Messari Development Overview of Polygon in the Second Quarter of 2023
Messari's Q2 2023 Polygon Development OverviewAuthor: Nicholas Garcia Translation: Huohuo/Baihua Blockchain
Key Points:
1. Polygon Labs has launched Polygon 2.0, a zero-knowledge layer 2 blockchain network. Its goal is to become the “value layer of the Internet” and bring significant updates to protocol architecture, token economy, and governance.
2. Polygon zkEVM has experienced stable growth, demonstrating significant collaboration and integration with industry participants. By the end of this quarter, it has achieved 200,000 unique addresses.
- What impact will the detailed analysis of the Curve attack incident bring?
- Are the 10 Web3 directions released by LianGuairadigm really the future of the industry?
- LD Capital An Analysis of KasLianGuai, a POW Public Chain Based on the GHOSTDAG Protocol
3. MATIC has been included in the SEC’s complaints against Binance and Coinbase. However, Polygon’s network fundamentals have not been affected by this news.
4. Polygon has expanded partnerships with renowned traditional companies and institutions, including Franklin Templeton, Securitize, Mastercard, and Warner Music Group. These additions complement the existing list, which includes Adobe, Adidas, Disney, Meta, Nike, Reddit, Robinhood, and Starbucks.
1. Basic Knowledge of Polygon
Polygon is a suite of Ethereum-based scaling solutions that allows developers to move computation and data storage from Ethereum to a low-cost, high-speed development environment. Polygon provides the following solutions:
Polygon PoS – Polygon’s flagship product is the Polygon PoS network, which is an EVM-compatible sidechain with delegated proof-of-stake (DPoS).
Polygon zkEVM – Ethereum’s zero-knowledge (ZK) layer 2 aggregation protocol, launched on the mainnet test version on March 27, 2023. Polygon zkEVM aims to achieve secure, fast, and low-cost transactions. As a ZK-rollup, Polygon zkEVM bundles transactions into batches that are executed off-chain.
Polygon Miden – Polygon Miden is an upcoming zero-knowledge (ZK) layer 2 aggregation protocol designed for Ethereum. Unlike zkEVM, Polygon Miden does not rely on the Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM). Instead, it uses the Miden Virtual Machine (MVM) written in Rust. This unique approach allows developers to build high-throughput and private application processes using modern smart contract languages like Rust, providing enhanced security and targeting the lowest fees while benefiting from the security of the Ethereum network.
Polygon Supernets – An application chain-centric scaling solution for Polygon PoS in the testnet. Polygon Supernets aims to extend the block space of Polygon PoS by providing layer 2 and layer 3 networks for specific applications. Polygon Supernets is EVM-compatible, allowing application processes built on Polygon PoS to achieve greater throughput and cheaper transaction costs.
Polygon ID – A privacy-protecting identity verification service provided for Web3 users. Polygon ID uses ZK proofs to privately verify users’ credentials without disclosing unnecessary personal information.
In June 2023, Polygon Labs launched Polygon 2.0, which is a layer 2 blockchain network with zero-knowledge technology. Its goal is to become the “value layer of the internet” and bring significant updates to protocol architecture, token economics, and governance. Polygon 2.0 represents the future of the Polygon ecosystem.
Key Metrics:
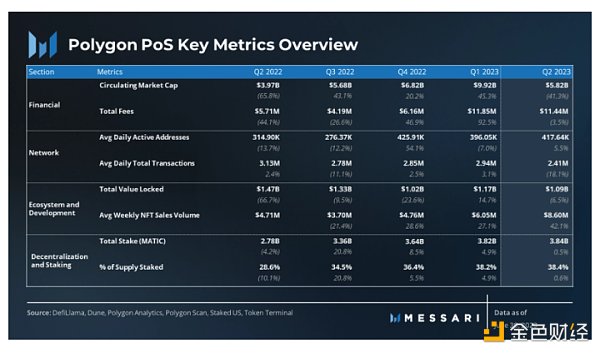
2. Polygon 2.0
1) Introduction
Polygon 2.0 represents an important milestone in the development of the Polygon blockchain, aiming to build it as the value layer of the internet. This set of enhanced features covers multiple areas including protocol architecture, token economics, and governance. The ultimate goal is to democratize global economic access through facilitating decentralized finance, digital ownership, and innovative coordination mechanisms. In this section, we will delve into the core attributes and implications of Polygon 2.0 revealed so far.
2) Infinite Scalability and Unified Liquidity
The core vision of Polygon 2.0 is to achieve infinite scalability and unified liquidity through the integration of zero-knowledge (ZK) technology. This upgrade aims to address the inherent scalability challenges faced by Web3, where adding new chains often leads to liquidity fragmentation and poor user experience. By leveraging ZK-supported layer 2 (L2) chains and a novel cross-chain coordination protocol, Polygon 2.0 creates a unified network that offers almost infinite scalability and seamless cross-chain interactions.
3) Upgrading Polygon PoS to zkEVM Validium
As part of the Polygon 2.0 upgrade, it is proposed to transition the Polygon Proof-of-Stake (PoS) chain to zkEVM validium. This change enables Polygon PoS to enhance its security, performance, and compatibility within the Polygon 2.0 ecosystem. With zkEVM validium, transaction data can be used off-chain, resulting in lower fees compared to traditional rollups while maintaining strong security guarantees. The proposed upgrade timeline is as follows:
– June 2023 – July 2023: Discussion and consensus before PIP
– October 2023 – November 2023: PIP release, discussion, and consensus
– November 2023 – January 2024: PIP implementation and testing
– February 2024 – March 2024: Upgrade, i.e., PIP activation on the mainnet
4) Protocol Architecture
The architecture of Polygon 2.0 is a key element in realizing its vision. It is divided into four protocol layers, each with specific purposes:
Staking Layer – Provides staking services for participating chains using Polygon’s native token. The staking layer is implemented on Ethereum through two contracts: the Validator Manager and the Chain Manager.
Interoperability Layer – Facilitates cross-chain message passing within the Polygon ecosystem. It supports secure shared access to native Ethereum assets and near-instant and atomic cross-chain transactions.
Execution Layer – Handles block production and transaction ordering.
Proof Layer – Contains high-performance ZK proof protocols for generating and verifying proofs across the Polygon chain.
5) Token Economics
Polygon Labs proposes a new native token POL as part of the Polygon 2.0 upgrade. The new POL token will be a 1:1 upgrade from the existing MATIC token and will inherit the initial supply of 10 billion MATIC tokens.
POL will enable holders to become validators for multiple Polygon chains and receive rewards for various services. This includes standard validation services such as accepting user transactions and determining their validity, as well as broader services such as generating zk validity proofs for transactions or providing data availability guarantees. It is worth noting that each Polygon chain can provide custom roles and rewards for its validators. Validators can choose to validate multiple chains simultaneously, compounding their rewards similar to the re-staking products on Ethereum with EigenLayer.
Finally, Polygon’s new token economic model removes the finite supply cap of 10 billion for its native token. Instead, POL will transition to an inflationary model to incentivize validators to participate and provide funds for the community treasury governance. Both categories are expected to have a 1% POL inflation rate over the next 10 years before the community decides whether to reduce the inflation rate.
6) Governance
Polygon Governance 2.0 introduces three main pillars of governance for the Polygon ecosystem: Protocol Governance, System Smart Contract Governance, and Community Treasury Governance. Each pillar has its own unique governance framework aimed at creating scalable and efficient governance mechanisms.
Protocol Governance: Driven by the Polygon Improvement Proposal (PIP) framework, providing a platform for proposing Polygon protocol upgrades.
System Smart Contract Governance: Addresses upgrades to protocol components implemented as smart contracts. These upgrades will be managed by an ecosystem committee governed by the community.
Community Treasury Governance: Creates a self-sustaining ecosystem fund – the Community Treasury – to support public goods and ecosystem projects. The governance process involves two stages, starting with an independent Community Finance Committee and gradually evolving into community-driven decision-making.
7) Financial Overview
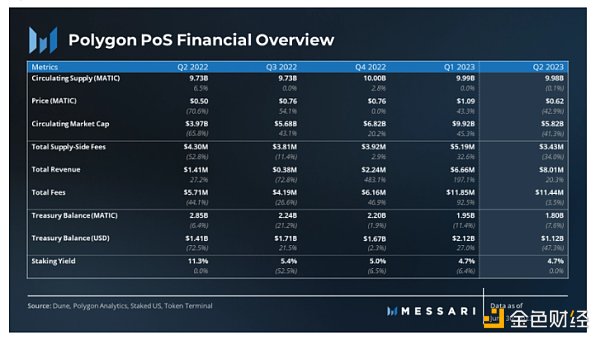
8) Market Capitalization and Revenue
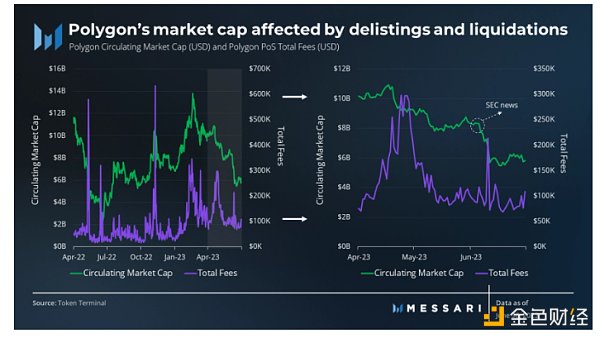
Polygon’s market capitalization experienced a significant surge in the first quarter of 2023, reaching nearly $14 billion in mid-February. Despite some retracement, Polygon’s market capitalization in the first quarter of 2023 still reached $9.92 billion, a 50% growth compared to the previous quarter, outperforming the market.
However, in the second quarter, Polygon’s market capitalization declined to $5.82 billion, a 41% decrease compared to the previous quarter. Part of this decline is due to the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) classifying Polygon as a security in its lawsuit against Binance and Coinbase, leading to its delisting from various trading platforms such as Robinhood and eToro. Despite the contraction in market capitalization, Polygon’s market capitalization still grew year-on-year.
The revenue of Polygon comes from network fees, which remain relatively stable month-on-month at $11.4 million, equivalent to an annualized revenue of $57 million.
Note: Polygon 2.0 will bring significant changes to Polygon’s revenue and value accumulation. For more details, please refer to the section on Polygon 2.0 – Infinite Scalability and Unified Liquidity.
9) MATICToken
Polygon’s native token, MATIC, has multiple functions within the network:
– Used as payment for network gas fees (native MATIC on PoS)
– Used as the exchange medium for the entire Polygon ecosystem (native MATIC and MRC-20 WMATIC on PoS)
– Staked for running validators (ERC-20 MATIC on Ethereum)
– Delegated to validators (ERC-20 MATIC on Ethereum)
– Used for rewarding validators (ERC-20 MATIC on Ethereum)
– Governance of the Heimdall layer (ERC-20 MATIC on Ethereum)
In October, MATIC achieved full redemption with a total supply of 10 billion tokens. MATIC follows the EIP-1559 upgrade, which includes a mechanism to burn a portion of the gas fees paid in native MATIC for each network transaction. The “base fee” (the fluctuating portion of gas fees) is burned, while the remaining fee is allocated as “priority fee” or tips to the proposed validators of the block. So far, a total of 16 million MATIC has been burned through this mechanism.
Note: Polygon 2.0 will replace the MATIC token with a new token called POL. For more details, please refer to the section on Polygon 2.0 – Token Economics.
10) Treasury
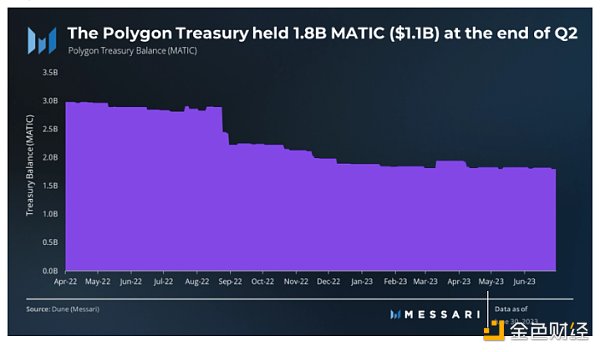
By the end of the second quarter of 2023, Polygon’s treasury holds 1.8 billion MATIC tokens, worth $1.12 billion. The treasury is controlled by Polygon Technologies, which has strategically allocated most of its expenses to the expansion of the Polygon network. These funds have been used for various purposes, including the acquisition of ZK projects and teams, the development of ZK-based solutions, talent recruitment, and research funding.
Note: Polygon 2.0 will provide funds for the community-managed treasury using a new token model. For more details, please refer to the section on Polygon 2.0 – Token Economics.
11) Network Overview
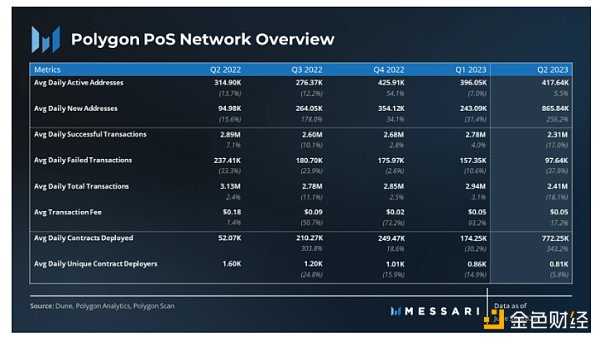
12) Use Cases
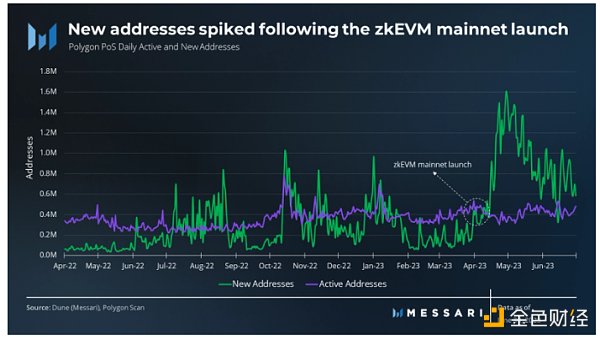
In the second quarter, the average daily new addresses on Polygon increased by 256% month-on-month, from 243,000 to 866,000. The network witnessed the creation of nearly 80 million new addresses throughout the quarter. The surge in new addresses coincided with the launch of zkEVM, indicating higher enthusiasm within the community.
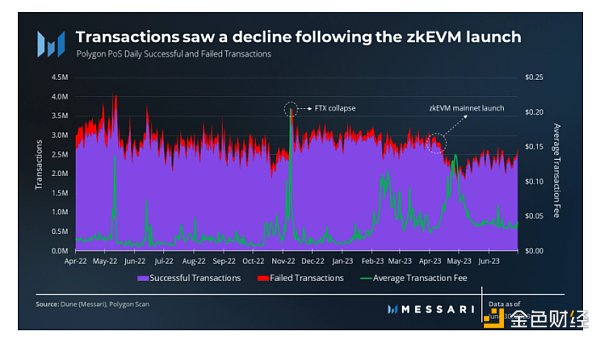
On the other hand, the number of transactions on the Polygon network decreased by 18% month-on-month, from 2.9 million daily transactions to 2.4 million. The decrease in transaction volume directly corresponds to the launch of zkEVM.
13) Development
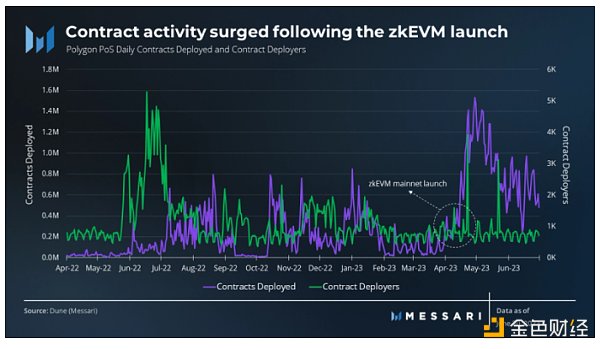
Polygon has demonstrated strong activity and commitment to the developer community. In the fourth quarter of 2022, it hosted multiple events and signed partnerships to strengthen developer relations. In the first quarter, Polygon Labs @ the Pit (later renamed DevX Global Tour) launched a global developer tour.
In the second quarter, Polygon continued to hold the DevX Global Hackathon. It visited Asian cities such as Tokyo, Hong Kong, and Kuala Lumpur, allowing developers to compete for a $125,000 prize. The hackathon will head to Europe in July, visiting Amsterdam, Zagreb, London, Paris, Lisbon, and Berlin. Additionally, in the second quarter, Polygon partnered with Google Cloud to provide resources and benefits to early-stage startups in the Polygon ecosystem. Polygon Copilot, an AI tool that provides support to developers, has also been launched.
According to data from Electric Capital, the number of contracts deployed by Polygon in the second quarter increased fivefold, and it ranked sixth in developer activity for the first half of 2023, with 201 full-time developers and a total of 837 developers.
3) Additional Solutions
1) Polygon zkEVM
Polygon zkEVM is Ethereum’s Layer 2 scaling solution, launched on March 27, 2023. It aims to achieve secure, faster, and cheaper transactions. As a ZK-rollup, Polygon zkEVM bundles transactions into batches executed off-chain. After the off-chain execution, Polygon zkEVM publishes the transaction data on-chain. In addition to transaction data, Polygon zkEVM also publishes validity proofs to cryptographically verify the correctness of the data published on-chain.
Throughout the second quarter, Polygon zkEVM had significant collaborations and integrations with industry participants such as Celer Network, Synapse, Balancer, and Uniswap (yet to be launched). Additionally, Polygon launched the Polygon Bridge to zkEVM, enhancing connectivity within the ecosystem. Monthly reports were released to highlight the activities and development progress of zkEVM.
This quarter, Polygon zkEVM showed continued growth, with 200,000 unique addresses and a total of 1.8 million transactions (equivalent to about 19,700 transactions per day). However, it is worth noting that activity on zkEVM is still only a small fraction of the PoS chain. As of the end of this quarter, Polygon zkEVM reported a TVL of $40 million, primarily driven by $20 million contributed by Quickswap.
2) Polygon Miden
Polygon Miden is an upcoming zero-knowledge (ZK) Layer 2 scaling solution designed for Ethereum. Unlike zkEVM, Polygon Miden does not rely on the Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM). Instead, it uses the Miden Virtual Machine (MVM) written in Rust. This unique approach allows developers to build high-throughput and privacy-focused applications using modern smart contract languages like Rust, with enhanced security and a focus on minimal fees, while benefiting from the security of the Ethereum network.
In anticipation of the launch of the Miden testnet, Polygon Labs has released a series of detailed blog posts explaining Polygon Miden. It introduces a unique transaction model that includes accounts, tickets, and transactions, enabling local execution, proofs, and efficient asset transfers. The state model combines Ethereum’s account model, Bitcoin’s UTXO model, and ZK proofs to solve the problem of state bloat by storing commitments instead of the complete state. Operators manage the global state while users are incentivized to store data locally, maximizing privacy and minimizing state growth.
3) Polygon Supernets
Polygon Supernets is an application chain-centric Polygon PoS scaling solution that entered testnet on May 18, 2023. It aims to scale the block space of Polygon PoS by providing Layer 2 and Layer 3 networks for specific application processes. Polygon SuperNet is EVM-compatible, allowing applications built on Polygon PoS to achieve higher throughput and lower transaction costs.
In the fourth quarter of 2022 and the first quarter of 2023, Polygon announced several partnerships and collaborations with companies developing their own supernets. Notably, the IDEX team shared their plans for XCHAIN, a zk-rollup application chain focused on DEX, which will utilize Polygon’s zkEVM as the Polygon ZK Supernet.
Polygon Supernets V0.9 was released in the second quarter of 2023, introducing expanded allowlist and transaction blocklist, staking and token separation support, NFT bridge integration, transaction fee management, deployment optimizations, and enhanced access control. It brings Polygon closer to its goal of creating a “supernet” with scalability and sovereignty. A comprehensive source code audit is underway to ensure compliance and security, with migration support planned for future versions.
4. Ecosystem Overview
1) Ecosystem Development Overview

2) TVL
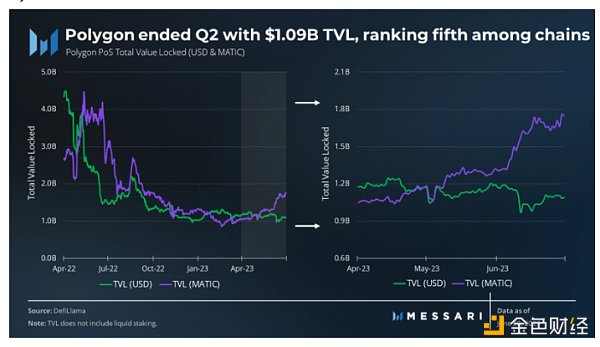
Polygon’s TVL experienced a challenging period during the 2022 bear market, with consistent declines in each quarter. However, in Q1 2023, the TVL stabilized, and this stability carried over into Q2 2023. Polygon concluded the quarter with a TVL of $1.09 billion, securing its position as the fifth-ranked chain in terms of TVL.
3) Top TVL Protocols
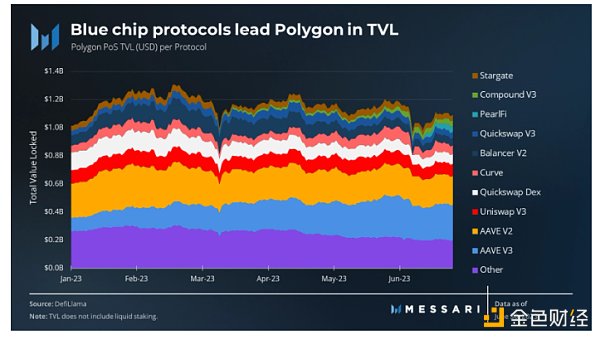
Polygon’s top TVL protocols demonstrated stability throughout the second quarter, maintaining their positions. The leading protocols in terms of TVL are the established blue-chip Aave (V2 and V3) with $206 million and $251 million respectively, followed by Uniswap V3 with $88 million TVL, Quickswap DEX with $71 million, Curve with $62 million, and Balancer V2 with $54 million.
Notably, two new additions were made to the top ten list this quarter. PearlFi, a ve(3,3) trading platform launched in mid-June, quickly gained attention and achieved a TVL of $42 million within weeks of its mainnet launch. On the other hand, Compound V3, a mature lending protocol, entered the top ten after its launch on Polygon in March. Its TVL steadily grew and reached $40 million by the end of the second quarter.
The total TVL of protocols outside the top ten is $200 million.
4) DEXs
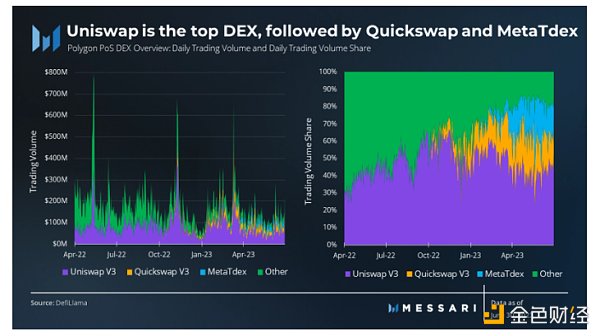
In the second quarter, the average daily trading volume of DEX on Polygon was $124 million, with a total quarterly trading volume of $11.3 billion. Uniswap V3 continued to maintain its leading position among DEXs on Polygon, accounting for 43% of the total DEX trading volume. Quickswap V3 followed closely behind, accounting for 21% of the total trading volume, and MetaTdex contributed 19% to the total trading volume. The remaining DEXs on the network accounted for 18% of the cumulative trading volume. Polygon’s total cumulative trading volume reached $138.94 billion, ranking third in historical DEX trading volume, only behind Ethereum and BNB Chain.
5) Liquidity Staking
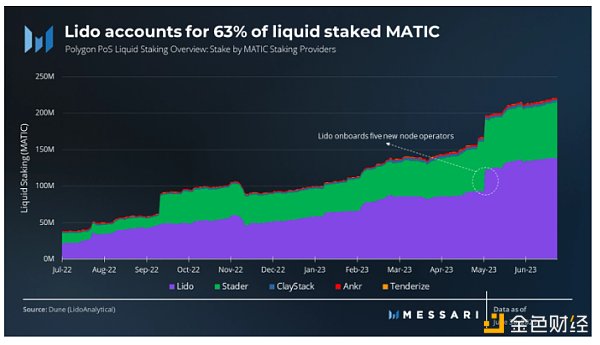
At the end of the second quarter, the liquidity staked in MATIC on Polygon increased to 221 million MATIC, a 37% increase compared to the previous quarter. This growth can be attributed to Lido integrating five new node operators in early May. Lido is the leading liquidity staking protocol on Polygon, with 138 million staked MATIC, accounting for 62% of the total. Stader follows closely behind, staking 77 million liquid MATIC, accounting for 35% of the total.
Liquid staking on Polygon only accounts for a small portion (5.8%) of the total staked MATIC.
6) Stablecoins
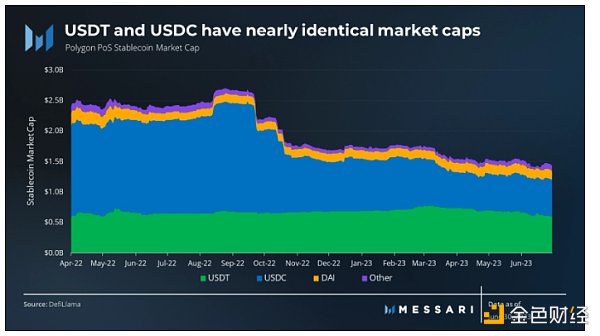
In the first quarter of 2023, USDC, which has traditionally dominated the stablecoin market on Polygon, experienced a significant decrease in market capitalization due to Circle’s exposure to Silicon Valley Bank. As of the end of the first quarter, USDT became the top stablecoin on Polygon, with a market capitalization of $735 million, accounting for 48% of the total stablecoin market cap. Meanwhile, USDC’s market capitalization remained stable at $593 million, accounting for 38% of the market cap.
In the second quarter, USDT’s market capitalization decreased by $137 million, ending the quarter at $598 million, accounting for 41.6% of the total stablecoin market cap. In contrast, USDC’s market capitalization remained relatively stable, reaching $600 million, equivalent to 41.8% of the total market cap, reclaiming a slight lead.
Overall, Polygon’s stablecoin market capitalization decreased by 7% from $1.54 billion to $1.44 billion. Polygon closed as the sixth-largest stablecoin market cap.
7) NFTs
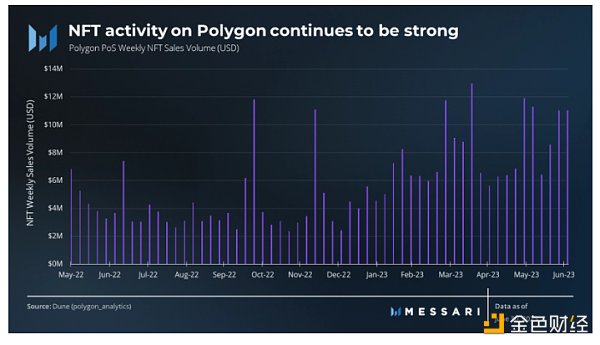
Polygon’s NFT ecosystem showed resilience during the bear market and continued to grow in the second quarter of 2023. The average weekly NFT sales volume on Polygon increased by 42%, reaching $8.6 million.
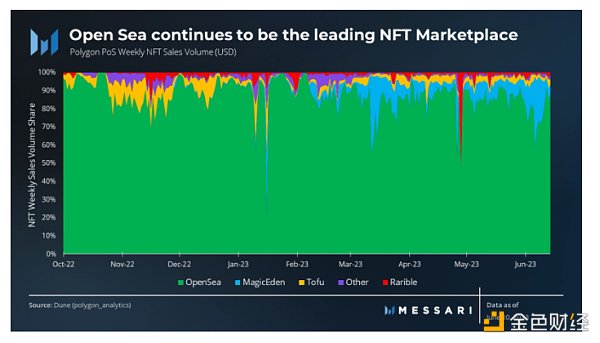
Open Sea remains the dominant NFT marketplace on Polygon, accounting for 84% of the total NFT volume in the second quarter. Magic Eden joined the network in the first quarter and ranked second with a market share of 9%.
Several leading NFT collections on Polygon have contributed to the success of the network, including Lama Kings, Doodle Changs, y00ts, Bungo Beanz, and Super Pengs.
The NFT ecosystem on Polygon has attracted the attention of major brands and organizations. Starbucks announced plans to launch a second NFT collection on Polygon, while Sports Illustrated chose to utilize Polygon to launch a new NFT ticketing service called Box Office. Additionally, attendees of the Monaco Grand Prix had the opportunity to receive NFT tickets on Polygon, demonstrating the practical applications of the network.
Polygon has also been actively promoting music NFTs and supporting the development of Web3 music applications. They have partnered with Warner Music Group to create the Music Accelerator Program to foster innovation in this field, further highlighting Polygon’s commitment to the intersection of music and blockchain technology.
8) Game
Polygon’s gaming sector has shown significant growth within the Polygon ecosystem. In the first quarter, Polygon had the highest number of active players among all EVM chains. Throughout the second quarter, the top-performing games on Polygon included Pixels, Arc8, Benji Bananas, Sunflower Land, Decentral Games, and Skyweaver. Furthermore, Polygon has previously announced several notable partnerships and collaborations involving companies such as Superlayer, Delab Games, AQUA, Immutable, and Nexon.
9) Other Highlights
Crypto-native
Taurus has integrated Polygon into its tokenization and custody platform, allowing clients to tokenize any asset and leverage the advantages of Polygon.
Solana wallet Phantom has expanded to Ethereum and Polygon, enabling users to transact across all three blockchains and providing features such as floor price data and direct market listings for NFT holders.
The Graph now supports Polygon. Developers on Polygon can begin migrating subgraphs to The Graph network.
Institutional
Franklin Templeton, one of the world’s largest asset management companies, has launched the Nasdaq-listed OnChain US Government Money Fund (FOBXX) on the Polygon blockchain, making it the first fund registered in the United States to trade and share ownership using blockchain technology.
The securitization of expanded liquidity potential and access to Hamilton Lane’s Senior Credit Opportunities Fund through Polygon, offering on-demand redemption and fully digital subscription processes.
BTG Pactual, headquartered in Brazil and the largest investment bank in Latin America, has launched its own stablecoin on the Polygon blockchain called BTG Dol, providing clients with USD-backed assets.
Mastercard is collaborating with Solana, Aptos, Polygon, and Avalanche to create universal cryptographic standards and develop Mastercard crypto credentials.
Sustainable Development
Regen Network has partnered with Toucan to launch a bridge to the Polygon network, enabling the issuance and tokenization of carbon credits on the Regen Network and creating Nature Carbon Tonnes (NCT) as the first digital carbon token in the Cosmos ecosystem.
Solid World is launching a carbon market liquidity pool on the Polygon PoS network, aiming to democratize access and scale financing for global nature-based carbon projects.
5. Decentralization and Equity Summary
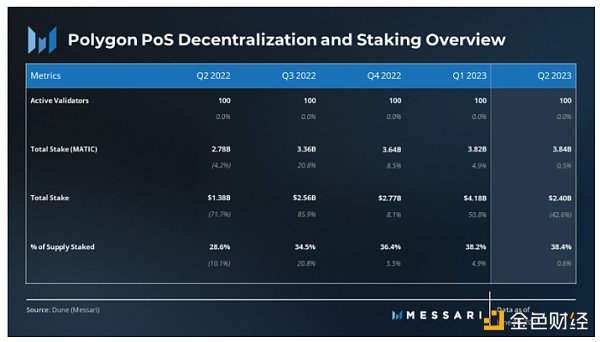
Polygon PoS, as an Ethereum-based Delegated Proof of Stake (DPoS) sidechain, allows users to become validators and contribute to network security while receiving rewards. However, the maximum number of active validators on PoS is 100. As of the end of the second quarter, the validator set is full, and new validators can only join if existing validators exit.
The staking rewards on Polygon PoS are distributed in the form of MATIC tokens on Ethereum. The rewards are proportional to the stake of validators relative to all active validators, including a 10% reward for successfully submitting checkpoints on the Heimdall layer. Validators can also earn native MATIC transaction fees by proposing blocks on the Bor layer.
As of the end of the second quarter of 2023, the five largest MATIC validators have cumulatively staked 1.52 billion MATIC tokens (accounting for 39.5% of the total staked MATIC, or 15.2% of the total token supply). The five largest validators are as follows:
– Luganodes: Staked 431.7 million ERC-20 MATIC tokens (11.3% of total stakes).
– BinanceNode: Staked 359.7 million ERC-20 MATIC tokens (9.4% of total stakes).
– Web3NodesValidator: Staked 263.4 million ERC-20 MATIC tokens (6.9% of total stakes).
– Coinbase Cloud: Staked 252.7 million ERC-20 MATIC tokens (6.6% of total stakes).
– Allnodes.com: Staked 209.6 million ERC-20 MATIC tokens (5.5% of total stakes).
Note: Polygon 2.0 will improve the validator model and validator payment scheme. For more details, please refer to the Polygon 2.0 – Architecture and Token Economics section.
1) Staking
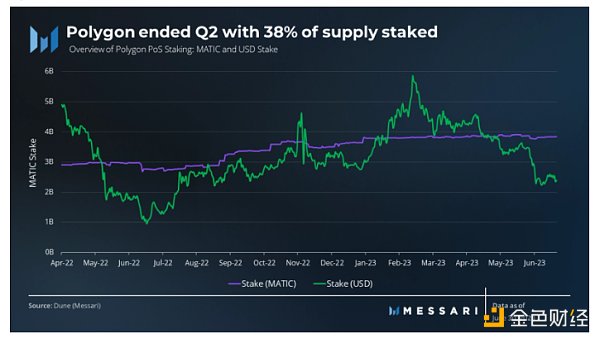
The proportion of MATIC staking continues to increase gradually and reached 3.84 billion MATIC tokens (38% of total supply) by the end of the second quarter.
2) Governance
Polygon Governance 2.0 introduces three main pillars for the Polygon ecosystem: Protocol Governance, System Smart Contract Governance, and Community Treasury Governance. Each pillar has its own unique governance framework aimed at creating a scalable and efficient governance mechanism.
Protocol Governance: Driven by the Polygon Improvement Proposal (PIP) framework, providing a platform for proposing Polygon protocol upgrades.
System Smart Contract Governance: Addresses upgrades to protocol components implemented as smart contracts. These upgrades will be managed by the community-governed Ecosystem Committee.
Community Treasury Governance: Create a self-sustainable ecosystem fund – the Community Treasury, to support public goods and ecosystem projects. The governance process involves two stages, starting from an independent Community Finance Committee and gradually evolving into community-driven decision-making.
Polygon Labs encourages community participation through feedback and suggestions. The PIP Bounty Program rewards outstanding submissions, with a total allocation of $40,000 within a year. This framework covers core improvements, Ethereum contracts, API specifications, and information PIP.
6. Summary
Despite becoming the SEC’s target for Binance and Coinbase in the second quarter, Polygon’s financials and network fundamentals have not been affected. Polygon announced a series of new protocol updates and partnerships this quarter, demonstrating continued resilience.
The most notable news this quarter is the launch of Polygon 2.0. This is a zk L2 network aimed to become the “Internet of Value”. Polygon 2.0 brings significant enhancements in protocol architecture, token economics, and governance, marking a crucial step in network development.
The concurrently running Polygon zkEVM continues its growth trajectory, showcasing impressive collaboration and integration. By the end of this quarter, the number of unique addresses has reached 200,000.
Polygon’s developer and user community is one of the largest in the cryptocurrency space, and it remains committed to breaking boundaries. As competition intensifies, the successful launch of Polygon 2.0 and the continued adoption of Polygon zkEVM will become increasingly important in the coming quarters.
We will continue to update Blocking; if you have any questions or suggestions, please contact us!
Was this article helpful?
93 out of 132 found this helpful
Related articles
- How far can a decentralized sorter go?
- The Battle of Tech Giants Digital Identity, Payments, Social Graphs, AI, and Universal Basic Income
- Messari Overview of SandBox Development in Q2 2023
- EthCC Experience Cryptocurrency VCs Not as Good as Dogs, Applications Upgraded to Infrastructure
- A Week After the Renaming Predicting the 8 Major Changes That Will Happen to the ‘New Twitter X
- How is the OP ecosystem now? Is it worth investing in?
- The Tech Giants’ Battle of X Digital Identity, Payments, Social Graph, AI, and Universal Basic Income (UBI)




