UBI Development History The Combination of Utopia and Fantasy
UBI Development History Utopia and Fantasy Combined
Written by: Spike @ Contributor of PermaDAO
Reviewed by: Lemon @ Contributor of PermaDAO
The History of UBI: The Combination of Utopia and Idealism
Universal Basic Income (UBI) is an economic and social concept that aims to provide a certain level of economic support to every citizen, regardless of their employment status. The emergence of this idea can be traced back to early economists and philosophers who deeply contemplated issues of social justice and wealth distribution.
- Wall Street Journal Binance Empire on the Verge of Collapse
- A Shenzhen University alumnus who graduated just a year ago donated 50 million yuan to his alma mater, and his first bucket of gold may have come from cryptocurrency.
- Binance He Yi’s Open Letter Perseverance and a Light Boat Will Cross Ten Thousand Mountains
In the late 18th century, philosopher Thomas LianGuaiine proposed a similar concept in his work “The Public Good”. He advocated for providing every citizen with a basic income to ensure their basic needs are met, thus achieving social fairness and justice. The idea was to distribute the resources and wealth of a nation equally among its citizens. He believed that people should share in the wealth of the nation, rather than relying solely on income from labor.
Subsequently, in the 1960s and 1970s, American economists Nils Alstrup Dahl and James Tobin also proposed similar concepts. They advocated for alleviating poverty and inequality by providing a fixed cash payment to all citizens.
In the early 20th century, economist Keynes also put forth a similar viewpoint. He believed that governments should stimulate the economy and promote consumption and investment by providing a basic income. Keynes believed that this policy could reduce the fluctuations of the socio-economic system and maintain social stability in a more robust manner.
Over time, the concept of UBI has gradually gained more attention and research from scholars and social activists. Since World War II, the idea of UBI has received increasing attention and exploration through pilot projects in countries and regions such as Finland, Canada, and Kenya, to explore the feasibility and effectiveness of UBI.
For example, the welfare state system in Europe, as well as minimum living allowances, unemployment insurance, and China’s subsistence allowances, can be considered as part of relevant practices. However, the concept of UBI in the usual sense also has some differences from the welfare system, which will be elaborated in the following text.
One of the earliest implementation attempts was the “Mincome” (Manitoba Basic Annual Income Experiment) project conducted in the province of Manitoba, Canada. The project, which took place from 1974 to 1979, aimed to test the effects of providing low-income families with a certain amount of basic income subsidy. The research results showed that the project did indeed contribute to alleviating poverty and improving social welfare. However, due to changes in government and financial pressures, the project was canceled after a few years.
Another early implementation attempt was the “Permanent Fund Dividend” program conducted in Alaska, USA. The program began in 1982 and provided a certain basic income to every eligible resident by distributing a portion of Alaska’s oil revenue. The program is still running today and pays out dividends of hundreds of dollars to residents each year.
In addition, the sovereign wealth funds of Gulf countries and Norway can also be seen as a UBI practice in a broad sense. For example, Norway’s sovereign wealth fund, established in 1996, currently has assets totaling $1.6 trillion. Based on the 2019 price calculation, each Norwegian can receive a dividend of $180,000.
The concept of UBI was not seriously discussed as a separate economic proposition until the 1970s when it began to be included in government policy design based on the related ideas of UBI.
For example, both developed countries and third world countries have made attempts, but the overall scale is not large and it is difficult to have a sustained impact:
- Canada: Canada was one of the first countries in the world to introduce a UBI pilot project. In 2017, the province of Ontario implemented a pilot project called the “Basic Income Pilot,” providing up to CAD 1,330 per month to 4,000 low-income families.
- Finland: Finland conducted a pilot project called the “Basic Income Experiment” between 2017 and 2018. The project provided a basic income of EUR 560 per month to 2,000 randomly selected unemployed individuals, regardless of whether they found employment. The goal of the pilot project was to test the impact of UBI on employment and the welfare system. However, no clear conclusions were drawn after the project ended in 2018.
- Kenya: A project called the “Basic Income Pilot” was initiated by the non-profit organization GiveDirectly in Kenya since 2016. The project started in 2016 and provided two years of basic income to some villages in Kenya. The goal of this project was to test the impact of UBI on poverty-stricken areas and its potential effects on individuals and communities.
- United States: Stockton, California launched a pilot project called the “Stockton Economic Security Project” in 2019, providing a basic income of $500 per month to 125 families.
At this stage, the main focus is on exploring UBI. The formation of effective practices will require the widespread spread of the COVID-19 pandemic. In this context, it has given rise to the actual quantitative easing measures implemented by governments and financial sectors in Europe and America. Furthermore, the development of AI, which serves as a substitute for human productivity, also plays a role.
These two factors complement each other. The pandemic has led to a decrease in social financing costs, with the lives of a large number of people being confined to their rooms and communities. Online platforms have become truly available spaces for production and living, while AI, benefiting from the lower social financing costs, has found real user groups and entered a practical stage of development.
In March 2020, the Federal Reserve launched an unlimited quantitative easing policy. Subsequently, major economies including the European Central Bank, the Bank of Japan, and the Bank of England chose to generate inflation to resist the economic crisis. This led to a huge amount of liquidity in the market. However, at the same time, the wealth gap between individuals and businesses, as well as between small and micro enterprises and listed companies, has been continuously increasing.
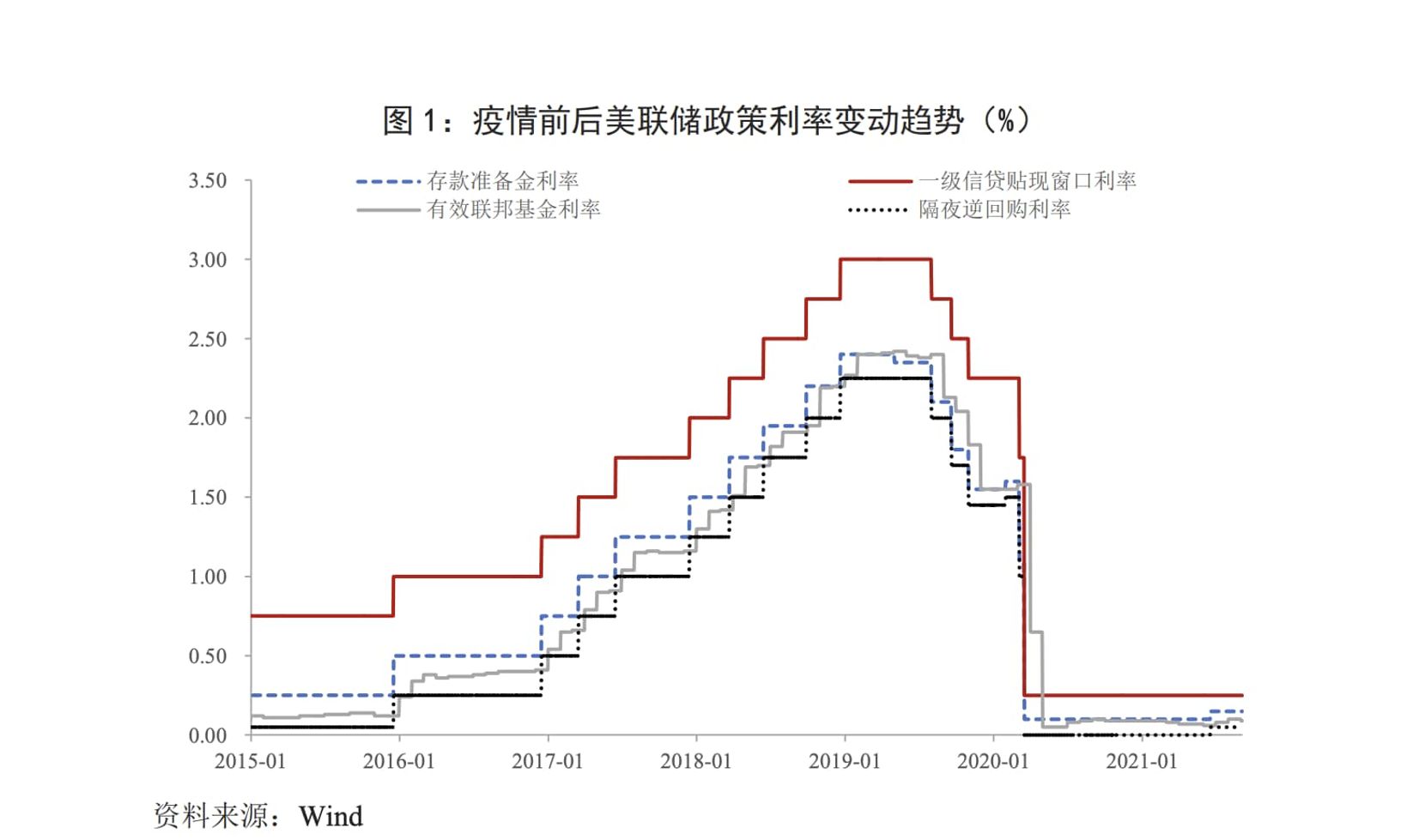
Image description: Trend of policy interest rate changes by the Federal Reserve before and after the epidemic. Image source: please visit the link
The Federal Reserve’s asset size has also expanded from around $4.2 trillion in March 2020 to around $8.35 trillion in September 2021, an increase of nearly 100%. As a result, AI has truly emerged.
Here, AI refers to OpenAI, which is named as such because it was originally a defensive move against Google’s acquisition of DeepMind. OpenAI hopes to make AI serve humanity in an open-source manner. It first received a $1.2 million investment from YC in 2016. Before Sam Altman joined and became CEO in 2019, OpenAI did not receive high donations and financing. The turning point came in July 2019 when Microsoft first invested $1 billion in it. Subsequently, there were more investments in 2021, and of course, the largest one was a massive $10 billion investment in January 2023.
OpenAI has become increasingly closed, no longer adhering to open-source standards, but it has indeed bet on the direction of LLM and become the first general artificial intelligence model (AGI). However, its revenue in 2022 is only $28 million, and it is still in continuous losses.
Another idea of Altman’s is Worldcoin, which creates a personal identity system offline, known as proof of personhood, and then puts it on the chain to create a UBI economic system that is shared and enjoyed by all. As a result, UBI and blockchain are officially linked together.
However, it should be noted that Worldcoin cannot fully guarantee the security of collecting user data. It adopts a distributor model rather than a direct-operated model by the company. Although it ensures that data scanned by Worldcoin hardware will be deleted, this is essentially a “promise” rather than a technically trustworthy solution.
In 2023, hackers stole the login credentials of the Worldcoin operator responsible for registering new users, allowing them to access internal information, not to mention the situation of profiting from selling user data. For example, even before the Worldcoin mainnet went live, intermediaries had acquired data from locals in Cambodia or Africa and sold it to professional data analysis studios.
Nevertheless, Worldcoin has popularized the concept of UBI on a large scale and deeply ingrained it in people’s minds. At least, it has achieved user popularization on a global level. People can participate equally in the value circulation of the global network. In the post-great navigation era of human history, this can be considered a remarkable feat.
Returning to the recognition of the universality of human values is the greatest value orientation of UBI.
Challenges and Controversies of UBI
UBI (Universal Basic Income) as a social welfare policy has some potential benefits. Firstly, UBI can provide economic security and alleviate poverty and inequality. By providing everyone with a certain amount of basic income, UBI can ensure that everyone has enough living expenses, thereby reducing the number of people living in poverty. In addition, UBI can also mitigate income inequality and make society more fair.
Secondly, UBI can promote innovation and entrepreneurial spirit. With a certain level of economic security, individuals can pursue their dreams and entrepreneurial opportunities more freely without worrying about economic risks. This will inspire people’s innovation and creativity and drive social progress and development.
Lastly, UBI can simplify the social welfare system and reduce administrative costs. Traditional welfare systems are often complex and require a large amount of administrative resources to manage and distribute. UBI, on the other hand, incorporates everyone into the same system, simplifying welfare management and reducing administrative costs.
However, UBI, as a new social welfare model, despite its many advantages and potential, also faces some challenges and controversies:
- Fiscal Feasibility: Implementing UBI requires a large amount of fiscal expenditure, including issues of funding sources and distribution. Some people are concerned that UBI could lead to fiscal deficits and inflation because funds need to be transferred from other social welfare programs to support UBI.
- Work Incentives: Supporters of UBI believe that providing everyone with a basic income can improve social fairness and people’s quality of life. However, some people worry that UBI could weaken people’s work motivation, leading to more people relying on welfare and being unwilling to work.
- Inequality Issues: Implementing UBI may result in wealth and income inequality. Some people worry that UBI could provide more income to the rich and relatively less assistance to the poor. Additionally, UBI may not address other social issues such as inequality in education and healthcare resources.
- Social Impact: Implementing UBI could have profound impacts on society. Some people are concerned that UBI could lead to social unrest and changes in people’s attitudes towards work. Additionally, UBI could have unpredictable effects on the labor market and economic structure.
In conclusion, the concept and practice of UBI have not yet been widely popularized and recognized, even in developed countries where its implementation is based on the social context of the pandemic. Once the pandemic is over, the Federal Reserve will decisively combat inflation to restore true socio-economic growth.
However, blockchain is a natural fit for UBI, especially from the perspective of DAO. Global collaboration, matching of labor types, smart contract and voting system management can all play important roles in promoting UBI. Taking PermaDAO as an example, let’s consider how the future UBI model should operate.
The Future Development Direction of UBI
The operation mode of UBI will be changed by blockchain technology.
With the continuous advancement of technologies such as AI, Web3, and DID, UBI will be reshaped from a technological paradigm.
- Blockchain technology innovation will change the way UBI collects and analyzes data. Traditional UBI practices mainly rely on centralized institutions such as governments, enterprises, or NGOs to allocate specific tasks. However, blockchain technology can use DID to verify people’s identities and maintain accounts and consensus by recording workloads on the chain, changing the previous unsustainable problems.
- AI will bring machines into all aspects of human life for the first time. In Altman’s view, one important trend is the power of AI, which is sufficient to meet the material needs of all humanity. Therefore, the fundamental problem is not to create more material increments, but to distribute wealth in a more moderate way. AI is based on algorithms and follows complete rationality, and what humans need is to ensure that their workloads are recognized by AI.
- Web3 will change the workflow and service model of UBI. Traditional UBI practices cannot solve the problem of funding sources and flows, that is, the phenomenon of transferring payments from developed countries to developing countries in the long run. People in developing countries cannot participate in the supply side and can only be passive recipients of donations. Once the funding chain is broken, the UBI model will quickly go bankrupt. Web3 will treat the workload of any group equally, no longer distinguishing by region, gender, or race.
Blockchain technology innovation will have a profound impact on the development of UBI. By changing the way data is collected and analyzed and thoroughly transforming the relationship between humans and material production through AI, UBI will truly have the potential for large-scale adoption in practice.
Conclusion
The development of UBI and the idea of “the world with great harmony” in the East, as well as the utopian thinking in the West, have underlying consistency. After being included in serious philosophical discussions and further developed into a practical economic proposition, a part of its ideology has been absorbed into the welfare system and widely recognized.
However, the operation mode of UBI itself is difficult to sustain in the long term, mainly due to the issue of income sources. In other words, UBI needs its own ability to generate income in order to break free from the charity of the rich or developed countries and operate independently.
Under the impact of the pandemic, the quantitative easing policies in Europe and the United States have stimulated the emergence of AGI-like OpenAI, and for the first time, there is the possibility of a reverse comparison between humans and machines. If AI can perform most of the work of humans, then where should the value of humans be sought?
The answer for most people may be hedonism, but it is also possible that in a society with highly developed material production, labor will become people’s primary demand. Of course, this will take a very long time to achieve.
We will continue to update Blocking; if you have any questions or suggestions, please contact us!
Was this article helpful?
93 out of 132 found this helpful
Related articles
- Andre Cronje The Lone Ranger’s Network Odyssey
- Popular Token Simple Rating CRV Achieves the Best Performance, OP Only Has Speculative Value
- Mixin’s aftermath of being stolen about 200 million US dollars Compensation plan includes bonds, Li Xiaolai’s Weibo questioned Where is the users’ money?
- Market value doubled within a year, will Azuki be knocked down How much longer can Pudgy Pengunis remain popular?
- Hot discussions among peers, uncovering the little-known stories of market maker DWF Labs and Lianchuang.
- Weekly Financing Report | 18 public financing events; Cryptocurrency gaming company Proof of Play completes $33 million seed round financing, led by Greenoaks and a16z.
- Weekly Notice | The deadline for FTX customers to submit claims will be September 30th; Bitget old users need to complete KYC verification before October 1st.




