Deep Analysis of the Past, Present, and Future of Full On-chain Games
Analysis of Full On-chain Games' History, Present, and FutureIntroduction: This article is a comprehensive analysis of Full On-chain Game by the LK Venture investment research team. Full on-chain games should take advantage of their fully on-chain capabilities, rather than simply migrating their operating logic to the chain. In other words, full-chain gaming is not a goal, but a means to an end.
TL;DR
-
What is a full-chain game?
-
Challenges and solutions faced by full-chain games
- New Project Preview | Interpreting Convergence: A Governance Aggregation and Profit Redistribution Layer Similar to Convex.
- Explanation of this week’s unlocked tokens: DYDX, TORN, and 7 other projects are set to unlock
- Hong Kong’s new encryption regulations come into effect: taking stock of the “first batch of pioneers”
-
Why do we need full-chain games?
-
Which chain is suitable for full-chain games?
-
What games are suitable for full-chain?
-
The past of full-chain games: Decentralization, no trust needed, let’s open a casino here
-
The present of full-chain games: High-performance public chains make full-chain games a viable option
-
The future of full-chain games: From full-chain games to on-chain society?
What is a full-chain game?
Full On-chain Game (Full on-chain game) refers to a game that stores game logic and data completely on the blockchain. The operation and interaction of this game are based on smart contracts, so it can fully utilize the advantages of blockchain technology, including decentralization, zero trust, verifiability, transparency and traceability.
Full-chain games are in contrast to Partial on-chain games. Partial on-chain games only store some game elements (such as game assets, transaction records, etc.) on the blockchain, while the game logic and data processing still rely on traditional centralized servers.
Depending on the content uploaded to the chain, Partial on-chain games can be divided into core logic on-chain, asset on-chain, and achievement on-chain.
Core logic on-chain generally stores the key data and algorithm of the game on the blockchain, ensuring its fairness and transparency. For example, putting the random number generator (RNG) or battle result calculation logic of the game on the chain can prevent cheating and manipulation. Or partially uploading the game’s economic system to the chain can design more diverse and innovative incentive mechanisms. For example, players can earn token rewards by mining, pledging, or participating in in-game activities.
By putting assets on the chain, virtual items, characters, or other resources in the game are usually represented in the form of non-fungible tokens (NFTs) or fungible tokens (FTs), enabling players to own, trade, and manage these assets, providing economic benefits to players, and encouraging them to participate in the construction of the game ecology.
Achievements on the chain usually refer to players unlocking certain achievements in the game and registering them on the chain as proof of their game level, or as vouchers for subsequent airdrops, but they cannot be traded directly. Compared with assets on the chain, achievements on the chain provide much less economic incentives to players, but also allow the game to return to its essence. “After all, the most important thing about a game is that it’s fun.”
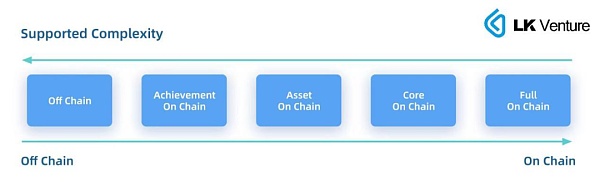
Game types defined according to the degree of chaining
Challenges and solutions facing fully chained games
Since the concept of fully chained games was proposed, it has not been widely adopted. According to LK Venture, this is because there are many problems at the practical level:
1. Performance and scalability issues: The processing power of the blockchain network is relatively limited, especially in terms of transaction throughput and confirmation speed. Fully chained games may cause network congestion and delay, affecting the game experience. To solve this problem, developers need to study scaling solutions such as sharding, state channels, and layer 2 scaling.
2. Transaction costs: Every operation in fully chained games needs to be submitted to the blockchain as a transaction, resulting in corresponding fees (such as Ethereum’s gas fee). If the transaction cost is too high, it may limit player participation and game playability. Reducing transaction costs requires considering optimizing transaction structures, using more energy-efficient consensus algorithms, and other methods.
3. User experience: Compared with traditional games, fully chained games may face challenges in terms of user experience. For example, users need to understand and use cryptocurrency wallets, handle private keys and transactions, etc., which may have certain thresholds and learning costs for ordinary users.
4. Privacy issues: Due to the public and transparent nature of the blockchain, player data and transaction information in fully chained games may face the risk of privacy leaks. Protecting player privacy requires the use of technologies such as zero-knowledge proofs and privacy computing, but these technologies may further increase system complexity and development costs.
5. Game design limitations: Due to the performance limitations of blockchain technology, full-chain games may not be able to achieve complex game mechanics and real-time interaction. This means that full-chain games may be limited in terms of game types and gameplay, making it difficult to adapt to high-performance games such as massive multiplayer online games and action games.
High-performance Layer1 and the recently popular Layer2 are expected to reduce transaction costs, improve confirmation speeds, and effectively alleviate problems 1 and 2.
Account abstraction AA can lower the user threshold and solve problem 3. ERC-4337 was audited and deployed on the mainnet on March 2, 2023, and the large-scale use of account abstraction is imminent.
Zero-knowledge proof technology has been proven to be effective in protecting privacy and solving problem 4. As for problem 5, do we really need to put all types on-chain? The answer is probably no.
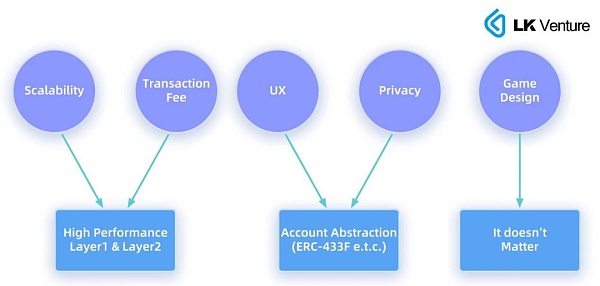
Main challenges and solutions facing full-chain games
Why do we need full-chain games?
With so many problems still plaguing full-chain games, why do we need them? This question is, to some extent, like asking why we need permissionless blockchains.
LK Venture believes that the market’s demand for full-chain games can be understood from the following perspectives:
1. Decentralized game world open to everyone: Full-chain games eliminate the reliance on centralized servers, making game operation more decentralized. This can increase the security and anti-censorship capabilities of the system, and reduce the risk of reliance on a single organization or individual.
2. Trustless and verifiable game fairness: Since the game logic and data are stored on the blockchain, game rules and status are transparent to everyone. This enables players to verify the fairness of the game and the correctness of the results, increasing the credibility of the game.
3. Not just usage rights, but ownership: Full-chain games can use non-fungible tokens (NFTs) to represent in-game items and characters, allowing players to truly own and control these assets. This ownership can incentivize players to participate in the game while providing them with real-world value and benefits.
4. First-tier on-chain, permanent operation: Due to game state and logic being stored on the blockchain, full-chain games have high sustainability. Even if the game’s original developer no longer supports the game, as long as this chain continues to produce blocks, the game can still run and develop.
5. Rely on community, dedicate to community: Full-chain games enable community-driven development and governance through smart contracts and decentralized autonomous organizations (DAOs). This makes the game better suited to player needs and market changes, increasing the game’s lifecycle and appeal.
6. Open collaboration, user creativity drives game iteration: Open-source code and an open system promote open collaboration among individuals. With the assistance of large AI models, users’ creative vitality will be fully released, and UGC or AIGC content will bring more diverse, richer, and more exquisite game experiences.
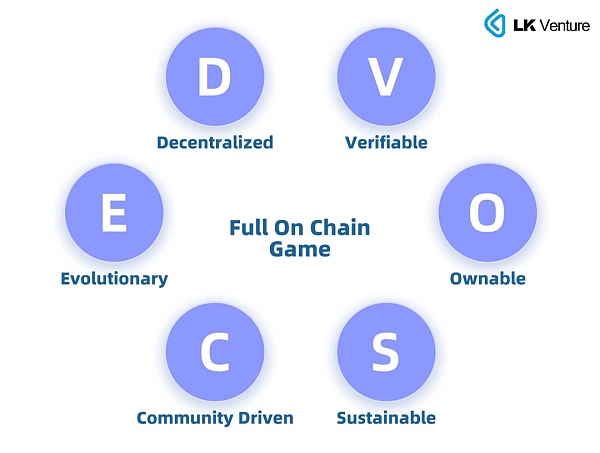
Analysis of demand factors for full-chain games in the market
What chain is suitable for full-chain games?
LK Venture compares TPS, confirmation time, transaction costs, security, and independence, and draws a five-dimensional chart, with a maximum score of 5 points.
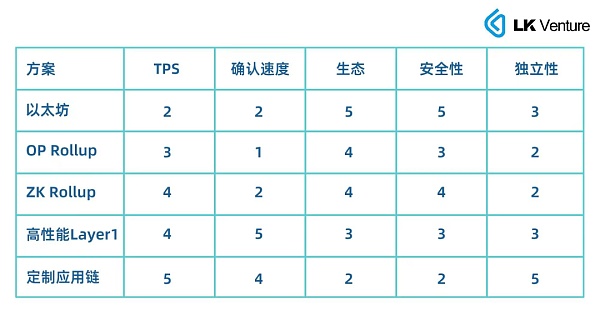
Parameter comparison of full-chain game infrastructure for major public chains
The primary premise of full-chain games is excellent transaction performance. Short confirmation times can bring a better game experience, a good ecology can provide supporting infrastructure for the game, security is crucial for protecting game assets, and independence ensures that the game is not affected by other events on the chain, causing network congestion.
There is no silver bullet in the real world, and each solution has its own advantages and disadvantages. Game projects can choose based on their own design characteristics.
What games are suitable for full-chain?
LK Venture believes that full-chain games should leverage their full-chain advantages, rather than simply migrating operational logic to the chain. In other words, full-chain is not the goal, but the means.
What types of games can leverage the advantages of blockchain? LK Venture believes that the most suitable types are two.
One approach is to use Multi-Party Gaming (MPG), which utilizes blockchain for open, transparent, and verifiable multi-party games. The interesting thing is that “Game” can be both a game solution and a game theory solution.
The “multi-party” feature means that the game is not a single-player game, not an interaction between people and fixed game logic, but an interaction between people, and the permissionless blockchain allows everyone to participate in the game.
The “game theory” feature means that the parties are adversarial, and we ensure the fairness of the game through the entire chain. The openness, transparency, and verifiability of the blockchain prevent game designers from tampering with the results.
The most direct MPG is gambling, but various board and turn-based strategy games can also be classified as MPG. The characteristic of MPG is that the number of interactions is relatively small, which tests the player’s thinking ability rather than reaction speed. Adversarial parties obtain a fair ruling through the blockchain.
Another approach is to use User-Generated Games (UGG), which utilizes blockchain for openness, autonomy, and ownership of user-generated games.
In this type, the initial designer of the game only sets a minimal core rule set, and users can use their imaginations and creativity based on the core rule set to explore various types of gameplay. With the support of AI large models, users can more easily put their creativity into practice and obtain the benefits of their creativity from the blockchain’s ownership.
There is no centralized organization on UGG, only the alliance between individuals. True autonomy is to delegate governance to everyone’s hands, which is the most extensive democracy. If you are not satisfied with the core rule set of the initial designer, you can modify it at any time and deploy a new contract to become a new world.
From the smallest seed, with the support of positive feedback, the game will eventually grow into a towering tree.
The past of blockchain games-decentralized, trustless gambling market
On November 1, 2008, Satoshi Nakamoto published “Bitcoin A Peer-to-Peer Electronic Cash System.” On January 3, 2009, the first block of Bitcoin was mined. As Bitcoin transactions gradually became known to the public, people began to use them for online gambling. In 2012, the first Bitcoin-based gambling game-SatoshiDice appeared.
SatoshiDice is a simple Bitcoin blockchain-based gambling game. Players place Bitcoin bets by sending them to the game, and the game returns a win or loss result based on a predetermined odds and a random number generator. At this stage, blockchain gambling games are mainly limited to the Bitcoin ecosystem, and the types of games are limited.
Satoshi Dice game homepage screenshot
In 2013, the launch of the Ethereum project had a significant impact on blockchain gambling games with its smart contract functionality. In 2015, with the launch of the Ethereum mainnet, blockchain gambling games began to shift from Bitcoin to Ethereum. Using Ethereum’s smart contract technology, developers can create more complex and interactive gambling games. This phase saw the emergence of many Ethereum-based gambling games and platforms, such as vDice and Etheroll.
In May 2014, Kevin McCoy and Anil Dash created the first known NFT. In 2017, CryptoKitties, as the first Ethereum-based non-fungible token (NFT) game, successfully attracted a large number of users. NFT technology has had a profound impact on the development of blockchain gambling games. NFTs can be used to represent unique assets within the game, such as limited edition gambling props or virtual tokens, and more and more gambling games are beginning to use NFT technology.
In the summer of 2020, DeFi Summer broke out, and decentralized finance (DeFi) began to rise, ushering in a new stage of development for blockchain gambling games. Gambling games began to integrate with DeFi projects and platforms, offering players richer financial features such as liquidity mining, staking, and borrowing.
During this period, the public chain track also exploded, with BSC, Polygon, Solana, Tron, and other public chains optimizing for Ethereum’s transaction costs, providing players with faster and cheaper transaction experiences.
As the blockchain gambling game market gradually matures, some innovative game types and gameplay have emerged. For example, prediction market platforms such as Augur and Gnosis allow players to bet on the outcomes of future events. These platforms use smart contracts and blockchain technology to create fair, transparent, and trustless gambling environments.
Gambling games were actually the first games on the blockchain. They are naturally full-chain, because games like guessing the size of a number are just mathematical calculations that can be verified by a simple hash function. Taking history as a mirror, we can know the rise and fall. Although most people have a negative impression of gambling, we should not forget that full-chain games started from here.
The current state of full-chain games – high-performance public chains make full-chain games a viable option
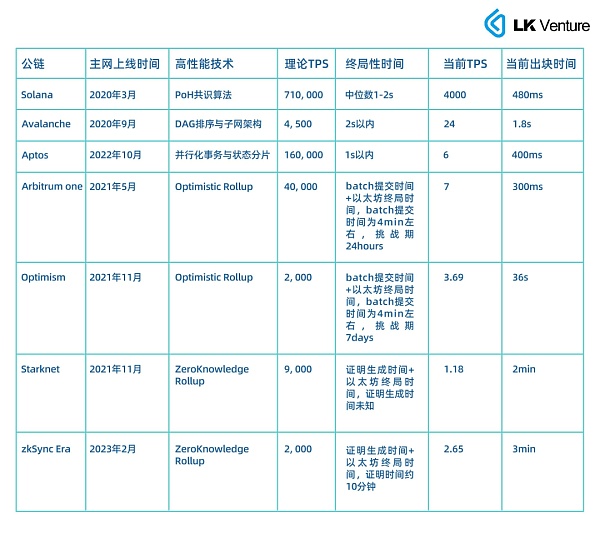
Some high-performance public chains comparison
With the rise of various high-performance Layer1 and Ethereum Layer2 expansion plans, full-chain games have gradually become a feasible reality. People’s exploration of full-chain games has also further deepened, among which the emergence of Dark Forest can be called a milestone event in the development history of full-chain games.
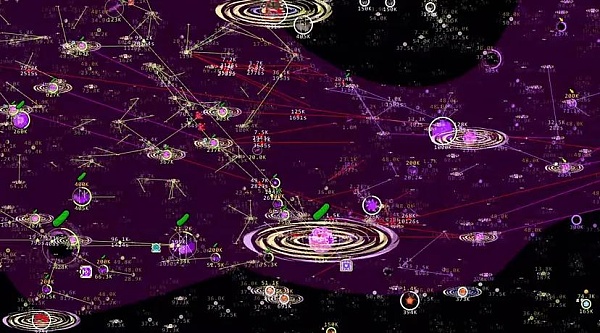
Dark Forest game screenshot
Dark Forest is the first incomplete information game on the entire chain, which not only utilizes the blockchain’s open, transparent, and verifiable properties, but also hides information that affects the game experience through ZK-SNARKS technology, achieving incomplete information games and reconstructing the environment of Dark Forest in “The Three-Body Problem” on the chain.
As an open MMO strategy game, Dark Forest encourages players to create their own gameplay inside and outside the game, thus spawning a massive community ecology. Some people have joined forces to establish guild organizations and have made huge contributions in plugin development, game exploration, and event planning. As a real-time strategic full-chain game, each interaction of the player is presented on the chain through contract invocation, and is updated in real-time between different players. The “fog of war” achieved through ZK-SNARKs technology hides the player’s field of vision and achieves incomplete information games, simulating the environment of Dark Forest.
Dark Forest has proved the feasibility and playability of full-chain games, and since then, the door to full-chain games has truly opened.
Major public chains are cultivating the full-chain game track, but the most active should be Starknet. On Starknet, many full-chain games have emerged, such as LootRealms, GO L2, Isaac, UnstopBlockingble Games, etc., and they are currently the most popular. However, considering the still high Gas Fee on Starknet, the mainnet launch of the game is still far away.
From the overall trend of various game projects, there are two game themes, one is strategy-type combat games similar to Dark Forest, and the other is casual games with prominent financial attributes. Considering the still high Gas Fee, only real economic incentives may make people participate in the game. From this perspective, the latter may be launched on the mainnet faster.
The Future of Full-Chain Games — From Full-Chain Games to Chain-Based Society?
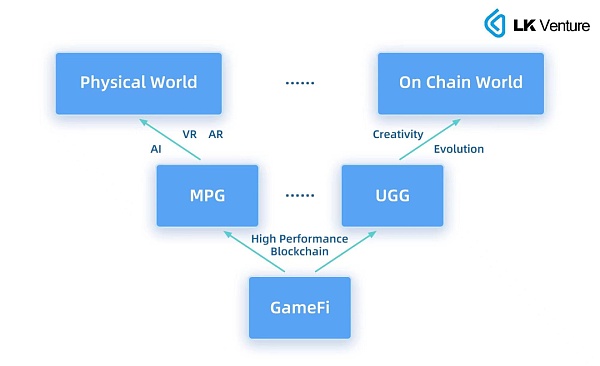
Evolution of the Full-Chain Gaming Ecosystem
In the short term, the role of Ethereum’s scaling solutions, led by Rollup, is still limited, and being anchored on Ethereum can be negatively impacted by other financial activities on Ethereum (for example, when the cryptocurrency market experiences large fluctuations, MEV bots attack, causing gas prices to spike), making it too expensive for more complex full-chain games to attract users based solely on gaming experience. On high-performance Layer 1s, because of their incompatibility with EVM, the number of developers is limited, and there are no large user bases.
Therefore, in the short term, GameFi, which brings higher economic incentives to players, may still dominate.
In the medium term, we believe that Ethereum’s monopoly position will be broken, and more high-performance Layer 1s will attract a large number of users due to lower costs and better experiences. ZK-Rollup technology will mature further, truly reducing gas fees to the level of traditional-world transactions. More customized dedicated chains will emerge to avoid network congestion caused by irrelevant activities. On this basis, various complex full-chain games will be truly deployed on the mainnet, exploring more possibilities of full-chain games in practice.
In the long term, games may generate real value from entertainment. The interaction records of each player in the game, the process of gaming, can all be used as material to train AI, to benefit real life. The blockchain’s real power allows each user to control their own data, and to earn profits from on-chain interactions. For example, a player’s reaction in a racing game can better train an autonomous driving system, at least providing many boundary cases that are difficult to appear in real life. The emergence of UGG will gradually bring games closer to the social ecosystem.
After all, human society is also created under a set of core natural laws, gradually established through exploration and creation between individuals. Who can say that a chain-based society cannot be developed?
About LK Venture
LK Venture is a digital investment and research institution focused on the Web3 field under Blue Harbour Interactive (08267.HK). Formerly known as Consensus Lab, it focuses on investing in infrastructure, trading platforms, technical protocols, and financial instruments at the forefront of the market. It has invested in more than 100 projects from North America, Asia, Europe and other regions, including FTX, Polkadot, Filecoin, Casperlabs, and Coin98.
References
1. The Future Of On-Chain Gaming, Alec Chen(https://eips.ethereum.org/all)
2. A Primer On Fully On-Chain Gaming, Naavik Digest(https://vitalik.ca/general/2022/01/26/soulbound.html)
3. Autonomous Worlds: The Case for Fully On-chain Games, Terry Chung(https://twitter.com/punk6529/status/1636807974176825344)
4. Web3 Gaming: On- and Off-Chain Considerations, Ray Chen(https://twitter.com/KaizenCorps_/status/1630572348217720833)
We will continue to update Blocking; if you have any questions or suggestions, please contact us!
Was this article helpful?
93 out of 132 found this helpful
Related articles
- Where is the next opportunity for NFT? An overview of the current NFTFi subdivisions.
- Inventory of 5 Ethereum ecosystem NFT projects that will “make waves” in June
- LSDFi Summer is coming, quickly understand 6 LSDFi projects worth paying attention to.
- Research Report on Interchain Operation Protocol LayerZero
- Introducing the important upgrade of MIM: the first Omnistable built on the OFT standard based on LayerZero.
- Which BRC20 projects can I actively participate in?
- First OrdiBots project with a thousand-fold increase? Understand the GBRC721 protocol with this article.






