What is Mantle Network? Ethereum Layer 2 Solution Guide
Mantle Network Ethereum Layer 2 Solution GuideAuthor: Alex Lielacher, BeinCrypto Compilation: Shan Ou Ba, LianGuai
Over the years, there have been many Ethereum Layer 2 scaling solutions, each aimed at making the leading blockchain supporting smart contracts more efficient. This guide focuses on Mantle Network, a solution that takes Ethereum scaling to a whole new level. Learn what Mantle is, how it works, and how it differs from other Ethereum L2 solutions.
Table of Contents:
-
What is Mantle Network?
-
MNT and Token Economics
-
Potential Use Cases for Mantle Network
-
Advantages of Mantle Network
-
Disadvantages of Mantle Network
-
Mantle Network is Ambitious
-
Frequently Asked Questions
What is Mantle Network?
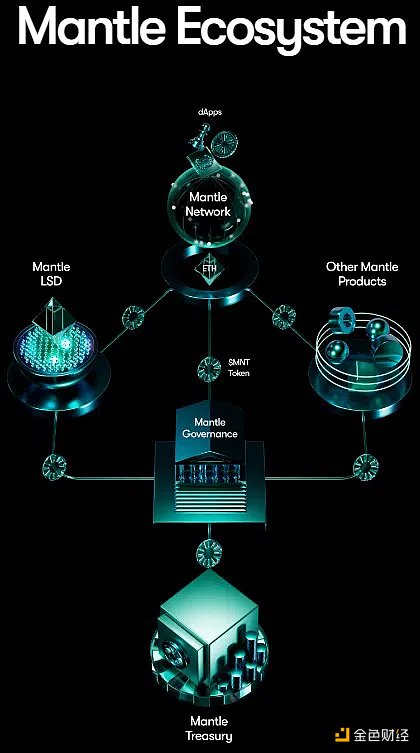
Mantle Network is a Layer 2 (L2) scaling solution compatible with the Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM). It uses optimistic rollups to facilitate cheap and fast transactions. The network achieves this by bundling and executing transactions off-chain, but all transactions are eventually settled on-chain. The founders of Mantle are anonymous.
In May 2023, Mantle merged with the BitDAO ecosystem to create a unified ecosystem under one brand and token: Mantle (MNT). BitDAO was founded in June 2021 by Daniel Yan and Ben Zhou, co-founders of the centralized exchange Bybit. This decentralized autonomous organization (DAO) is known for its large treasury.
The merger of BitDAO and Mantle makes the new Mantle ecosystem the largest treasury in the crypto industry, valued at over $3 billion at the time of writing this article. The network’s DAO passed a proposal to allocate $200 million from the ecosystem fund to support early DApp development on Mantle.
After the merger with BitDAO in May, Mantle announced the mainnet alpha version at EthCC in Paris in July 2023.
Prior to the release, Mantle went through a six-month testnet phase, processing over 14 million on-chain transactions.
How Does Mantle Work?
Modular Design
Mantle elevates scalability with its modular design, which combines optimistic rollups with a separate data availability layer. As a result, Mantle does not execute the four key blockchain functions on a single network layer like most holistic blockchains. Instead, it processes these processes on different layers.
Transaction execution occurs on the Mantle-compatible EVM execution and settlement layer. Mantle’s sequencer generates blocks on the L2 execution layer and submits state root data to the main blockchain.
The Ethereum L1 network is responsible for consensus and settlement functions.
Mantle performs the final function of data availability with the help of EigenDA technology. Eigen Data Availability (EigenDA) storage typically broadcasts callback data to L1 in traditional aggregation. EigenDA is a data availability layer built on top of EigenLayer.
The following figure shows an example of modular chain design:
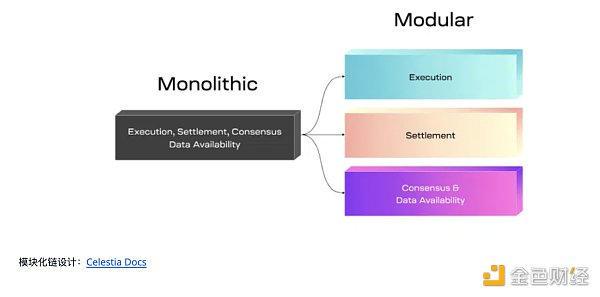
Compared to the underlying layer, Mantle’s modular architecture significantly reduces transaction costs. Due to the layering, it also improves network efficiency and minimizes overall load on nodes through optimistic aggregation.
What is EigenLayer?
EigenLayer is a decentralized Ethereum protocol that enables ETH re-collateralization. It allows EigenDA-supported Mantle data availability layer to obtain security from Ethereum. This means that Ethereum stakers can re-collateralize ETH with pegged digital assets such as rETH and stETH to protect the data availability layer of Mantle.
In addition to helping make the Mantle data availability layer highly secure, EigenLayer also provides transaction throughput of up to 1 TB or more per second.
Network Participants
Mantle Network has four nodes: Sequencer, Aggregation Validator, DA Node, and Threshold Signature Scheme (TSS) nodes.
The Sequencer receives transactions from users in real time, generates blocks on L2, aggregates transactions into batches with execution state roots, and publishes block data to the underlying layer and L2. The initial Mantle sequencer is centralized. However, the project plans to decentralize it over time.
TSS nodes validate batches of transactions aggregated by the sequencer. After signing these transactions, they broadcast these batches on Mantle.
The Aggregation Validator synchronizes aggregated data, initiates fraud proofs, and verifies state roots from the sequencer. They also provide block data to users. Optimistic aggregation assumes that batch transactions are valid unless their credibility is challenged within a 7-day window. In such cases, aggregation initiates anti-fraud measures to check for errors.
DA nodes store copies of Mantle transaction data for easy access when needed. These nodes also sign block data when providing transaction data, ensuring its availability.
Transaction Lifecycle
Transactions on Mantle are divided into the following three stages.
Triggering
In the triggering stage, wallet users or DApps initiate tasks. Performing these tasks incurs costs. Therefore, users must have sufficient funds to settle transaction fees. Additionally, they must sign the transaction with a private key and submit it to Mantle. The sequencer nodes on the network then receive the transactions for processing.
Processing
The transaction activates the standard state verification process executed by the EVM software. The verification process ensures that the transaction is valid and has been paid. Next, the transaction updates the local state and becomes part of a pending block awaiting processing.
Then, the sequencer aggregates the transactions in the pending block into batches. These batches eventually land on L1. Mantle spreads the fixed cost of many transactions into a bundle to minimize user transaction fees.
Once the sequencer node takes effect, TSS nodes will intervene to validate the block data. The aggregated validators also validate the state root at this stage.
Storage
The sequencer broadcasts the state root data on L2 and the main chain. In addition, the aggregated validators synchronize the block data for user access. On L1, the state root data goes through the consensus process and validators add it to the blockchain. DA nodes store synchronized block data in exchange for MNT rewards.
Bridging
Mantle Bridge allows users to transfer digital assets from Ethereum to L2 and from L2 to Ethereum. Bridges are important as they enable interoperability between connected networks while allowing for secure token transfers back and forth. Bridging is essentially a technology that connects L1 and L2 networks, L1 and L1 blockchains, or multiple L2 networks.
Governance
Mantle’s governance takes place off-chain, where the core contributors or community members can initiate discussions. The initiator introduces the topic on the forum for a wider community view. If the matter attracts enough positive interest, it progresses into a Mantle Improvement Proposal (MIP), similar to Ethereum’s EIP.
Once the MNT holders approve the proposal, the core contributors are responsible for implementing it. The core contributors consist of a growth team and a product development team.
MNT holders can only vote after delegating their voting rights to themselves or other eligible addresses. The authorization adjustment allocates voting weights among voters with different interests and areas of expertise.
Functionality of MNT and Token Economics
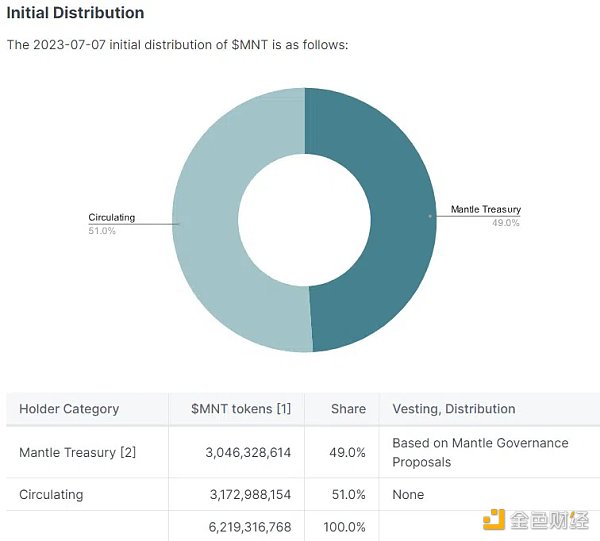
MNT Token Economics: Mantle
MNT is an ERC-20 token and the primary asset used in the merged Mantle ecosystem. According to the approved proposal, Mantle converts BIT tokens (native BitDAO assets) into MNT at a conversion ratio of 1:1. However, the project does not convert 3 billion BIT tokens from the treasury into MNT. Mantle will send the unconverted BIT tokens to a specified burn address. BIT token holders received MNT tokens through an airdrop on July 17, 2023.
MNT is a utility and governance token. As a governance token, MNT grants holders the right to vote in favor or against ecosystem decisions. In light of this, MNT holders have passed a proposal to reduce the MNT in the treasury from 6.05 billion to 3.05 billion. Additionally, the approved proposal maintains a circulating supply of MNT at 3.17 billion and reduces the fully diluted supply from 9.2 billion to 6.2 billion.
This proposal changes the token allocation of Mantle. Previously, the project allocated 65.6% of MNT tokens to the treasury and 34.4% to the circulating supply. Now, the tokens in the treasury account for 49% and the circulating supply accounts for 51%.
As a utility token, Mantle users use MNT to pay for gas fees. In addition, Mantle Network nodes can use MNT as collateral assets. This incentivizes node participation in the network, maintaining network stability and security.
Mantle achieves hyper scalability, while other L2 networks do not
In general, L2 networks are difficult to scale because they rely on the overall architecture of the underlying layer. Therefore, the gas cost saved on these layers is not enough to support widespread adoption.
Mantle uses optimistic rollups and a separate data availability (DA) layer, enabling it to provide cheaper and faster transactions. This architecture is different from other Ethereum Layer 2 scaling solutions such as Cartesi, Loopring, Polygon, and Arbitrum. While Mantle is not the only L2 using a separate DA layer, its EigenDA-driven layer is decentralized. This is different from other L2 networks that use centralized data availability layers.
Mantle’s security is derived from Ethereum
Mantle leverages Ethereum’s consensus mechanism and validator set. This means that Ethereum validators verify the state transactions of Mantle in the same way as they verify L1 transactions. Therefore, Mantle obtains security from the Ethereum blockchain, making it more secure than other L2 networks that use their own consensus models.
Potential Use Cases of Mantle
Gambling
Mantle’s modular design makes it an ideal choice for games as it can support high transaction throughput and low gas costs. This can encourage developers to build game dApps on Mantle, allowing players to enjoy frictionless experiences. Mantle is collaborating with Game7 and HyperPlay, two projects initiated by BitDAO before the merger. These projects focus on building important tools for game developers.
Mantle has already started its journey to implement this use case by adding the web3 game metaverse Bullieverse to its ecosystem. The metaverse project will launch on Mantle in March 2023.
Decentralized Finance (DeFi)
Mantle can help advanced DeFi protocols built on it become cost-effective and widely adopted. Increased adoption of DeFi may encourage developers to create innovative financial products and services that are not currently available in the cryptocurrency space.
Advantages of the Mantle Network
Lower transaction fees
Mantle Network significantly reduces gas fees. The project believes that transaction costs can be reduced by more than 80% through batch transactions and modular design. By bundling transactions into batches, gas fees are distributed across multiple transactions within each batch.
Higher efficiency
With the help of EigenDA, Mantle introduces a separate decentralized data availability layer, allowing it to improve Ethereum’s efficiency. EigenLayer has the potential to achieve throughput of up to 1TB/s or higher. By leveraging EigenDA, Mantle can provide users with higher transaction throughput than the underlying layer.
Protected by Ethereum
Mantle transactions use the same validator set and consensus process as Ethereum transactions. This means that Ethereum validators add all Mantle transactions to Ethereum, allowing them to benefit from the security of one of the industry’s most secure blockchains.
In addition, thanks to EigenLayer, Mantle’s DA layer gains security from the Ethereum blockchain. This protocol allows Ethereum stakers to re-stake their ETH using collateralized assets such as stETH, thereby protecting the security of the Mantle DA layer.
Evaluation of Compatibility
Mantle Network is EVM compatible, allowing developers to deploy Ethereum DApps on it. It also enables developers to use Ethereum smart contract development frameworks such as Remix, Truffle, Hardhat, and Foundry on Mantle.
Drawbacks of Mantle Network
Mantle is still new
Mantle was launched on the mainnet alpha version in July 2023, so there is still a long way to go to fully unleash its potential. Additionally, the Mantle DAO is currently discussing key proposals such as ETH staking strategies and the possibility of utilizing zkEVM.
Not fully decentralized yet
The core team of Mantle initially uses their own centralized sequencer nodes. Although it plans to decentralize the sequencer nodes in the future, this exposes the network to the risk of censorship resistance. The sequencers are responsible for receiving transactions and generating blocks. Entrusting this role to a centralized team poses the risk of transaction censorship for users.
Mantle Network is not lacking in ambition
Mantle Network is an ambitious project that aims to change the L2 scaling landscape in new innovative ways. It also indicates that the industry is making progress in scaling L1 blockchains and is not far from achieving the goal of improving performance. Therefore, it will be interesting to see how Mantle and other innovative L2 scaling solutions develop in the coming years.
We will continue to update Blocking; if you have any questions or suggestions, please contact us!
Was this article helpful?
93 out of 132 found this helpful
Related articles
- Interview with Hyper Oracle Programmable zkOracle Building the Supercomputing of the Future World
- Sei’s Ultimate Marketing Rule The King of Rolls in the Post-Airdrop Era
- Insights on the future development of Ethereum How to unlock statelessness?
- MEV Track Overview Have we underestimated its importance?
- SEC is expected to give the green light to Ethereum futures ETF expected to be listed as early as October, with a total of 16 applications pending approval.
- Wood Sister’s Long Push Raising interest rates by the central bank is a more important goal than controlling inflation – bursting the Chinese bubble
- Full text of the speech by Hong Kong Chief Executive Carrie Lam at the 2023 Summit on Innovative Technology and Art Development






