4.0, and the number of BTC NFT minting started to soar.
Ordinals has brought many innovations to Bitcoin, but the story of Ordinals is far from over. On June 12th, Raph, the new chief developer of the Bitcoin protocol Ordinals, merged the “Recursive Inscriptions #2167” proposed by Casey Rodarmor on Github into the Ordinals protocol. Finally, in version 0.6.2, recursion was officially updated and launched. Along with the introduction by one of the anonymous developers of Ordinals, Leonidas.og, recursive inscriptions were born.
Recursive inscriptions are one of the innovations in the Bitcoin Ordinals community. Their appearance is expected to completely change the Bitcoin NFT ecosystem and redefine the current parameters of blockchain-based file storage.
- X-explore In-depth study of the behavior patterns of airdrop experts. What can we learn from it?
- Against the trend, what new patterns will the social application friend.tech bring to NFTs?
- How does Layer2 make a profit?
Bitcoin Ordinal Inscriptions
To understand what recursive inscriptions are, we first need to understand what Bitcoin ordinals and ordinal inscriptions are.
The concept of ordinals was proposed by Casey Rodarmor in 2023. It refers to a numbering scheme that assigns a number to each sat (satoshis) on the Bitcoin network. This process of assigning numbers to sats is called ordinal theory. These sats are numbered according to the order of mining, which means that even if a sat is eventually transferred to a different wallet, its assigned number remains unchanged. These data can be in any format and are directly recorded on the Bitcoin blockchain.
Inscriptions refer to creating Bitcoin native digital assets by engraving content on sats. Inscriptions are stored in the witness field of Bitcoin transactions. This is thanks to the implementation of Segregated Witness (SegWit) soft fork in 2017, which restructures Bitcoin transactions by separating them into transaction and witness components, optimizing data storage efficiency. Building on the upgrade of SegWit, another important Bitcoin soft fork called Taproot was launched in November 2021, further increasing the data storage capacity for inscriptions to the current maximum limit of 4MB. This means that inscriptions can store up to 4MB of data on the Bitcoin blockchain without taking up too much space.
With ordinals, Bitcoin is no longer just digital gold. It integrates data directly into the blockchain, opening up channels for creating unique digital assets and bringing the fields of art, collectibles, and intellectual property into the decentralized finance domain. By leveraging ordinals, artists and creators can verify and tag their works on the immutable Bitcoin blockchain. The scarcity of Bitcoin NFTs has attracted creators and collectors, injecting new potential into the NFT market. Therefore, ordinals quickly gained popularity in the Bitcoin community.
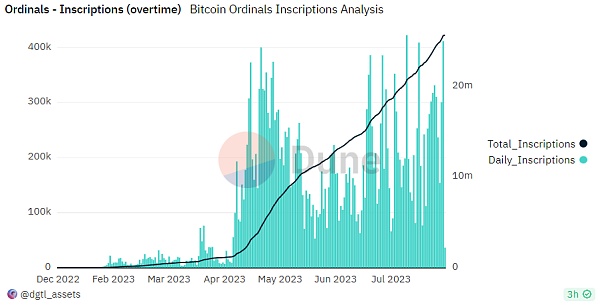
The Number of Inscriptions Changing Over Time
Although Bitcoin has been upgraded, writing data directly to the blockchain still takes up a lot of space and is still limited to 4MB. The introduction of recursive inscriptions solves this problem.
Recursive Inscriptions
What are Recursive Inscriptions
Recursive Inscriptions is a new feature of the Bitcoin blockchain that allows for the creation of complex data structures that can be stored on the blockchain. By working with a series of inscriptions, each inscription refers to previously created inscription data. This allows for the creation of arbitrarily large data structures, as each inscription can point to another inscription. In short, recursive inscriptions call upon data in previous inscriptions and merge that data into new inscriptions, allowing users to surpass the 4MB limit per inscription. Recursive inscriptions elevate ordinal inscriptions to a new level by expanding the Bitcoin NFT network.
Recursive inscriptions eventually allow developers to run software entirely on the chain by linking data through a series of calls. Many also see recursive inscriptions as another step towards interoperability in the Bitcoin network, as well as more complex ordinal use cases beyond minting Bitcoin NFTs. For example, users can create a recursive inscription that includes a video game. Inscriptions can call upon data from other inscriptions to store graphics, music, and code for the game. This would enable the storage of large and complex games on the Bitcoin blockchain without being limited by the 4MB block size.
In the past, when we minted inscriptions, if we wanted to mint 1000 images, we had to upload these images one by one to the Bitcoin network and then generate them. This process was not only labor-intensive, but also limited by the block capacity of the Bitcoin network. The size of each image had to be limited to a small range to control the cost of inscription, which would sacrifice the quality of the images. The approach used by recursive inscriptions is to first extract all the features from these images. Each inscription represents a feature in the image. Then, 1000 recursive inscriptions are created, and each recursive inscription uses the “/-/content/:inscription_id” code to request the image on the “feature inscription”. Finally, the complete image is rendered through programming. This approach is like movable type printing. Before movable type printing, to print a book with 1000 pages, 1000 stone tablets had to be carved. However, with movable type printing, only a limited number of typefaces need to be created, and fixed blocks of characters can be taken directly from the typefaces for combination and assembly, allowing the composition of the book to be printed in a short period of time.
Innovative Breakthrough of Recursive Inscriptions
Improved Storage Efficiency: Recursive inscriptions use the special “/-/content/:inscription_id” syntax to request the content of other inscriptions, which allows users to create inscriptions on the Bitcoin chain with less capacity and lower fees. Enthusiasts of recursive inscriptions, such as Leonidas, have been advocating for their potential. Recursive inscriptions can not only increase use cases for ordinals, but also reduce transaction costs by reducing the amount of data inscribed on each satoshi. The ability to recycle stored data through recursion can effectively eliminate the need for storing duplicate copies of files, significantly improving storage efficiency.
Enhanced Interoperability: The flexibility, composability, and low cost advantages of recursive engravings bring unlimited possibilities to engravings. Users can engrave complex images, videos, 3D games, and other forms of content on the chain. Compared to previous independent engravings, it enhances their interactivity. In the future, NFT engravings will evolve from being viewed unidirectionally by users to interactive bidirectional interactions.
Enriched Forms of Engravings: In addition to the original text engraving type, recursive engravings also add “JS” and “CSS” types, which means that recursive engravings can display almost any content on a webpage. Recursive engravings can also reference other engravings, similar to how local webpages upgrade to the internet, greatly enriching the forms of engravings.
Representative Projects
Recursive Playground
Recursive Playground is the first interactive recursive NFT engraving project that allows users to interact with NFTs. Users can change the state of the visuals by simply dragging the mouse. This transforms NFT engravings from static and view-only to dynamic and real-time interactive. Currently, Recursive Playground has not revealed the team behind it. But as the debut of “interactive recursive engravings,” it brings more possibilities to NFTs.
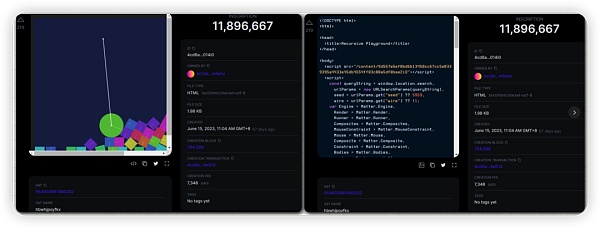
OnChainMonkey
Projects like OnChainMonkey have realized the potential of recursive engravings. They use recursion to engrave various data packets as serial numbers on Bitcoin, enabling them to create 3D artworks that are less than 1KB by calling these data packets. OCM Dimensions is a 3D animated engraving on Bitcoin with a total supply of 300. As a 3D interactive artwork, Dimensions is built on top of the Bitcoin network to create detailed 3D animation rendering, all of which are done on the Bitcoin blockchain. Each Dimensions uses less than 1KB of block space.
Empowering the Bitcoin Ecosystem with Recursive Engravings
The emergence of recursive engravings brings unlimited possibilities to the Bitcoin ecosystem. Recursive engravings enable hosting a large number of files directly on the Bitcoin blockchain, and their impact is not limited to entertainment and file storage. It also opens up technical opportunities to create new software by allowing users to call existing complex code or data in an engravings repository. For example, implementing permissionless contracts enforced by Bitcoin’s persistent storage without new encryption measures. Developers can leverage pre-existing engravings repositories to bypass the current 4MB limit by utilizing data stored on another engraving. This reduces the cost of hosting files on Bitcoin.
Furthermore, recursive engravings have also been proposed as a way to improve the functionality of Bitcoin smart contracts. Smart contracts are software that can automate transactions on the blockchain. However, due to the non-Turing completeness of Bitcoin’s script, its smart contract functionality is limited. The integration of recursive engravings and serial numbers can promote similar smart contract functionality and other permissionless contracts on the Bitcoin blockchain, opening the door to a range of complex software use cases. Recursive engravings can also create new types of software by allowing users to call existing complex code or data in an engravings repository.
The Potential and Risks of Recursive Inscriptions
Potential
Recursive inscriptions enable files to use specified syntax to retrieve other inscriptions, allowing for the creation of complex data structures that can be stored on the blockchain. This expands the data storage capacity of the Bitcoin blockchain and breaks the limitations of previous inscription methods, opening up infinite possibilities for free combinations between new inscriptions. It not only solves the issue of inscription capacity but also enriches the forms of inscription creation, while reducing costs. The introduction of recursive inscriptions has brought revolutionary impact to the blockchain.
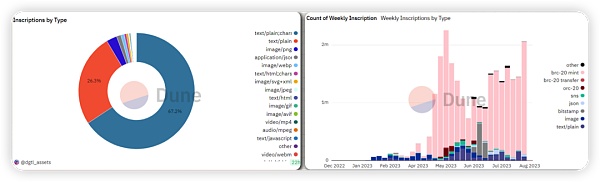
After the introduction of recursive inscriptions in July, people have regained interest in Bitcoin inscriptions. As of the time of writing, text format inscriptions have surpassed all previously created inscriptions. Images rank second, while applications have a smaller proportion.
Risks
One of the risks of recursive inscriptions is the potential creation of cursed inscriptions. Cursed inscriptions are inscriptions that are created due to the incorrect use or intentional misuse of opcodes, resulting in them becoming invalid and unrecognizable. Cursed inscriptions reference themselves in a loop, making them unexchangeable as there is no way to break the loop. Cursed inscriptions may also contain malicious code to steal funds or damage the Bitcoin blockchain. However, currently, cursed inscriptions can also be created using serial numbers, so this is not a new problem. In addition, the community seems to have accepted cursed inscriptions to some extent.
Another risk of recursive inscriptions is their potential use in creating spam or other malicious content on the blockchain. In the long run, this could burden the Bitcoin network, with countless spam inscriptions piling up in the Bitcoin memory pool, leading to network congestion and higher transaction fees.
Summary
In summary, recursive inscriptions mark another milestone in the Ordinals narrative, further opening up the interoperability and programmability of the Bitcoin network, driving innovation in the Bitcoin ecosystem. Although recursive inscriptions are still in the early stages and face challenges in development and testing, their emergence has changed the potential of Bitcoin applications, especially in creating more complex applications and increasing accessibility for mainstream users, which should not be underestimated. Recursive inscriptions can overcome storage limitations and unleash new possibilities for NFTs and smart contracts, reshaping the future of Bitcoin.
We will continue to update Blocking; if you have any questions or suggestions, please contact us!
Was this article helpful?
93 out of 132 found this helpful
Related articles
- Friend.Tech A New Approach to Web3 Social or Just a Flash in the Pan?
- The higher the road, the taller the devil. Has the story of airdrops come to an end?
- All or Nothing’ The roller coaster ride of ScienceCoin, discussing the memes in the crypto community
- Survival Skills in the Cryptocurrency Dark Forest Wallet Security Strategies and Risk Level Management
- FastLane Atlas Protocol Use Case Analysis What is the potential for development?
- Why has friend.tech become popular?
- The Past and Present of OPNX – From Bankruptcy Alliance to Hundredfold Increase






