20,000-word explanation of the RWA tokenization track: the next wave of the crypto narrative?
20K-word explanation of RWA tokenization as the next big thing in the crypto world.Author: Stefanie
Overview
Blockchain brings trust, liquidity, transparency, security, efficiency, and innovation. However, the bear market in the cryptocurrency industry seems to find it difficult to find new growth points. The cryptocurrency industry urgently needs a track to carry new narratives. RWA tokenization can open up the channel between traditional finance and cryptocurrency finance, carry trillions of dollars of asset markets, and can be the lifeblood that surpasses the bull and bear cycles for the cryptocurrency industry. Therefore, RWA tokenization, which the blockchain has been trying since its inception, has been hindered by multiple factors such as technology, regulation, and the market. Nowadays, the RWA track is being discussed again, and many institutions are starting to lay out. RWA projects have shown a variety of characteristics, mainly DeFi, high returns, and high risks. They have gradually entered the public’s field of vision, but there are still problems such as poor liquidity, early stages, and lack of price discovery in the overall project. Whether the RWA track can erupt in the next few years also depends on the development of infrastructure and the improvement of the regulatory system. This research report also proposes that token standardization and compliance are the only way for the development of the RWA track. Although the RWA track faces multiple challenges, industry development always moves forward. We have seen the emergence of many innovative projects, especially those based on US bonds and stocks, financing for small and medium-sized enterprises, and physical assets. These projects are mainly characterized by:
- Cooperation with traditional financial institutions;
- Maximizing the project and token’s income;
- Introducing more legitimate third parties.
These features can partially solve the problems encountered in RWA tokenization, including regulation, centralization, on-chain and off-chain identity, and asset valuation. We look forward to more projects enriching the RWA track in the future.
1. Brewing Narrative
After more than a year of bear markets, the market value of the entire cryptocurrency market has seriously shrunk, funds have continued to flow out, on-chain activities have withered, and DeFi income is no longer attractive, causing severe infighting within the market. At present, we cannot imagine what the cryptocurrency industry should rely on to start the next bull market. There is still a big gap between the cryptocurrency market and the traditional financial market. But we can also see huge business opportunities from some thunder events that occurred during the bear market.
- Looking back on the innovation path of DeFi, how did Uniswap evolve from a founder to a culmination?
- Ordinals protocol has been updated to version 0.6.2, which supports recursive inscriptions and brings randomness to inscriptions.
- Analysis of “Azuki” in Bear Market: Development Plan and Status
It can be said that the main reason that led to the bankruptcy of some large institutions in 2022 was the use of altcoins for financing and borrowing. When altcoins plummeted during the bear market, it further aggravated the settlement of loans, and the death spiral began. We see that it is institutions and credit that have driven the bull market in 2021, and it is also they who have contributed to the bear market in 2022. In fact, credit has driven business worth trillions of dollars and most of the development of the global economy. The potential it brings is huge. Currently, more and more protocols are entering traditional credit markets such as equity and debt financing in the DeFi market. Although it brings some risks, this is the only way to introduce traditional financial markets of more than 80 trillion US dollars into the chain. What we need to do is tokenize real-world assets to bridge the huge gap between the cryptocurrency market and traditional finance.
In the first half of this year, the traditional and crypto industries began to focus on the RWA sector.
First, Goldman Sachs announced the official launch of its digital asset platform GS DAP, which has already helped the European Investment Bank (EIB) issue a €100 million two-year digital bond. Soon after, private equity firm Hamilton Lane, which manages more than $100 billion in assets, tokenized part of its $2.1 billion flagship equity fund on the Polygon network and sold it to investors; and electrical engineering giant Siemens also issued €60 million in digital bonds on the blockchain for the first time. Second, some government agencies are also starting to dip their toes into RWA, including the Monetary Authority of Singapore (MAS), which is partnering with JPMorgan and DBS Bank.
In April, Binance announced that it had become a node operator for the Layer1 blockchain Polymesh. MakerDAO, Aave, Maple Finance and other DeFi protocols are also making frequent moves in the RWA field, and more crypto investment companies are seeking RWA projects. Currently, there are over 50 RWA projects, mainly in financial assets, including fixed income and TradFi, with a small number in real estate and carbon credits. Recently, concept tokens in the RWA sector have risen, with some gaining more than 10 times in value. Does the buildup in the first half of 2023 indicate that RWA will lead the crypto narrative in the coming years?
2. The Past and Present of RWA
The concept of RWA is not unfamiliar to the blockchain industry. The earliest RWA project was BTM Bytom Chain’s “asset on-chain”. Currently, the most successful RWA is the digital dollar USDT, USDC, which maps the dollar onto the chain and tokenizes it. Stablecoins have quietly influenced the entire crypto industry and have become an important cornerstone.
RWA stands for tokenization of real-world asset values, the process of converting ownership value (and any associated rights) of tangible or intangible assets into digital tokens. This makes the digital ownership, transfer and storage of assets possible without central intermediaries, and their value can be mapped onto the blockchain for trading. RWA can be tangible or intangible assets.
- Tangible assets include: real estate, artwork, precious metals, transportation, sports clubs, horse racing, etc.
Intangible assets include: stocks and bonds, intellectual property, investment funds, synthetic assets, revenue sharing agreements, cash, accounts receivable, etc.
2.1 Current Status of RWA Track
The RWA track has a wide variety of projects, mostly focused on DeFi, and can be classified into three main categories: 1. Fixed income projects based on off-chain assets such as US Treasuries, stocks, real estate, and art; 2. Public credit projects issued or traded on public markets; 3. Trading market projects based on virtual assets such as carbon credits. In addition, there are also infrastructure projects such as vertical public chains.
- Fixed income projects based on the US Treasury and stock markets provide loans to individuals and institutions. The only difference between these projects and other DeFi lending projects is that collateral can be real-world assets.
- Public credit projects can establish investment funds for crypto users by tracking US Treasuries or other bonds.
According to RWA.xyz, eight RWA lending protocols, including Centrifuge, Maple, GoldFinch, Credix, Clearpool, TrueFi, and Homecoin, have issued a total of $4.38 billion in loans, with an average APR of 10.52%. These credit lending protocols offer higher returns than most DeFi lending, but in the 2022 institutional default event, Maple Finance defaulted on $69.3 million in debt.
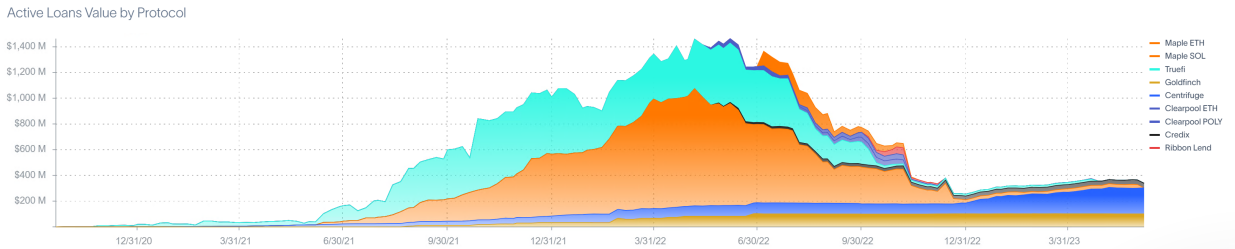
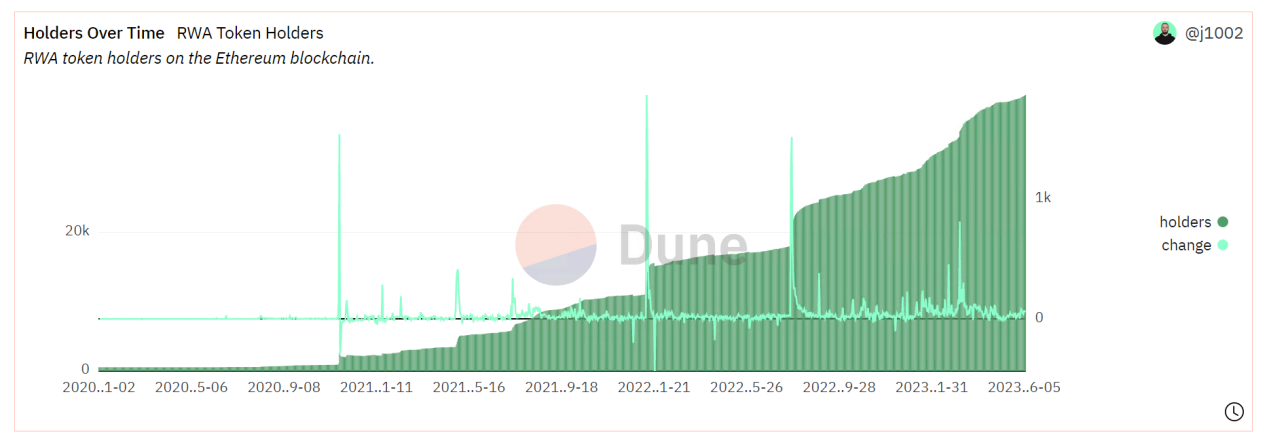
According to Dune Analytics, the number of holding addresses for RWA projects on Ethereum, including $wCFG, $MPL, $GFI, $FACTR, $ONDO, $RIO, $TRADE, $TRU, and $BST, is also increasing and has now reached 3.9k.
2.2 Benefits of Asset Tokenization
Ideally, any valuable asset can be tokenized. The advantages of asset tokenization are also based on the underlying decentralized and blockchain technology, creating some ecosystem applications to solve the shortcomings of traditional finance. Specifically:
(1) Bring a potential huge market and attract investors and individual investors
As leading financial institutions hope to benefit from the efficiency and economic potential brought by blockchain, the tokenization of real-world assets is being noticed by institutions, and some tokenization products have been developed. RWA projects will also stimulate investment returns in DeFi.
By tokenizing real-world assets, enterprises can access capital at a low cost via the DeFi ecosystem and benefit from lower entry barriers and new forms of financing, particularly for emerging markets. At the same time, the DeFi ecosystem gains new opportunities for investment returns, access to diversified off-chain markets, and expanding the customer base of traditional finance.
(2) Improving capital flow efficiency and promoting positive feedback of asset tokenization
The traditional financial trading market is labor-intensive, while blockchain technology can provide real-time settlement and 24-hour trading, reducing operating costs and market access for participants. Furthermore, asset tokenization can turn real-life assets with poor liquidity into small share portfolios, and investors do not require extensive paperwork, money, and time consumption. This creates a fairer market and creates new business and social models, such as shared property ownership or shared rights.
On the securities front, tokenization can be a useful tool for securitization or refinancing low-liquidity assets into more liquid security tools.
Bringing real-world assets onto the chain and into the DeFi ecosystem will bring unique collateral or investment opportunities, market efficiency, and liquidity that traditional markets cannot obtain. The improvement in capital efficiency will further promote the development of the RWA track and form a positive feedback loop.
(3) Lowering the entry barrier for retail investors and increasing the liquidity of physical assets
Tokenization eliminates the barriers that currently hinder the division of real-world assets, making it possible for most retail investors to access asset categories that are typically limited to some high-net-worth individuals or institutional investors, especially in physical assets. Retail investors can invest in cross-regional products or collectively invest in a property or a work of art, which would require extremely high barriers to entry in traditional finance. And these physical assets may have very low liquidity in small markets, but once they are on the chain, they will face investors from all over the world. In addition, issuers can access a wider range of investor groups and create new asset categories. Retail investors can enter previously inaccessible markets and make wiser investment decisions based on transparent data.
(4) Relying on the advantages of blockchain technology, RWA transactions are more efficient and secure
Blockchain technology ensures transparency, immutability of transaction records, higher efficiency and lower operating costs, more robust risk management, clear ownership, and more composability and fairer market environment. In the future, as blockchain technology continues to evolve, there will be higher-performance public chains or layer2 solutions, stricter smart contract audit mechanisms, and privacy projects based on zk technology to protect transactions, all of which provide a solid foundation for the development of the RWA track.
3. Prerequisites for the outbreak of the RWA track
The only key point of the RWA track is asset securitization. Solving this key point also requires two foundations, one is the improvement of blockchain infrastructure, and the other is legal supervision. Blockchain involves the interoperability, security, and privacy of various protocols and tokens. Legal supervision is whether there is corresponding legal and regulatory support for off-chain assets, on-chain identities, and so on. Many issues are being actively discussed, and two are mainly explored here: token standards and review systems.
3.1 Diversification of token standards
According to the on-chain token standards, Ethereum has ERC-721 and ERC-20, which correspond to the non-fungible NFT and fungible token standards, respectively. In traditional finance, asset attributes are diverse, including tangible and intangible assets. For use on the blockchain, we also need to create corresponding token standards based on the attributes of the assets to tokenize them. Fungible and non-fungible tokens have the following characteristics:
- Fungible tokens: They are interchangeable and each unit has the same market value and validity, which means that token holders can exchange assets with each other and be confident that their value is the same. They are also divisible, and assets can be split into as many decimal places as needed when issued, and each unit will have proportional value and validity.
- Non-fungible tokens represent unique value and have unique information and attributes. They are not interchangeable because each unit represents a unique value. Non-fungible tokens are usually indivisible, although there are some methods to split investment costs to provide partial ownership, such as in commercial real estate.
Most assets can also be represented by fungible token standards, while some assets, such as bonds and derivatives, may be better represented by non-fungible tokens. As the RWA project gradually gains popularity, more diverse forms may appear, and ERC-20 and ERC-721 alone may not be able to meet the needs of RWA tokenization. Many vertical public chain projects for RWA have already realized this and started to create standards that conform to RWA tokenization, such as Polymesh. From the current development of RWA projects, most of them are built on Ethereum, so developing more widely applicable ERC token standards is more practical. The currently discussed ERC-3525 may be more suitable for RWA tokenization, and more token standards may emerge in the future, especially after the baptism of BRC-20. We believe that the token standard that can serve RWA projects well needs to have the following two characteristics:
- Good operability and flexibility for the RWA token issuer, with the dual characteristics of ERC-721 and ERC-20;
- A certain degree of privacy to protect transaction information and user information.
3.2 Strict Review System
Safety is an important part of tokenizing real-world assets, especially when they are used as collateral sources. For RWA issuers and investors, it is important to conduct due diligence on DeFi protocols and prioritize technologies or services that provide collateralized loans, strict regulatory compliance, and high-quality open source code. RWA-related project teams may need to provide two necessary solutions:
- Avoid KYC / AML risks–conduct KYC (know your customer) or AML (anti-money laundering) checks on users and/or transactions on the platform. Avoid users from having potential interactions or transactions with opponents or political public figures listed on OFAC and other sanction lists directly or indirectly.
- Provide effective monitoring methods–products and services that monitor and detect suspicious activities of DeFi users.
Therefore, projects need to set up compliance teams to review and approve or reject user access to the platform based on customer identity, risk assessment, verification, and due diligence. In addition, continuously monitor customer activity to detect any suspicious activity or behavior that may involve fraud or money laundering.
4. Analysis of Representative RWA Projects
There are multiple subcategories in the RWA track, and in this report, we provide a detailed analysis of 19 representative RWA projects from multiple dimensions such as the tokenization mechanism, protocol status, token functionality and performance, protocol advantages, and risks. Through the analysis and summary of these projects, we can gain insight into the overall development and existing problems of the RWA projects, as well as their future potential.
4.1 US Treasury Bonds
(1) MakerDAO
In 2020, MakerDAO officially included RWA in its strategic focus and released guidelines and plans for introducing RWA. In addition to issuing the stablecoin DAI, Maker also expanded the types of collateral beyond ETH, including tokenized real estate, invoices, and accounts receivable. The main source of income for the Maker protocol is the borrowing interest and liquidation fines of stablecoin DAI.
Protocol Status: In terms of TVL, Maker is one of the top three DeFi protocols, ranking behind Lido and AAVE, and is the number one CDP (Collateralized Debt Position) protocol. Currently, it only operates on Ethereum. According to Defillama as of June 2, 2023, TVL is $6.29 billion, 30-day protocol income is $23.53 million, the treasury amount is $68.4 million, and the governance token $MKR has been listed on mainstream exchanges such as Coinbase, Binance, Kucoin, Kraken, OKX, Huobi, Bybit, and Gate, with a 24-hour trading volume of $13.58 million and a 30-day average trading volume of nearly $20 million.
Token Functionality: The $MKR token, as the governance token of MakerDAO, has poor price performance mainly due to weak protocol value capture ability, but it plays an important role in governance. The utility of $MKR tokens includes the following four aspects:
- Governance: MKR token holders have governance rights over the MakerDAO system. They can participate in voting and make decisions on important matters such as system parameters, risk management measures, and protocol changes. The voting results of token holders have an important impact on the development and operation of MakerDAO.
- Collateral stabilization: MKR tokens can be used as collateral in the MakerDAO system. When users generate stablecoins (such as DAI) by locking a certain amount of cryptocurrency (such as Ethereum), they need to pay a certain amount of MKR as collateral. This mechanism aims to ensure the stability and security of the system.
- System stability buyback: MKR tokens, as collateral, are also used in the system stability buyback mechanism. When the value of stablecoin DAI in the MakerDAO system falls and deviates from the anchored value of the US dollar, the system will automatically initiate the buyback of MKR tokens and destroy them to stabilize the system.
- Risk sharing: MKR token holders bear the risks in the MakerDAO system. If the system’s debt cannot be repaid or other problems occur, the value of MKR tokens may be affected. This motivates MKR token holders to participate in and supervise the operation of the system, ensuring the safety and stability of the system.
Protocol Advantages : 1. Based on the EVM and L2 ecosystems, the RWA protocol has a more loyal user base and stable network support compared to other public chains. 2. Institutional advantages have withstood the test of bull and bear cycles, including strict admission thresholds for collateral, excess collateral, and a sound auction system, which can ensure that DAI is pegged to the dollar at a ratio of 1:1 in most cases. In extreme cases, the protocol also has emergency shutdown measures.
Protocol Risks: 1. Governance attacks. Short-term large-scale convergence of MKR tokens may lead to the concentration of governance power, resulting in a series of governance attacks such as adding junk collateral, emergency shutdown, and malicious manipulation of risk parameters. With the increase in the value of MKR and sufficient risk control measures of the protocol, most of these risks can be prevented. 2. Market price risk. In the case of increased volatility of mainstream tokens, a series of protocol auction liquidations will actively increase the supply of tokens in the market, exacerbating market liquidity problems. This has happened frequently in the past two years when mainstream tokens experienced large-scale declines, but the protocol itself did not incur large-scale losses.
(2) Ondo Finance
Ondo Finance is one of the most watched RWA projects in the first half of this year. In April, it raised a $20 million Series A led by Founders Fund and Blockingntera Capital. Ondo Finance is a decentralized investment bank that mainly invests in US-listed money market funds off-chain and conducts on-chain stablecoin lending business in cooperation with Flux Finance, including USDC, FRAX, DAI, and USDT, with an average borrowing rate of around 5%. The protocol’s revenue comes from a 0.15% annual management fee.
Users need to go through the KYC/AML process before trading fund tokens and using these fund tokens in permitted DeFi protocols. Ondo Finance has launched four tokenized bond products for investors to choose from, including:
- US Money Market Fund (OMMF): Ondo Money Market Funds, which invest in high credit-rated US government bonds, short-term bonds, and other debt instruments, with the maximum goal of capital preservation and an annualized return of 4.5%.
- US Treasury Bonds (OUSG): Ondo Short-Term US Government Bond Fund, which invests in short-term US Treasury note ETFs, with an annualized return of 4.85% and $100.87M TVL.
- Short-Term Bonds (OSTB): Ondo Short-Term Investment Grade Bond Fund, an actively managed exchange-traded fund (ETF) that aims to maximize current income while ensuring capital preservation and daily liquidity. The ETF mainly invests in short-term investment-grade debt securities, whose average investment portfolio maturity usually does not exceed one year, with an annualized return of 5.77%.
- High Yield Bonds (OHYG): Ondo High Yield Corporate Bond Fund, which mainly invests in high-yield corporate bonds, with an annualized return of 7.9%.
Current situation of the agreement: TVL $100.5m on ETH, defillama RWA ranks first in classification. OUSG has the largest usage scale. OUSG holders can also deposit in Flux Finance, a decentralized lending protocol developed by Ondo Finance, to earn profits. Tzedonn, an investor of Tioga Capital, mentioned in the latest report that the existing market value of bond tokens is 168 million US dollars, and Ondo (OUSG) has a 61% market share, of which 28% is deposited in Flux Finance. Currently, the total supply of Flux Finance has exceeded 40 million US dollars, and the market value of OUSG has exceeded 100 million US dollars. The lending agreement FLUX has been sold to the Neptune Foundation.
Token functions: The governance token $ONDO has the following four functions:
- Platform fee payment: Users may need to pay certain fees when conducting transactions, borrowing, or other financial activities on the Ondo Finance platform, and these fees can be paid using Ondo Finance tokens.
- Voting rights and governance: Holders of Ondo Finance tokens can participate in the governance and decision-making process of the platform. They can vote on issues such as platform upgrades, parameter adjustments, and proposal approvals, and express their opinions and suggestions on the development direction of the platform.
- Rewards and incentives: The Ondo Finance platform may use token rewards and incentive measures to attract users to participate in platform activities and ecological construction. These rewards can be issued in the form of Ondo Finance tokens, encouraging users to contribute to and support the development of the platform.
- Borrowing and collateral: On the Ondo Finance platform, users can use Ondo Finance tokens as collateral to obtain borrowing services. Users who hold Ondo Finance tokens can use them as collateral to obtain more borrowing quotas or lower interest rates.
Protocol advantages: Compliance – products are either low-risk US government-related debt instruments or high-risk ETFs, all of which are compliant products with third-party accounting disclosures. At the same time, users also need to go through KYC/AML procedures.
Protocol risks: 1. Off-chain risks – the main products are off-chain ETFs, US government debt instruments, etc., compliance can be guaranteed but may also bring external market risks, credit risks, etc., especially high-risk corporate bonds such as OHYG; 2. Exiting risks – the project is currently peeling off decentralized products and turning to operate in a centralized and compliant direction. The use of governance tokens may be stripped and marginalized, and blockchain technology may only be used for item profit sharing, accounting, and selling share purposes without developing towards the overall decentralization direction, which is contrary to the purpose of most projects in the cryptocurrency circle.
(3) Maple Finance
Maple Finance Protocol has been developed for three years, and its main business is lending/institutional credit loans. The on-chain business provides lending services for USDC and wETH, but the lending business is managed by independent centralized pool managers, including borrowers, credit limits, interest rates, and strategies. Although Maple Finance does not seem to be a qualified RWA project, in April it announced plans to launch a loan pool for investment in US Treasury bonds, allowing non-US DAOs, offshore companies, etc. to invest in funds restricted by Maple Finance.
Protocol Revenue: Maple Finance’s revenue mainly comes from the following aspects,
- Lending fees: Maple Finance charges borrowers a certain amount of lending fees by providing funds. These fees are calculated based on the loan amount and loan term and depend on the interest rate set by the lending pool.
- Loan processing fee: As a platform provider, Maple Finance can charge fees related to loan transactions. These fees may include loan application fees, loan disbursement fees, and loan settlement fees.
- Token mining rewards: Maple Finance may distribute rewards to participants through token mining mechanisms. Users holding Maple tokens can earn rewards by providing liquidity or participating in lending pools.
- Platform governance fees: As managers of lending and borrowing pools, Maple Finance may charge a certain percentage of platform governance fees. These fees are used to support and maintain the platform’s operation, including developing new features, conducting security audits, and maintaining community governance.
Protocol Status: In terms of TVL, Maple Finance ranks 145th on defillama, but it is the number one unsecured loan protocol, with a total TVL of $48.56m, on-going debt of $32.22m, and cumulative earnings of $45.6m. There are 18 on-going debts (since the provided credit guarantee debt is centralized, the borrowers are large institutions, and the number is small), and 8 cash pools (7 USDC + 1 ETH, with an average 30-day yield of 7% annualized). In addition, Maple Finance also has a small amount of TVL on Solana, but with the decline of on-chain activities on Solana, the current TVL is only about $16.4k, and most (99%) of the TVL comes from the ETH main network.
Token Functionality: MPL token is the native token of the Maple Finance platform, with the following functions,
- Payment fee: MPL tokens can be used to pay for transaction fees when borrowing and lending on the Maple Finance platform. Users who hold MPL tokens may enjoy discounts or other benefits to encourage their use and holding of the token.
- Community governance: MPL token holders can participate in governance decisions on the Maple Finance platform. They can propose, vote, and express their opinions, influencing the platform’s development direction and important decisions.
- Voting rights: MPL token holders have certain rights in voting on the platform and can participate in decisions on protocol parameters, protocol upgrades, and other important matters.
- Share dividends: Users who hold MPL tokens are eligible to share profits from borrowing and lending pools on the Maple Finance platform. These profits may come from interest paid by borrowers or other sources of income, distributed proportionally to MPL token holders.
- Incentive mechanism: The Maple Finance platform may provide incentives to MPL token holders to promote the development of its ecosystem. These incentives may include airdrops, rewards, or other forms of returns to encourage users to participate in and support the platform’s growth.
Protocol advantages: There is a certain degree of security, and the borrowing and lending risks are managed by the pool manager, who charges a certain management fee as a return. Liquidity providers can enjoy borrowing and lending rates while assuming smaller default risks.
Protocol risks: 1. Credit risk, the pool manager and borrower are audited by centralized institutions, and the debt is mainly based on credit collateral rather than asset collateral (the collateral assets come from the pool manager), so once there is a large-scale institutional default, there may be a situation of insolvency; 2. High threshold, in order to ensure the safety of the debt, the borrowing threshold is relatively high, not suitable for most users, so the community is not very active.
4.2 TradFi
(1) Polytrade
Polytrade is a decentralized trade financing platform designed to provide seamless loans to businesses in multiple industries. Currently, the project is transitioning from V2 to V3. Since January 2022, there have been no debt defaults, and LP losses are 0. The NFT function of real-world assets is expected to be added to V3, and a secondary NFT trading market may be available in the future.
Current status of the agreement: The governance token TRADE has been listed on exchanges such as Kucoin, Gate, MEXC, and Bitfinex, with the main trading pair on MEXC. The TVL of the project on defillama is only $10,984, which is far from the fully unlocked market value of the project token of $17.27m, indicating a high risk of overvaluation. On March 30, 2023, the project raised $3.8m in seed funding from companies such as Polygon Studios, Matrix, CoinSwitch, and Alpha Wave Global.
Token function: TRADE is the governance token of the project, mainly used to vote and make decisions on protocol revenue and updates. More detailed token functions may be disclosed after the release of V3.
Protocol advantages: 1. Lower transaction costs on the Polygon network, with natural EVM advantages in terms of gas fees, transaction speed, and other factors. 2. Advantages in the market, with official support from Polygon, which is expected to maintain a competitive advantage on the Polygon EVM.
Protocol risks: 1. Credit risk, although lending transactions are conducted on the chain, the borrowers, business, and audit processes are all off-chain, and the project claims that transactions are protected by institutions such as AIG and Mercury, but offline defaults cannot be avoided. 2. Technical risk, the project is in the process of migrating from V2 to V3, and the protocol code has not yet provided third-party audit reports, so there may be unknown technical bugs in the code.
(2) Defactor
Defactor aims to provide financing opportunities and liquidity to businesses by linking traditional financing with DeFi. The project is still in its early stages and has not yet been launched. According to its roadmap, it is still in the stage of investment, recruitment, and development in the second half of 2023. According to the project’s website, $FACTR is the native token of the defactor ecosystem, which aims to lower the barriers to entry for applications and infrastructure. It can coordinate interests and incentivize ecosystem growth.
4.3 Lending
(1) Goldfinch
Goldfinch is a decentralized credit protocol for debt funds and fintech companies serving offline entities, similar to Maple Finance. Goldfinch offers zero-collateral USDC credit line loans. Goldfinch’s model is similar to that of traditional banks, but with decentralized auditors, lenders, and credit analysts. Borrowers can exchange USDC for fiat currency and deploy it to the final borrower in the local market. Before applying for a loan, borrowers must obtain the approval of the protocol’s decentralized auditors. The auditor is an independent entity that must pledge governance token GFI to verify borrowers in exchange for rewards.
Source of Protocol Income: 10% of all interest payments made by Goldfinch are reserved in the protocol treasury. Additionally, there is a 0.5% fee charged on redemptions from the junior pool which is also deposited into the protocol treasury.
Protocol Status: Currently, the total outstanding principal of all loans in the Goldfinch protocol is $101.34 million with a total loss rate of 0%. The total principal and interest paid back is $25.1 million. In the last 30 days, the protocol generated $100,100 in revenue. There have been no defaults to date.
Token Functionality: Goldfinch currently has two native ERC20 tokens, GFI and FIDU.
- GFI is the core native token of Goldfinch and can be used for governance voting, auditor staking, auditor voting rewards, community grants, supporter betting, protocol rewards, and can be deposited into the member treasury for membership rewards to ensure the protocol’s development.
- FIDU represents the deposits of liquidity providers into the junior pool. When liquidity providers deposit funds into the junior pool, they receive an equivalent amount of FIDU. FIDU can be exchanged for USDC in the Goldfinch dApp at a rate based on the net asset value of the junior pool minus a 0.5% withdrawal fee. Over time, the exchange rate of FIDU increases as interest payments accrue in the junior pool.
Protocol Advantages: The mechanism used reduces borrowing thresholds and can help users with lower credit ratings obtain loans to some extent. Compared to traditional platforms, Goldfinch has stronger usability, with the process mainly handled by smart contracts.
Protocol Risks: The adoption of DeFi is global, but different laws in different countries may lead to higher costs and problems for Goldfinch’s business. Also, because there is no collateral, there is a risk of default in the Goldfinch junior pool.
(2) Centrifuge
Centrifuge was launched in 2017 and is one of the earliest DeFi projects to enter the RWA space. It is also a technology provider behind leading protocols such as MakerDAO and Aave. Similar to the above lending protocols, Centrifuge is also an on-chain credit ecosystem aimed at providing a way for small and medium-sized business owners to collateralize their assets on-chain and obtain liquidity.
Centrifuge allows anyone to launch an on-chain credit fund and create a collateralized loan pool. Centrifuge has created Tinlake, an open asset pool based on smart contracts. Borrowers can tokenize real-world assets using Tinlake. The physical collateral is split into two types of tokens, DROP and TIN, based on risk and return, representing fixed interest rates of higher priority and floating interest rates of lower priority, respectively. Investors can choose to invest in DROP or TIN based on their risk tolerance and return expectations. Currently, the Centrifuge protocol does not charge any fees.
Project Status: On May 23, Centrifuge announced the launch of its new Centrifuge App to replace Tinlake. The new Centrifuge App improves KYC and investment participation speed and adds KYB (Know Your Business) process automation, laying the foundation for future multi-chain support. Tinlake will be automatically migrated to the new application. According to official data, the current TVL of Centrifuge is $201 million, and the total amount of financing assets is $397 million.
Token Functionality: The native token CFG of the Centrifuge Chain is used as an on-chain governance mechanism, and CFG holders can manage the development of the Centrifuge protocol. At the same time, CFG is also used to pay transaction fees on the Centrifuge Chain.
Project Advantages: 1. Low financing threshold, while allowing investors to earn income from real assets. Centrifuge essentially simulates the enterprise credit process in traditional finance; 2. Committed to compliance, Centrifuge is built on the legal structure of US asset securitization.
Project Risks: Risk of loan overdue default. According to rwa.xyz data, Centrifuge has $10,194,481 in loans overdue for more than 90 days.
Clearpool: Clearpool is a DeFi lending protocol that provides unsecured loans to institutions. Clearpool has two products, Prime and Permissionless. Clearpool Prime is only available to whitelisted institutions, and collateral is not required for Prime lending. Borrowers create a funding pool with specific terms in the core smart contract. Once the pool is created, borrowers can invite any other whitelisted institutions to provide funding to the pool. The loan assets are automatically transferred directly to the borrower’s wallet address without the need for Clearpool custody. Clearpool Permissionless requires the borrower to be a whitelisted institution, but there are no requirements for the lender.
Protocol Revenue: Clearpool charges a 5% protocol fee on all interest payments received.
Protocol Status: Clearpool has generated a total of $398 million in loans and currently has an outstanding balance of $16.58 million and Permissionless TVL of $20.78 million.
Token Functionality: CPOOL is the utility and governance token of Clearpool. CPOOL holders can vote on the whitelist of new borrowers.
Protocol Advantages: Clearpool’s advantages lie in the fact that it does not require collateral and its loans are issued solely through the protocol, greatly improving efficiency.
Protocol Risks: Without collateral, if the market environment worsens, Clearpool’s current whitelist and credit scoring mechanism may not be able to prevent borrower defaults.
4.4 Public Fixed Income
(1) Swarm Markets
Swarm Markets provides compliant DeFi infrastructure for RWA token issuance, liquidity, and trading, and is supervised by German regulatory authorities. Swarm Markets tokenizes US Treasury bills and stock tokens. By issuing entity SwarmX to acquire publicly traded stock securities as the underlying asset for on-chain tokens, these assets are held by institutional custodians.
Protocol Revenue: Swarm will receive 25% of pool exchange fees or 0.1% of exchanged assets (whichever is greater).
Protocol Status: Swarm currently offers TSLA (Tesla), AAPL (Apple) stocks and TBONDS01 (iShares Asco US Treasury Bond 0-1 Year ETF), TBONDS13 (iShares Asco US Treasury Bond 1-3 Year ETF) bond ETFs. On April 25th, Swarm officially announced the launch of BLK (BlackRock), COIN (Coinbase), CPNG (CouBlockingng), INTC (Intel), MSFT (Microsoft), MSTR (MicroStrategy), NVDA (Nvidia) stock tokens.
Token Functionality: $SMT is the native token of Swarm Markets, which enjoys transaction discounts and rewards. When traders choose to pay with $SMT, they can get a 50% reduction in protocol fees. $SMT holders can enjoy loyalty rewards, the specific ratio of which will vary according to different levels. Similar to the concept of platform coins on centralized exchanges.
Advantages and Risks of the Protocols: Swarm’s advantage lies in providing more choices for DeFi users, combining blockchain and traditional assets, and blending TradFi with DeFi. However, Swarm currently offers few stocks and bonds, and its depth cannot compare with traditional markets.
(2) Acquire.Fi
Acquire.Fi is a crypto M&A market that provides real-world returns for fractional ownership of crypto companies, traditional businesses, and real-world assets to everyone. At Acquire.Fi, equity will be NFT-ized and can be bought and sold on the secondary market. Sellers, buyers, and investors in the pool all need to go through KYC (subsequently, investments below $250 may not require KYC).
Protocol Income: Acquire.Fi uses a multi-tiered commission structure. For business values below $700,000, commission will be fixed at 15% of the sale price. Between $700,000 and $5,000,000, commission will be reduced to 8%. Commission for values exceeding $5,000,000 will be further reduced to 2.5%.
Protocol Status: Currently, Acquire.Fi’s market offers a wide range of companies selling equity in various sectors such as NFT market, Metaverse, media, DAO, etc. According to official statistics, over 2k online business sales have been completed.
Token Functionality: $ACQ is the utility token of Acquire.Fi. Staking $ACQ allows for exclusive access to investment pools, crypto M&A transaction flows, LP mining rewards, and other exclusive benefits.
Protocol Advantages: Using Acquire.Fi for online business sales eliminates the need to purchase additional services or contact website hosting providers, while also receiving more attention. Compared to other platforms, it has the advantage of being more convenient and faster.
Protocol Risks: There are still legal risks associated with M&A or purchasing equity through Acquire.Fi, especially when the buyer and seller are not within the same legal entity scope.
4.5 Summary of Financial Products
Lending protocols are the most successful example of RWA projects. The unsecured lending model was welcomed by institutions during the bull market, but it also served as a catalyst for the bear market, so the most difficult part of credit protocols lies in default risk. Projects based on US bonds and stocks are more mature, and users can also get higher returns in bear markets. TradFi projects are relatively few, and the business is currently still focused on financing for small and medium-sized enterprises.
The development space for institutional credit business is very limited, and user benefits mainly come from stablecoins + protocol tokens. Due to inadequate collateral, borrowers need to bear a certain amount of bad debt risk. In the bull market phase, the risk-free return of DeFi is also high, so institutional credit business may not be sustainable.
Similar to the national bonds or currency funds launched by Ondo, we believe that they are potential directions for the future. First, these funds are popular choices for investors in traditional finance and have low risks. Second, they provide different choices for on-chain users while reducing entry barriers.
Although RWA projects in the financial sector are in the early stage, there are already many interesting use cases. With the enhancement of the combinability of various protocols, many gameplay and high-yield projects may be generated, which is a sub-track worth looking forward to.
4.6 Real Estate Concept
(1) RealT
RealT is a real estate tokenization platform founded in 2019, mainly serving real estate projects in Detroit, Cleveland, Chicago, Toledo, Florida and other states in the United States. Investors can purchase RWA tokens to invest in real estate. So far, the platform has processed more than 52 million U.S. dollars and tokenized real estates of 970 houses.
The protocol has no native ecosystem tokens and uses $DAI (XDAI/WXDAI) for value exchange within the ecosystem. Realtokens are issued for each real estate asset as collateral to obtain rental revenue sharing.
Tokenization packaging process:
- Off-chain: The third-party property management agency confirms the ownership of the property based on the property contract, and divides the member rights into equal units. Tenant rent is exchanged for US dollars through property management services. Legal support: RealToken submits a file to apply for a securities exemption under the U.S. Securities Act D and S regulations, and cannot provide or sell RealToken within the United States or for the benefit of Americans.
- On-chain: RealToken investors need to use stablecoin DAI deposit and loan services through the RMM application (RealT market maker) to exchange realtokens as collateral according to the oracle price. On-chain, DAI is sent to the digital wallet address of the relevant RealToken for daily payment in the form of 1/30 of the total DAI amount.
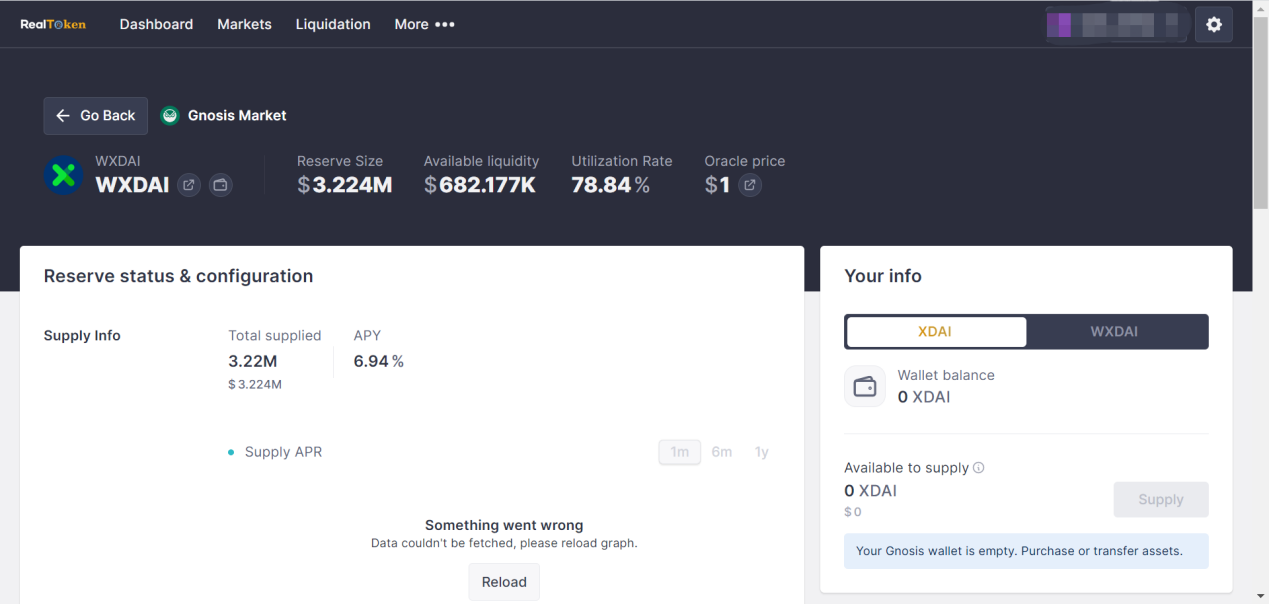
Protocol Revenue: No specific revenue model found. Possible revenue sources include DAI fund pool storage and lending interest rate differential, off-chain on-chain rent extraction.
Protocol Status: Current protocol market size is $10.51m, XDAI total supply is $3.224m, supply APY is 6.94%, total borrowing is $2.54m, and borrowing APY is 9.93%. There are 40+ real estate properties available to invest in within the protocol’s market.
User Income Status: There are 17 people who earn more than 1k DAI in weekly rental income, with the highest income being 6187.83 DAI/week.
Protocol Advantages: Since its launch in 2019, the protocol has maintained a market size of millions of dollars with consistent cash flow income.
Protocol Risks: Due to the impact of real estate leasing market prices and supply-demand relationship, there may be differences between expected rental income and actual rental income.
(2) Tangible
Tangible is an RWA tokenization project that provides users with a way to access RWA tokenization by launching a native revenue stablecoin, Real USD. RWAs include but are not limited to art, fine wine, antiques, watches, and luxury goods.
Tokenization packaging process:
- Off-chain: There are four tokenization product categories available on the platform, including gold, wine, watches, and real estate.
- For the transaction and storage of gold bars, Tangible uses the services of Swiss company PX Precinox.
- For wine, they work with London-based Bordeaux Index.
- For watches, they cooperate with BQ Watches based in the UK.
- For real estate, Tangible has created native special purpose entities (SPVs). These are legal entities set up for each property. The SPVs manage the property by finding tenants, collecting rent, or managing repairs. All properties are rented out, and rental income is paid to TNFT holders in USDC form.
- Legal support: Each UK property has its own UK SPV. This is because real estate cannot be directly tokenized. However, legal entities can be. Real estate TNFT holders have beneficial ownership of the SPV, giving them beneficial ownership of the real estate. However, the legal ownership of both remains with Tangible’s legal entity (i.e., BTS TNFT Ltd., registered in the UK. Tangible has also registered a similarly named entity in the British Virgin Islands).
- On-chain: Tangible has launched a native revenue stablecoin, Real USD (USDR), supported by real estate. Users can mint USDR at a 1:1 ratio using TNGBL or DAI. On Tangible, users can use USDR to purchase valuable physical goods, including but not limited to art, fine wine, antiques, watches, and luxury goods. When users purchase RWAs listed on Tangible, they will mint TNFT (“Tangible non-fungible token”), which represents the physical item. Tangible will store the physical items in a physical insurance vault and send the TNFT to the buyer’s wallet. TNFT can be freely transferred and traded.
- Overcollateralization method and liquidation mechanism:
- If the CR of USDR falls below 100%, half of the rent income will be kept in the USDR collateral pool. Therefore, daily rebalancing will decrease by 50%. In other words, USDR holders will earn less interest until the CR returns to 100%.
- The treasury that supports USDR always holds a diversified portfolio of liquid assets for quick liquidation (e.g., DAI, all protocol liquidity, and TNGBL).
- If all DAI and other reserves are exhausted, the real estate TNFT will be liquidated. In this case, users will receive pDAI instead of real DAI. pDAI is an IOU Token that represents a claim to real DAI and can be redeemed once the liquidation is executed.
Protocol income: TNFT owners need to pay storage fees. For example, the storage fee for gold bars is 1% per year. The transportation fee must be paid by the redeeming TNFT holder.
Protocol status: Protocol TVL $33,665,846, total collateral price $35,367,224. According to the USDR white paper, its collateral structure should be as follows: 50-80% tangible real estate; 20-30% tokens; 20-30% protocol-owned liquidity; 5-10% insurance fund; 0-10% TNGBL. The actual USDR collateral structure is quite different from the proposed collateral structure.
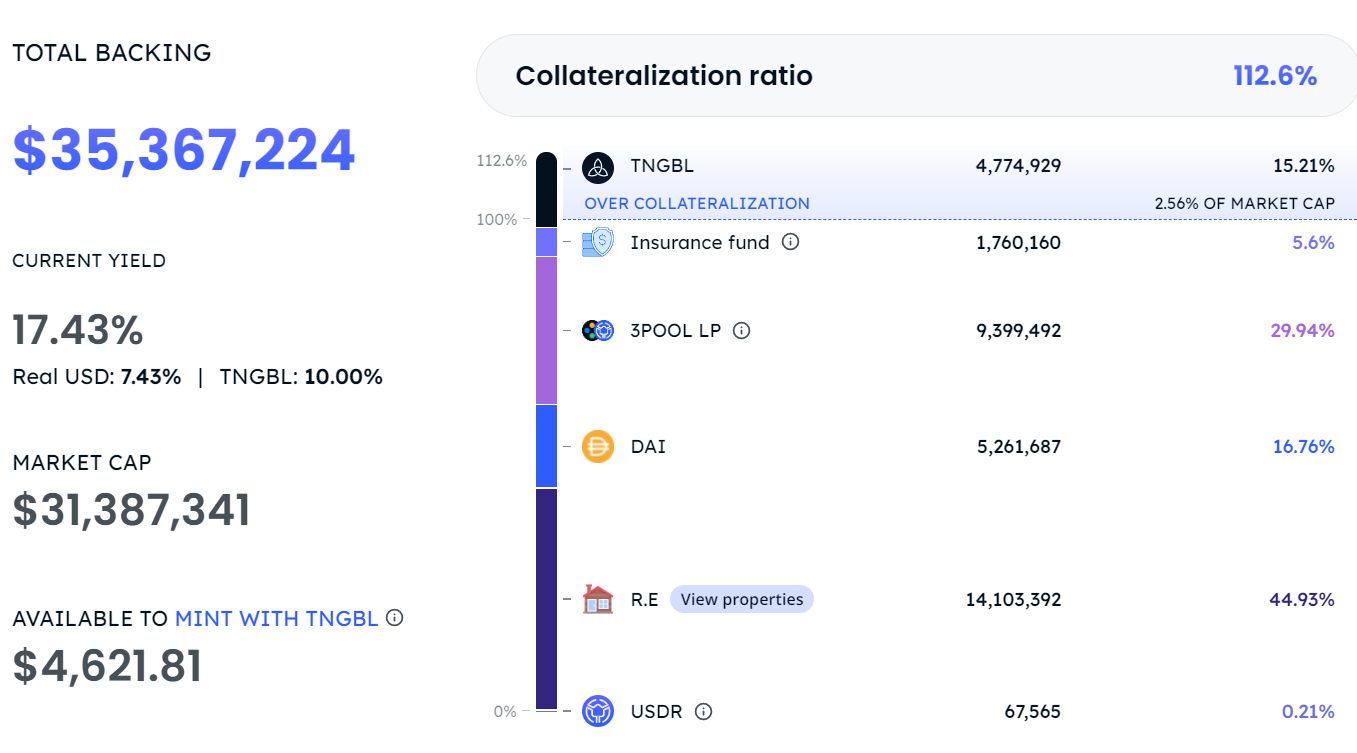
Token function: $TNGBL passively earns USDC after locking in minted NFTs; serves as reward tokens to incentivize the use of the market and subsidize USDR income; can be used to mint USDR.
Token secondary market performance:
- $TNGBL only circulates on Uniswap, without support from centralized exchanges, and has poor liquidity. The daily trading volume is mostly a few hundred to thousands of dollars, and the highest daily trading volume in history is $32,000. The project’s market value is $110 million, and there are 1,021 on-chain addresses holding the token.
- The stablecoin USDR has a decent trading volume since its launch at the end of March. It has been listed on multiple DEXs and supports ETH, BSC, Polygon, Optimism, and Arbitrum. The 30-day average daily trading volume is $0.7 million, the price is above $1, and the current price is $1.053.
Advantages of the Protocol: Building the TNFT market and obtaining a large amount of circulating token lockups, as well as introducing the purchase of other physical goods, including art, fine wines, antiques, watches, luxury goods, etc.
Risks of the Protocol: SDR anchor risk. Centralization risk, the team is both the issuer of TNFT and the custodian of the underlying assets.
(3) LABS Group
LABS Group was originally positioned as a real estate tokenization platform that allows homeowners to tokenize their homes to raise funds without intermediaries, and investors can also access other higher liquidity real estate tokens through the secondary market. Currently, LABS Group has launched a Web3 vacation platform Staynex, which provides members with the right to use global resorts every year and can earn rewards by holding membership status. By tokenizing “check-in” with blockchain technology and embedding it into NFTs, hotels and resorts can create, design, and cast their own timeshare plans on NFTs, and NFTs represent member identity and accommodation days.
Due to cross-border investment, LABS Group’s exchange was approved by the government after submitting a complete set of business plans. LABS Group has obtained compliance licenses for retail investment.
Protocol Revenue: LABS Group’s primary platform, secondary exchange, and decentralized lending platform can obtain various business income such as consulting fees, transaction fees, listing fees, and handling fees.
Protocol Status: The vacation industry is rich in resources, with 60 hotels and cooperation with Arsenal Football Club as its official member platform for hotels. Currently, LABS Group is the best-performing project in the real estate RWA track. $LABS has received support from centralized exchanges such as kucoin, gate, and bitmart. It received high attention when it was listed in March 2021 and had a single-day trading volume of more than $35 million at the beginning of the listing. The trading heat has since declined, with a single-day trading volume of less than $100,000 in the past year, a market value of $1.47 million, an FDV of $6.66 million, and 11,911 on-chain holding addresses.
The community has a high level of activity, with 58,000 followers on Twitter, 19,000 followers on Telegram, and 511 online users.
Token function: The token primarily serves as a reward token, and other functions include governance (voting), buyback and burn mechanism, with a planned 80% burn, of which the first phase is 50%. In addition, 10% of each transaction on the platform is sent to the liquidity pool for permanent locking. There have also been phased staking activities in the past, such as staking $LABS to predict football matches (https://www.support2win.io/), which has ended.
Protocol advantages: It adopts the time-sharing vacation mode, which means that a person has the right to use a certain vacation asset during a specific period of time each year, which is very popular in today’s digital nomad culture. In addition, the team has its own vacation industry resources, with 60 hotels and cooperation with Arsenal Football Club as its official hotel member platform.
Protocol risks: Poor capture of token value, mainly used as rewards, and the main empowerment is on NFTs. And time-sharing vacations have their own disadvantages: high annual management fees, difficult sales, unethical players, and fraud.
Summary
Currently, the overall market size of real estate projects in RWA is very small, with a lack of liquidity and poor mechanism transparency. It requires large centralized entities to endorse and regulate, and the practical tokens issued by related protocols are generally poorly accepted in the encryption market. This is mainly due to the fact that physical assets need to be strictly regulated, and the project party also needs to perform complex operations on the ownership of assets.
Tokenization of real estate can solve: 1. The cross-regional and real-time trading of blockchain can solve the problem of low liquidity of existing real estate; 2. The threshold is low, and retail investors can also invest in real estate globally and obtain profits. However, the most difficult problem to solve in the tokenization of real estate is the proof and valuation of real estate, and the proof determines the authenticity of real estate information, and the valuation determines the price of loans and clearing. The Tangible project has boldly tried in these aspects: using the Chainlink oracle to price RWA tokens, the information of the oracle mainly comes from the price provided by hometrack.com; in terms of real estate authenticity, Tangible uses a third-party auditor to independently verify the ownership of the property. In these projects, we can see that third-party participation is still needed before real estate is on the chain, including evaluation, finance, and legal related institutions. All of these require process compliance and legal perfection.
4.7 Concept of Carbon Credits
Carbon credits refer to the amount of carbon dioxide that a company has reduced or offset through the Verified Carbon Standard (VCS) certification process, similar to the “voluntary emission reduction (VER)” in China’s carbon trading system.
(1) Toucan
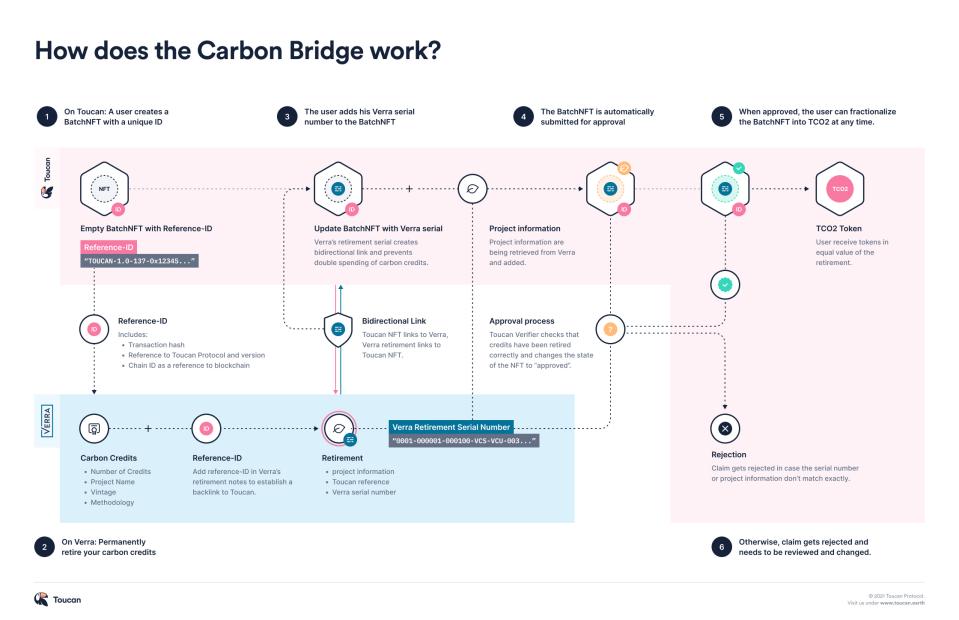
Toucan Protocol is a protocol deployed on Polygon that aims to convert carbon credits into tokens to promote carbon credit transactions through decentralized financial means and ultimately achieve carbon neutrality. The carbon credits traded by Toucan Protocol come from carbon offset credits registered on Verra. Verra is a non-profit organization that registers carbon credits.
Tokenization Packaging Process:
The Toucan carbon stack consists of three modules: Carbon Bridge, Carbon Pools, and the Toucan registry.
- Carbon Bridge
Anyone can bring their carbon credits onto the chain through Carbon Bridge. Toucan only supports carbon credits that have been exited from the Verra registry, and Carbon Bridge is an irreversible one-way bridge.
- A BatchNFT representing a batch of carbon credits is minted at the beginning of the bridging process.
- The carbon credits to be tokenized are permanently exited from the Verra registry and assigned a unique serial number.
- The received serial number is written into the BatchNFT, linking it to the exit record in the original registry.
- After the BatchNFT updates the serial number, it is automatically submitted for review.
- After approval by the Toucan Verifier, the batch of carbon credits becomes fully tokenized, and users can fragment it into ERC20 tokens TCO2 at any time.
BatchNFT can be used to mint an equal number of fully fungible ERC20 tokens TCO2, with 1 TCO2 token representing 1 carbon credit, and its value is 1 tCO2e.
The TCO2 token contract still carries all the attributes and metadata of an NFT, making it specific to a particular project and year, as the trading price of voluntary market carbon credits varies greatly. TCO2 is the general term for fungible tokenized carbon credits. When you fragment BatchNFT, the ERC20 token will have TCO2- as a prefix, followed by an informative name that includes the original registry, project, year, etc. For example: TCO2-GS-0001-2019.
- Carbon Pools
- Exchange fee for Carbon Pool tokens
- Bridging fee for carbon pools
- Protocol status
- Token functions:
Carbon Pools bundles tokens of TCO2 from multiple specific projects into more liquid carbon index tokens, achieving price discovery of different categories of carbon assets. Each pool has a unique configuration and specific logic that indicates which tokens TCO2 can be deposited into. The Toucan team has partnered with KlimaDAO to deploy the first Carbon Pool, the Base Carbon Tonne (BCT), which requires that TCO2 tokens must be Verra VCU (Verified Carbon Units) and that their vintage must be 2008 or later. TCO2 tokens that pass the logic filter can be pledged in the Carbon Pool, and depositors receive Carbon Pool tokens (such as BCT). Users can redeem at any time, with redemption burning the Carbon Pool tokens and sending the underlying tokens to the user. Automatic redemption (exchanging the lowest-ranked TCO2) and selective redemption (redeeming specified TCO2 for a fee) are available at redemption.
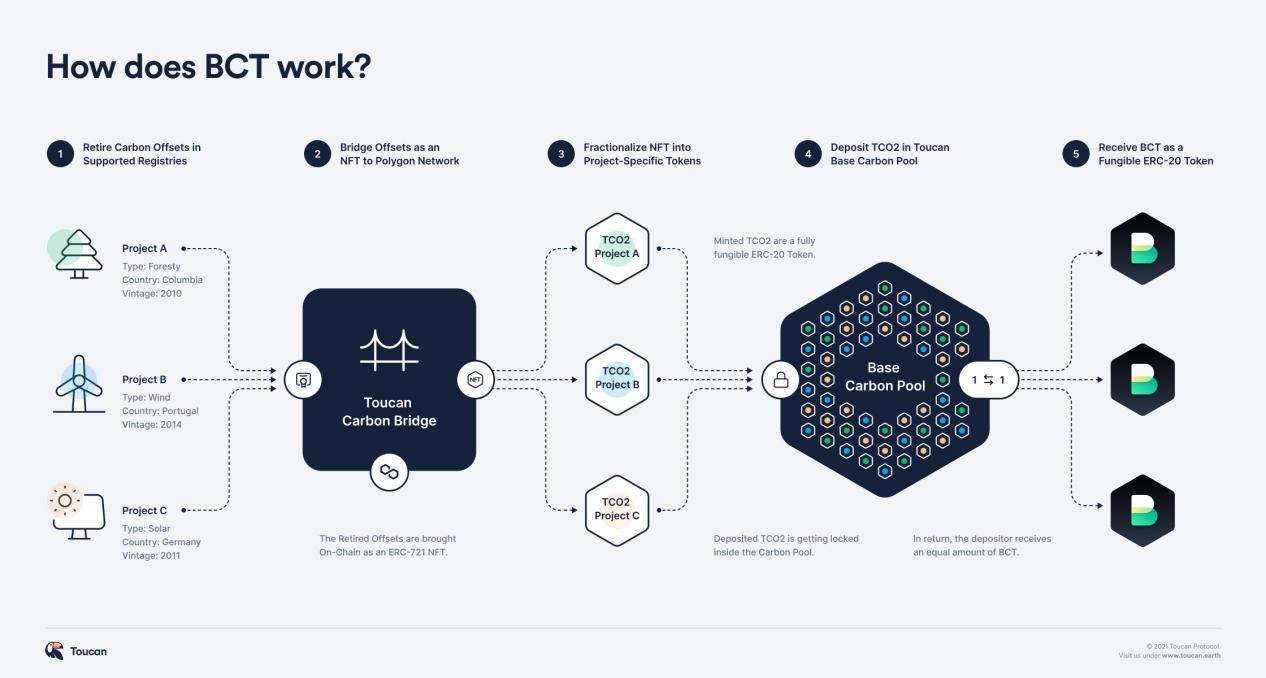
There are currently two Toucan Carbon Pools, BCT (Base Carbon Tonne) and NCT (Nature Carbon Tonne).
Toucan Protocol charges a fee when exchanging Carbon Pool tokens. Part of this fee is used to burn low-value carbon credits, while the other part is given to Toucan to build the protocol. The exchange fee for the BCT pool is 25%, and for the NCT pool, it is 10%.
Currently, this fee is set to 0.
Toucan was launched in October 2021 and currently supports Polygon and Celo. Carbon credits worth 21,889,951 tons have been uploaded to the blockchain through Carbon Bridge, offsetting 298,173 tCO2e of carbon credits, with a carbon supply of 19,908,799 (the amount pledged in the BCT and NCT pools) and total liquidity of $2,946,585 (total liquidity of BCT and NCT on various exchanges).
NCT is an abbreviation for Nature Carbon Tonne, a standardized reference token tied to all carbon credits deposited in Nature Carbon Tonne.
BCT is an abbreviation for Base Carbon Tonne, a standardized reference token tied to all carbon credits deposited in Base Carbon Tonne.
Staking TCO2 tokens that have been screened through logic in the carbon pool will earn corresponding tokens; conversely, both tokens can be used to exchange for tokenized carbon credits.
Protocol Advantages: To some extent, it realizes the tokenization of carbon credits and improves the liquidity of carbon credits.
Protocol Risks: Toucan Carbon Bridge is an irreversible one-way bridge, and the tokenization process cannot be redeemed for actual off-chain credits; Verra Registry currently does not support the marking of carbon credits and prohibits practices based on the creation of tools or tokens for exiting credits. Toucan’s choice to exit from the original registry to prevent duplicate calculations is not the best solution.
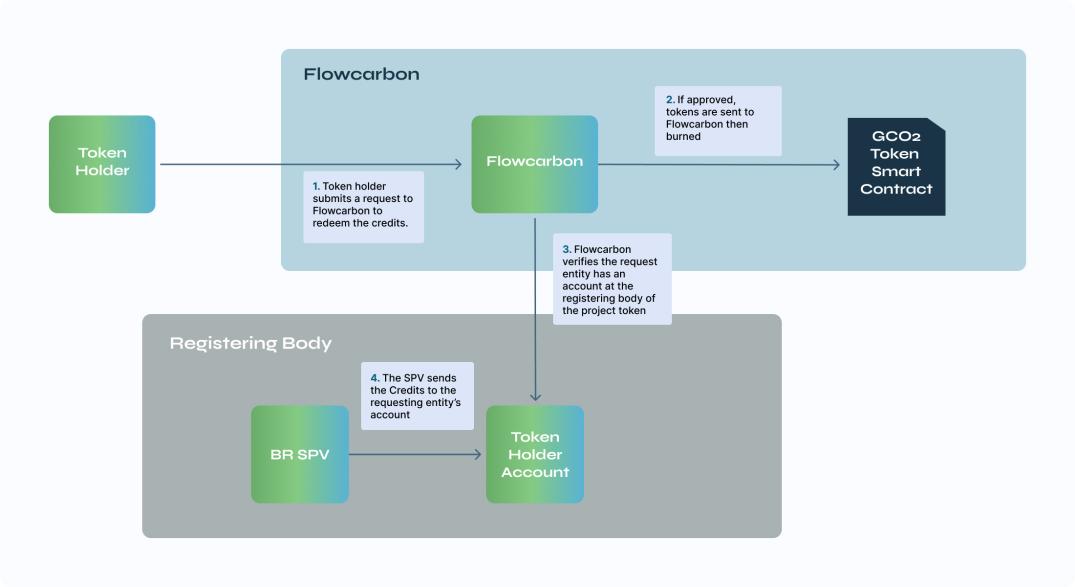
(2) Flowcarbon
Flowcarbon is a blockchain startup created by Adam Neumann, co-founder of WeWork, which hopes to vertically integrate the entire carbon credit lifecycle and provide strategies and solutions for carbon project initiation and financing, credit sales, and corporate carbon investment portfolio management. In May, it completed a $70 million financing round, led by a16z, with participation from General Catalyst and Samsung Next. The carbon credit spot market is not yet online. Goddess Nature Token (GNT) will be the first token bundle.
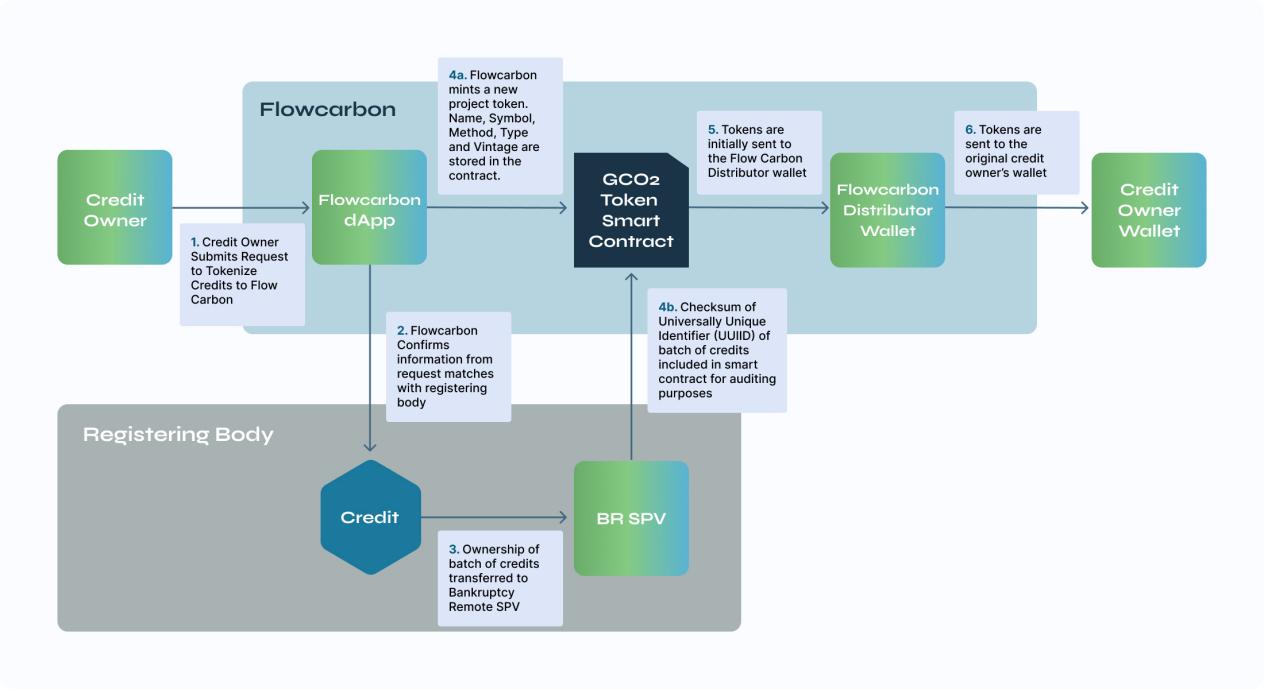
Tokenization packaging process:
- Tokenization of carbon credits
All requests to tokenize carbon credit quotas are submitted via a form on the Flowcarbon website. After submitting the tokenization request, Flowcarbon verifies the information with the designated registration agency. Once the ownership of the account, project type, and credit quantity are confirmed, the carbon credit is transferred to the bankruptcy-isolated special purpose entity (SPV). Once the batch information is verified and the credit is stored in the SPV, a new instance contract is created.
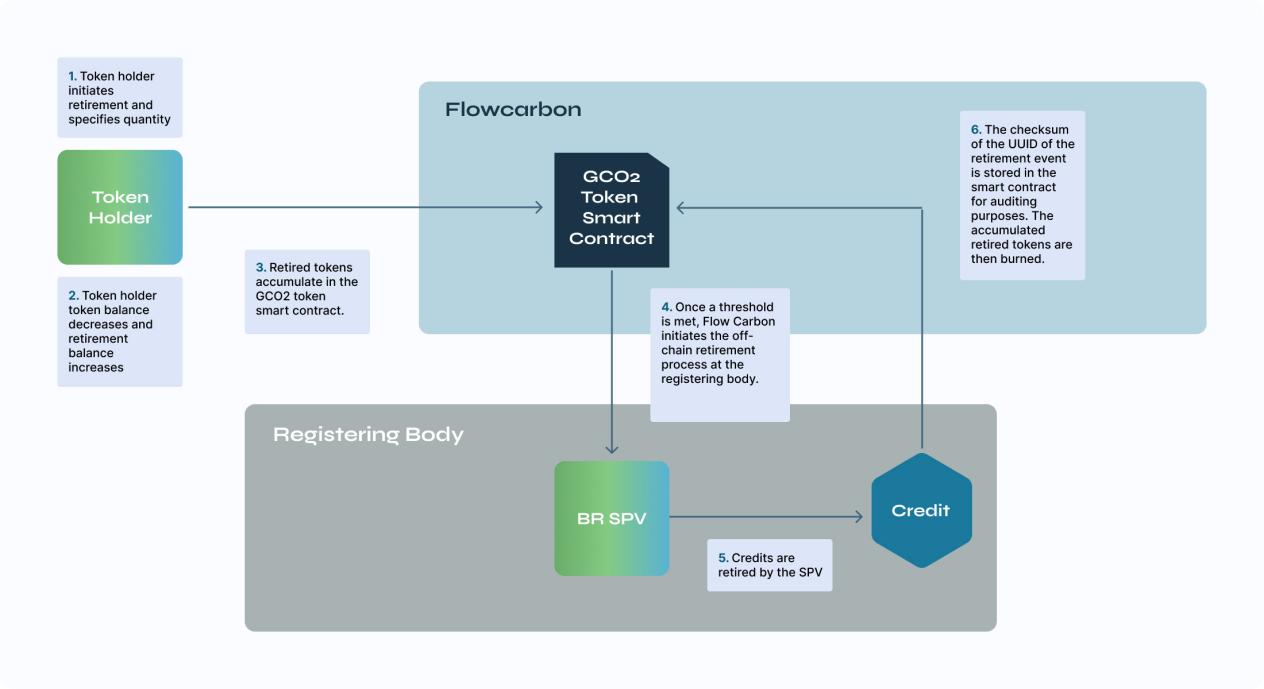
- Retirement
The token holder initiates a token exit with Flowcarbon and specifies the quantity she wishes to exit. This reduces the token holder’s balance and increases her exit amount. The tokens retired transparently in the contract accumulate until they exceed a pending batch size. Once the threshold is reached, the bankruptcy-isolated SPV will exit the carbon credit in the underlying registry.
- Redemption
Redemption refers to the process of the token holder exchanging their GCO2 tokens for actual off-chain credits. The token holder initiates the redemption process by submitting a request to Flowcarbon. After the request is approved, Flowcarbon confirms that the requester has an account at the appropriate registration agency. Then, the GCO2 tokens are destroyed by the GCO2 smart contract, and the physical carbon credit quota is transferred from the bankruptcy-isolated SPV to the requester’s account.
There is a standard fee of 2% for redemption. If a GCO2 holder requests to redeem 100 GCO2 tokens, they will receive 98 off-chain carbon credit quotas.
- Liquidity
Users can store GCO2 tokens in a bundle via Flowcarbon’s dApp in exchange for bundled tokens. Bundled tokens are issued on a one-to-one basis; if a GCO2 token holder stores 50 GCO2 in a bundle, she will receive 50 bundled tokens as a reward. Bundled tokens are designed to provide liquidity, so users can buy them directly. Bundled tokens can also be redeemed.
Protocol Income:
Unbundling, swapping, exiting, and redeeming functions all have related dynamic fees, and carbon credit actions in more recent years are more expensive than those in longer periods. This is to incentivize the exit of older carbon credit quotas. Dynamic fees are implemented through a “rake back” contract. When one of these functions is initiated, the contract representing the user’s account executes the function, and the rake back contract determines how much of the maximum fee should be returned to the requester. For example, if the maximum fee is 15%, and Sarah requests to unbundle 100 bundled tokens into 2020 GCO2, the bundled token contract will automatically charge 15 GCO2 into the fee account, and 85 GCO2 will be sent to the rake back contract. The rake back contract will contain logic about the actual fee situation; 2020 is a relatively new year, and the actual fee is 10%. Therefore, in this case, the rake back contract will extract 5 GCO2 from the fee and send 90 GCO2 back to Sarah.
Protocol Advantages: Flowcarbon offers a “bidirectional bridge” that allows GCO2 tokens to be exchanged off-chain for underlying carbon credits.
Protocol Risks: Carbon credits are transferred to an SPV and tokens are created for on-chain transactions, but true carbon credit tokenization is not achieved.
(3) PERL.eco
PERL.eco is Perlin’s latest project, focused on bringing real-world biotic assets onto the blockchain, one of the first available assets being tokenized carbon credits. The product is not yet officially launched.
Tokenization Packaging Process:
PERL.eco collaborates with the fully regulated carbon exchange ACX operator AirCarbon Group to establish the PERL.eco Carbon Exchange (PCX), which directly obtains PFCs (PERL.eco Future Carbon, tokenized carbon credits for high-quality carbon projects reviewed by PERL.eco, which have not yet been issued) and other high-quality carbon assets from carbon projects and partners that PERL.eco audits and retails them on PCX.
Protocol Status: Token $PERL has been listed on Binance, but the social media attention is low, the project progress is slow, and the white paper has not been updated for over a year. The PFC pilot soft launch is scheduled for Q3 2023, and the early prototype of PERL.eco Carbon Exchange (PCX) will also be released. The PCX Alpha version will be released in Q4 2023, and the PCX Beta version will be released in 2024.
Token Functionality:
$PERL is the governance token of PERL.eco. PERL plays a critical role in determining the incentive system, establishing a broad stakeholder base, and promoting economic value flow in the network. PERL holders can vote on fee models and distribution, as well as other important decisions. By participating in governance, users can receive carbon credit airdrops to offset their emissions.
Protocol Advantages: Collaboration with regulated carbon exchanges reduces risk;
Protocol Risks: PERL.eco only acts as a distributor, which increases target exposure but does not really improve liquidity.
Summary
The off-chain carbon credit market faces problems such as lack of price discovery, poor liquidity, and poor market transparency. Web3 carbon credit projects are committed to building trading pools through the tokenization of carbon credits to provide better liquidity for carbon credit trading.
However, Web3 carbon credit projects face problems such as strong isolation and low credibility. Also, due to the impact of the place of origin registration, project, and year, carbon credits are not priced consistently, making it difficult to achieve true homogeneous tokenization. For example, Toucan, which already has some trading data, currently only supports two types of carbon credit carbon index tokens, which can be pledged through logical screening. Flowcarbon currently only plans to provide one type of bundled token, which must meet three requirements. In addition, the carbon credit trading process is complex and cannot bypass some centralized verification agencies managed by independent non-governmental entities, such as Verra and Gold Standard. Verra has explicitly stated that it does not currently support carbon credit tokenization. Blockchain technology can change many of the problems existing in the traditional carbon credit trading market, but there is still a long way to go in improving credibility and enhancing market uniformity and liquidity.
4.8 Vertical Public Chain
It is precisely because of the diversity of real-world asset properties that the realization of asset tokenization requires a dedicated public chain to meet the needs of institutional users. These include: 1. Stronger security and privacy; 2. More convenient operations, such as providing SDK and other tools; 3. Diversification and operability of token standards; 4. May require permissioned chains to build a regulatory and compliant process system.
Regarding token standards, from the Ethereum ERC-20 standard perspective, issuers cannot implement behaviors such as token recovery, share management, identity management, batch processing, off-chain authorization, etc., which brings greater difficulties to asset management. Therefore, the existing public chains cannot implement the complex asset management operations of the existing financial market. A new token standard needs to be developed on a new public chain.
(1) Polymesh

Polymesh is an institution-level Layer 1 blockchain tailored for regulated assets such as security tokens, with a circulating market value of 90 million US dollars. Binance has recently announced that it has become one of its nodes. Polymesh is a public permissioned blockchain that uses the nomination proof of stake (NPoS) consensus model developed by Polkadot to clarify the roles, rules, and incentives of the network. Inspired by ERC-1400, the on-chain token standard provides more functionality and security to facilitate the issuance and management of on-chain assets.
The core team of Polymesh has a financial, technological, and legal background. Most of them have experience in building the first security token platform on Polymath and leading ERC-1400. The team members are public, and the team information is available at: https://polymesh.network/team#.
Project advantages/features
- Designed for regulation: Due to regulatory constraints, permissionless public chains such as Ethereum may be difficult to meet the trading requirements of RWA assets, so vertical application chains established specifically for RWA assets have emerged.
- Transparency guarantee: All issuers, investors, pledgers, and node operators need to complete the identity verification process, that is, customers need to conduct due diligence. In particular, node operators must be licensed financial entities. This enhances network security. On-chain interactions can be traced back to known real-world entities. All transactions are authorized by licensed entities.
- Preventing hard forks: Forked chains will cause significant legal and tax issues for physical asset tokens, and the POLYX industry-leading governance model eliminates the occurrence of hard forks.
- Confidentiality: Polymesh has designed a secure asset management protocol to enable the issuance and transfer of confidential assets. It meets the confidentiality requirements of real-world market participants for positions and transactions.
- Real-time settlement: Inheriting Polkadot’s GRAND Blocking finality gadget, combined with the above identity verification requirements, compliance verification, and no hard forks, Polymesh’s transactions can be settled in real time.
Token Functionality:
$POLYX, a native token, is classified as a utility token under Swiss law, according to guidance from the Swiss Financial Market Supervisory Authority (FINMA). POLYX is used for governance, securing the chain through staking, and creating and managing security tokens.
The token’s inflation rate is 10.12%, which is fairly normal.
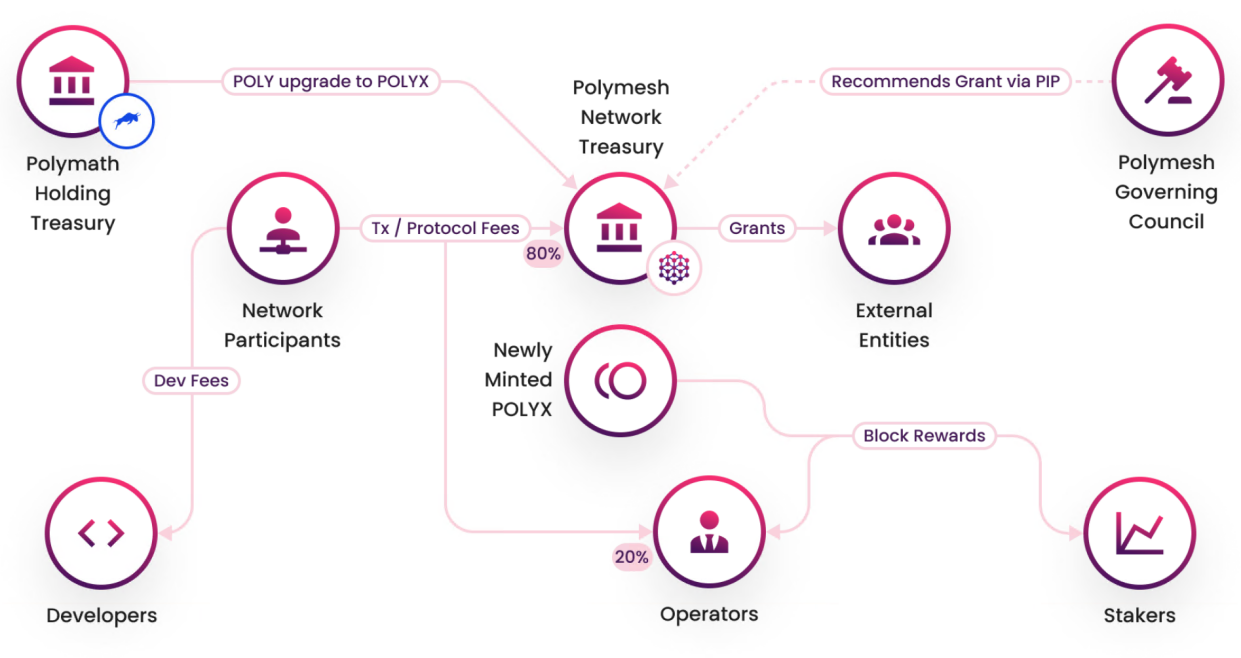
POLYX Token Circulation Chart
Ecosystem:
Current participants in the Polymesh ecosystem include cryptocurrency exchanges, seasoned players in the tokenization space (Polymath), and companies with sizeable portfolios of security tokens (RedSwan). The Polymesh Association aims to facilitate further development through two initiatives:
- Grant Program for individuals and enterprises building open-source functionality on Polymesh.
- Ecosystem Development Fund for companies integrating Polymesh’s proprietary technology.
The current main ecosystem includes:
- Tokenise – the first CSD, broker, and exchange for digital assets – chose to build its infrastructure on Polymesh and has begun creating digital assets
- DigiShares – a white-label tokenization platform – became the first recipient of the Polymesh Ecosystem Development Fund to integrate Polymesh
- Stably – a regulated stablecoin infrastructure provider and creator of the USDS token – is working to launch the first stablecoin on Polymesh
- ABC Tokens – a tokenized real estate provider – is using Polymesh to offer investors decentralized commercial real estate

Overview of the Polymesh Ecosystem in October 2022
Asset Tokenization Mechanisms:
- Configure Security Tokens
Configure security tokens on the blockchain to represent physical or digital assets. On Polymesh, tokens are created at the protocol layer, eliminating the need to add smart contracts for each security token at the chain top. Tokens can be easily configured using basic programming languages and the Polymesh SDK or tokenization platforms for issuers who want a completely code-free approach.
- Set Compliance Rules
Flexibly set ownership and transfer rules using Polymesh’s compliance engine. Ensure transfer restrictions can be enforced and that your tokens comply with regulatory requirements such as KYC/AML requirements and securities laws.
- Token Distribution
One-click mint your tokens and send them to existing shareholders, affiliates, or reserve accounts while fulfilling broader compliance requirements. Set prices in ways that make sense for your token and (if necessary) designate qualified custodians to manage collections securely and reliably.
- Manage Company Behavior
Execute company actions on-chain to address issues related to interests, restructuring, capital allocation, and voting. The issuer only needs to input some details. From there, the engine can determine rights, arrange record dates, allocate capital (if needed), and update records.
Project Status:
Currently, there are 3.8K accounts, 357M $POLYX tokens are staked, accounting for 47.7% of the total issuance. 43 node operators. The on-chain daily trading volume ranges from 2K to 11M $POLYX. On April 20th, due to Binance’s announcement to become a node operator, the on-chain transfer volume reached 138M.
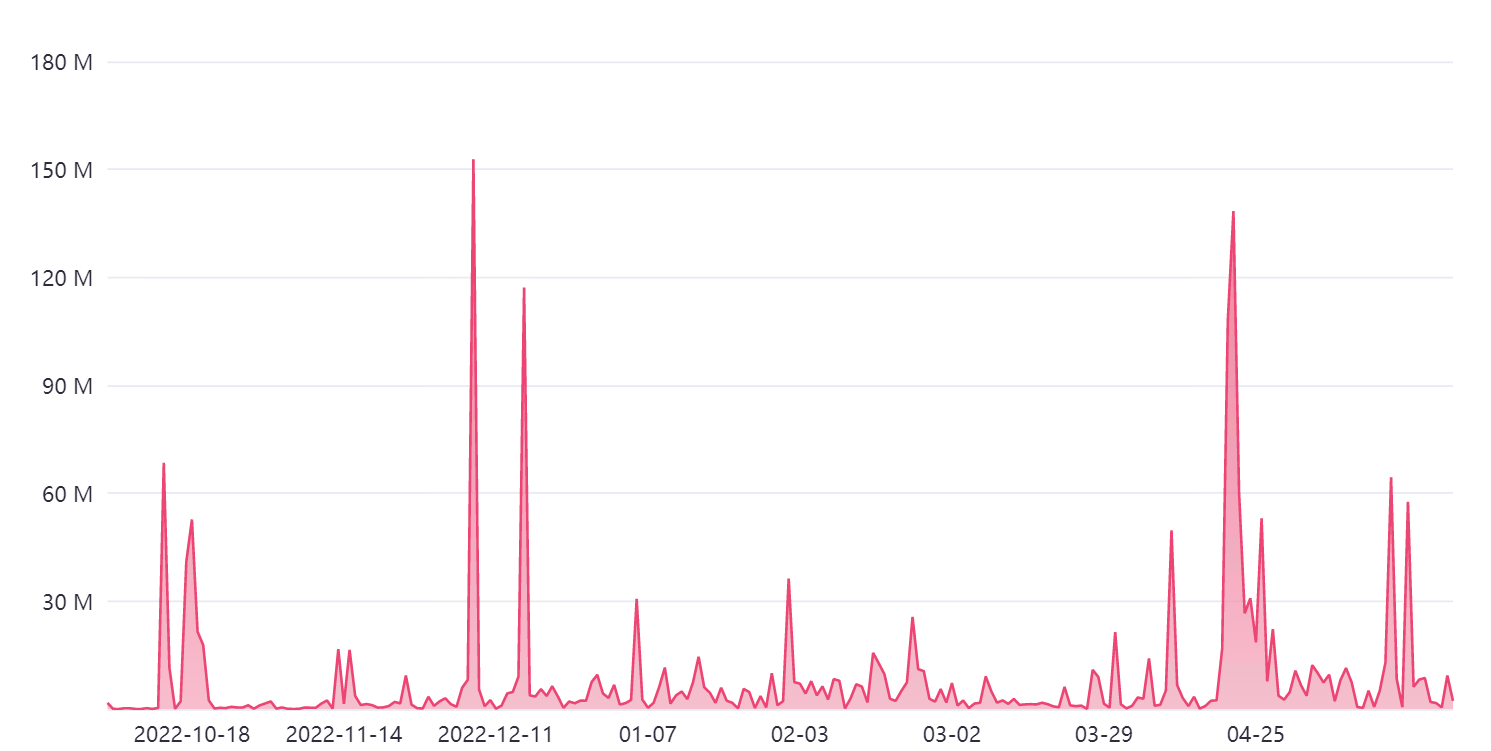
Polymesh on-chain transaction volume
In the future, Polymesh will introduce smart contract functionality and bring defi applications, NFT support, etc.
Project Evaluation:
Technically, Polymesh utilizes the development framework of Polkadot, but does not belong to a parachain. It inherits the security and technological superiority of Substrat. In terms of ecological development, Polymesh provides on-chain issuance and management tools for independently set RWA tokenization, meeting the needs of various asset tokenization. It provides an institutional-level solution for RWA tokenization, but there are two risk points: (1) identity verification ensures a certain degree of transparency and security, but there must be supporting insurance plans in case of problems; (2) attracting institutional developers is key, and more cooperation is needed.
(2) MANTRA Chain

MANTRA (formerly MANTRA DAO) was founded in 2020 and is part of the MANTRA ecosystem Omniverse, which also includes MANTRA Nodes, MANTRA Finance, and other projects with a circulating market value of about $19 million. MANTRA Chain is an L1 blockchain built on the Cosmos SDK, aiming to become a network for inter-enterprise collaboration, attracting enterprises and developers to build any application from NFTs, games, metaverse to compliant DEX, etc. MANTRA Chain can achieve interoperability with other Cosmos ecosystems through IBC cross-chain, and is also compatible with EVM chains.
The MANTRA project spans RWA and Hong Kong concepts, with a cumulative financing of one time and main investors including LD Capital, Shuidi Capital, GenBlock Capital, etc.
Project Advantages/Features:
- Strong Identity System: MANTRA Chain has a powerful decentralized identity (DID) module to meet all KYC and AML requirements. This module helps in developing products that utilize enhanced functionalities and the ecosystem.
- Complete Ecosystem Chain: With MANTRA Finance as the mainstay, it has developed nodes, DAO organizations, and public chain infrastructure.
Token Functionality:
$OM is the native token of OMniverse, with functions including governance, network staking, DAO token access/airdrop rewards. MANTRA Chain’s native token $AUM will be launched soon.
Ecology and Status:
The first dApp on MANTRA Chain is MANTRA Finance, which aims to be a globally regulated DeFi platform, bringing the speed and transparency of DeFi to the opaque TradFi world, allowing users to issue and trade RWA tokens.
Currently, it has launched some crypto-based yield-generating DeFi products, followed by a Central Limit Order Book (CLOB) DEX, which will offer swap functionality and traditional financial products such as debt, stocks, and other real-world assets (RWA). After the success of these products, MANTRA Finance plans to expand its decentralized exchange (DEX) product by offering derivative products.
Project Evaluation:
The MANTRA project started in 2020, developed based on Polkadot, but did not have good development. The project roadmap has also undergone several major changes, with slow product progress, and there is currently no launch of relevant RWA products or corresponding solutions for enterprise and institutional levels.
(3) Realio Network

Realio Network was formerly an end-to-end digital asset issuance and P2P trading platform focused on real estate private equity investments, headquartered in New York, established in 2018. Currently, Realio has established its own L1 blockchain network developed based on Cosmos SDK, and the mainnet was launched in April. The Realio platform utilizes blockchain technology to provide a range of services, including tokenization, digital asset issuance, and secondary market trading, with applications including realioVerse and the upcoming Freehold wallet, which will not only be in the real estate field, but also in securities.
Realio’s platform also includes providing services such as KYC/AML compliance, investor verification, and investor management tools, which also serve third-party issuers to digitize their assets and raise funds within the network. All actions must meet SEC compliance requirements.
Team member information is public, with multiple financial and real estate advisors.
Project Advantages/Features:
- Security assurance: One of Realio’s unique features is its distributed key management system. Helps ensure secure validators and delegates. They will receive their block reward share based on their contribution amount by binding $RIO or $RST.
- Compliance: All token issuance must meet SEC compliance requirements.
Ecosystem construction:
Currently, the Realio Network mainnet has just launched, but Realio’s native tokens $RIO and $RST have long been issued, and the project has also launched the Realio Platform Wallet and Realio.fund investment platform.
- Realio Platform Wallet
Realio Wallet is a non-custodial, multi-chain wallet that currently supports Bitcoin, Ethereum, Algorand, Stellar, Raven, and Fusion, including any assets on these multi-chains, and supports more blockchains under development. The wallet is a non-custodial wallet that simplifies storage of private keys and transaction signing, and will soon launch features to access the DeFi ecosystem, etc.
- Realio.fund
A P2P investment platform that provides multi-chain, real-time token issuance tools, fully automated compliance workflows, and investments can be made using cash or cryptocurrencies supported by Realio.
Token Functionality:
The blockchain network adopts the native dual-token equity proof-of-stake model, $RIO and $RST, with network staking, governance, key management, and other functions.
$RST was issued by Realio in cooperation with Algorand in 2020 and is an equity token held by technical platforms and network maintainers. $RST is sold as an Algorand Standard Asset (ASA) and has interoperability with other supported blockchains and platforms such as RealioX. RST tokens will be sold globally in private placements based on Regulation D Rule 506(c) and Regulation S exemptions. Currently, there is no secondary public market trading. $RST is a hybrid digital security that enjoys platform revenue distribution and can also be staked on the Realio Network to earn validator rewards. The maximum supply is 50 million, and it is sold through presales and Security Token Offering products on the realio.fund platform.
$RIO is the native gas and utility token of the Realio Network, issued on multiple chains including Ethereum, Algorand, and Stellar. There is no pre-mining, and additional supply is generated through block rewards and liquidity mining. The maximum supply is 75 million, and the circulating market value is approximately $1 million. It has been listed on OKX and MEXC, with daily trading volumes increasing to around $1-4 million from March to May.
Project Status:
Currently, the platform is focused on cryptocurrency trading. It has also launched a liquidity mining fund for the BTC ecosystem called $LMX, and token holders can also participate in other DeFi ecosystems, similar to stETH. Twitter followers: 29.7K.
The Alpha mainnet has been launched, and network staking functionality has been partially released. According to the Realio project roadmap, the realioVerse virtual real estate project will launch in 2023 Q3, with the Land Bank built on top of it, where players can buy and sell land, build houses, and make money.
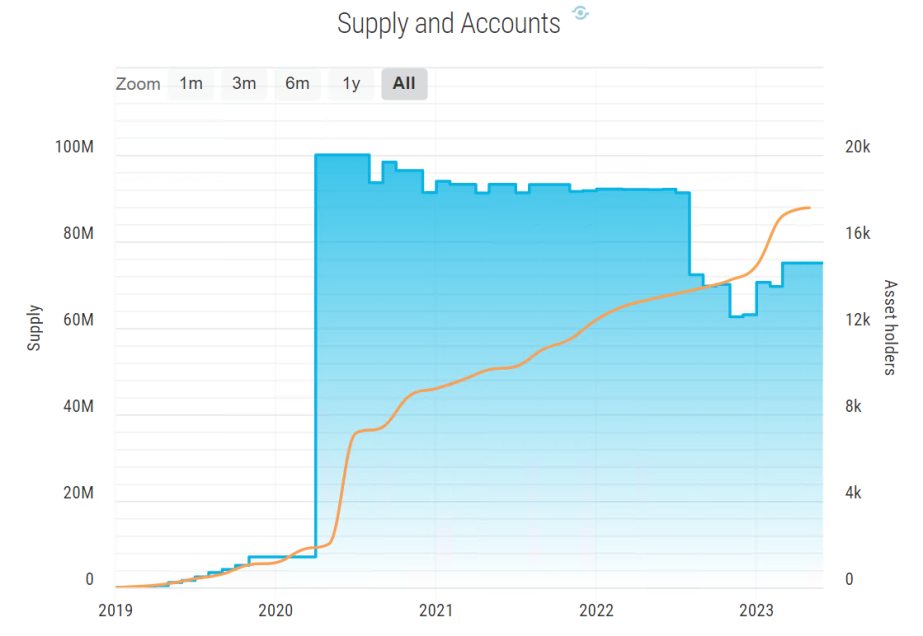
$RIO Token Circulating Supply and Holder Count Changes
Project Evaluation:
The project is still in its early stages, but the entire team was established in 2018. Apart from issuing tokens, no tokenized projects related to RWA or real estate have been carried out. The future development is still unknown. There are no new technologies or marketing points for blockchain construction or ecosystems, making it difficult to see any advantages at present.
Conclusion
Although the Ethereum ecosystem is vast, most existing RWA projects are also built on top of Ethereum. However, Ethereum is not entirely suitable for the development of the RWA track, including node anti-censorship, public chain performance issues, and so on. Especially, various different real-world assets need to be realized in token standards and smart contracts, which require a new underlying setting to support programmability, verifiability, and compliance with existing regulatory systems. Currently, it seems that vertical public chains for RWA have considered the above requirements. But the development of the entire track is slow, with few users and developers participating, and the underlying public chain is still developed based on existing public chain technologies, such as Polkadot and Cosmos. The current competitive landscape of public chains seems to have been established, and attracting users still requires the support of upper-layer applications.
- Is the end of public chains the alliance chains?
The concept of alliance chains is not unfamiliar, and its development time is comparable to that of public chains. However, due to its strict admission and review system, it does not have a wealth effect for users and seems to be excluded from the encrypted world. An alliance chain refers to a blockchain jointly managed by several organizations or institutions, with each organization or institution controlling one or more nodes, jointly recording transaction data, and only these organizations or institutions can read, write, and send transactions in the alliance chain. Well-known alliance chain projects include Hyperledger and the Blockchain Service Network (BSN).
Alliance chains have the following characteristics: (1) “partially decentralized”, each node usually has a corresponding physical institution, and can only join or exit the system with the approval of the alliance. The number of nodes is limited, and the data will not be made public by default, but verification of transactions or publication of smart contracts requires alliance permission; (2) Strong controllability, once the block information of the public chain is formed, it cannot be tampered with, but in the alliance chain, as long as most of the institutions reach consensus, block data can be modified; (3) Fast transaction speed, with few nodes, it is easy to reach consensus.
These characteristics of the alliance chain undoubtedly point to the vertical public chain of the RWA track, but we do not think that the alliance chain is the end of the RWA track: 1. The development of the encryption industry cannot do without decentralization and openness. The alliance chain does not bring wealth effects and can only be used as a technical means, which is difficult to attract investors and institutions; 2. The development of the RWA track, especially in compliance and whitelist, does have some characteristics of the alliance chain, but the power of the alliance chain is too centralized, it is impossible to achieve democratization and openness, and concentration also represents a certain degree of opacity; 3. The advantages embodied by the alliance chain can be applied in the process of physical assets on the chain. Currently, many alliance chains are doing similar things, but the effect is not good, so the underlying logic of the public chain is still needed.
- Risks and Challenges
The RWA market is expected to reach $500 million by 2025. In Citibank’s latest research report, the RWA track is highly expected, and it is believed to be the killer to drive the blockchain industry into a market of hundreds of trillions of dollars. According to statistics from BCG (Boston Consulting Group), the RWA track may reach an overall scale of 16 trillion US dollars by 2030. The huge potential brought by the RWA track cannot be ignored. However, the current encryption industry is in a downturn, and the overall market value has not exceeded that of Apple. The industry has frequently been hit by regulatory crackdowns in various countries in the past year. The encryption industry is still in its early stages, and it will take a long time for the industry to achieve a market size of hundreds of trillions of dollars.
Looking at the development of RWA tracks, there are more problems than advantages. From the current situation, RWA projects generally face problems such as poor liquidity, high management costs, and complex settlement processes. The projects still have not solved the mechanism problem and are not as efficient as traditional finance. Some protocols have only a very small number of users, but the valuation of native tokens is very high.
From the perspective of project types, there are many types, but the business scope of the head protocols is too limited, mainly based on stablecoin credit lending projects. These projects have higher risks than other lending protocols, and have not really brought off-chain assets onto the chain, which has led to the limited development of the RWA track. Lending protocols based on securities, bonds, and physical assets have not developed much.
From the perspective of user behavior, RWA projects may not be able to accumulate energy in a bull market. The real investment demand of users is the high returns brought by on-chain RWA projects. Due to the low returns of DeFi in the bear market, investors have been unable to meet their needs, and the yield of US Treasury bonds can reach 5%, and many centralized financial products invest in US Treasury bonds and stocks. This makes RWA projects with the concept of US Treasury bonds popular. But once the crypto industry enters a bull market, can the returns of these RWA projects still be generally higher than other DeFi protocols?
The fundamental reason for limiting the expansion of the RWA track is that the following problems have not been solved either technically or procedurally:
- Regulatory uncertainty
Regulation is the biggest challenge facing the RWA track, and its uncertainty is reflected in two aspects:
- The imperfection of the legal system for the crypto industry, especially whether tokens are commodities or securities, is still uncertain. From the current perspective, all cryptocurrencies except for Bitcoin will be classified as securities. This requires regulation of assets, issuers, trading markets, and even on-chain contracts and public chain nodes. In order to comply with the existing regulatory system, most RWA projects will carry out KYC/AML processes for users.
- Real assets are geographically restricted. The core of RWA lies in the credit mechanism, and the key to promoting global circulation is to establish internationally applicable bills, and relevant bills should also have the ability to be enforced. But at present, the compliance resistance of RWA is still very large. Perhaps a small number of crypto-friendly areas will become pilot areas, such as Hong Kong and Singapore.
- Identity Solution
Based on the KYC/AML process, RWA projects need to conduct strict scrutiny and verification of off-chain centralized entities and individuals, among which the tangible real estate project has an SPV legal entity as a feasible path. However, most of the verification tasks are still undertaken by the project party, and the degree of trustworthiness is unknown. Currently, many private credits such as MAPLE and TrueFi have experienced bad debt situations. To solve these problems, it is urgent to have a third-party off-chain compliance agency to deal with the correlation between on-chain identities and off-chain entities. Related to this, there are also supporting legal and technical support such as perfecting laws and regulations, possible identity and data privacy solutions, and solutions that connect on-chain and off-chain data.
- Balancing Decentralization and Centralization
The core feature of blockchain technology is decentralization, while RWA projects inevitably need to use centralized means in various links to comply with audits, including asset audit processes, vertical public chain nodes, user qualification reviews, etc., even many processes are executed by the project party itself, and smart contracts of blockchain have become a castle in the air. The prosperity of RWA track requires the blessing of decentralization. In this regard, introducing more trustworthy third parties can solve the problem of excessive centralization, which can refer to the practice of ABS.
(4) Mechanisms for Valuation, Liquidation, and Protection of Off-chain Assets
The price of off-chain assets, especially the market price of physical assets, is difficult to estimate. Although some websites provide estimated market price services, the real price can only be reflected in market transactions. Asset valuation also has a great impact on the liquidation mechanism. In addition, due to the fact that the collateral is not a liquid ERC-20 token, liquidating these assets to recover the borrower’s capital will be much more troublesome than lending using encrypted collateral. Many private credits have already experienced bad debt situations. Some asset protection mechanisms also face challenges, such as who will be responsible for safeguarding these cross-border physical assets, such as art and real estate. It is difficult to gain user trust in these mechanisms until they are fully understood.
All of these issues require the improvement of the infrastructure of the RWA track, including tokenization process infrastructure, digital collateral infrastructure, custody platforms, etc. Although there is great resistance to bridge traditional finance and crypto finance, with the continuous development of the crypto industry, more and more RWA projects will emerge and explore introducing more valuable assets to web3, and we will see more and better solutions. The RWA track still has the hope of becoming the narrative of the next bull market.
References:
- Bitwu on RWA: The future of DeFi, unlimited liquidity
https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/hJguFEU9r1cL1O49600dDQ - Big institutions such as Binance and Goldman Sachs are competing to invest in RWA. Is it the next growth engine for DeFi or just a flash in the pan?
https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/ADHl__hVvrcsqZooc2iMZw - Real World Assets: The Bridge Between TradFi and DeFi
https://research.binance.com/en/analysis/real-world-assets - Money, Tokens, and Games—Blockchain’s Next Billion Users and Trillions in Value
https://icg.citi.com/icghome/what-we-think/citigps/insights/money-tokens-and-games - https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Carbon_offsets_and_credits
- https://docs.toucan.earth/
- https://docs.flowcarbon.com/introduction/context
- https://docs.perl.eco/
We will continue to update Blocking; if you have any questions or suggestions, please contact us!
Was this article helpful?
93 out of 132 found this helpful
Related articles
- Who are the internal “leakers” behind Binance’s multiple regulatory accusations?
- Gary Gensler’s Crypto Game: Stealing the Spotlight from Congress to Illuminate the SEC’s Path
- Understanding the Distributed AI Computing Network Gensyn
- Office of the New York Attorney General Provides Tether-Related Documents in Response to CoinDesk
- How should investors hedge their risks during the “storm” of encryption?
- Uniswap v4: What’s Next for the Top DEX?
- Evening Reading | USDT Faces Serious Selling Pressure: Are Market Makers Exiting?






