Overview of EDCON Super Demo Winning Projects at Ethereum Conference 2023
EDCON Super Demo Winners at Ethereum Conference 2023EDCON, the Ethereum conference, will be held in Montenegro from May 19th to 23rd, 2023.
The Super Demo event held during EDCON has received strong support from the Ethereum Foundation and many members of the Ethereum community, and the winning projects will be showcased on the main stage of the EDCON conference, so it has attracted attention from the community.
EDCON Super Demo is jointly organized by the EDCON team and the global non-profit blockchain education institution, the University of Ethereum (UETH). The event aims to provide a platform for start-ups or projects that promote the development of Ethereum technology and ecosystem, to encourage technological innovation and promote the application and adoption of Ethereum and blockchain.
Each person/team that has successfully applied for EDCON Super Demo will have 15 minutes to showcase their project to the judges. At the end of the competition, the most innovative projects will be awarded, and the top three teams will be able to showcase their projects to the world on the main stage of the EDCON conference.
- Ethereum client Prysm releases version v4.0.5, including significant improvements to proof aggregation.
- Arbitrum’s High-Quality Project Inventory: What are the new projects worth looking forward to?
- Inventory of 13 potential zero-cost airdrop projects: Shardeum, Base, Scroll…
The EDCON 2023 Super Demo contest projects are mainly divided into four categories: 1. ZK/Privacy; 2. Public goods/ReFi/ESG; 3. Decentralized Applications; 4. Other.
On May 23rd, 2023, the last day of the EDCON 2023 conference, the EDCON Super Demo judges selected four winning projects from the contestants: EthStorage, Ethereum Attestation Service, Aspis Protocol, and Nerif Network.
Blocking reporter takes you on a quick tour of these four projects:
EthStorage
A one-sentence summary: Ethereum storage expansion project.
EthStorage aims to enhance Ethereum’s storage capacity, increasing it from terabytes (TB) to petabytes (PB). This will reduce Ethereum’s storage costs by a factor of 1,000.
EthStorage features: programmable large-scale KV storage – smart contracts can be programmed for CRUD operations for large-value reads/writes of over PB capacity; storage proofs for large dynamic datasets – uses random sampling and dynamic data sharding to prove data retention and encourage recopying; data availability proofs for publication – uses KZG commitments and Reed-Solomon codes supported by Danksharding to improve data upload speed; web3:// access protocol – decentralized access to dynamic web objects hosted by smart contracts and EthStorage.
Comparison with other decentralized storage projects:
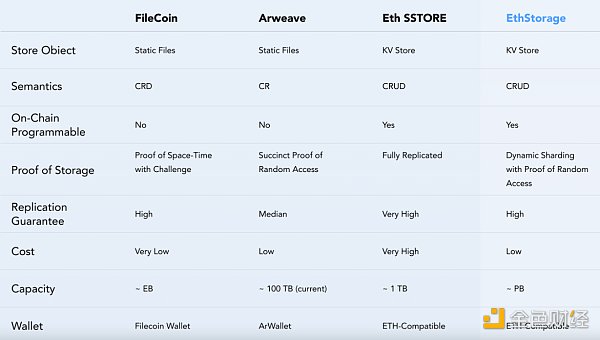
It is worth noting that the EthStorage test network is being tested and users can participate in the test to receive potential future airdrops.
Ethereum Attestation Service
A one-sentence summary: a public layer for creating, verifying, and revoking on-chain/off-chain attestations.
The Ethereum Attestation Service (EAS) slogan is “Attest to anything and everything” – prove anything.
EAS aims to create a public layer for attestations that can be used and integrated by various applications and protocols for creating, verifying, and revoking on-chain/off-chain attestations. The Ethereum Attestation Service will create a generic open-source attestation layer that can be used to verify the authenticity and integrity of information across different systems and communities.
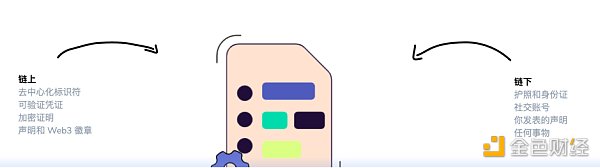
EAS only requires two smart contracts to operate, one to register a schema for any subject (or use an existing one), and another to attest using that schema.
EAS features:
-
Open source, anyone can use it.
-
Decentralized, meaning it is not owned by any individual or company, but supported by the ETH community.
-
Tokenless, because all transactions are settled through Ethereum.
-
Public interest, meaning it can be used for free and created for the greater good of the Ethereum ecosystem.
-
Interoperable, meaning different parts of the attestation layer can work together smoothly.
-
Composable, meaning attestations can be stacked and built upon each other like LEGO blocks.
-
Permissionless, meaning you do not need permission from a central entity, individual, or group to use EAS.
Use cases listed on the Ethereum Attestation Service website include:

Aspis Protocol
A one-sentence summary: a custom on-chain treasury for DeFi asset management.
Aspis is a no-code platform that enables users to create custom asset management vaults while also providing a friendly, transparent, and secure alternative for passive investment.
Its goal is to provide a toolkit for the creation, fundraising, and operation of decentralized autonomous funds, aimed at managing the relationship between the vault creator/manager and investors by moving the logic behind the list of legal terms to smart contracts.
Aspis consists of three main components:
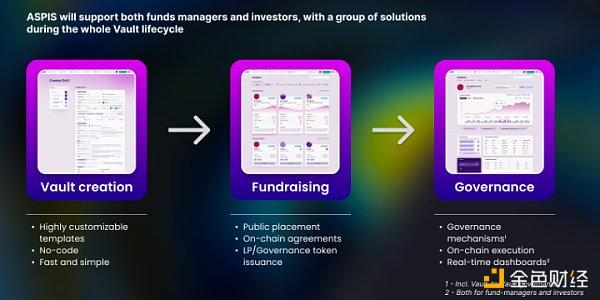
Aspis Use Cases:
Customize a vault to manage assets, raise funds for a user’s vault through LaunchBlockingd, manage assets in the vault with the highest level of transparency, directly access major DeFi venues from the vault balance, automate on-chain key accounting processes, automatically release tokens to contributors, control manager expenses through a limited activity list and management restrictions, participate in decision-making through on-chain voting.
Nerif Network
One-line Introduction: Decentralized cross-chain smart contract automation platform.
Nerif Network can automate dApp execution across multiple chains without relying on any off-chain programs.
Its working mechanism is as follows:
1. Set the execution trigger: Define the off-chain or on-chain event or condition that will trigger the workflow;
2. Add operations: Specify the operations the workflow should perform based on the trigger;
3. Activate the workflow: Put the automation workflow online and ready to run;
4. Monitor and manage dApp automation: Use comprehensive monitoring and management tools to easily supervise and control automation workflows.
We will continue to update Blocking; if you have any questions or suggestions, please contact us!
Was this article helpful?
93 out of 132 found this helpful
Related articles
- Preview of a New Project | Analyzing the Arbitrum Ecosystem’s Non-Liquidation Lending Protocol – Ghast Protocol
- Preview of New Project | DeFi Operating System Root – Planning to Develop the First Full-Chain ve (3,3) Governance Aggregation Flywheel
- 13 Potential Airdrop Projects You Can’t Miss
- Outlook on Ethereum staking market: Potential opportunities in a dynamic competitive landscape
- Comprehensive Explanation of Dolomite, a Currency Market Protocol Based on GMX
- Exploring the middleware Babylon Chain: Inspired by Eigenlayer, borrowing “Bitcoin security” for other POS chains
- Understanding ZK Cross-Chain Protocol Lagrange in 3 minutes






