Web3 Social (1) Profit is the Essence of Socialization, Financialization of Social Interaction
Web3 Social - Profit as the Essence of Socialization and Financialization of Social InteractionAuthor: Barrons, LBank Labs
Before discussing Web3 social, it is necessary to clarify the relationship between the development of Web3 social and Web2 social, whether they are mutually exclusive or complementary. This will allow us to delve deeper into the potential and necessity of Web3 social development.
- Web 2.0 social focuses on information exchange. Its value lies in facilitating interaction between users, and the behavioral traces left by users on the Internet can be further monetized.
- Web 3.0 social focuses on value exchange. Value exchange can be achieved in two ways: the first is through monetizing social behavior, and the second is by making investment behavior more social. Therefore, Web 3.0 social is often referred to as SocialFi, which is the best summary of Web 3.0 social.
Web3 social is not only a social behavior, but also a financial behavior. Similar to the development of Bitcoin originating from a small technical community, the idea of sovereign currency by Satoshi Nakamoto also attracted some cypherpunks to participate in discussions and development. Eventually, with the help of his social skills, Satoshi Nakamoto built a successful community. As the community grew, the price of Bitcoin also skyrocketed. In Web3 social, social behavior not only contributes to financial behavior, but financial behavior also contributes to social behavior. Take CryptoPunks as an example, as the price of CryptoPunks rises, people are buying CryptoPunks as their avatars, and the financial element becomes a symbol of social status.
- Former SEC Official Can a Spot Bitcoin ETF Be Approved? What Benefits Will Cryptocurrencies Have If the Republican Party Wins in 2024
- 9 Major Market Indicators Inventory Bullish or Bearish?
- How to capture the signals of recovery and survive the cold winter in a cooling market
1. Reconstructing Web3 Social Network
From a technical perspective, assets, wallets, social protocols, and DApps collectively provide social services on the blockchain network. The following is a step-by-step explanation of how these components interact with each other.
1. Assets: Reputation
In Web3, the value of social protocols is used for value interconnection between users. Users are social values mapped onto cryptocurrencies and other assets. In social services, assets can be used for various purposes, such as incentivizing users, rewarding content creators, or providing exclusive features in services. Social services can use cryptocurrencies, utility tokens, governance tokens, or NFTs to represent value or rights within the platform.
2. Self-owned Account: Wallet
Users of blockchain social services need a wallet to manage their digital assets. Wallets are gateways for users to interact with the blockchain network, enabling them to store, send, and receive cryptocurrencies and tokens. Wallets can also facilitate interaction with DApps through transaction signing and interaction with smart contracts.
3. Social Network: On-chain Behavioral Interaction
Social protocols include the rules, governance, and consensus mechanisms of the blockchain network. It is crucial for ensuring the secure and transparent operation of social services. For social services on the blockchain, social protocols can include token allocation mechanisms, voting systems, dispute resolution, or any other rules governing user interactions.
In summary, wallets, assets, social protocols, and DApps are combined to provide social services on blockchain networks. Users interact with DApps through wallets and conduct transactions with assets according to the rules defined by social protocols. The decentralized nature of blockchain technology allows these services to provide higher security, transparency, and user authorization.
2. Wallets: Self-management and ownership of identity and assets
Blockchain social protocols are decentralized systems designed to facilitate communication, collaboration, and value exchange among users. These protocols typically rely on digital wallets to manage and store digital assets such as cryptocurrencies, tokens, or non-fungible tokens (NFTs). Wallets play a crucial role in these systems. These tools utilize the blockchain as a database, improving transparency, data consistency, and availability. Transparency includes contributor dashboards, goal tracking, and more innovative use cases, including service provider accountability, crowdsourcing consensus, and contributor mining.
Here are some key aspects of digital wallets in blockchain social protocols:
- Identity and access management: Wallets serve as digital identities, allowing users to access and interact with blockchain social protocols. Each wallet has a unique public address that can be shared with others to receive assets or participate in transactions. The associated private keys of wallets must be kept secure and confidential, as they provide control over the assets stored in the wallet.
- Asset storage and management: Wallets store and manage various digital assets, such as cryptocurrencies, utility tokens, governance tokens, or NFTs. These assets can represent value, access rights, or voting rights within the blockchain social protocol. Users can use wallets to send, receive, and manage assets.
- Smart contract interaction: Wallets enable users to interact with smart contracts on the blockchain, which can automatically execute various functions and processes within the social protocol. Users can trigger specific smart contract functionalities by sending transactions through wallets.
- Governance and voting: In decentralized social protocols, wallet holders can participate in governance decisions through voting. Users can use wallets to vote on proposals or changes to the protocol based on the tokens they hold.
- As wallets play a more important role in identity verification and asset management within social protocols, custodial wallets will gradually be replaced by non-custodial wallets. Although custodial wallets may be easier to use, users may face more risks due to third-party control over private keys. Non-custodial wallets allow users to have full control over their private keys, ensuring higher security and autonomy.
With a large number of Web2 users entering the Web3 social field, private key management strategies and user interface designs will become key factors in wallets competing for the future Web3 social user market. A noticeable trend is the introduction of MPC wallets and smart contract wallets that focus more on user experience. These wallets ensure that users own their private keys while also providing a better user experience.
In summary, wallets play a central role in blockchain social protocols, providing users with identity verification, secure transactions, and storage and management of digital assets. Understanding the functionality of wallets is crucial for those who want to participate in blockchain-based social networks or platforms.
III. Web3 Social Reputation: On-chain Credentials
The self-account feature of wallets empowers individuals with self-identity and asset management capabilities, making on-chain credentials one of the most important assets for users. They are a trustless, secure, and transparent way to verify and share information about individuals, entities, or devices. By leveraging the immutability and consensus mechanisms of blockchain technology, on-chain credentials can provide proof of identity, achievements, skills, or other attributes without relying on centralized institutions.
On-chain credentials can be used to create and manage digital identities that are secure, private, and controlled by the users themselves. These identities help in authenticating users in decentralized applications (dApps) or granting access to restricted resources based on verified attributes.
People will be able to translate their online behavior into “reputation” on the blockchain. This may happen in the Lens Protocol community, the Sound music platform, and ENS. Each wallet tied to an NFT profile interacting with cryptographic applications will establish a history and begin building an on-chain identity based on cryptographic means. This identity can unlock different things: airdrops (fully monetized) or access to a secret chat room on a social level.
Here are some key roles that on-chain credentials play in the Web3 network:
Source: LBank Labs
In conclusion, on-chain credentials provide a secure, decentralized, and verifiable way to manage and share important information. By leveraging the unique properties of blockchain technology, on-chain credentials can create new opportunities for trustless and transparent interactions in various industries and applications.
Use Cases
Source: LBank Labs
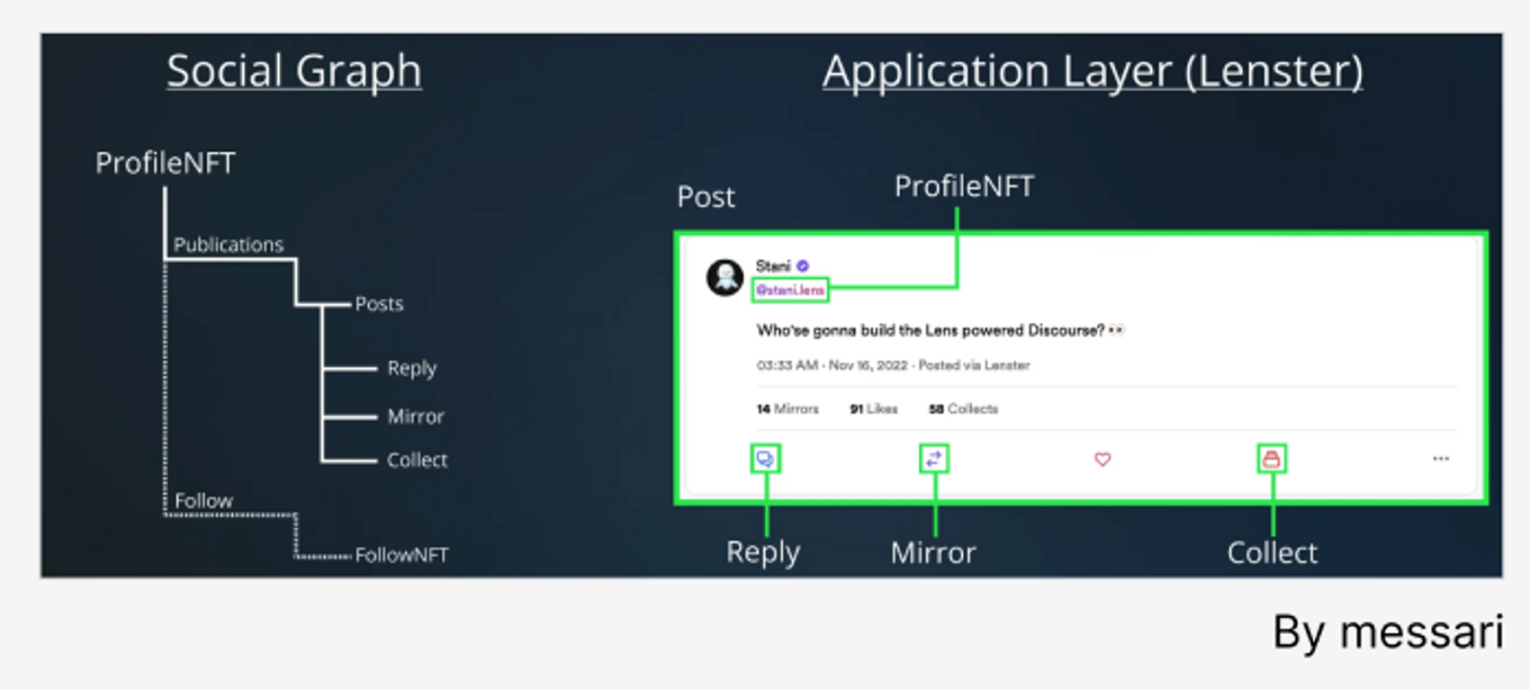
By combining NFTs with on-chain reputation systems, Web3 platforms can create new ways to attract and incentivize users while increasing trust, transparency, and accountability within their ecosystem. Only users who possess NFT profiles can establish identities and gain community reputation on Lens Protocol. The core functionality of Lens Protocol is built on three ERC-721 NFT contracts: ProfileNFT, FollowNFT, and CollectNFT. These tokens interact with independent contracts called modules, allowing Lens users to follow, post, collect, and comment on the content published by ProfileNFT. As interactions are recorded on-chain, users gradually build their on-chain accounts and reputation through continuous engagement with their unique NFT profiles.
Source: Messari's report "Solving The DAO Data Problem"
In summary, NFTs play an important role in the Web3 network by implementing unique digital asset ownership, promoting decentralized markets, increasing user engagement, and providing new methods for managing assets and identities.
Trends
On-chain credentials for different application scopes have different user characteristics. From the perspective of application scope, whether in terms of project quantity or user quantity, we can see that “NFT as a reputation indicator” is its most important use case. We can analyze different user activities from representative projects in four domains: ENS, LianGuairtyDAO, POAP, and Lens Protocol.
Source: LBank Labs (Data: Dune.xyz)
- ENS has relatively high user activity. Users can use ENS to register, update, and transfer domain names, and can also map domain names to smart contract addresses. With the popularity of DeFi, NFTs, and Web3 applications, ENS is expected to maintain a high level of activity.
- LianGuairtyDAO’s user activity may fluctuate with the volatility of the NFT market. During periods of market prosperity, users may be more actively involved in collective bidding activities organized by LianGuairtyDAO. However, during market downturns, user activity may decrease. In addition, with the development and innovation of the NFT market, as well as the emergence of new co-ownership models and auction methods, the user activity of LianGuairtyBid may be affected to a certain extent.
- POAP’s user activity may fluctuate with the number of events and activities. When events and activities are frequent, users may be more actively claiming and trading POAP badges. However, when events and activities are less frequent, user activity may decrease.
- The user activity of Lens Protocol may depend on various factors such as platform functionality, user experience, and community building. To maintain high activity, Lens Protocol needs to provide valuable features, attractive content, and a good user experience. In addition, an actively engaged community is also key to maintaining user activity. As the platform develops and innovates, user activity may gradually increase.
IV. On-chain Social: SocialFi
SocialFi, short for social finance, is an emerging field that combines social networks with financial services to connect people in innovative ways. The core idea of SocialFi is to promote financial activities through social interactions, enabling people to establish trust, share information, communicate, and conduct financial transactions on online platforms.
To understand SocialFi, the following key elements need to be considered:
- Trust and transparency: In the field of SocialFi, trust and transparency are built on the basis of public credit scores, transaction records, and personal experience sharing. This helps establish trust between individuals and reduces transaction risks. Therefore, on-chain credentials are the foundation of the SocialFi ecosystem.
- Financial inclusivity: SocialFi aims to involve more people in financial activities, especially those who have been overlooked by traditional financial systems. Social finance can help these people access credit, investments, insurance, and other financial products and services.
- Community support: Social finance platforms encourage users to support each other within the community by sharing experiences and knowledge. This helps reduce risks, improve financial literacy, and ultimately benefit more people.
- Investment innovation: SocialFi provides investors with more choices and innovative ways. For example, investment can be customized based on personal preferences and risk tolerance. In addition, social finance advocates collective investment, allowing users to collectively share risks and rewards.
- SocialFi includes various financial products and services that are disseminated and traded through social networks. Here are some common directions of SocialFi:
- Social investing and wealth management: These platforms encourage users to share investment experiences, advice, and strategies within the community. Investors can follow other successful investors on the platform, learn from their investment strategies, and make investments according to their own needs.
- Group fundraising and crowdfunding: These platforms harness the power of social networks to help project creators raise funds. Through group fundraising and crowdfunding, individuals and companies can more easily obtain the funding they need for innovative projects.
- Creator economy: The creator economy refers to the economic system formed around independent content creators, artists, and influencers who use digital platforms to create, distribute, and monetize their work. The development of social media, streaming platforms, and other online channels allows creators to establish their own brands, connect with audiences, and directly generate income from their content.
1. Social Investing and Wealth Management
Social investing and wealth management is an innovative approach to personal finance that combines the principles of social networking with traditional investment and wealth management practices. This approach allows individuals to share knowledge, insights, and investment strategies while fostering a sense of community and collaboration in the pursuit of financial success.
The key aspects of social investing and wealth management include:
- Social Networks: Social investing platforms leverage the power of social networks to connect like-minded investors, enabling them to share ideas, insights, and strategies. These networks help foster a sense of community and facilitate collaboration among users, leading to wiser investment decisions.
- Knowledge Sharing: Users of social investing platforms can access a wealth of information from other investors, ranging from market analysis and investment ideas to personal experiences and lessons learned. This open sharing of knowledge can help users make more informed decisions and improve their investment skills.
- Trade Copying and Tracking: Many social investing platforms offer features that allow users to follow or “copy” the trades of more experienced or successful investors. This can provide valuable learning experiences for novice investors and potentially lead to better investment outcomes.
In summary, social investing and wealth management is an innovative approach to personal finance that harnesses the power of social networks to facilitate knowledge sharing, collaboration, and community building among investors. By connecting like-minded individuals and fostering a spirit of cooperation, these platforms can help users make wiser investment decisions, improve their financial skills, and achieve their financial goals.
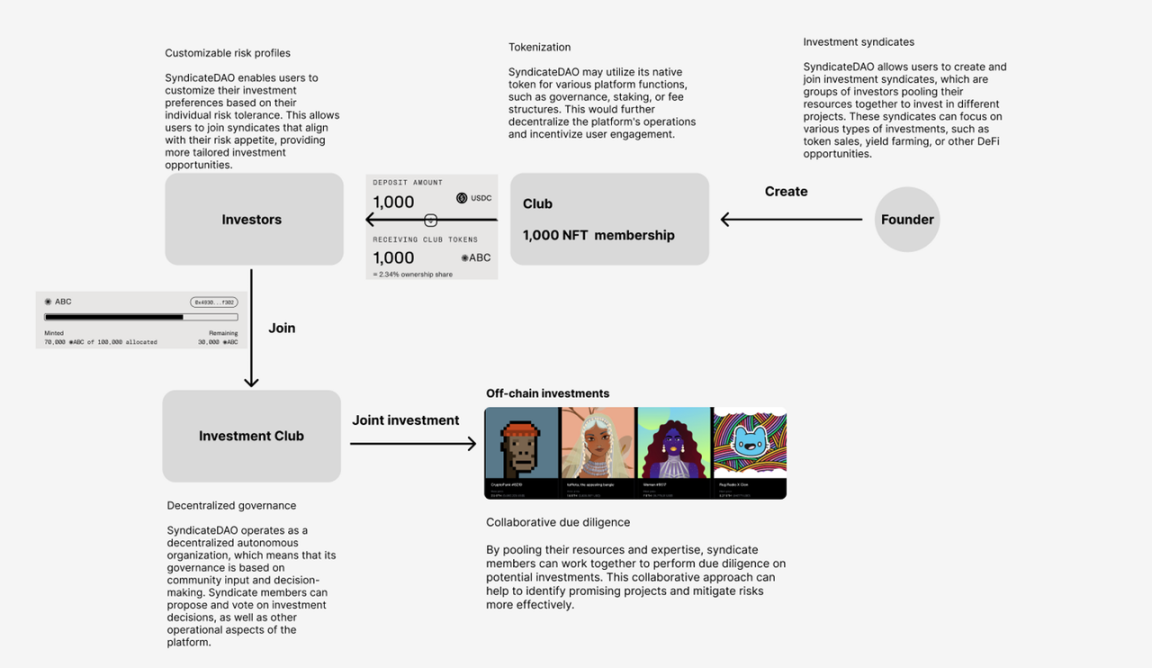
Use Case: SyndicateDAO
SyndicateDAO is a decentralized autonomous organization (DAO) dedicated to providing an innovative platform for decentralized investment groups. It aims to create a more inclusive and accessible investment environment for the decentralized finance (DeFi) world, allowing users to pool resources and invest in various projects as a collective.
Source: LBank Labs
Syndicate DAO has a total investment amount of $7,967,293 and has established 6,735 investment clubs.
2. Crowdfunding and Fundraising
Crowdfunding and fundraising are innovative methods of raising funds for projects, causes, or businesses using the power of social networks and online platforms. These methods allow individuals, organizations, and entrepreneurs to raise funds from a large number of people, typically in small amounts, to achieve their financial goals.
Various specialized crowdfunding platforms like Kickstarter, Crowdfunder, and Gitcoin enable users to create fundraising campaigns, showcase their projects, and solicit donations from supporters. These platforms often provide tools and resources to help users effectively promote their campaigns and achieve their fundraising targets.
Their types of crowdfunding include donation-based crowdfunding, reward-based crowdfunding, and equity-based crowdfunding. Each type has its own unique characteristics and may be suitable for different projects or funding needs.
- Gitcoin: Donation-based crowdfunding accepts supporters’ donations without expecting any tangible returns.
- Kickstarter: Reward-based crowdfunding offers supporters benefits or rewards such as products or services in exchange for their contributions.
- Crowdfunder: Equity-based crowdfunding allows investors to gain ownership in a company or project as an investment return.
The popularity of collective fundraising and crowdfunding is due to their innovative methods of utilizing the power of social networks and online platforms to raise funds. These methods enable individuals, organizations, and entrepreneurs to obtain support from a large number of people, helping them achieve financial goals and making their projects, causes, or businesses successful. The specific advantages are as follows:
- Project promotion and marketing: Successful crowdfunding campaigns often rely on effective promotion and marketing strategies to attract attention and support. Campaign creators can use social media, email campaigns, press releases, and other communication channels to spread project information and attract potential supporters.
- Community engagement: Establishing a supportive and engaged community is crucial for successful collective fundraising and crowdfunding campaigns. Campaign creators typically interact with supporters through updates, comments, and other communication channels to maintain interest, build trust, and encourage more support.
- Fundraising goals and deadlines: Crowdfunding campaigns often set specific fundraising goals and deadlines to create a sense of urgency and encourage donations. In some cases, platforms may adopt an “all or nothing” fundraising model, where creators can only receive funds if they reach the target within a specified time.
Use Cases
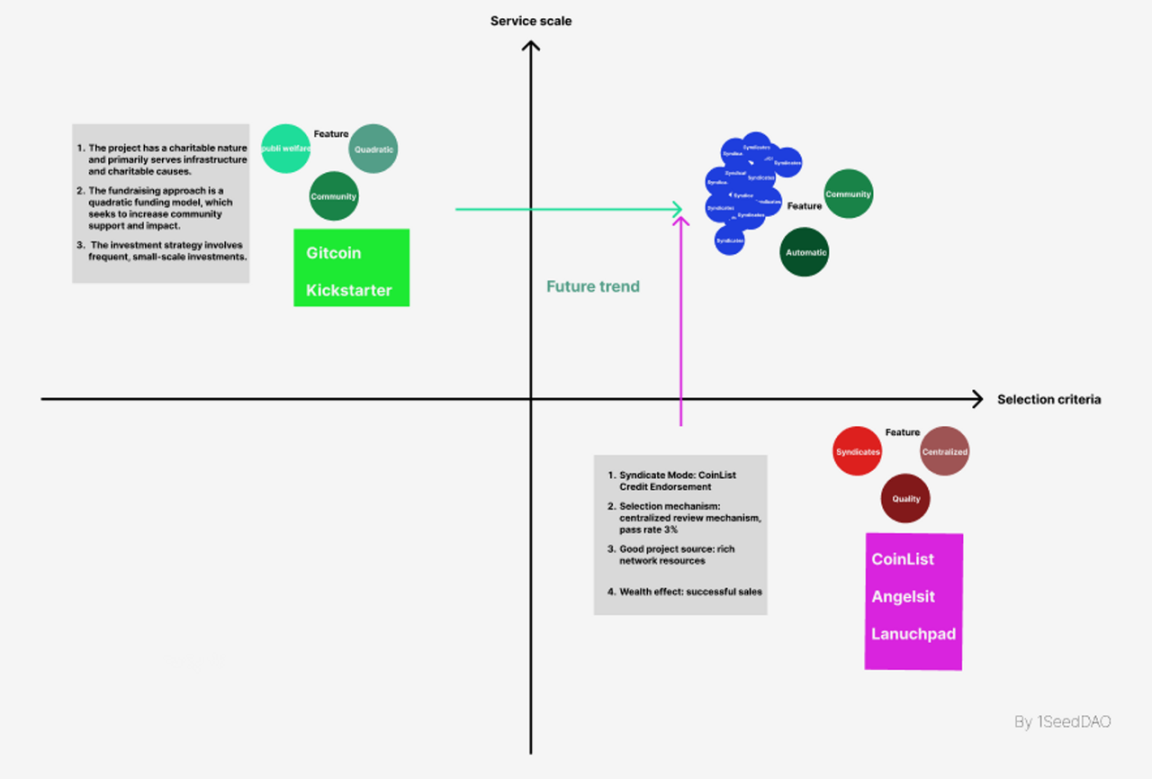
Based on the scale of services and selection criteria, we can present the following market map of collective fundraising and crowdfunding. From the market map, it can be seen that there is still a blank area where both project quality and large-scale market services can be guaranteed. This will be the most worthwhile direction to explore in the future. Taking Gitcoin as an example, it attempts to improve the quality of platform-funded projects while ensuring large-scale services, while Coinlist expands the scope of services while ensuring high standards for projects. How to expand the scale of services while ensuring project quality is still a challenging issue worth solving and exploring.
Source: 1Seed website
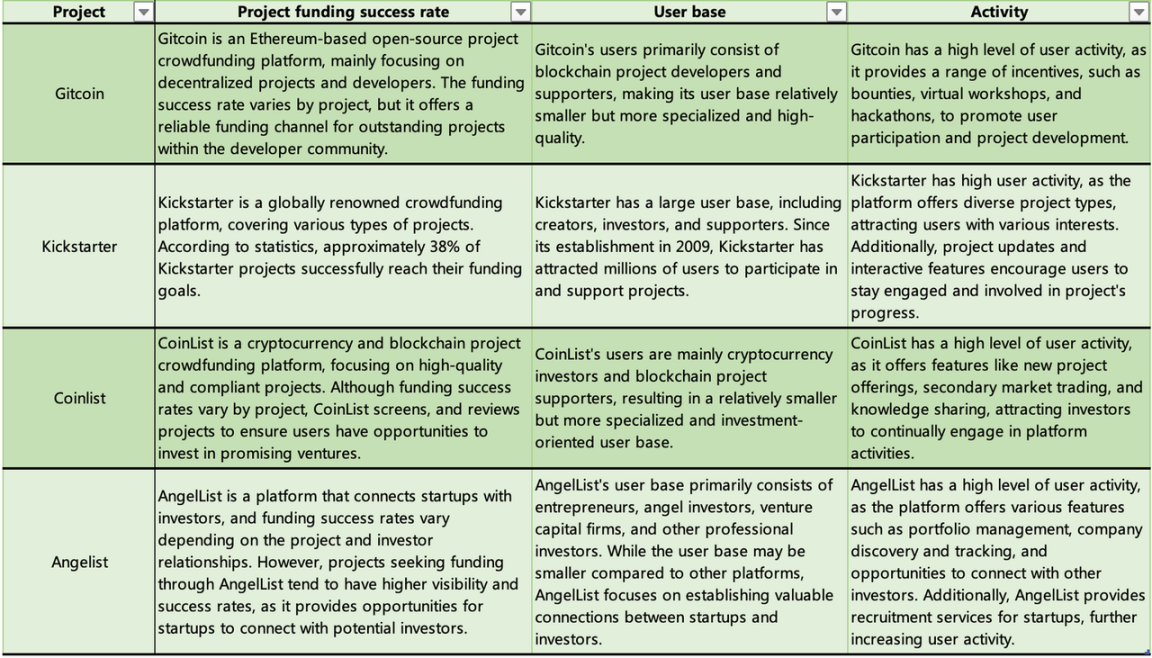
The following is an analysis of Gitcoin, Kickstarter, CoinList, and AngelList, focusing on three aspects: project funding success rate, user base, and user activity.
Source: LBank Labs
In summary, Gitcoin, Kickstarter, CoinList, and AngelList are all important platforms in their respective fields, but they differ in terms of project funding success rate, user base, and activity. Gitcoin and CoinList primarily focus on the blockchain and cryptocurrency industry, while Kickstarter and AngelList specialize in creative projects and startups, respectively. These platforms provide users with unique value and opportunities to seek investment or raise funds in different fields.
3. Creator Economy
The creator economy refers to the economic system formed around independent content creators, artists, and influential individuals who create and monetize their work using digital platforms. The development of social media, streaming platforms, and other online channels has enabled creators to establish their own brands, connect with audiences, and directly generate income from their content.
The main aspects of the broader creator economy include:
- Content creation: Creators produce various types of content, such as videos, podcasts, blog articles, music, art, etc. They usually specialize in specific fields to cater to the interests and preferences of their target audience.
- Monetization: Creators can monetize their content through various revenue streams, such as advertising, sponsored content, affiliate marketing, merchandise sales, donations, and subscription models. The flexible combination of these methods allows creators to establish sustainable and diversified sources of income.
- Audience engagement: In the creator economy, building a loyal and highly engaged audience is crucial for creators. They often interact with fans through comments, live streams, social media, and other channels to foster community awareness and maintain audience interest.
- Creator tools and services: The ecosystem of tools and services supporting creators is growing, enabling them to produce high-quality content, manage their businesses, and optimize their income. These tools include video editing software, analytics platforms, content management systems, and financial services designed specifically for creators.
- Overlap with the gig economy: The creator economy often intersects with the gig economy, as many creators are freelancers or independent contractors. This work model offers flexibility and autonomy but also presents challenges such as unstable income and lack of benefits.
In summary, the creator economy is a rapidly growing field driven by independent content creators who share their work on digital platforms, interact with audiences, and generate income. With the emergence of blockchain technology and new platforms, the creator economy may continue to evolve, providing new opportunities and challenges for creators worldwide.
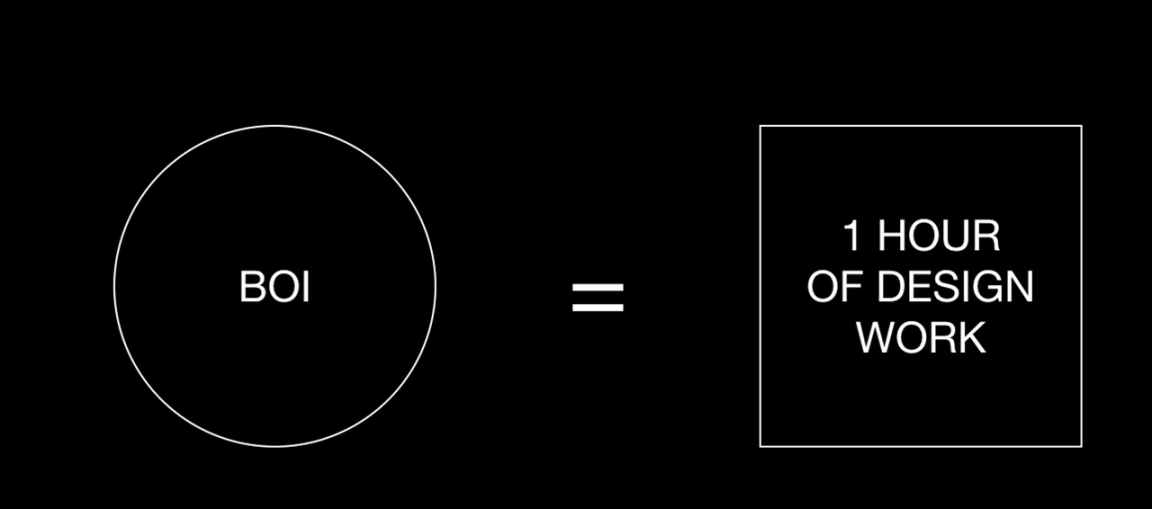
One of the advantages of a Web3-based creator economy is the ability to achieve broader financialization for creators. One of the most interesting cases is the tokenization of personal time, such as the 100 BOI tokens issued by Matt, which represent 100 hours of his work. These tokens can be exchanged for any services ranging from UI/UX design, prototyping, to brand design.
Source: Boi Website
As stated on the official website of DAPP Boi:
“I recently fell in love with the idea of personal tokens – tokens based on cryptocurrency whose value comes from human performance.”
One aspect of blockchain that has a significant impact on the creator economy is the issuance platforms such as Mirror, Sound, and DOPE. They allow creators to publish content in the form of smart contracts and monetize the content through various mechanisms including subscriptions, pay-per-view, and other forms of microtransactions. These platforms also allow creators to maintain ownership of their content and track engagement through analytics. Here are some key features:
- Ensuring decentralization, transparency, and security of content and transactions. This helps creators maintain their intellectual property rights while minimizing the risks of censorship and third-party intervention.
- Creator economy and tokenization: They support the tokenization of creations through the issuance of tokens, non-fungible tokens (NFTs), and crypto art. This allows creators to set prices, sell their works, and profit from them.
- Community-driven: They adopt a community-driven approach to decide who can become creators on the platform. Existing creators can vote to determine whether new creators should be admitted, ensuring high-quality content on the platform.
- Crowdfunding and sponsorship: Creators can use the platform to crowdfund projects and issue tokens as rewards to supporters. Additionally, creators can create sponsorship programs, allowing fans to directly support their work by purchasing tokens.
- Web3 compatibility: The platform fully embraces Web3 technology, providing decentralized identity verification, transactions, and content ownership management for creators. This enables creators to fully enjoy the advantages of the decentralized internet while maintaining control over their works.
Use Cases
Mirror
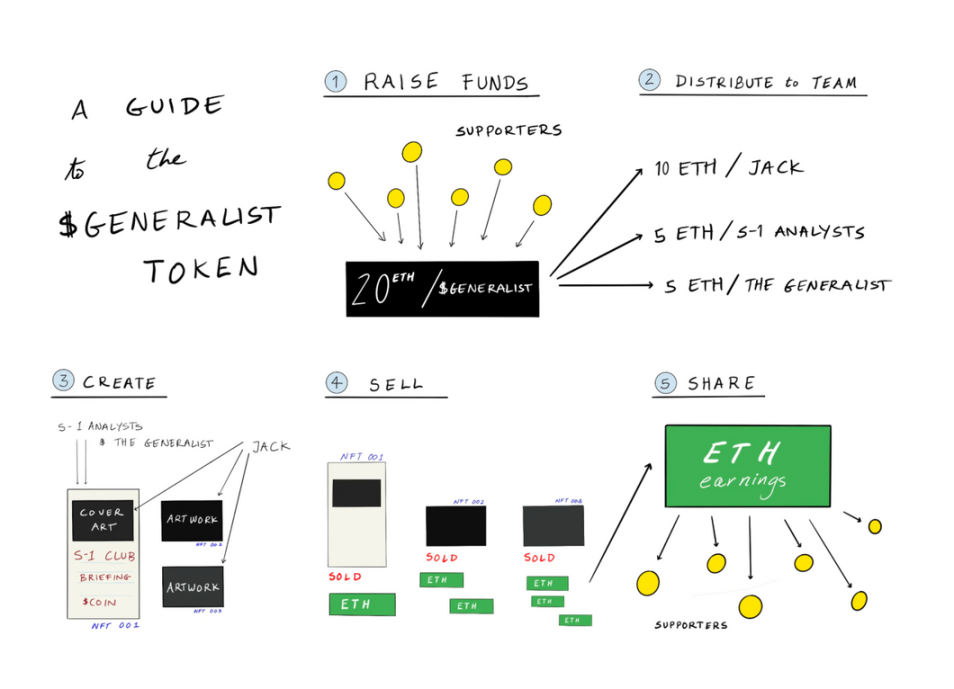
Mirror’s features include content creation, fundraising, revenue sharing, and the creation and distribution of tokens (NFT+ERC20). The following diagram, created by Mirror, illustrates the business and economic operations of creators on the platform.
Source: Mirror Blog
Mirror has helped creators raise a total of 11,079.91 ETH so far. Mirror has a total of 19,509 exclusive sponsors.
DOPE
Music economy companies play the roles of discoverers, investors, artist advisors, and owners and managers of commercial and copyright revenue streams in the music ecosystem.
Music creators (12%) – Record companies (76%) – Spotify (12%) – Fans
In the Web2 music industry, music economy companies play the most central role in resource allocation, namely discovering and incubating early-stage artists and pushing them to the market to gain significant commercial value. 76% of the industry’s revenue belongs to record companies. This model is commercially viable and will continue to be an important channel for musicians to enter the market in the future.
However, the emergence of music NFTs has brought another possibility to this industry, as music NFTs can also play the role of record companies!
Music creators (50%) – Music NFTs (45%) – Dope (5% fee) – Fans
Source: LBank Labs & Dope
Summary
The difference between Web3 social networks and Web2 social networks lies in the underlying technical architecture and the different data storage and transmission methods of blockchain, which also brings new functions to Web3 social networks. The biggest change brought by blockchain to Web3 social is the financial attribute of social interaction. Therefore, social reputation with financial attributes, creator economy, crowdfunding, etc. will be better integrated with Web3 social networks. Of course, Web3 social networks not only have financial attributes, but also have community self-organization attributes or DAO attributes. We will discuss this issue in the next article.
We will continue to update Blocking; if you have any questions or suggestions, please contact us!
Was this article helpful?
93 out of 132 found this helpful
Related articles
- Glassnode Weekly Report Bitcoin volatility index reaches historic low, market to remain in a sideways trend.
- The Economist Old Article How did Bitcoin become a Trust Machine?
- MicroStrategy’s latest holding of $4.5 billion in Bitcoin exposed, these eight Chinese listed companies also boldly bet on encrypted assets
- Can the presidential candidate’s stance on Bitcoin make Argentina the next El Salvador?
- LianGuai Morning Post | Europe’s First Spot Bitcoin ETF Listed, Embedded with Renewable Energy Certificates
- LD Capital interprets the past and present of OPNX How is the price performing? What challenges exist?
- What’s happening to the whales on the Bitcoin rich list now?