Waterdrip Capital: Exploring NFTFi Leasing for New Breakthroughs in NFT Liquidity
Waterdrip Capital: Exploring NFTFi Leasing for Improved NFT LiquidityOriginal Authors: Ryan, gt, coucou Mentor Guidance: Jademont, Elaine, Bill @Waterdrip Capital
1. Introduction
1.1 NFTFi
Before explaining NFTFi, there are two foundational concepts about NFTFi that need to be understood.
NFT (Non-Fungible Token): A type of digital asset based on blockchain technology, each NFT has a unique identifier and value. Unlike interchangeable tokens in cryptocurrencies, NFTs represent unique assets such as digital art, virtual real estate, virtual items, game props, etc. The uniqueness and indivisibility of NFTs make them very popular in the digital collectibles and cultural fields.
DeFi (Decentralized Finance): A financial system built using blockchain and cryptocurrency technology, aimed at achieving decentralized, transparent, and trustless financial transactions. DeFi applications provide various financial services such as lending, debt collateralization, trading, asset management, etc. through smart contracts, without the need for traditional financial intermediaries.
- DeFi protocol Concordia raises $4 million in funding, co-led by Tribe Capital and Kraken Ventures
- Tether responds to FUD rumors: no intention to engage in time-consuming and fruitless US litigation
- Evening Must-Read | Explaining the RWA Tokenization Track: The Next Wave of Cryptographic Narrative?
NFTFi, or “NFT Finance”, is actually NFT + DeFi, which refers to the emerging ecosystem of decentralized protocols and applications primarily providing financial utility for NFTs. In practice, NFTFi protocols provide DeFi functionalities to NFTs, unlocking their leasing, lending, and fractionalization abilities, creating derivatives and prediction markets around them, and so on.
1.2 NFT Leasing
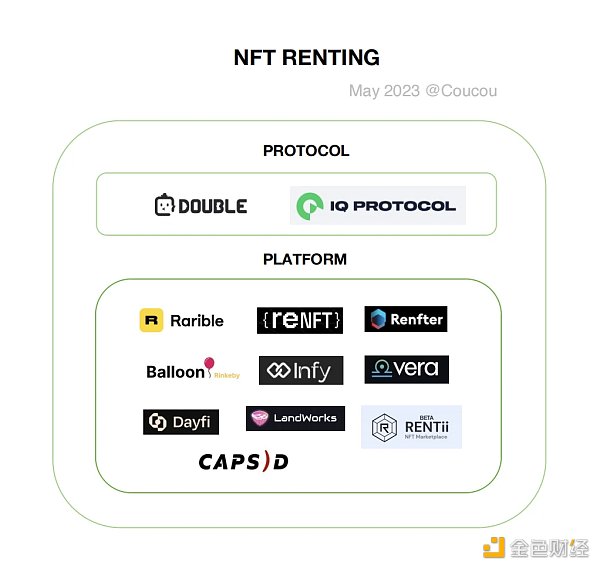
NFT leasing refers to the process of trading NFTs as rental assets. In traditional leasing models, people can rent various items such as cars, houses, or equipment, while in NFT leasing, people can rent digital art, game props, virtual real estate, or other types of NFTs. The NFT leasing track can currently be divided into two categories: protocol and platform. In terms of protocols, Double Protocol and IO Protocol are well-known NFT leasing protocols. In terms of platforms, Rarible and reNFT have high visibility.
Common NFT leasing methods:
-
Fixed leasing period: Users rent NFTs and select a fixed leasing period, such as one week, one month, or longer. Users pay the corresponding rent and can enjoy the usage rights of NFTs during the period. Once the leasing period ends, users will lose the usage rights to NFTs.
-
On-demand leasing: Choose the time to rent NFTs according to your own needs, without being limited by fixed leasing periods. Users may need to pay rent calculated by the hour, day, or other time units. This method provides greater flexibility, allowing users to decide the leasing duration based on actual needs.
-
Shared leasing: Multiple users can jointly rent the same NFT and share usage rights and rental costs in the agreed upon manner. This method can share the leasing costs among multiple users, reduce the burden on individual users, and enable more people to enjoy the value of NFTs.
-
Lease-to-purchase: Some NFT leasing platforms offer lease-to-purchase options, allowing users to choose to convert the paid rent into the purchase cost of NFTs after the leasing period ends. This method gives users the opportunity to understand and experience NFTs during the leasing period and decide whether to purchase them.
At the same time, they can be divided according to whether they are collateralized assets:
-
Collateralized NFT leasing
Collateralized leasing is a kind of NFT leasing based on collateral. Usually, the lessee needs to provide a certain amount of cryptocurrency as collateral to ensure payment ability and responsibility during the leasing period. The collateral can be ETH, BTC and other digital assets, or other NFTs. In this leasing mode, the NFT owner mortgages their NFT in a smart contract to obtain tokens representing the collateral. Lessees can use these tokens to lease NFTs. When the lease period expires or rent is not paid on time, the collateral will be deducted a certain amount of penalty or be confiscated.
Projects that adopt collateralized leasing can better ensure the lessee’s payment ability and responsibility, while also providing certain risk protection for NFT owners. Some NFT projects that use collateralized leasing have already appeared, such as reNFT, NFTfi, etc.
-
Non-collateralized NFT leasing
Non-collateralized NFT leasing allows users to rent NFTs without providing collateral and return them after the lease period ends. This model is very attractive to users who do not have enough collateral or do not want to take on collateral risk.
Double Protocol proposes a new NFT type called doNFT, which has an expiration date and can ensure the expiration time. This means that users can rent NFTs for a certain period of time, and after the lease period ends, the NFT will be automatically returned to the original holder. This model is different from the traditional NFT ownership model. It is more like a leasing agreement that can help users save costs and reduce risks. In addition, Double Protocol also provides an NFT wrapping method called wNFT. Users will not receive the original NFT directly, but will receive a wrapped NFT with the same characteristics and supported by the original NFT. When the lease period expires, the wrapped NFT will be destroyed to ensure the security of the original NFT.
The difference between IQ Protocol and Double Protocol is that it does not use doNFT, but achieves non-collateralized leasing through wrapping. Users can use ETH or other cryptocurrencies to pay the rent without providing collateral. At the end of the lease period, users will receive the corresponding rent and the leased NFT. Overall, this model can provide additional sources of income for NFT holders while ensuring security.
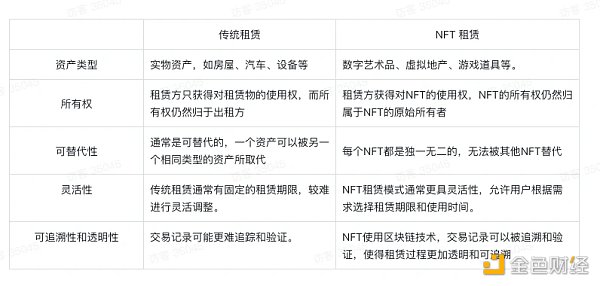
1.3 Comparison of NFT Leasing and Traditional Leasing Models
There are significant differences and distinctions when comparing NFT leasing models with traditional leasing models:
II. Operation Mechanism of NFT Leasing
This section will analyze the protocol standards for leasable NFTs. ERC-4907 and ERC-5006 mentioned in this article are relative to ERC 721 and ERC 1155.
2.1 Basic Principles of Leasable NFTs
ERC-4907
In NFT leasing, the lessor usually transfers the NFT to a designated smart contract and sets lease terms and fees. The lessee can obtain the right to use the NFT by paying a certain lease fee, and during the period of use, the lessee can enjoy the benefits brought by the NFT, such as income and voting rights, while also bearing certain risks, such as a drop in NFT prices resulting in losses for the lessee. After the lease term ends, the NFT will automatically transfer back to the lessor’s wallet. The following figure shows an example of a leasing function:
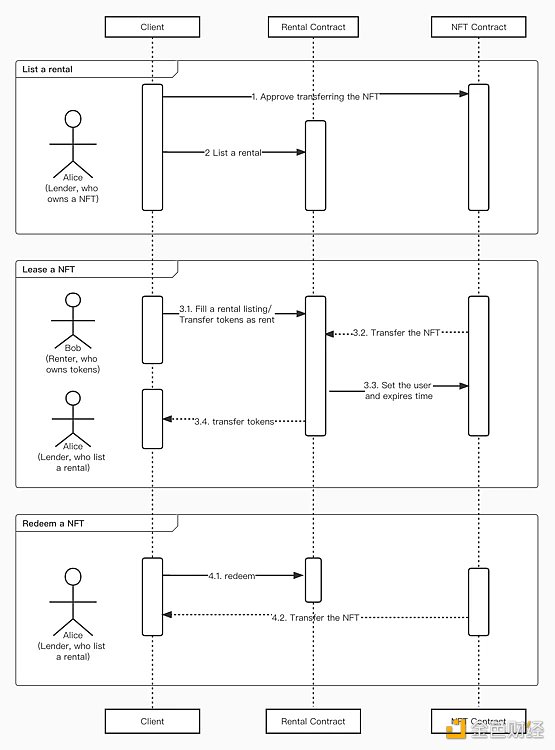
Now, assuming Alice holds an NFT, and Bob intends to rent this NFT. Then there will be four business logics, which are:
-
Alice authorizes the leasing contract to transfer the NFT she holds.
-
Alice “lists” her NFT, marked as leasable.
-
Bob selects the rental time according to his own needs, and after selecting it, he transfers the rent to the leasing contract. The rent is calculated based on the unit rental price and rental time. After transferring the rent, the leasing contract transfers the NFT listed by Alice to Bob and sets the lessee as Bob, and the expiry time is Bob’s rental time.
-
After the lease expires, Alice can retrieve her NFT from the leasing contract.
The ERC 721 protocol does not support the separation of NFT usage rights and ownership rights, that is, only the NFT owner has usage rights. The ERC 4907 protocol constructs an additional role that can grant addresses, and automatically cancels the leasing relationship after the role expires, realizing the separation of NFT ownership and usage rights, providing technical support for on-chain “native leasing,” and is an important infrastructure for solving the problem of NFT liquidity shortage.
ERC-5006
ERC-4907 is the counterpart of the ERC-721 standard, defining a model where an ID corresponds to a user. In contrast, the ERC-1155 standard allows for multiple users to correspond to a single ID. However, from a fundamental perspective, ERC-5006 and ERC-4907 do not differ much. In terms of specific implementation, ERC-1155 is more complex and introduces some new variables.
2.2 Analysis of NFT leasing protocol function (ERC-4907)
ERC-4907
The core of NFT leasing implementation is to separate the right of use from ownership. ERC-4907 uses two roles, owner and user, for permission division, and the roles have an expiration date, meaning that the lessee’s permission automatically terminates when it expires without any on-chain operation.
ERC-4907 mainly provides three functional interfaces, namely, setUser, useOf, and userExpires. The following will introduce these three interfaces.
-
setUser mainly sets a new user and expiration time for the NFT on the shelf. Internally, the function first verifies whether the NFT is owned by the initiator, and if so, writes the lessee’s information.
-
userOf can query the current user of a certain NFT. If the current NFT is not leased or the lease has expired, an empty address is returned.
-
userExpires can query the lease expiration time of a certain NFT.
ERC-5006
ERC-5006 is an extension of ERC-1155, proposing an additional role, user, and defining two core variables:
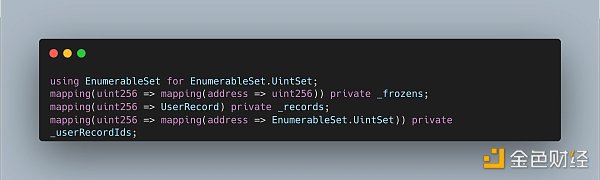
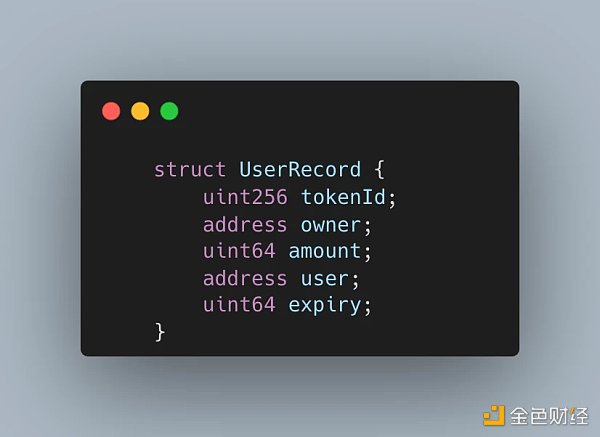
UserRecord defines lease records.
_frozens defines the frozen balance of the address corresponding to the token ID after the lease.
_records defines a mapping table that records token lease records. UserRecord records a token lease record, recording the two roles, owner and user, for permission division.
_userRecordIds defines an ID and a Mapping for each token ID, and the Mapping records the relationship between each user address and the token lease record ID.
ERC-5006 mainly provides five functional interfaces, namely, usableBalanceOf, frozenBalanceOf, userRecrodOf, createUserRecord, and deleteUserRecord.
-
usableBalanceOf is used to query the available balance of a token leased by a lessee.
-
frozenBalanceOf is used to query the frozen balance of a token held by a lessor.
-
userRecrodOf is used to query a token leasing record.
-
createUserRecord is used to create a token holding record.
-
deleteUserRecord is used to delete a token holding record.
III. Application areas of NFT leasing
3.1 Application of NFT leasing in Web 3 games
Classification of game players
Users can be divided into four quadrants based on whether they like games and whether they hold encrypted assets:
-
Game enthusiasts who hold encrypted assets
They like games, enjoy the fun of games, and hold encrypted assets.
-
Game enthusiasts who do not hold encrypted assets
They like games, enjoy the fun of games, but do not hold encrypted assets. Playing encrypted games has a high threshold for entry.
-
Non-game enthusiasts who want to try encrypted games
They are not game enthusiasts but want to try encrypted games.
-
Non-game enthusiasts who hold encrypted assets
They are not game enthusiasts but want to earn money through activities such as game outsourcing.
Pain points of Web 3 games
As a traffic entry point for Web 3, Web 3 games are responsible for educating Web 2 players and guiding more Web 2 users to enter Web 3. However, due to the particularities of Web 3 games, the following problems exist:
-
The high threshold continues to discourage traditional users.
-
Most games adopt the method of stitching Web 2.5, where non-encrypted players play the non-blockchain version of the game, and Web 3 players play the blockchain version, resulting in a split economic system.
Therefore, there is a need for a way to lower the barrier to entry and allow non-crypto users to smoothly experience Web 3 games. One approach is to directly lower the threshold, such as by using abstract accounts. Another approach is to transfer the high threshold to Web 3 players, similar to helping open ChatGPT accounts. NFT lending is the second approach. It not only allows more non-crypto players to enter the game, but also allows players with low or even zero assets to enter the game.
Web 2 game market leasing
In fact, leasing also exists in the Web 2 game market, and the core is resource allocation, that is, the exchange of time and money between the group of “plenty of time but insufficient wealth” and the group of “insufficient time but sufficient wealth”. Here, leasing can be divided into two categories according to purpose:
-
Obtaining rent:
And in Web 3, there is not only rent, but also additional gold farming.
-
Spending money to get achievements and experience in the game:
And in Web 3, this situation is almost nonexistent.
However, the advantage of Web 3 is that an trustless environment is ensured through algorithms built by blockchain and smart contracts. In most Web 2 games, leasing is unofficial and off-market, and there are many scams and distrusts. Although the cost of identity fraud on the chain is too low and everyone can easily create anonymous addresses, in the game scene, game data has become the hidden cost of fraud.
Among the traditional “insufficient time but sufficient wealth” players, they either only pay money to get a better game experience, or earn fixed money (that is, entrance fees, without continuous income). But in Web 3, leasing is more like an investment. Individual investors can invest their assets more reasonably through borrowing, thereby continuously gaining income.
Early exploration of NFT leasing
In the early days, many well-known GameFi projects also appeared off-market NFT lending, such as Axie Infinity and StepN. From this, we can also see that NFT leasing exposed some problems in the GameFi 2.0 era:
-
Renting out NFTs leads to a mature gold-farming industry, disrupting the game’s economic system balance and accelerating the death spiral of the game. However, this problem cannot be avoided even if leasing is not allowed. Additionally, most players in current GameFi games are focused on gold-farming.
-
Renting out NFTs releases too many uncertain and uncontrollable factors, making it difficult to control game values and accelerating the game’s collapse.
However, the advantages of leasing are also obvious. From the number of players in Axie and StepN, it can be seen that leasing is beneficial to both parties:
-
Lowers the user threshold, opens up the game market, allows more players who are not just interested in making money to enter the game, and is beneficial to the game ecosystem.
-
Because leasing to others can earn more money, it increases the willingness of whale investors to invest money.
The current application of NFT leasing in Web 3 games
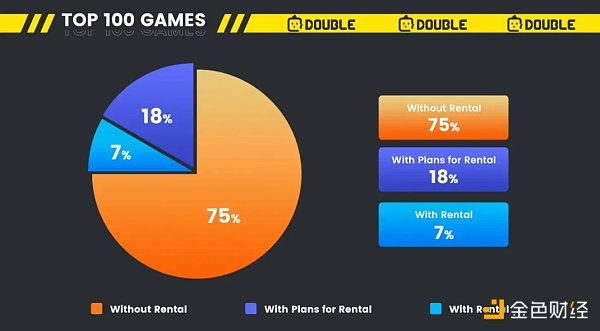
According to data from mymetadata.io ranking the games with the highest number of independent active users per day in the last 30 days as of June 12, 2022, we can see that at the current stage of Web 3 games,
-
Games with their own NFT leasing market/function account for 7%.
-
Games that have not yet implemented NFT leasing but have publicly expressed interest or commitment to do so in the future account for 18%.
-
Games that have not yet implemented NFT leasing and have not publicly expressed interest or made commitments account for 75%.
However, even though only 7% of games have their own NFT leasing market/function, the share of players who lease games is as high as 20.4%, showing a disproportionate ratio.
Special forms of NFT leasing in Web 3 games
The characteristics of the game have also created new forms of organization for NFT leasing in Web 3 games, including guild leasing and project-built-in leasing systems.
One of the most famous examples of guild leasing is YGG (Yield Guild Games), which initially became known for providing Axie rental services to Axie Infinity players. The model is based on guilds purchasing large amounts of game assets and then renting them out to game users, but it also brings a lot of pressure to the game side. To the game side, the guild is a growth tool, but it also brings a potential “Sword of Damocles”. Therefore, if the game side can acquire new customers at low cost and find healthy and appropriate users, they are unlikely to choose a guild.
However, the form of guild leasing can also be opened by the project party itself, which is more efficient and convenient to manage, and can directly bypass the guild. From the perspective of the project party itself, they may not be able to avoid the occurrence of leasing, so opening their own leasing system may be a better choice.
3.2 NFT Leasing in the Metaverse
NFT leasing of virtual land in the metaverse is a major part of NFT use cases, helping to connect the virtual world with the physical world. Just like in the physical real estate business, Decentraland LAND owners can lease their virtual land to tenants, who can use them to host events or develop them into shopping malls, offices, entertainment centers, etc. In July 2022, Decentraland and Double Protocol launched an on-chain NFT leasing solution that can be used in conjunction with LAND. In short, Double provides an infrastructure that streamlines the leasing process while providing more diverse leasing services, benefiting both LAND owners and potential tenants.
Brief Analysis of Leasing Solution
By utilizing ERC-4907, the Double NFT Leasing Protocol runs on two main smart contracts: the “Market” contract and the “doNFT Factory” contract. The “doNFT Factory” smart contract adds new NFT contracts to the platform, while the “Market” smart contract handles all NFT leases. The Double NFT leasing protocol allows the leasing of any ERC-721 based NFT.
When tenants pay rent for an NFT, they receive a doNFT. The doNFT contract, created by the doNFT factory, mints doNFTs. DoNFT is ERC-721 compatible and has a duration list that includes start and end times. The duration specifies that the owner of the doNFT has the right to use a certain NFT within the agreed time.
The lessee has multiple usage rights throughout the lease period, including subleasing and developing virtual land. The doNFT contract automatically revokes the borrower’s usage rights at the end of the lease term. An example of leasing on Decentraland is shown below.
The fashion industry enters the metaverse
The metaverse land leasing business will shine in the process of the fashion industry entering the metaverse. The Second Metaverse Fashion Week (MVFW) hosted by Decentraland officially opened in March 2023, with brands such as Adidas, Dolce & Gabbana, Balmain, Coach, and Tommy Hilfiger all appearing. Although the heat of the metaverse has weakened after entering 23 years, many brands have increased their investment in the metaverse, trying to use new products and marketing methods to obtain growth (whether it is users or profits) in a new track.
They have acquired digital real estate, invested in virtual advertising, held wearable competitions and fashion shows. This includes Adidas, Burberry, Dior, Dolce & Gabbana, Gucci, Nike and more. At the same time, more and more native digital brands are emerging like mushrooms, such as DressX, which sells virtual wearable devices, from basic sweatshirts to warrior costumes made of digital metal. This, coupled with the creator economy and the scope of digital ownership brought by NFTs, may democratize traditional elite industries.
However, due to the expensive price of metaverse land, plus the continued depression of the NFT market (actually the entire crypto market), not all brands are willing to spend a high price to acquire a piece of metaverse land that may quickly depreciate. At this time, NFT leasing business is very important. On the one hand, metaverse land leasing can give non-first-tier brands the opportunity to enter the metaverse track without taking too much risk. Brand owners can choose how much land to lease, how long to lease, etc. according to their own needs and capabilities. On the other hand, the idle land in the hands of players can also be called up. Many NFT holders are restricted by the depressed market environment and are forced to hold them, waiting for the subsequent rise in NFT prices. The emergence of leasing business can help these “smashing hands” holders sit on revenue-generating assets and add sources of income.
3.3 Application of NFT Leasing in Communities
Community equity NFT leasing first appeared in 2019, mainly as an attempt and exploration in the Ethereum community. With the continuous development of blockchain technology and smart contracts, the application scenarios and business models of community equity NFT leasing are also constantly expanding and deepening. Community equity NFT leasing refers to renting NFTs that represent specific community or organizational rights to users, allowing them to enjoy the relevant rights of the community or organization during the lease term. The lease term, rent, and usage rules can all be encoded in smart contracts to ensure transparency and security in the leasing process. Its main function is to allow non-community members to obtain relevant rights of community members within a certain period of time, such as voting rights, community resource usage rights, etc. Equity NFT leasing has a wide range of application scenarios and can provide new sources of funding and reward mechanisms for various types of communities, while also providing more flexible and secure usage rights for renters, helping them to obtain better experiences and benefits.
Business Model
The community is the foundation of community equity NFT leasing. The community can be a virtual community or a physical community. Renters are the core participants in community equity NFT leasing. Renters can rent community NFT tokens through leasing platforms and enjoy the right to use specific community rights for a certain period of time. During the lease period, renters can participate in community activities as NFT holders or receive corresponding community rewards. The rent paid by the renters will be paid to the leasing platform, and a portion of the rent will be used as the leasing platform’s earnings, while another portion will be used as rewards for community contributors or holders. In addition, the leasing platform is an intermediary platform for community equity NFT leasing. The leasing platform provides NFT leasing services to the community and charges a certain percentage of the rent as its own earnings. The leasing platform can also promote its brand and services through NFT leasing activities.
The business model of community equity NFT leasing mainly includes the following aspects:
1. Platform Fees: The rental platform charges renters a certain fee or rent.
2. Community Benefits: The rental platform collaborates with the community, taking a certain percentage of the rent as its own profit and distributing the remaining rent to the community’s contributors or holders.
3. Brand Promotion: The rental platform brings exposure and attention to its own brand through NFT rental activities.
Fourth, the advantages and challenges of NFT leasing
4.1 Advantages of NFT leasing
To summarize the advantages of the above three scenarios, the advantages of NFT leasing are as follows:
-
Lowering the threshold: NFT leasing can lower the threshold and cost, allowing more users to enter, which is beneficial to the ecology, encourages more users to participate, enhances interactivity and community cohesion.
-
Increasing asset liquidity: NFT leasing can increase asset liquidity, making it easier for people to buy, rent, and invest in virtual assets.
-
Providing financial support: NFT leasing can increase the flow of funds, providing financial support for the sustainable development of the project ecology and promoting its development and growth.
-
Creating new economic models: NFT leasing creates a new economic model. It can promote the effective use and transaction of assets, create value for owners, lessees, and developers, and provide them with new sources of income.
4.2 Challenges and risks faced by NFT leasing
To summarize the above three scenarios, the challenges and risks faced by NFT leasing are as follows:
-
Market bubble risk: The excessive speculation of NFT market prices may lead to instability and investment risks.
-
Regulatory risks: The ownership and leasing rights of virtual assets may involve complex legal and regulatory issues, and the risks of compliance and legal protection need to be carefully considered.
-
Technical security risks: Using NFT leasing for transactions may involve technical obstacles, smart contract vulnerabilities, and network security risks.
-
Market demand and acceptance risk: The successful implementation of NFT leasing also requires market demand and wide acceptance.
-
Uncertainty of leasing prices: Leasing prices are influenced by market supply and demand and other factors, and prices fluctuate greatly, making it difficult to guarantee the stability and fairness of leasing prices.
-
Lack of norms: The NFT leasing market lacks unified norms and standards, and there may be uncertain factors and unpredictable risks in the leasing process.
5. Future Development of NFT Leasing
Summarizing the three scenarios above, we believe that the future development of NFT leasing will demonstrate the following three trends:
-
In the future, NFT leasing will achieve a higher degree of automation and autonomy with the support of smart contracts and blockchain technology. In addition to technical specifications, market norms and standards will be designated to create a smoother, more accessible user experience, while ensuring the rights of all parties. The future NFT leasing model will be more flexible, intelligent, and diverse, with personalized settings based on the needs of participants to meet different usage scenarios and business models.
-
As NFTs develop, their applications will become increasingly diverse, including social, metaverse, gaming, and other fields. As more rights and scenarios emerge, NFT leasing will also benefit from these new application scenarios, with more gameplay and empowerment. At the same time, the trend towards globalization will also bring more opportunities for NFTs, promoting the global development of NFT leasing, attracting more participants and users. In this context, NFT leasing will continue to innovate and develop, becoming an indispensable part of the future Web3 ecosystem.
-
NFT leasing, as a way to reduce barriers, can bring more opportunities for users to participate in the Web3 ecosystem, reverse-empowering NFTs and Web3, and promoting the development and mass adoption of Web3. The existence of NFT leasing allows more users to own NFTs, thus promoting the expansion of NFT application scenarios, helping to prosper and develop the NFT ecosystem. At the same time, NFT leasing can also provide empowerment for more Web3 scenarios, bringing more possibilities and opportunities to different application scenarios in the Web3 ecosystem by reducing barriers and providing more usage scenarios, promoting diversity and development in the Web3 ecosystem.
6. Conclusion
This article first introduced the basic concept of NFTFi leasing, pointing out that the difference between NFT leasing and traditional leasing is that people can lease digital artworks, game props, virtual real estate, or other types of NFTs. Secondly, from a technical perspective, this article analyzes the more widely used ERC-4907 and ERC-5006 protocols and briefly introduces the functional interfaces of these two protocols. Due to the rapid development of NFT leasing, its application areas are also becoming more and more diverse. Web3 games, metaverse, and community equity NFTs are all typical application scenarios for NFT leasing, and this article explains in detail the business logic and representative projects of NFT leasing in these three fields. Finally, the article summarizes the advantages, challenges, and risks of NFT leasing, and looks forward to its future development direction.
We will continue to update Blocking; if you have any questions or suggestions, please contact us!
Was this article helpful?
93 out of 132 found this helpful
Related articles
- Deep research on Proto-danksharding and its operating principles
- 101 Key Points About Ethereum
- Exclusive Interview with Polygon zkEVM: Decentralized Order Book on Layer2 More Important than Regulatory Issues Facing Ethereum
- After Hong Kong’s new encryption policy, banks are not cooperating with account opening. Regulatory agencies are pressuring multiple banks.
- Uniswap V4 Upgrade Analysis: Four New Features Leading DeFi Innovation
- As the ZK Rollup track becomes increasingly crowded, what are the first-mover advantages of zkSync Era?
- Lens Protocol: Introducing Lens Improvement Proposals (LIPs), Analyzing the First Three Proposals Launched Today






