LD Capital An Analysis of KasLianGuai, a POW Public Chain Based on the GHOSTDAG Protocol
LD Capital - Analysis of KasLianGuai, a POW Public Chain using GHOSTDAG ProtocolAuthor: duoduo, LD Capital
KasLianGuai is a POW public chain built on the GHOSTDAG protocol. Compared to Bitcoin, KasLianGuai mainly changes the structural pattern of the blockchain. Bitcoin adopts a single chain structure, while GHOSTDAG adopts a directed acyclic graph (DAG) structure, where one block can point to multiple blocks.
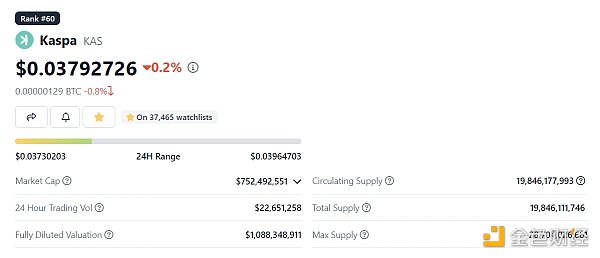
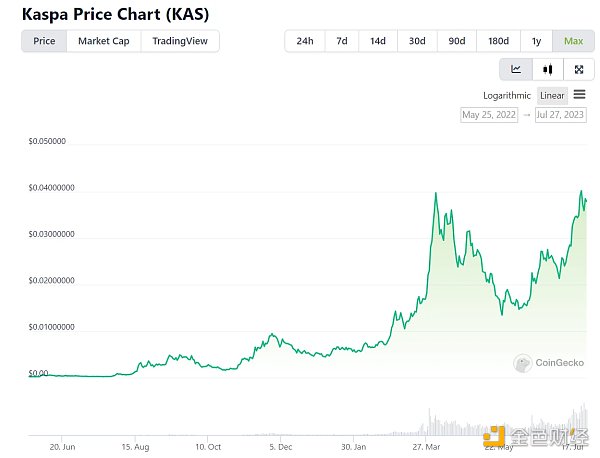
The token KAS was launched in November 2021, with a total supply of 28.7 billion and a circulating supply of 19.8 billion, accounting for 69% of the circulating supply. Its market value is $750 million and the FDV is $1.08 billion. Since the token was launched, its price has increased by hundreds of times.
- How far can a decentralized sorter go?
- The Battle of Tech Giants Digital Identity, Payments, Social Graphs, AI, and Universal Basic Income
- Messari Overview of SandBox Development in Q2 2023
1. Team
The KasLianGuai team has some reputation. The founder, Yonatan Sompolinsky, is currently a postdoctoral fellow at Harvard University, specializing in transaction ordering and MEV. As early as 2013, he and his doctoral advisor conceived the GHOST protocol, and related papers were cited in the Ethereum white paper.
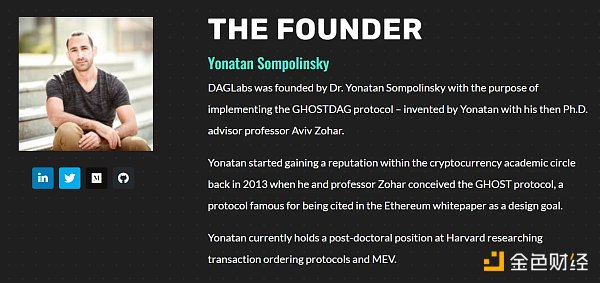
Source: KasLianGuai official website
The following is a partial quote from the Ethereum white paper:

Source: Ethereum white paper
In addition to the founder, there are 5 core developers. Michael Sutton researches parallel algorithms and distributed systems. Shai Wyborski is one of the authors of the GHOSTDAG paper and researches classical and quantum cryptography. Mike Zak and Ori Newman research distributed system development. Elichai Turkel is an applied cryptographer and a high-performance blockchain open source contributor.


Source: KasLianGuai official website
2. Technical Principles
The current technical principles of KasLianGuai are mainly described in its 2021 paper “PHANTOM GHOSTDAG: A Scalable Generalization of Nakamoto Consensus”.
Bitcoin is essentially an open and anonymous node network that collectively maintains a public transaction ledger. The ledger uses the “longest chain” principle to link honest blocks and protect the security of the network. This design artificially suppresses the throughput of the network and has low protocol scalability. Currently, the Bitcoin blockchain produces one block every 10 minutes, with 3-7 transactions per second.
Structural Model: Directed Acyclic Graph (DAG) Structure
KasLianGuai proposes the PHANTOM protocol, which is a proof-of-work permissionless ledger protocol that extends the blockchain defined by Satoshi Nakamoto to a directed acyclic graph (blockDAG). PHANTOM can reference multiple previous blocks, provide a total order of all blocks and transactions, and output a set of consistent accepted transactions.
PHANTOM includes a parameter k to control the protocol’s tolerance for concurrent block creation, allowing the parameter to be set to accommodate higher throughput. When k = 0, it means there are no forks, similar to Bitcoin’s single-chain, longest-chain structure.
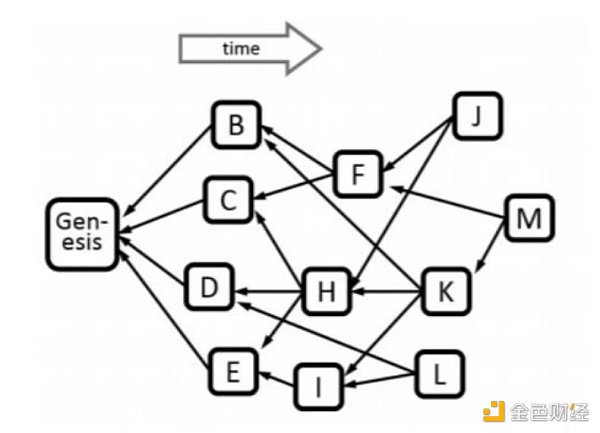
Source: “PHANTOM GHOSTDAG: A Scalable Generalization of Nakamoto Consensus”
Let’s first understand several different types of blocks in a DAG. In the following examples, we will need to adopt the corresponding concepts. In the above diagram, let’s take block H as an example:
LianGuaist(H)={Genesis, C, D, E} — Blocks that directly or indirectly point to H before its creation;
future(H)={J, K, M} — Blocks that directly or indirectly point to H after its creation;
anticone(H)={B, F, I, L} — Blocks that are not in past(H) or future(H), and have no direct or indirect relationship with H;
tips(G)={J, L, M} — Leaf blocks or end blocks that will be referenced by the block header of new blocks.
Identifying honest blocks and malicious blocks
PHANTOM solves the problem of identifying honest blocks and malicious blocks. Malicious attacks have a characteristic: the connectivity between blocks generated by malicious nodes and blocks generated by honest nodes is low, while the connectivity between blocks generated by honest nodes is high.
The criterion for judgment is the parameter K mentioned earlier. For a specific block X, if the intersection between anticone(X) and honest blocks is higher than the value of k, it means that the connectivity between block X and honest blocks is low, and X will be considered as an attack block; otherwise, it indicates that the connectivity between block X and honest blocks is high, and X is considered an honest block.
The following diagram illustrates the judgment of honest blocks and attack blocks. The value of K here is 3. After checking, the blue part represents honest blocks, and the red part represents attack blocks.
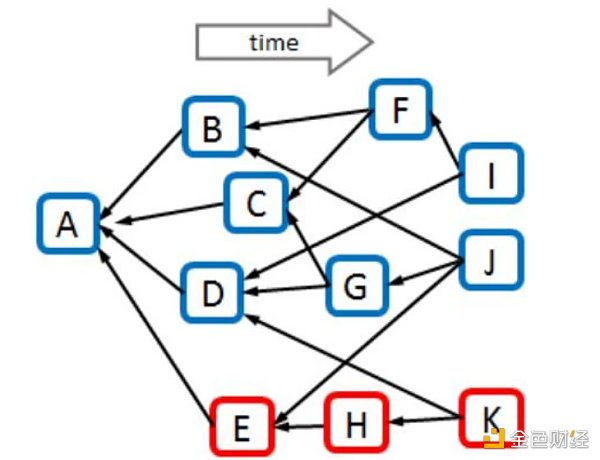
Source: “PHANTOM GHOSTDAG: A Scalable Generalization of Nakamoto Consensus”
Linear Sorting
To solve the double-spending problem, the project team has used the GHOSTDAG protocol. The principle is to score each block based on its connectivity (the number of elements in the past block set) and select the block with the highest total score as the main chain, which will form the initial subset. The remaining blocks will be voted in the order of the main chain. The entire network will vote in a trend from high to low connectivity.
The following diagram shows how GHOSTDAG completes the sorting process with the parameter K = 3. The small circles on each block X represent its score, which is the number of blue blocks in the past DAG.
In step 1, starting from the block M with the highest score, we select blocks K, H, D, and the genesis block in order, and mark them with a blue background and a black border. This forms the initial subset. When visiting block D, the past block of D is only the genesis block.
Step 2, visit block H. The past blocks of H are C, D, E. After identifying honest blocks and attack blocks using the aforementioned method, C, D, E belong to honest blocks and are added to the subset, marked with a blue border.
Step 3, visit block K. The past blocks of K include H, I. After identification, they both belong to honest blocks and are marked with a blue border.
Step 4, visit block M. The past blocks of M include K, F. K belongs to honest blocks and is added to the subset, marked with a blue border.
Step 5, block V is a virtual block, and its past is equal to the entire current DAG.
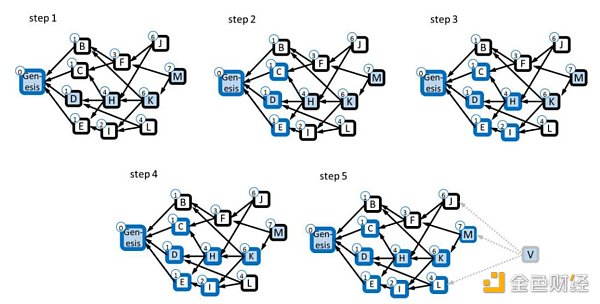
Source: “PHANTOM GHOSTDAG: A Scalable Generalization of Nakamoto Consensus”
At this point, KasLianGuai completes the discussion of the new consensus architecture and puts it into practical use. The official website shows the visualization process of DAG:
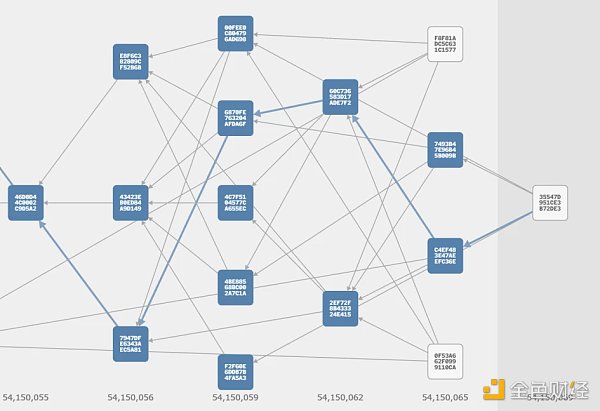
Source: KasLianGuai official website
III. Computing Power Situation
KAS mining algorithm is kHeavyHash, supporting GPU mining alone or dual mining with ETHW, ETC, supporting partial FPGA and ASIC mining machines.
According to the official blockchain explorer, KasLianGuai’s computing power is 2.6 – 2.7 PH/s. According to the data from Mining Pool, KasLianGuai’s computing power ranks around 30th, after BCH, BSV, DASH, and before DOGE, LTC.
KasLianGuai’s computing power shows a trend of continuous growth. In October 2022, December 2022, February 2023, and July 2023, there were 4 significant increases in computing power. In March of this year, a mining machine manufacturer launched professional mining machines to improve miners’ mining efficiency.
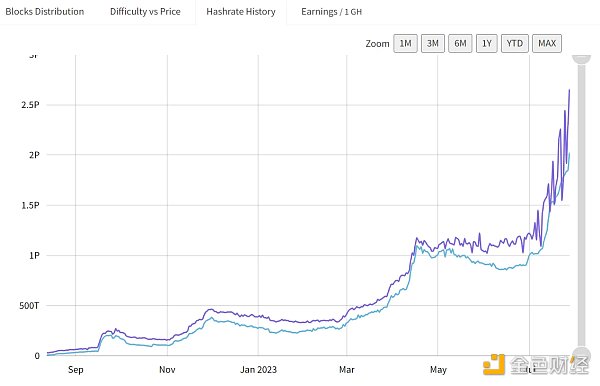
Source: miningpoolstats
From the perspective of computing power distribution, the concentration of computing power is not too high. In the latest 999 blocks, the output of the top five mining pools accounts for 37.1%; more than 56.7% of the blockchain is produced by unmarked addresses.
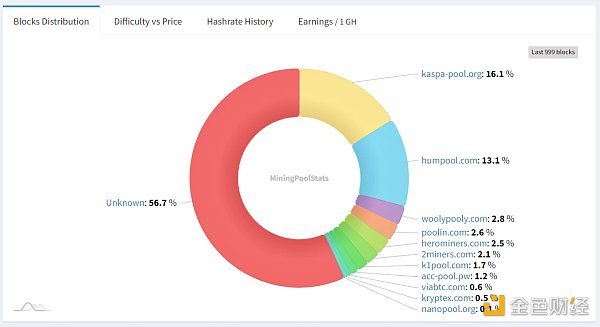
Source: miningpoolstats
IV. Token Economy Model
Token Allocation
KAS was launched in November 2021 with no pre-mining, no pre-sale, and no token allocation. The total supply is 28.7 billion tokens, with a circulating supply of 19.8 billion tokens, accounting for 69% of the total, and a market value of $750 million, FDV $1.08 billion.
Token Release
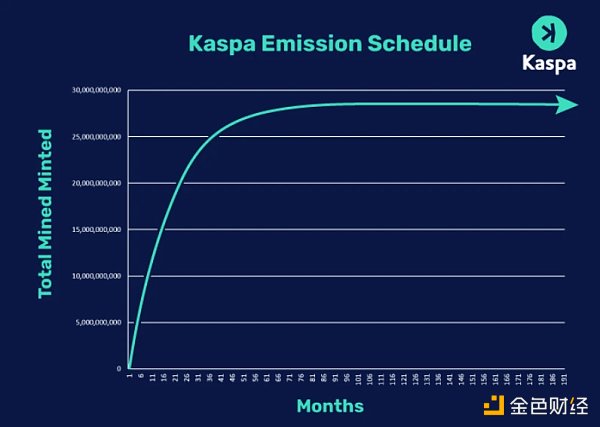
According to the emission plan, KAS reduces its output every month in a given way, resulting in a halving of output each year. The following figure illustrates the release process, showing a higher release rate in the early stages and a large amount of chips accumulated by early miners. The specific release date schedule can be found on the official website (https://kasLianGuai.org/wp-content/uploads/2022/09/KASLianGuai-EMISSION-SCHEDULE.pdf).
Based on the token emission schedule, the monthly emission volume and release value of KAS tokens from July 2023 to June 2024 have been calculated as shown in the table below. If calculated at a price of 0.037, in July 2023, KAS will release tokens worth $19 million, gradually decreasing thereafter; by June 2024, the emission value will be approximately $10 million.
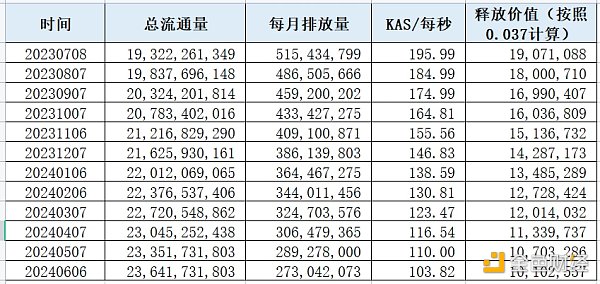
Source: KasLianGuai official website, LD Capital
According to data from f2pool, KasLianGuai’s 24-hour output value is currently ranked fourth, surpassed only by Bitcoin, Dogecoin, and Litecoin, and higher than ETC and BCH.
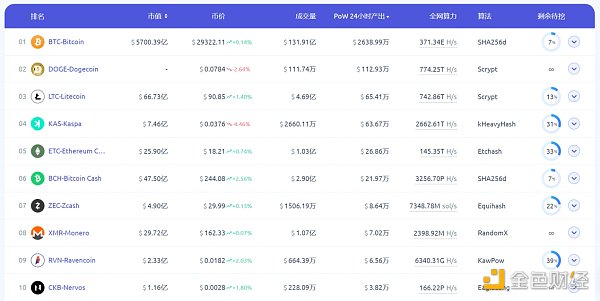
Source: f2pool
Holdings
There are a total of 267,000 addresses holding 1 or more KAS tokens. The token distribution is relatively concentrated, with the top 10 addresses holding 17.299% of the tokens, mainly in exchange wallets; the top 100 addresses hold 26.13%; and the top 1000 addresses hold 61.35%.
In terms of token flow, in the past 30 days, addresses holding 100 – 10K tokens have seen a decrease in holdings, while addresses holding 0 – 100 tokens and 10K or more tokens have seen an inflow. In the past 7 days, addresses holding 100 – 10K tokens and Humpback addresses holding 100m to 1b have seen a decrease in holdings, while other addresses have seen an inflow.
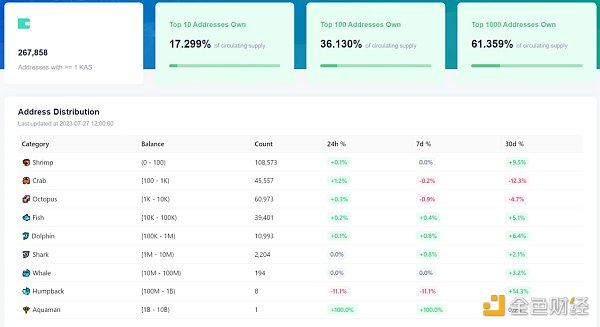
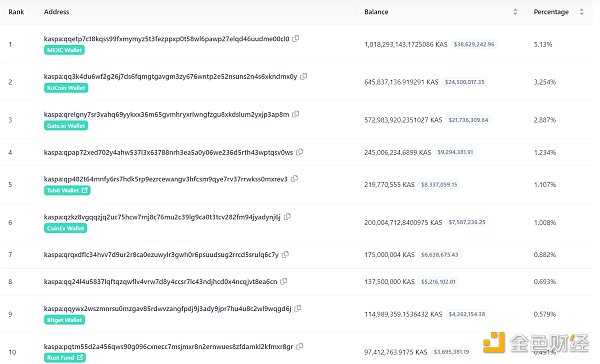
Source: KasLianGuai blockchain explorer
5. Current Progress and Development Plans
The official website has disclosed some important progress and recent development plans since 2023.
Completed
In February 2023, project core developer Michael Sutton published a paper on DagKnight Consensus, an evolution of GHOSTDAG consensus mechanism that theoretically lays the foundation for faster transactions and confirmation times.
Under Testing
-
Code rewriting using Rust programming language
Currently, KasLianGuai is written in GoLang. Michael Sutton is rewriting the code using the Rust programming language, which will improve the performance and transaction speed of KasLianGuai.
-
Mobile Wallet Development
There is a strong demand from users for high-performance mobile wallets, and the development is expected to take 3-4 months.
-
Integrate KasLianGuai for use on Ledger
Users will be able to send and receive KAS using the hardware wallet Ledger.
Under Development
-
Upgrade consensus mechanism according to DagKnight Consensus
-
Further increase the number of blocks per second and transactions per second
Currently, KasLianGuai produces 1 block per second, with a goal of increasing it to 32 blocks per second. The current testnet can produce 10 blocks per second.
-
Release project whitepaper
There are several research papers on the technology of KasLianGuai, but the official project whitepaper has not been released yet and is being organized.
-
Improve archival nodes
Currently, the standard nodes of KasLianGuai can only access transactions from three days ago. By improving archival nodes, more historical data can be retrieved.
Development Plan
-
Implement smart contracts and establish an ecosystem
KasLianGuai hopes to implement smart contracts, Defi, and Layer 2 applications on its public chain, establishing a corresponding ecosystem.
The development and deployment of smart contracts are the most important factors for further development. If smart contracts can be deployed in a timely and smooth manner, and an ecosystem with a certain level of activity can be established, there is still room for KasLianGuai’s market value to rise further. However, if smart contract deployment is not smooth and the ecosystem fails to develop, there will be obvious bottlenecks in future development.
VI. Conclusion
The project team has strong technical capabilities and a good development foundation. They have proposed a new blockchain model and explored new development directions. They obtained computing power transferred from Ethereum in the early stages and have continued to increase their computing power.
The market value is relatively high, having increased by over a hundred times. Currently, the market value of KAS is $750 million, ranking around 60th. The market has already priced in the valuation of the technical team and the growth in computing power. Future growth will require stronger expectations to support it.
There is a potential selling pressure on the tokens. Early miners hold a large number of low-priced chips, and there is also continuous daily production. If they sell, it will cause significant price shocks.
We will continue to update Blocking; if you have any questions or suggestions, please contact us!
Was this article helpful?
93 out of 132 found this helpful
Related articles
- EthCC Experience Cryptocurrency VCs Not as Good as Dogs, Applications Upgraded to Infrastructure
- A Week After the Renaming Predicting the 8 Major Changes That Will Happen to the ‘New Twitter X
- How is the OP ecosystem now? Is it worth investing in?
- The Tech Giants’ Battle of X Digital Identity, Payments, Social Graph, AI, and Universal Basic Income (UBI)
- After a massive layoff of 73%, can Star Atlas, a 3A masterpiece born in a bull market, still be launched as scheduled?
- After LSDFi, will the liquidity provided by derivative LPDFi trigger the next wave of DeFi narrative?
- Bybit Payroll Manager Steals Large Amounts of USDT, Singapore Court Elaborates on Cryptocurrency Property Attributes





