How does Hourglass tokenize “opportunity cost” when time is money?
How does Hourglass break down the concept of "opportunity cost" within the context of time being valuable?Author: Poopman
Translator: Kxp
Time is money, and when tokens are locked up, the opportunity cost of time increases. However, on Hourglass, you can “tokenize” the lockup time of your assets and trade your time-bound tokens whenever you need liquidity.
Background Information:
- Analysis of the Jimbos Protocol Attack: Was the Project that Brother Maji Invested in Hacked?
- What is Polyhedra, the cross-chain project that everyone is talking about recently? This article explains in detail the differences between it and L0.
- Here’s a list of 10 noteworthy projects recently invested in by Blockingradigm: Ulvetanna, Code4rena, Conduit…
Hourglass was created by Charlie Pyle, the founder of ZetaChain. Recently, Hourglass received a seed round investment totaling $4.2 million from Electric Capital, Coinbase Ventures, and other institutions.

1. What is Time-Bound Token (TBT)?
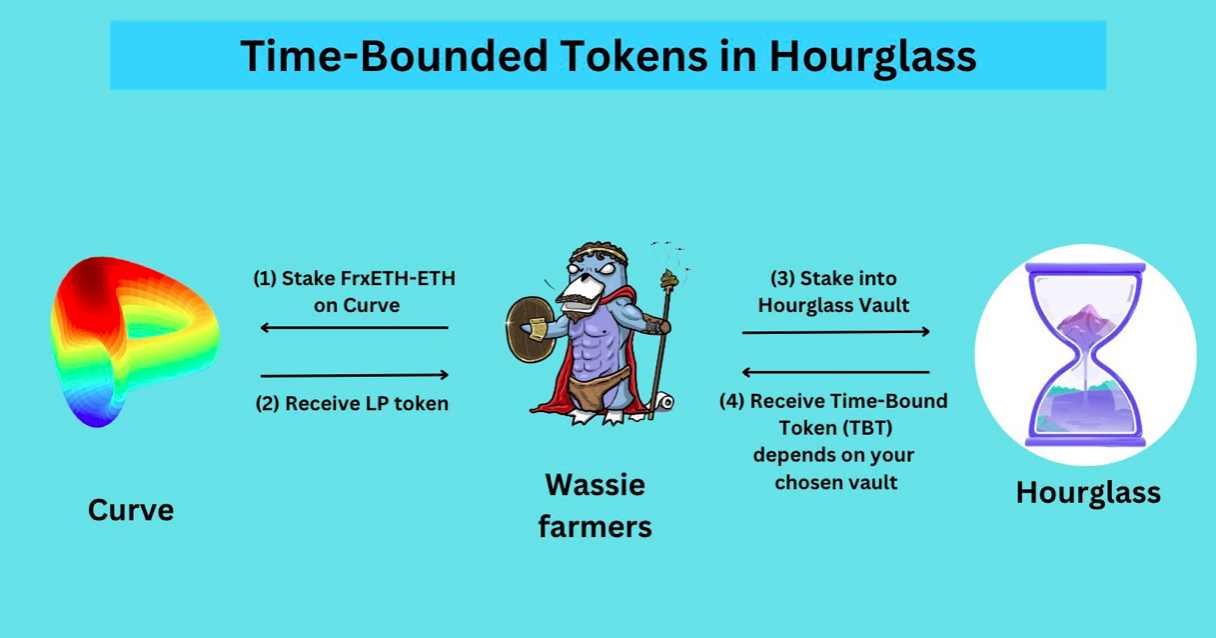
Time-Bound Token (TBT) represents assets that have been staked for a certain period of time on Hourglass. For example, 10 frxETH/ETH LP Tokens with a lock-up period of 3 months will be converted into 10 frxETH/ETH TBTs with a 3-month term on Hourglass.
2. What is Hourglass?
Hourglass is a platform that provides time-bound token services and allows users to trade TBTs. To achieve this goal, Hourglass relies on two main mechanisms:
- Hourglass staking
- HourglassTBT trading market
3. Hourglass Mechanisms
Hourglass Staking
First, Hourglass has a smart contract called Hourglass Custodian that creates a staking repository for each type of asset. In the staking repository, users can stake LP tokens to a proxy staking repository with different expiration dates (currently only supports the frxETH/ETH Convex trading pair).

Each time frxETH/ETH LP Tokens are deposited into Hourglass, it is equivalent to staking Curve LP Tokens locked up in Frax Finance Farm through Convex Finance. Currently, there are only 4 staking repositories with different expiration dates on Hourglass, ranging from May to December.

Users who stake LP Tokens in the proxy staking vault will receive TBT (an ERC1155 Token) as a “receipt” for their staked assets. Once the staked assets expire, they can be redeemed by ERC1155 holders in the expiration vault.
Reward Distribution
Users who hold TBT will receive regular earnings through Merkle airdrops, which is a reward distribution mechanism that verifies whether a Token holder is eligible to receive rewards using Merkle trees and proofs.
4. HourglassTBT Market
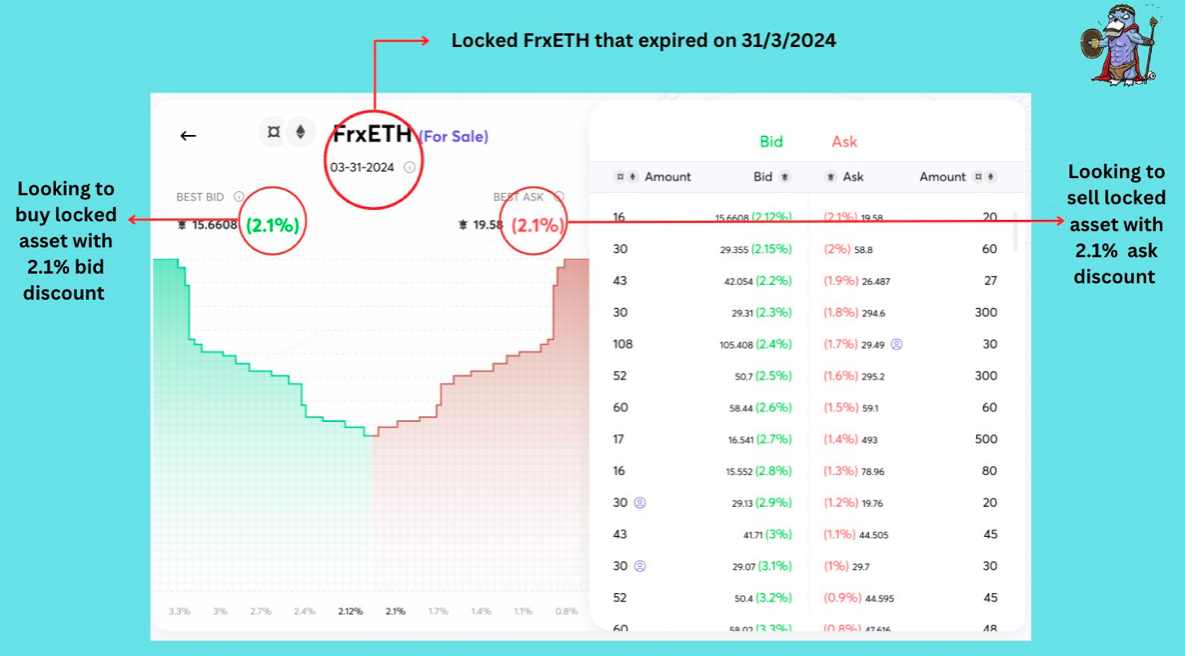
Hourglass uses an order book model to enable trading of TBTs with different expiration dates.
For example, suppose User A can purchase 10 frxETH/ETH LPs that will unlock on May 30th and expire on June 30th at an extremely low discount (1%). The discount size will vary depending on the proximity of the expiration date (assuming the APY remains constant). This is because the user will not be able to use the underlying assets over the next month, and the discount essentially compensates for the opportunity cost of time.
Currently, there are only a limited number of orders (with specified prices) available on the Hourglass market. Users can view the buy/sell prices, discounts, and liquidity depth for a specific expiration date. Then, users can “fill” existing orders to buy or sell TBTs.
5. Synergy with stETH
Since stETH is already withdrawable, withdrawals are likely to be congested during periods of high traffic and may take weeks to complete.
The Hourglass market allows users to trade Lido’s withdrawal request NFTs and exit their positions early if necessary.
6. Poopman’s Thoughts
Through Hourglass, the protocol can secure locked liquidity for its product while achieving higher yields (e.g., 4-year veCRV lockup gains on Curve). On the other hand, the market provides higher capital efficiency for locked assets.
At the same time, users should monitor the liquidity depth of the TBT market, as it is the most critical parameter in determining whether they can exit their positions. Otherwise, even if the price of the underlying assets crashes, users may have to wait until the expiration date.
Additionally, Hourglass’s scalability is limited by underlying revenue streams (such as Frax), just like other yield aggregators like Convex. To understand why, read Messari’s report, which analyzes the project’s profitability and sustainability in detail.
Nonetheless, I remain very excited about the future of Hourglass and hope to see more staking pools added in the future.
We will continue to update Blocking; if you have any questions or suggestions, please contact us!
Was this article helpful?
93 out of 132 found this helpful
Related articles
- Quick look at a16z’s investment landscape for Q1 2023
- Exploring the truth behind PulseChain’s 13.7 billion fundraising: ultimate innovation or Ponzi scheme, risk or opportunity?
- Interpreting Injective (INJ): A comprehensive evaluation of DeFi project based on SWOT
- zkML: zk+Machine Learning Emerging Project and Infrastructure
- Overview of EDCON Super Demo Winning Projects at Ethereum Conference 2023
- Ethereum client Prysm releases version v4.0.5, including significant improvements to proof aggregation.
- Arbitrum’s High-Quality Project Inventory: What are the new projects worth looking forward to?






