A Summary of Projects Using OP Stack
Projects Using OP Stack OP Stack is a software stack that consists of the following components: - Operating system: Ubuntu - Programming language: Python - Web framework: Django - Database: PostgreSQL This article summarizes some projects that use OP Stack. ## Project 1: Online Marketplace An online marketplace where users can buy and sell items. Features: - User registration and login - Item listing - Shopping cart - Payment processing Technologies Used: - Front-end: HTML/CSS, JavaScript - Back-end: Python (Django), PostgreSQL ## Project 2: Inventory Management A web application that allows businesses to manage their inventory. Features: - Inventory tracking and management - Purchase and sales order management - Reporting and analytics Technologies Used: - Front-end: HTML/CSS, JavaScript - Back-end: Python (Django), PostgreSQL ## Project 3: Social Network A social network where users can connect with friends and share content. Features: - User registration and login - Profile creation and management - Friend connections - Content sharing (text, photos, videos) Technologies Used: - Front-end: HTML/CSS, JavaScript - Back-end: Python (Django), PostgreSQL Conclusion: These are just a few examples of projects that use OP Stack. With its powerful components, OP Stack is ideal for building robust web applications.Author: LeftOfCenter Compilation: BlockBeats
BNB Chain has launched its own Layer 2 chain, and officially launched the Layer 2 testnet “opBNB” on June 19. With the support of the Layer 2 expansion chain, BNB Chain can greatly improve transaction speed and reduce transfer gas costs to $0.005, greatly enhancing BNB Chain’s already strong processing performance.
Interestingly, this application chain named “opBNB” is built on OP Stack (more precisely, the first official version of Bedrock based on OP Stack). It is worth noting that OP Stack is Ethereum’s Layer 2 expansion framework, while BNB Chain is a smart contract public chain launched by Binance. To some extent, the two are in competition. So, what prompted BNB Chain to actively adopt Ethereum’s development framework OP Stack to build its own chain?
In fact, L2 is not unique to Ethereum’s needs. With the surge in transaction volume in GameFi and other areas, even high-performance public chains like BNB Chain are facing the problem of network congestion and high gas fees. The original design and architecture can no longer meet the new scalable demand, and opBNB has emerged in this situation.
- If BlackRock’s Bitcoin ETF is approved, which projects will be the winners behind it?
- What is the current status of the transition from classical DeFi projects to RWA MakerDAO?
- Introducing the Bitcoin Script Project: Grasping the Pulse of Bitcoin Development Amidst the Noise
opBNB is a recent member of the OP Super Chain, but not the only one. In fact, we have seen many well-known projects join the OP Chain camp one after another. In addition to Optimism blockchain developed by themselves (now renamed OP Mainnet), there are also Base Chain developed by Coinbase, World App, an ecological wallet under Worldcoin (the encryption project of OpenAI CEO), Zora, an NFT trading market invested by Blockingradigm, and Magi, a Rust-written client launched by top VC a16z. Together, they create a grand narrative of the super chain.
These projects themselves have a large number of users, high-quality resources, and many partners. Their entry will inevitably attract more developers, applications, and users to the OP ecosystem, and ultimately generate cash flow. It can be said that this “one-to-many” mode supported by giants will become the main focus of early ecological expansion of Optimism.
Take the NFT platform Zora as an example. While launching its own application chain Zora Network, it also brings 35 partners including Sound.XYZ, Rainbow Wallet, and PleasrDAO into the Optimism super chain, along with 130,000 users. The OpenAI CEO-initiated Worldcoin, which adopts OP Stack, can bring 1.7 million users. Tiago Sada, the core developer of Worldcoin, told BlockBeats, “At present, Worldcoin is in the first stage of migration to the super chain, and World App accounts are being migrated to the Optimism rollup mainnet.”
It can be said that the narrative of Optimism has gradually landed and begun to collapse into reality. Although the ultimate vision has not yet been realized, the summer of this application chain has really come.
OP Stack Progress
Technologically, Optimism’s progress is reflected in its actual savings of a lot of on-chain fees for users.
Data shows that since the release of OP Mainnet, the usage fee of Ethereum has been massively reduced and can be compressed to below 90%. Compared with Arbitrum One, the early OP Mainnet saved more transaction fees, and subsequent upgrades of both sides will compress or further widen the gap in fees.


In addition, after the Bedrock upgrade of the mainnet was completed on June 7 this year, the fee was reduced by about 50% and the deposit time was shortened. The average gas fee per transaction has dropped by about 75%, making Optimism Mainnet the cheapest Ethereum L2 network for token exchange. Bedrock makes Optimism closer to a “super chain”.

Optimism Bedrock is the architecture of the modular network and the first implementation of OP Stack. It uses the Ethereum virtual machine (EVM) as the execution layer, equivalent to the EVM, and uses Cannon as its interactive fault proof on the settlement layer.
The upgrade of Bedrock also makes Optimism more flexible and modular as a whole. If Ethereum introduces new transaction types through EIP-4844 in the future, Optimism can also introduce them at the same time to greatly reduce handling fees again.
Optimism is gradually gaining a foothold through OP Stack, which is reflected not only in its technological progress, but also in the increasing number of project parties joining the OP Stack camp.
In addition to Coinbase, which joined in the beginning (based on OP Stack launched its own L2-Base), more and more project parties have joined the super chain camp, launching their own application chains based on OP Stack. This includes top venture capital firm a16z developing a Rollup client based on OP Stack components, ChatGPT founder Sam Altman creating Worldcoin, which will migrate from Polygon to Optimism, Zora launching a second-layer NFT casting platform Zora Network for NFT creators, brands and collectors, and bringing in 35 partners, even public chains like BNBCHAIN have used OP Stack to build their own application chain opBNB.
What are the projects that adopt OP Stack?
OP Stack is known for its one-click deployment, but it is not the only option available on the market. In fact, projects like Worldcoin, Coinbase, and BNB Chain have all considered building their own public chains or adopting other frameworks to build Layer 2 chains, but ultimately none of them chose OP Stack. What is the reason behind this? In addition, what strategic significance does the application chain based on OP Stack have for each project?
Zora and its 35 eco-partners
Zora Network has launched a Layer 2 NFT minting platform based on OP Stack, which is aimed at NFT creators, brands, and collectors, providing a series of NFT creator tools and reducing minting costs to below $3.
With a focus on creating the best user experience for creators and collectors, Zora will provide a faster, lower-cost, and better on-chain experience.
As Zora Engineering tweeted, “An interesting fact is that the cost of ‘bridging’ to L2 + ‘minting’ is less than the cost of a single mint on the mainnet.”
Zora Network will seamlessly integrate with the existing infrastructure of the Zora market. This means that existing users of artists, brands, and collectors on the platform will seamlessly join the new Layer 2 network, including 35 Web3 project entities such as the music NFT platform Sound.XYZ, wallet application Rainbow Wallet, Web 3.0 innovation incubator Seed Club, and PleasrDAO, as well as the existing 130,000 users.

“By adopting OP Stack to develop an application chain, we hope to minimize the cost of creators and make Zora a place for media and culture to thrive on the chain.”
To commemorate this release, Zora has issued an open NFT called Energy, which fans can mint in the next 10 days.
According to data, since its launch on the 21st, Zora Network has bridged more than 38,012 addresses and has a TVL of 375 ETH, equivalent to about $700,000.
opBNB, the BNB Chain application chain
L2 is not exclusive to Ethereum, and with OP Stack, new public chains can also join Ethereum’s L2 game, such as the opBNB Layer 2 application chain built on OP Stack.
On June 19th, the BNB Chain launched a Layer 2 testnet based on the Optimism OP Stack (expected to launch the mainnet in Q3 2023), using OP Stack Rollup to move computation and state storage off-chain, thus relieving congestion and reducing transaction costs.
opBNB can further improve processing speed, with performance exceeding that of BNB Chain.
According to the official description, the opBNB block time is 1 second, the transfer Gas fee is as low as $0.005, and the processing capacity per second (TPS) exceeds 4,000, compared to the current Layer 1 BNB Smart Chain processing speed of 2,000 transactions per second. The average cost per transaction is about $0.109, almost twice the speed of BNB Chain’s mainnet and significantly lower in cost.
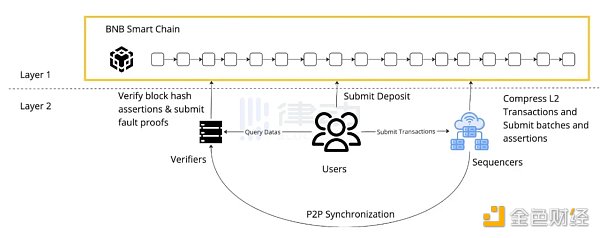
opBNB is a Layer 2 network (Layer 2) built on OP Stack on the BSC. Like Optimism Rollup, opBNB calculates transaction data off-chain and submits it to Layer 1 for performance optimization, ultimately achieving high TPS, low gas fees, and consistent security with Layer 1.
So why did opBNB choose to build its own application chain using OP Stack?
In fact, L2 is not unique to Ethereum. With the surge in transaction volume in GameFi and other areas, even high-performance public chains like BNB Chain face the problem of network congestion and high gas fees. The original design and architecture can no longer meet the new scalability requirements, leading to the emergence of opBNB.
As early as September last year, BNB Chain launched the zkBNB testnet (i.e., the second layer network using zero-knowledge proofs). However, because zkBNB is incompatible with EVM (incompatible with EVM means that it cannot interact with applications on Ethereum), BNB Chain turned to develop a new Layer 2 solution “opBNB”.
opBNB can introduce improved data availability, batch transactions, and up to 100M Gas limits to the BNB public chain ecology. Meanwhile, EVM-compatible OP Stack can also simplify the process of migrating Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM) code from Ethereum to BNB Chain, making it easier and faster for developers to create open ecosystems and expand their user base.
Unlike Optimism and Coinbase’s Layer 2 scaling solution Base, opBNB is built on BSC (not Ethereum), which itself outperforms Ethereum, and opBNB will further improve performance, surpassing not only BSC but also other scaling solutions such as Optimism.
Most importantly, using the OP Stack to build Layer 2 application chains on the BNB Chain has strategic significance. For the BNB Chain, building an application chain using the OP Stack not only allows for the high security provided by layer 1 Ethereum, but also allows BNB to continue to be used as a gas fee payment token. This means that as more use cases emerge in the future, the application scenarios for BNB can be greatly expanded, and these benefits can all be captured by BNB. In the long run, BNB Chain may even become a strong competitor to Ethereum’s continuously developing L2 ecosystem.
Base, developed and incubated by Coinbase
Base (@BuildOnBase), which was launched in February of this year, is one of the earliest application chains launched using the OP Stack. It was incubated by Coinbase and is one of the earliest application chains to join the Optimism superchain ecosystem, apart from Optimism’s own projects.
In addition, the Base development team is also a core contributor to the OP Stack codebase and has been deeply involved in and promoting EIP-4844. It can be said that the Base team is the biggest help in OP Stack research and development.
Base, an application chain that focuses on financial services, has the characteristics of security, low cost, developer friendliness, and ease of deployment of dApps. So why did Coinbase choose to develop the Layer 2 network Base as the largest and compliant centralized cryptocurrency exchange in the United States?
Developing Base at this stage is in line with Coinbase’s future roadmap. In fact, after the previous stage goal of “developing and investing in a large number of decentralized applications to provide users with convenient application layer access to cryptocurrencies” gradually took shape, it is time to realize Coinbase’s ultimate goal of “eventually creating a globally open financial system that reshapes the current financial system.”
However, creating an open financial system requires support from a public chain and its ecosystem. Previously, Coinbase also had the idea of creating its own public chain, but it ultimately gave up due to cost, difficulty, regulatory, and strategic considerations.
Choosing to use the OP Stack to build Base not only allows for the reuse of existing Optimism development results, but also allows for “one-click chain launch”. Its modular framework supports high openness and composability, including the chain execution layer (which virtual machine to choose), proof method (fraud proof or ZK), data availability DA layer, settlement layer, and so on, which are all optional, truly modular Lego-style.
The most important thing is that becoming an OP Chain means that Coinbase joins the Ethereum lineup and can handle Ethereum traffic in the future. In addition, Base will also be a member of the “Super Chain”, which can not only exchange resources with other OP Chains in the ecosystem, but also contribute to this “Super Chain” system that may reach Internet-level scale in the future. Plus, with Coinbase’s existing user base (nearly 110 million users and over 8 million monthly trading users in Q3 2022), customers can seamlessly access the financial service protocols hosted on Base, and use Base as an entry point to cross over to Ethereum L1, other L2s, and other L1 ecosystems, greatly increasing the chances of Base’s future success.
With the powerful resources behind Coinbase, even during the launch phase, nearly 60 projects have joined Base as its ecosystem partners, including infrastructure and tools such as Chainlink, Nansen, Dune Analytics, and The Graph, as well as well-known projects originally deployed on Ethereum, such as Sushiswap, Balancer, and PoolTogether.

According to the development plan, Base will not directly host C-end users in the future, but will introduce more decentralized applications to provide services to C-end users. To this end, since its launch, Base has joined forces with many developer communities and organizations such as Upside DAO, Developer DAO, GenTwo, thirdweb, QuickNode, Google, and Blockdaemon to hold hackathons and developer competitions around the world to attract more developers.
Worldcoin and its on-chain identity system
In May of this year, the Worldcoin Foundation and Tools for Humanity (TFH) early protocol contributors announced their support for Optimism Collective to jointly build a scalable blockchain ecosystem based on the OP Stack.
As the first step in entering Optimism Collective, the decentralized privacy identity protocol World ID under Worldcoin will go live on the OP mainnet, and its native wallet World App will be migrated to the OP mainnet in the future.
In fact, as early as 2020, Worldcoin independently developed and launched a simple payment-only Optimistic Rollup application chain Hubble, and released a test version of World App. However, after the release, the team found that the test results were not ideal, and user needs were not limited to simple payment functions, which far exceeded Hubble’s carrying capacity, and later migrated to Polygon PoS.
Now, Worldcoin has turned to rebuild the application chain using the OP Stack. However, the focus of this collaboration will be on building an on-chain identity system.
For Optimism, a decentralized identity system on-chain is key to achieving its economic self-growth, unlocking not only democratic governance and innovation, but also enabling individuals to better control their finances and participate in the global economy on their own terms.
To this end, Optimism has deployed the identity primitive AttestationStation, an experimental identity system that allows anyone to attest to any other address, thereby assigning a trust score to a specific on-chain address, measuring the true social relationship (influence) of that address.
For Worldcoin, the identity system is equally important. Since it is necessary to distribute digital currency for free to the 7.9 billion people around the world and achieve fair distribution of wealth, a method is needed to determine the user’s identity and prevent the same person from claiming tokens multiple times under different identities. To this end, the team has developed World ID as the underlying identity protocol for Worldcoin, which ensures that each person can only register one account with their iris. In addition, the team has developed a set of biometric devices that verify a person’s uniqueness by scanning their iris, while ensuring the privacy of the verified person through zero-knowledge proofs.
Currently, Worldcoin has over 1.6 million registered users of the beta version and over 500,000 World App active users per month. This means that Worldcoin, which has joined the Superchain ecosystem, will bring a huge number of users to the OP ecosystem. In the long run, considering that Worldcoin’s research and investment in the identity system are leading in the industry, this can enhance the governance capabilities of the key component “Citizens’ House” of the Optimism ecosystem and promote the progress of the on-chain reputation system AttestationStation, ultimately expanding the Web3 identity system in the Optimism network and laying the foundation for decentralized governance.
The Worldcoin team has not yet announced the development progress of its application chain. However, Twitter user Spreek posted a tweet and found that someone had deployed a large number of gnosis safes accounts on the Optimism network. According to statistics, a total of about 300,000 gnosis safes accounts were deployed on the Optimism network, and each account generated about 10,000-15,000 transactions within a week. Worldcoin’s core developer Tiago Sada claimed this “achievement” and told Blockbeats, “These Safe contract operations are related to the migration of World App accounts to the Optimism rollup mainnet. Currently, Worldcoin is in the first phase of migrating to the Superchain.”
a16z’s Rollup client Magi
Magi is a second-layer Rollup client solution launched by a16z Crypto in April of this year. It is written in the Rust language, based on the OP Stack, and serves as a consensus client in traditional Ethereum execution/consensus splits, providing new blocks to the execution client to advance on-chain transactions. Magi performs the same core functions as the reference implementation (op-node) and works with execution nodes like op-geth to sync to any OP Stack chain.
The goal of Magi is to become an independently developed direct replacement for op-node, which will increase client diversity for Rollup.
A16z hopes to build a new client based on Rust that will encourage the entire OP stack to be more secure and active and bring more contributors to the ecosystem.
As one of the most well-known investors in the crypto space, a16z has more than $7.6 billion (approximately RMB 50 billion) available for investment in the field (as of May of last year). As one of the investors in the Ethereum scaling project Optimism, a16z Crypto is leading the development of the Magi client on OP Stack, not only as an investor but also as a developer, marking the first step for a16z in the Optimism Collective.
On-chain games: OPCraft, Keystone, and Loot
On-chain games typically have high-frequency interactive scenarios, meaning that speed and cost requirements are extremely high. This means that on-chain games require customized blockchain infrastructure, and many scaling solutions have launched scaling solutions specifically for on-chain games.
OP Stack is one of the most popular infrastructures for on-chain games, with one of the most representative on-chain game experiments, OPCraft, built on Op stack.
OPCraft is an on-chain virtual world where every river, blade of grass, and snow on the mountaintop exists on the chain, and every action that occurs there is a transaction on Ethereum. Like most pixel-style games, you can explore procedurally generated landscapes, mine ore, place materials, and craft new items in OPCraft. Players can build magnificent buildings, erect monuments, and transform the land alone or with other players.
OPCraft built on OP Stack can achieve higher throughput and shorter block times with simple debugging.
Keystone is another chain made with OP Stack. It uses custom precompiles to embed game tick and ECS into the chain, increasing on-chain game speed by 100 times and providing a more powerful gaming experience.
Additionally, Adventure Gold DAO, a Loot ecosystem project, recently announced that it will use OP Stack to build Loot Chain, a new Ethereum L2 network dedicated to the Loot community, in order to reduce gas fees and use its native token AGLD as a gas token. The chain also uses Polygon as a data availability layer, significantly reducing the cost of building, deploying, and operating Loot Chain.
Conclusion
“One-click deployment + modularization” is not something new, but relying on the highly open freedom and composability of OP Stack based on the Ethereum ecosystem has attracted a large number of ecological partners. After all, joining the OP Stack ecosystem means that resources can be shared in parallel with Ethereum, and while enjoying the high security of Ethereum, you can still choose to use your own native token as a gas token. Who can refuse such a good thing?
We will continue to update Blocking; if you have any questions or suggestions, please contact us!
Was this article helpful?
93 out of 132 found this helpful
Related articles
- How to Choose the Financing Method and Legal Documents for Web3.0 Blockchain Project Financing?
- What is the development direction of the new NFT project with the Azuki crash and BAYC debut?
- dYdX Chain’s public testnet will officially launch at 01:00 (Beijing time) on July 6th.
- Further observation on the staking track: What other potential projects are there besides EigenLayer?
- Understanding the five core principles and unique features of ZKStack
- Comprehensive Interpretation of the StarkNet Ecosystem: Which Projects are Worth Paying Attention to
- Proto-Danksharding may become the biggest narrative of the year, which projects will benefit?






