Interpretation of the ‘Tokenization of Hong Kong Bonds’ Report Using Evergreen ‘Green Bonds’ as an Example, Reviewing the Theory and Practice of Bond Tokenization.
Analyzing the 'Tokenization of Hong Kong Bonds' Report through Evergreen 'Green Bonds' as an Illustration, Examining the Theory and Implementation of Bond Tokenization.
Author: Spike @ Contributor of PermaDAO
Reviewed by: Kyle @ Contributor of PermaDAO
Recently, the Hong Kong Monetary Authority (HKMA) released a report titled “Bond Tokenisation in Hong Kong”, which detailed the theory and practice of bond tokenisation using the first tokenised bond issued by the Hong Kong government in February, the Evergreen “Green Bond”. everLianGuaiy has also collaborated with Asian digital banks to issue offshore RMB stablecoin ACNH, believing that RWA will lead the next wave of DeFi development. Therefore, PermaDAO has compiled the key points of the report to share with readers:
- Blockworks From the Blockchain Impossible Triangle to the Big Convergence
- Beyond Ethereum – Third Generation Blockchain Will Drive Mass Adoption
- MakerDAO chooses Solana as the application chain? It’s too early to draw a conclusion, at least 3 years are needed to achieve it.
1. It discusses the experience brought by the collaboration between the HKMA and the Bank for International Settlements (BIS), and introduces their assistance in the issuance of the first digital bond by the Hong Kong Special Administrative Region government (the Evergreen project);
2. Evergreen demonstrates the possibility of conducting real capital market transactions using distributed ledger technology (DLT) within the existing legal framework in Hong Kong, and showcases the potential of DLT to improve efficiency, liquidity, and transparency in the bond market;
3. The report also discusses the technical and platform design details to be aware of in digital bond transactions, and provides guidance and reference for issuers interested in bond tokenisation;
4. Finally, the article explores the future development direction and action plan of digital bond tokenisation, emphasizing the importance of addressing challenges and adjusting existing legal and regulatory systems.
In terms of timing, the global tokenised bond market is expected to exceed $3.9 billion between 2021 and 2023, which is in line with the development during the previous bull market. A large amount of infrastructure has been accumulated to support large-scale usage.
The typical process of issuing bonds can be broken down into the following steps:
1. Preparation and issuance of bonds: including the tokenisation and preparation work for bond issuance, such as tokenisation and initial issuance of bonds;
2. Participant onboarding: existing platforms can only be accessed by specific participants, including issuers, central securities depository, payment agents, distributors, custodians, and secondary bond dealers;
3. Issuance and subscription: bond issuance involves both off-chain and on-chain processes. In the off-chain stage, standardisation and pricing of bonds need to be conducted. After being put on-chain, smart contracts are used to represent the rights of the bonds and tokenize them, and then subscription work can be carried out;
4. Allocation, settlement, and delivery: on the issuance date, banks transfer the corresponding cash into the real-time settlement account of the central securities depository. Then, all parties are brought together to facilitate allocation, settlement, and delivery activities, aiming to improve efficiency and reduce settlement delays and settlement risks;
5. Application of securities regulations: The issuance of digital bonds needs to comply with the requirements of securities regulations, including provisions on securities issuance and licensing requirements;
6. Credit rating: Issuers may consider obtaining credit ratings for digital bonds.
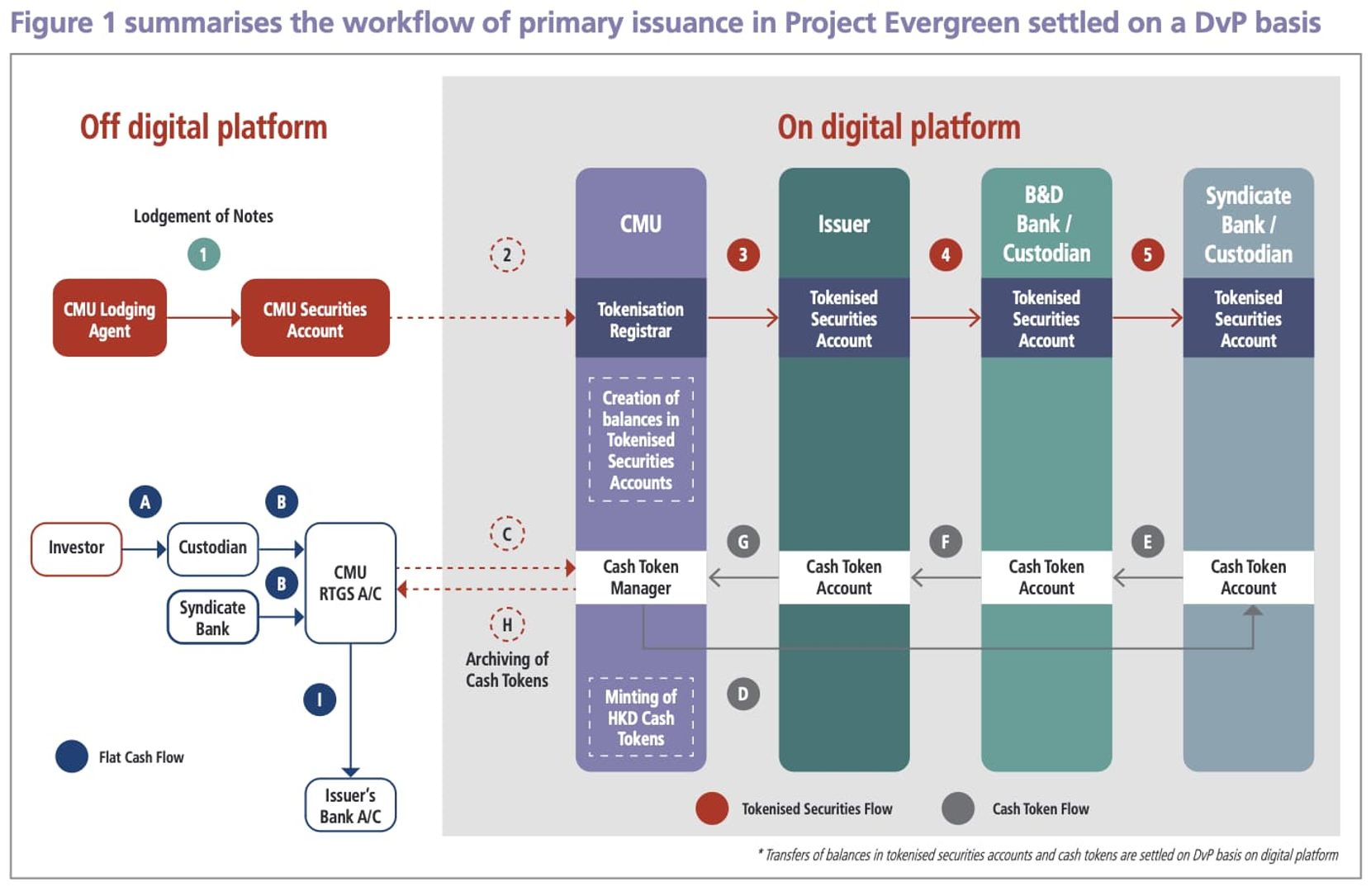
In practice, DLT (distributed ledger technology) has once again demonstrated its advantages. In the process of tokenized bond issuance, the Hong Kong Monetary Authority has also summarized the following technological advantages of DLT:
- Paperless creation: In the process of tokenized bond creation, the need for physical certificates and manual marking can be eliminated, saving time and eliminating the risk of manual processing errors;
- Facilitate interaction between different parties on a common DLT platform: A common DLT platform gathers all different parties on the chain, and participants have specific permissions, real-time verification, and involvement in multi-party workflows, thereby improving processing efficiency;
- Atomic DvP Settlement: Bond transactions and cash payments are conducted on the DLT platform, allowing for instant settlement and reducing settlement delays and risks;
- End-to-end DLT adoption across the bond lifecycle: Using DLT in primary issuance, secondary trading settlement, coupon payments, and maturity redemption can greatly reduce multiple manual processes, reduce service time and costs, and eliminate the need for synchronization between different channels, achieving significant operational improvements;
- Enhanced transparency: DLT achieves real-time data synchronization among different participants, thereby improving system transparency.
In terms of system construction, it can be roughly divided into four layers from bottom to top, namely Layer 1 and Layer 2 as the public chain infrastructure, followed by the smart contract layer and the user interaction interface. Of course, this part is more technical, so only a brief introduction will be provided.
- Layer 1 blockchain: The digital platform uses Hyperledger Besu 4 as the Layer 1 blockchain, which is a private Ethereum blockchain used for communication between nodes and as the consensus layer;
- Layer 2 blockchain: The digital platform uses Canton as the Layer 2 blockchain, which is a distributed ledger technology (DLT) that supports privacy and scalability. It is used to interpret and execute smart contracts and maintain consistent execution efficiency among participating nodes;
- Smart contract solution: The digital platform has chosen Digital Asset Modeling Language (Daml) as the smart contract solution. Daml is an enterprise-grade, privacy-focused open-source smart contract language used to define workflows, patterns, semantics, and transaction execution among participants in the Canton DLT network;
- Interaction interface: Participants in the digital platform can use node hosting, application programming interfaces (APIs), or user interfaces (UIs).
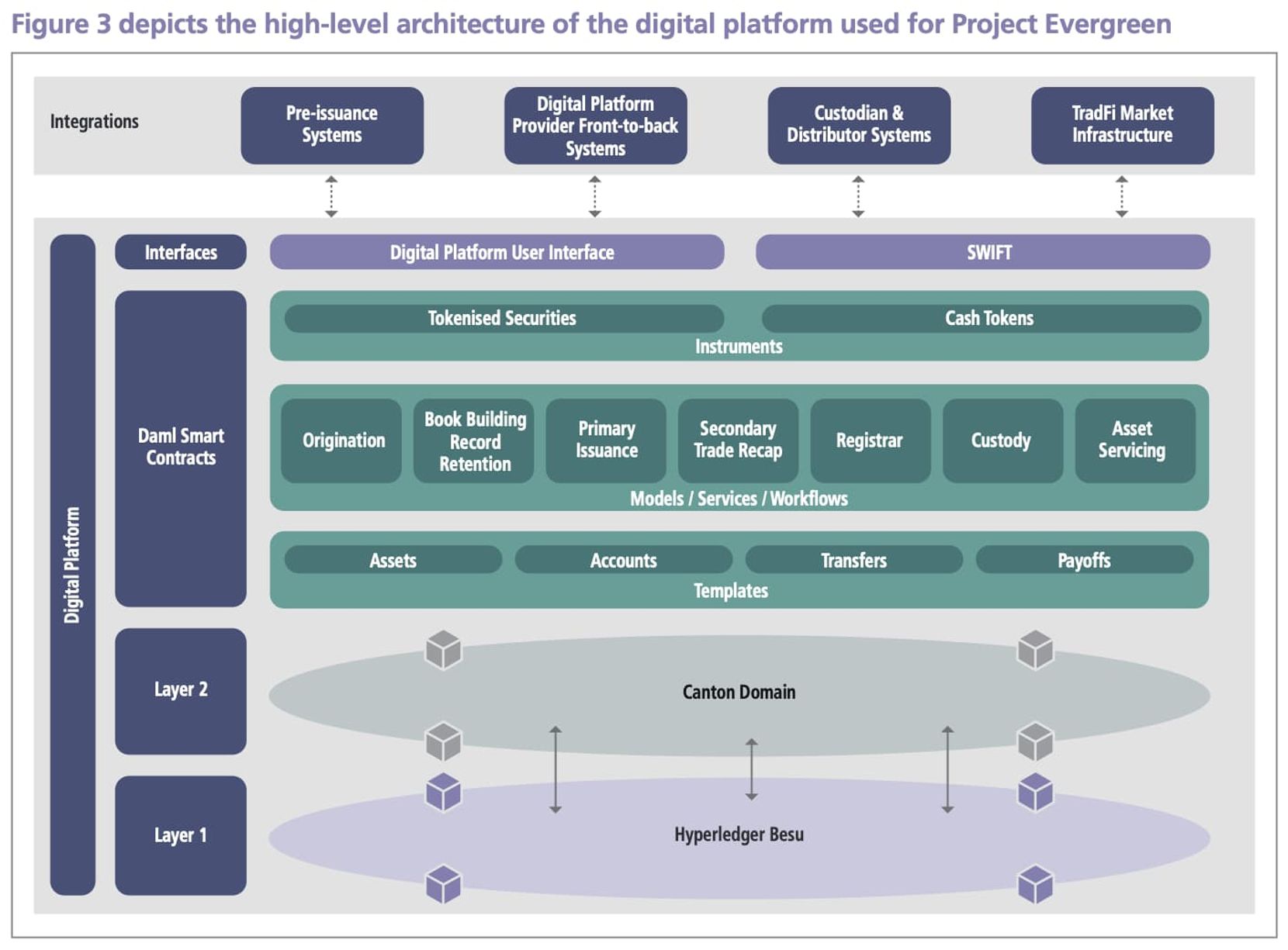
In addition, the DLT platform also designs secondary transactions, which refers to the trading of the rights and benefits of digital bonds outside the digital platform through traditional over-the-counter (OTC) transactions, while only settlement and transfer are conducted on the digital platform.
Similar to traditional bonds, OTC transactions allow participating parties to negotiate the terms and conditions of the transaction directly. If the DLT platform can include transaction functions such as security token trading, it can enhance the liquidity and transparency of the secondary market, provide standardized and automated processes and protocols, and may reduce counterparty and settlement risks by utilizing blockchain technology and smart contracts to achieve more secure and efficient verification and settlement.
Of course, including such transaction functions has complex technical and legal requirements, and the impact of cost, time, and infrastructure settings needs to be considered. At the same time, the legal impact of the trading platform business also needs to be considered, which may be included in the plan in the long term, but may not truly be pushed to the market.
Furthermore, DLT technology will also improve the existing market and product situation in multiple aspects, with potential applications in the following areas:
- Cross-platform: Establish cross-platform interoperability and connectivity, link assets between different public chains and DLT platforms, and build communication bridges between off-chain and on-chain;
- Stablecoins: Support not only the digital Hong Kong dollar but also issue on-chain versions of other fiat currencies, issue stablecoins of commercial nature, or further integrate into off-chain payment systems;
- Standardization: Promote on-chain standardization of protocols, facilitate the interconnection of assets, and even provide practical references for global asset classification and regulatory frameworks.
DLT is expected to fundamentally change the operation of financial markets, and this report basically covers the ideological framework of DLT technology and verifies it experimentally in Evergreen’s practice.
As early as July, PermaDAO produced an article titled “Ideas and Practices of RWA“, which introduced the green bond issuance by the Hong Kong government as the strongest example of compliance. Today, the Hong Kong Monetary Authority has introduced a report based on this example. PermaDAO believes that the compliance framework in the future will also be built based on this practice, and then the truly broad off-chain assets will usher in a real period of application explosion.
We will continue to update Blocking; if you have any questions or suggestions, please contact us!
Was this article helpful?
93 out of 132 found this helpful
Related articles
- Arbitrum vs. Optimism A new round of Red vs. Blue battle begins with Layer3.
- In-depth explanation of Aerodrome’s core mechanisms, the generation of flywheels, and development prospects.
- LianGuai Daily | French data regulatory agency inspects Worldcoin office; CyberConnect to introduce new proposal and appoint experts to audit cross-chain bridges.
- Game Revelation of the Whole Chain A Comparison of the Value Chains of Web2 and Web3 Games
- Intent-centric Narrative Outlook Unlocking New Scenarios for Cryptographic Applications
- Under the narrative of re-collateralization, how to value EigenLayer?
- zkSci How is zero-knowledge proof applied in scientific research?