In-depth Research Can Algorand, a public chain focusing on developer and marketing, stage a comeback?
Can Algorand, a public chain focused on developer and marketing, make a comeback through in-depth research?Author: DongHyun Kang, Xangle
Translation: Felix, LianGuaiNews
This report is written by Xangle and translated by LianGuaiNews with authorization for joint publication.
1. Algorand: A Blockchain Created by Cryptography Pioneer Silvio Micali
Similar to Cardano and EOS, the mainnet of Algorand claims to be a third-generation blockchain that can solve the trilemma of blockchain. The project was founded by Silvio Micali, an outstanding professor at MIT and a pioneer in cryptography. In 2012, he was awarded the Turing Award for his groundbreaking contributions to verifiable random functions (VRF) and zero-knowledge proofs, which are now widely used in the encryption industry. His deep expertise in cryptography played a crucial role in shaping Algorand’s strong technological foundation.
- Leading Ethereum-based project ETHS launches virtual machine, innovation seems to return to its origins.
- EigenLayer in-depth research report Ethereum’s middleware protocol leading the narrative of re-staking
- LianGuai Observation | All In Imports Elements of the Coin Circle, Coin with the Same Name Rides on the Heat
However, despite Algorand’s hopeful start, the growth of its ecosystem has been slower than expected. Additionally, the project recently faced a “security” issue that has affected its development speed (note: the U.S. SEC accused the ALGO token of being an “unregistered security”). Nevertheless, Algorand’s technological advantages and Silvio Micali’s reputation have facilitated partnerships with various organizations and countries.
This article will comprehensively analyze the technological advantages and challenges faced by Algorand and explore its potential opportunities.
2. Algorand Advantages: Powerful Technology Enhances User Experience
One of Algorand’s key advantages is its technical capabilities, thanks to Silvio Micali’s expertise in cryptography. This technical prowess enables Algorand to provide a seamless user experience. This section will delve into Algorand’s technology.
2.1. Dual Node Structure Enhances Network Decentralization
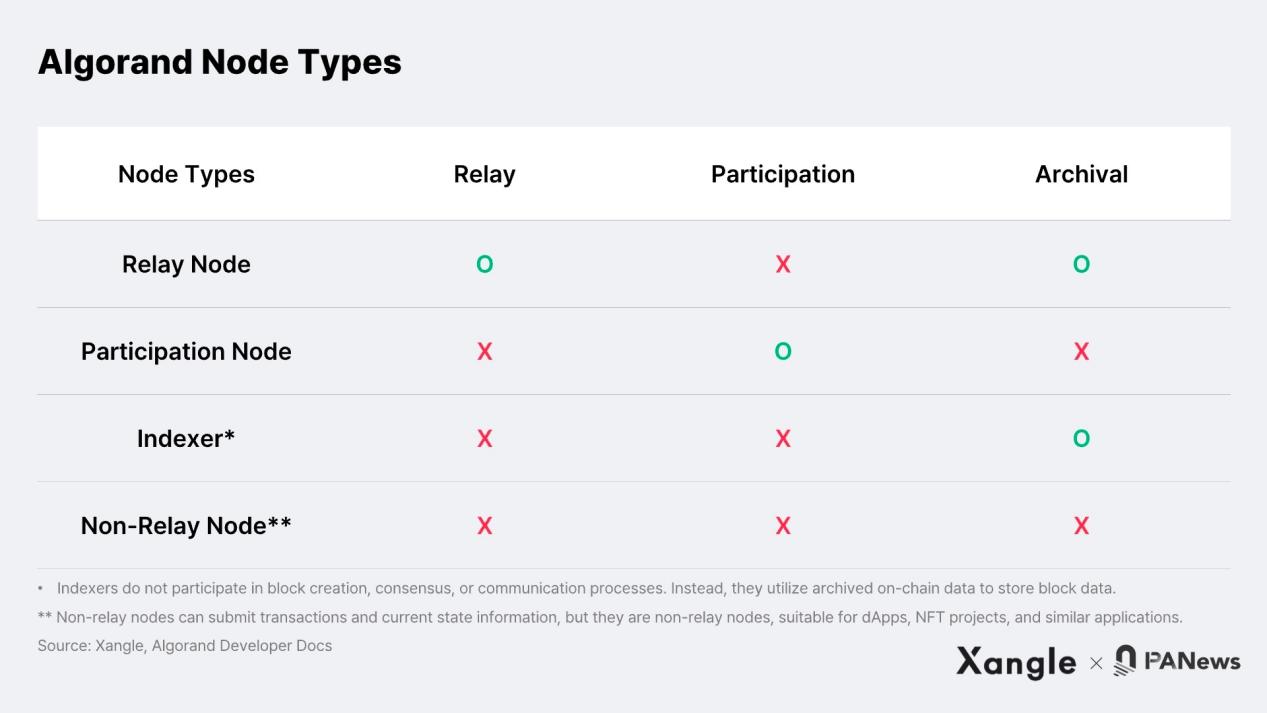
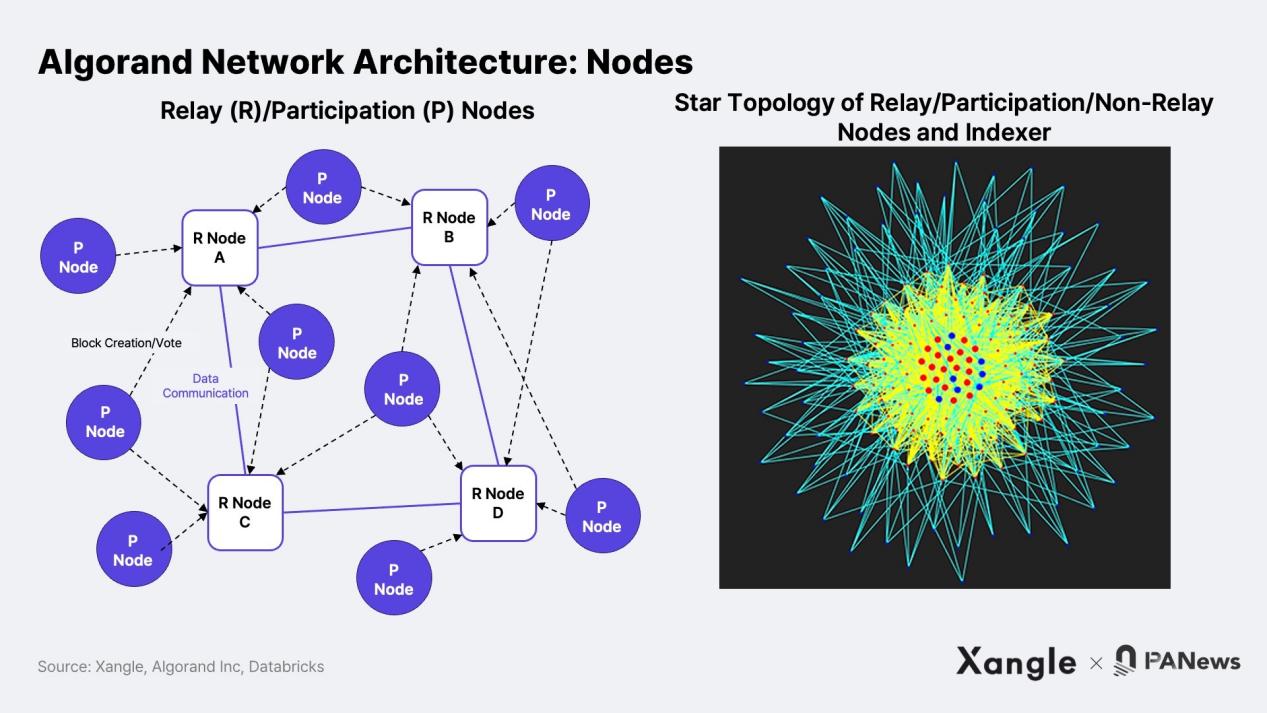
To address the trilemma of blockchain, Algorand adopts a structure that categorizes nodes based on their roles in relaying, participating in the consensus process, or archiving data. First, relay nodes do not participate in block creation and consensus. Instead, they serve as data connection points where relays retrieve block data from participating nodes during the consensus process. In other words, relay nodes facilitate communication among nodes. They also serve as archivers, storing blockchain data and accelerating the process of block creation and consensus by propagating blocks among relay nodes.
Participating nodes are the nodes that participate in block generation and consensus based on their held stakes. These participating nodes are also connected to multiple relay nodes and submit the consensus process to relay nodes. Unlike relay nodes, participating nodes do not archive all block data. Instead, they store the 1,000 most recently created blocks to ensure accurate validation. On the other hand, indexers and record submission nodes do not participate in relaying and consensus; they can be set up for specific purposes such as on-chain data usage and transaction submission. The structure of relay nodes and participating nodes is shown in the following figure.

<Algorand Participation Node Count and ALGO Staking Amount, Source: Metrics.algorand>
In addition, node decentralization is achieved through the Algorand Foundation. Although theoretically all nodes can participate, Algorand is currently evolving towards a model where participating nodes can participate autonomously, and the number of relay nodes is gradually increasing under the management of the foundation. Since its establishment, the Algorand Foundation has been committed to the geographical distribution of relay nodes, which are operated by universities, non-profit foundations, financial institutions, and various other entities across multiple continents and countries. The foundation is also gradually increasing the number of relay nodes through pilot relay node programs and community relay node programs. As of the second quarter of 2022, the Algorand Foundation reported a total of 120 nodes and plans to further increase that number in the future. As of July 24th, there are already 1,332 participating nodes, and this number is expected to grow over time.
2.2. Pure Proof of Stake System Enhances Algorand’s Scalability
Algorand uses pure proof of stake to improve scalability. The core cryptographic technology used in pure proof of stake is verifiable random function (VRF). VRF accepts user input and generates randomly generated output (hash) values. The output is unpredictable from the outside, and anyone can use the public key of VRF to verify the validity of the output at any time. In other words, randomness is used to protect selected users in an encrypted manner while still allowing others to verify the randomness.
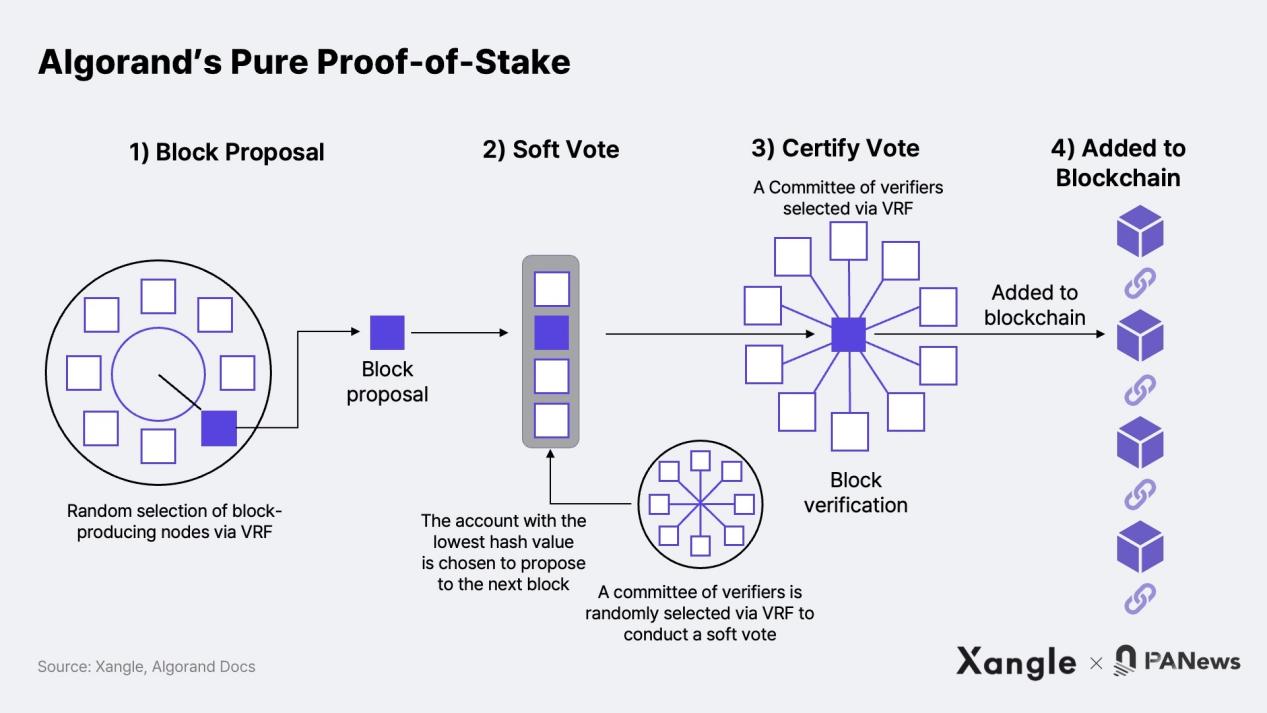
Proof of stake consists of four steps: 1) block proposal → 2) soft voting → 3) certification voting → 4) adding to the blockchain. First, in the block proposal phase, a node responsible for block generation and proposal is selected through VRF. Then, the selected node proposes a block that records transactions and state values, and spreads the proposed block using the VRF output, proving that the account is a valid proposer.
Even though a single node is selected through VRF, it is still possible to have multiple blocks proposed simultaneously due to concurrency issues or malicious nodes. To ensure that only one block is certified, the next step is to filter the number of proposals submitted in the soft voting phase to 1. First, a committee of 1,000 validators is randomly selected to conduct soft voting using VRF. Then, the committee compares the VRF hash values and selects the account with the lowest VRF hash value to propose the next block.
Then comes the certification voting phase, where the new committee checks if the block proposal has overspending, double spending, or any other issues. Similarly, committee members are selected using VRF, and they vote on the validity of the block. Once the required number is reached, the block is considered valid and certified by the committee, and it is finally added to the Algorand blockchain.
The consensus mechanism of Algorand ensures instant block finality, with a block delay of approximately 3.3 seconds. Unlike other PoS chains, blocks are not generated in slots in the Algorand consensus protocol. Instead, the consensus process is completed block by block, allowing for faster finality than other PoS chains.
Another advantage of PPoS is that it does not require node participants to lock their tokens, eliminating the risk of slashing. However, from a protocol perspective, the lack of token locking may increase selling pressure and there is no proper mechanism to punish malicious nodes.
2.3. Participation Keys and Key Updates
Algorand ensures the security of node participants and the convenience of users by adopting participation keys and key update technology.
Firstly, Algorand provides a set of keys called participation keys to node participants for voting and proposing blocks. To participate in the consensus process, the account must be online and marked, which increases the risk of spending key leakage. To address this security issue, Algorand grants participation keys to participants in the consensus process. Participants generate and register participation keys for specific rounds, generating temporary keys for each round and deleting them after the process is completed.
Using participation keys has significant advantages, especially in protecting the tokens of node participants, even if the participating nodes are compromised. In addition, participation keys and temporary keys for each round are deleted from the key file after each round is completed, ensuring the continuous security of the blockchain and preventing attacks on previous blocks.
On the other hand, key update is a technique that allows users to change their private keys without changing their public addresses. This process uses encrypted multi-signature technology and includes the following steps:
- Firstly, the user generates a new key pair (public key and private key).
- The user creates a transaction requesting the Algorand network to regenerate the key. This transaction includes the new public key.
- Network participants verify the key change transaction and encrypted multi-signature. This validates the transaction’s validity, and the owner of the new key is the owner of the old key.
- Once the key change transaction is authorized, the old private key is replaced with the new private key.
Algorand simplifies the process of key update, making it more convenient for users. Users can change their private keys by sending a key update transaction without creating a new wallet, even if their current private keys are exposed. This feature has proven to be particularly advantageous for institutions and countries that need to arbitrarily change public keys to ensure transaction continuity.
3. Challenges for Algorand: Collaborating with environmentally friendly institutions and countries to expand the ecosystem
3.1. Collaboration with organizations and countries
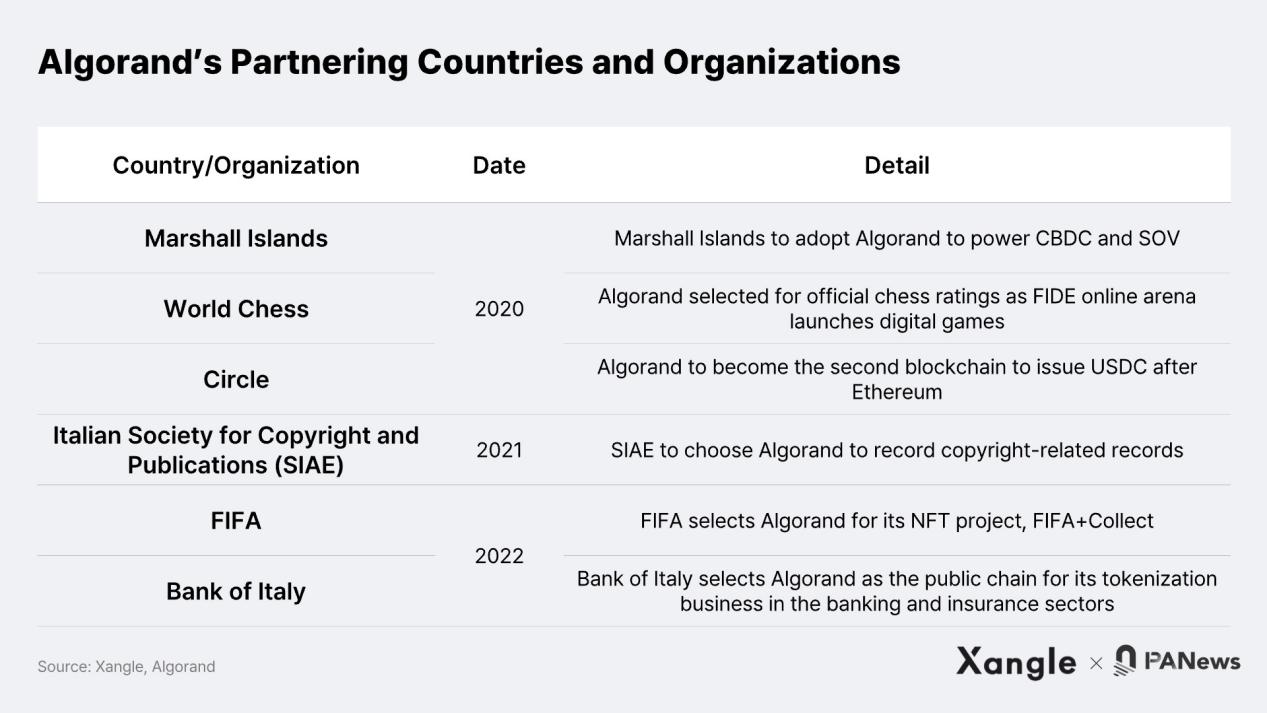
With the aforementioned background and technological advantages of Silvio Micali, Algorand has adopted a strategic approach to attract institutions and countries to expand its ecosystem. It is worth noting that Algorand has made contact with countries and institutions that are skeptical of PoW due to environmental, social, and governance (ESG) issues by promoting low-carbon green blockchain.
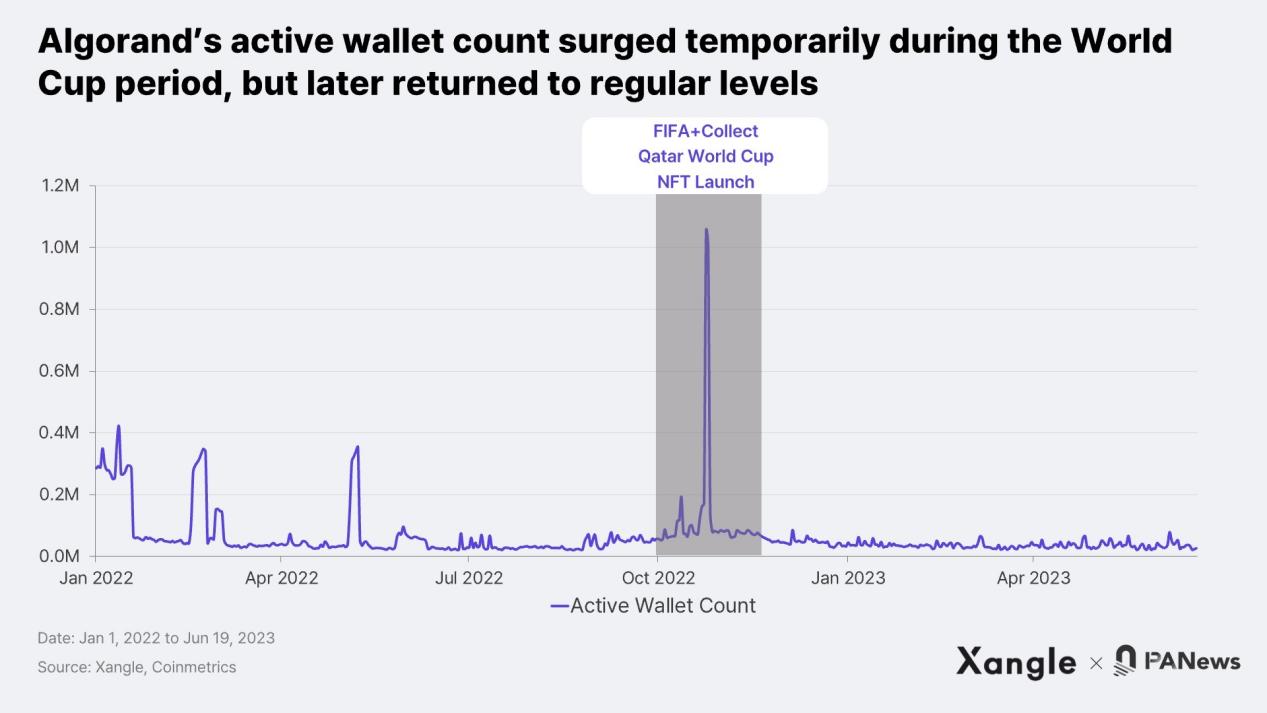
Through these efforts, Algorand has achieved several important milestones, such as creating a central bank digital currency (CBDC) for the Marshall Islands in 2020 and launching the sovereign currency SOV. It has also become the second blockchain to issue USDC after Ethereum. In addition, Algorand has reached an agreement with the International Chess Federation’s FIDE Online Arena to record matches on the blockchain. In 2021, the Italian Society of Authors and Publishers (SIAE) chose Algorand to record copyright-related records. Furthermore, in 2022, an Italian bank selected Algorand as the public chain for its tokenized business in the banking and insurance sectors. One of the most noteworthy partners is FIFA, with whom Algorand collaborated in May 2022 to launch the FIFA World Cup NFT project FIFA+Collect. This initiative enables FIFA to create and sell “great moments” from past World Cups, including the 2022 Qatar World Cup.

<Example of a 2022 Qatar World Cup NFT moment, source: FIFA+Collect>
However, the results of Algorand’s collaborations have been mixed as it seems to have encountered challenges in maintaining cooperation with certain organizations and countries. For example, there have been no significant updates or progress on the SOV (CBDC) project in the Marshall Islands since 2020. FIFA+Collect experienced a temporary increase in user engagement during the Qatar World Cup, but this increased interest did not translate into long-term sustained participation. As for the collaborations with the International Chess Federation and SIAE, there have been no recent updates or news since the announcements, making it difficult to confirm whether the data is actually being recorded on the blockchain as expected.
3.2. Low maturity of the ecosystem
Algorand currently faces challenges in attracting developers and users. Unlike other cryptocurrencies that adopt widely accepted standards such as EVM and ERC-20 tokens, Algorand uses its own state machine, AVM (Algorand Virtual Machine), and ASA (Algorand Standard Assets). The programming languages used on Algorand are not Solidity, but TEAL and PyTEAL, which are unique to the platform and are not as familiar or easy to use for developers.
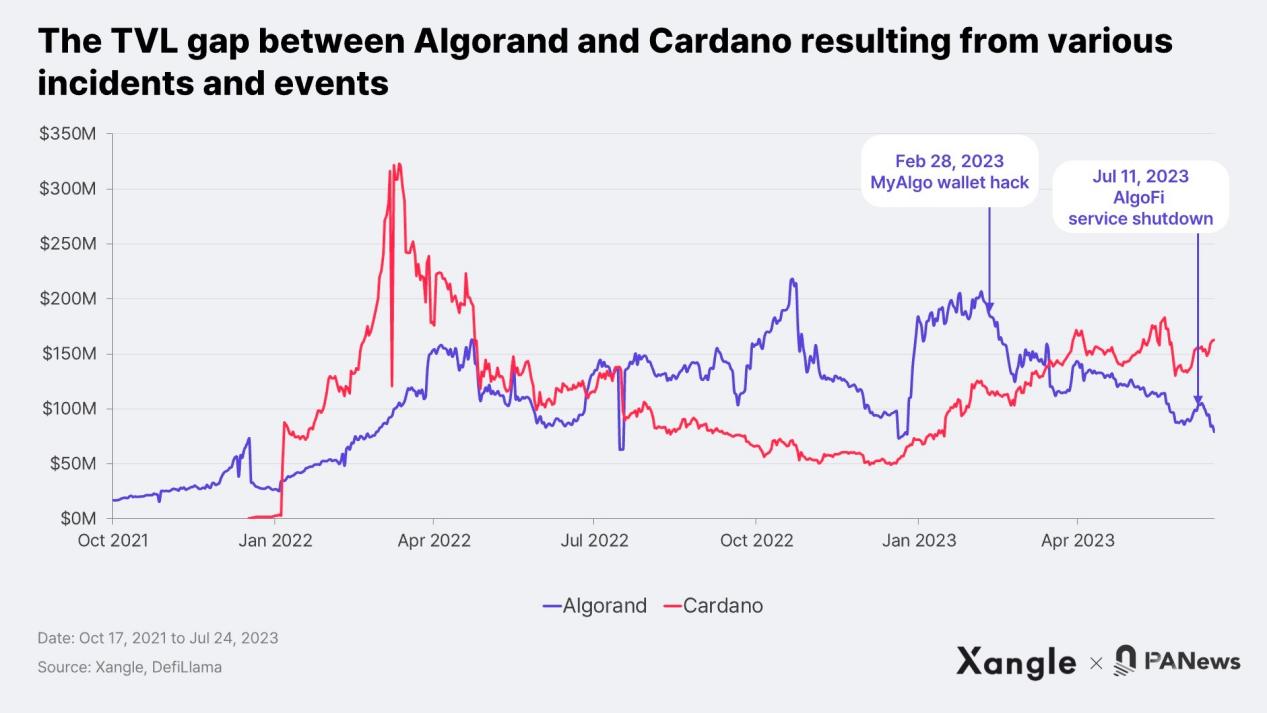
The DeFi ecosystem on Algorand is even lagging behind its third-generation blockchain competitor Cardano, which has seen a 300% year-on-year increase in TVL since 2023. In contrast, Algorand’s TVL has declined due to various events, including the MyAlgo hack and the closure of AlgoFi. The closure of AlgoFi had a particularly significant impact as it accounted for 55% of Algorand’s TVL before its closure, greatly affecting Algorand’s DeFi ecosystem.
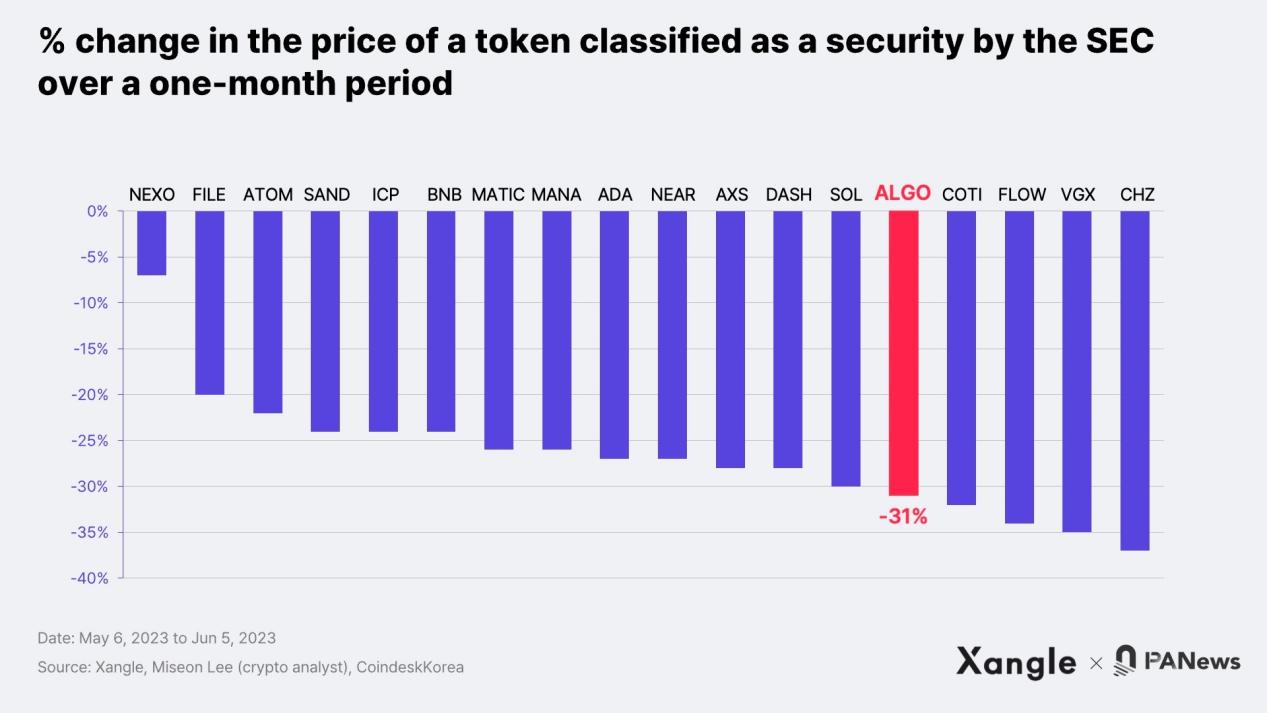
Algorand’s NFT ecosystem is even worse. According to data from CryptoSlam, the total trading volume on Algorand is currently $39 million, despite the existence of NFT projects such as PIXELS, MNGO, and AlgoRaccoon. This trading volume is similar to Solana’s 7-day trading volume of $42 million. Even the highly anticipated FIFA+Collect has performed poorly, with a total transaction volume of $552,000. In addition to these challenges, Algorand has recently faced charges from the SEC, leading to a significant drop in its token price and potentially exacerbating capital outflows from the Algorand ecosystem.
4. Algorand’s Revival: AlgoKit’s Active Marketing and Developer Onboarding
4.1. Active Marketing, Expanding Target Markets
Recently, Algorand has recognized the importance of this bottom-up ecosystem and has taken proactive measures in marketing. In a recent interview with Real Vision Crypto, Staci Warden, CEO of the Algorand Foundation, reflected on the company’s previous belief that technical strength alone would attract developers and users. Realizing the need for change, the company appointed Jessica Tsai Chin, who has worked at Nike, WhatsApp, and Apple, as the Chief Marketing Officer, marking the beginning of marketing activities.
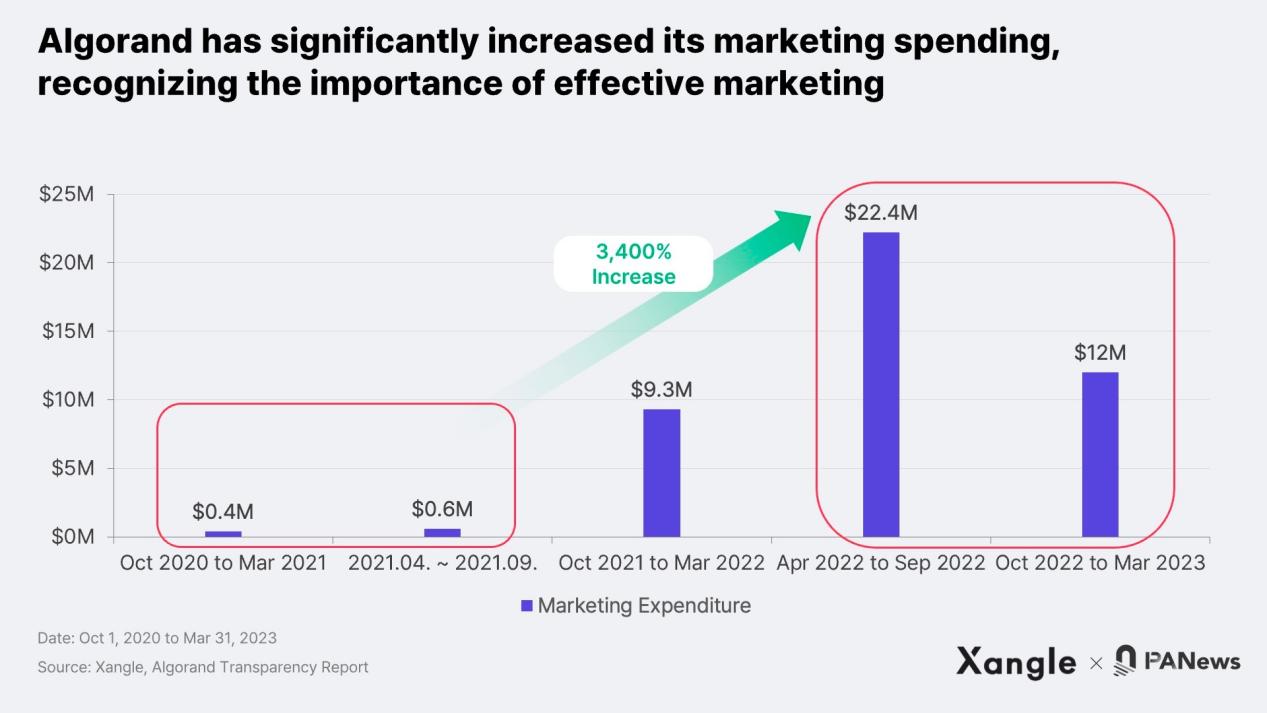
The recent focus on marketing by Algorand is evident from the increase in its spending. Algorand releases two transparency reports annually, and the latest report shows a significant increase in marketing expenses, soaring from around $1 million in 2020-2021 to $34.2 million in the past year, a growth of approximately 3,400%. According to the author’s research, this major investment is mainly targeted at promising yet unknown projects that Algorand believes in.
Algorand has also been actively utilizing a funding program called AlgoGrant and establishing a direct investment entity called Algorand Ventures. Instead of providing funding to dApps (which could lead to issues like Rug Pool), Algorand aims to acquire project equity and jointly solve the liquidity problem of projects through direct investment. In particular, the company has been expanding its business in Asia rather than North America, as regulatory restrictions in North America may hinder operations. Algorand Ventures actively supports Asian startups by launching the Asia Pacific Accelerator Program, which runs from September 2022 to March 2023. Through this initiative, Algorand aims to promote the growth and development of promising startups in the region.
4.2. Using AlgoKit to Extend Supported Languages and Simplify the Development Process for Web2 Developers

<Algokit, developed for the convenience of Algorand developers, source: Algorand Developer Portal>.
In March 2023, Algorand launched a developer tool called AlgoKit to make it easier for developers to get started. AlgoKit addresses the complexity of Web3 by simplifying the setup process and providing various libraries and templates that can be used to easily build Algorand dApps. This approach allows existing Web2 developers to use familiar languages on the Algorand platform without the need to learn unfamiliar languages.
AlgoKit also simplifies the development, testing, and deployment process in Web3. Compared to other mainnets, deploying a dApp requires developing the contract, testing it on the testnet, and then deploying it to the mainnet for final testing. AlgoKit offers a more efficient method. Developers can directly test and deploy on the Algorand mainnet by temporarily opening an isolated space called the “local network.” In other words, AlgoKit simplifies the complex testing process on the testnet and mainnet.
According to Algorand’s July announcement, since its launch in March, AlgoKit has been downloaded over 9,200 times, with nearly 8,000 developers joining. Although this number is relatively small compared to the estimated 200,000 Solidity developers, it is worth noting that AlgoKit has only been launched for three months, indicating future growth potential.
5. DApps Worth Paying Attention to in Algorand
This section will explore some notable dApps in the Algorand ecosystem. Although there are no killer dApps in Algorand yet, there are several dApps that hold significant value and importance to the Algorand Foundation. Two prominent dApps in Algorand are Folks Finance (currently a leader in DeFi within the network) and Lofty (a real estate tokenization project).
5.1. Folks Finance
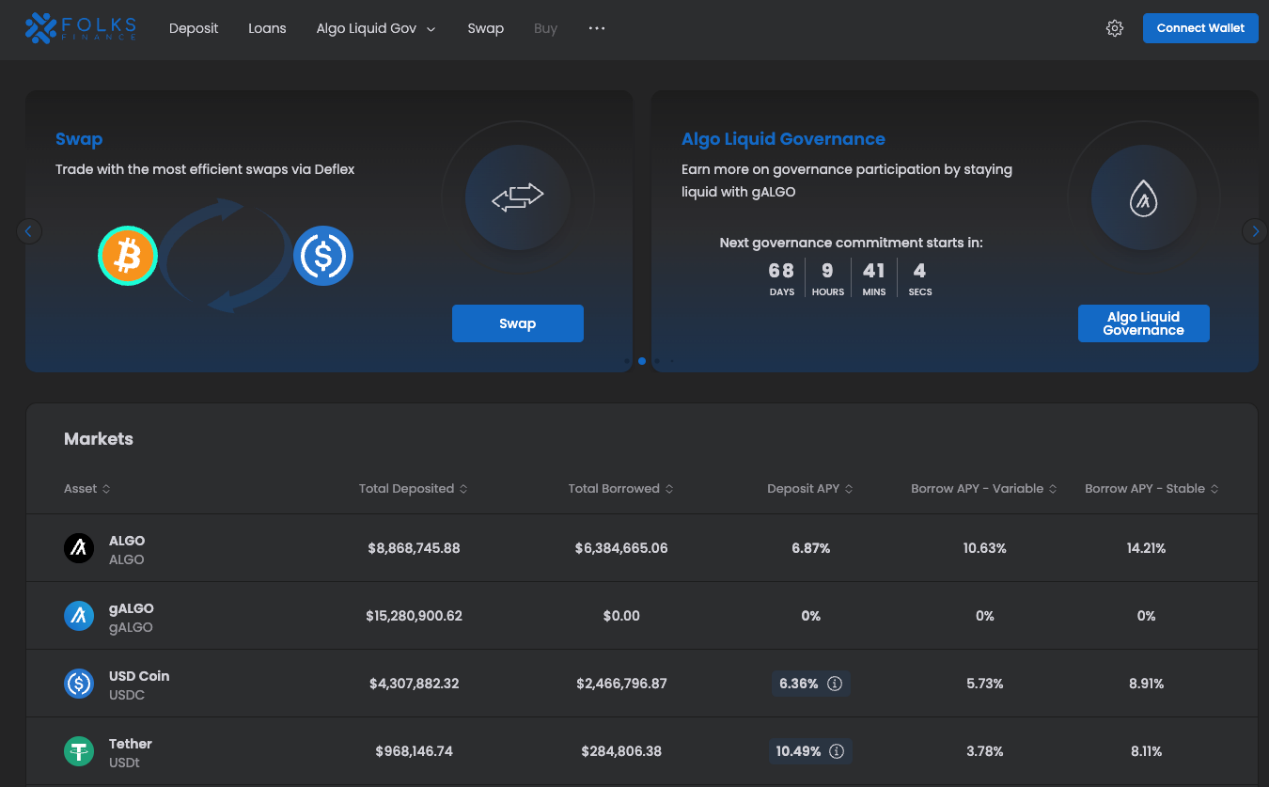
Folks Finance is Algorand’s flagship DeFi project, particularly after AlgoFi’s closure. Folks Finance serves as both a DEX and a lending platform. One notable feature of Folks Finance is the use of gALGO and xALGO tokens. gALGO represents a securitized version of ALGO, where users can convert ALGO into gALGO, which can be used in DeFi applications, providing opportunities to earn staking and DeFi rewards simultaneously. xALGO functions similarly to gALGO in terms of reward acquisition, but it is converted to BRC-20 and can be connected to LianGuaincakeSwap on the Binance Chain.
5.2. Lofty AI
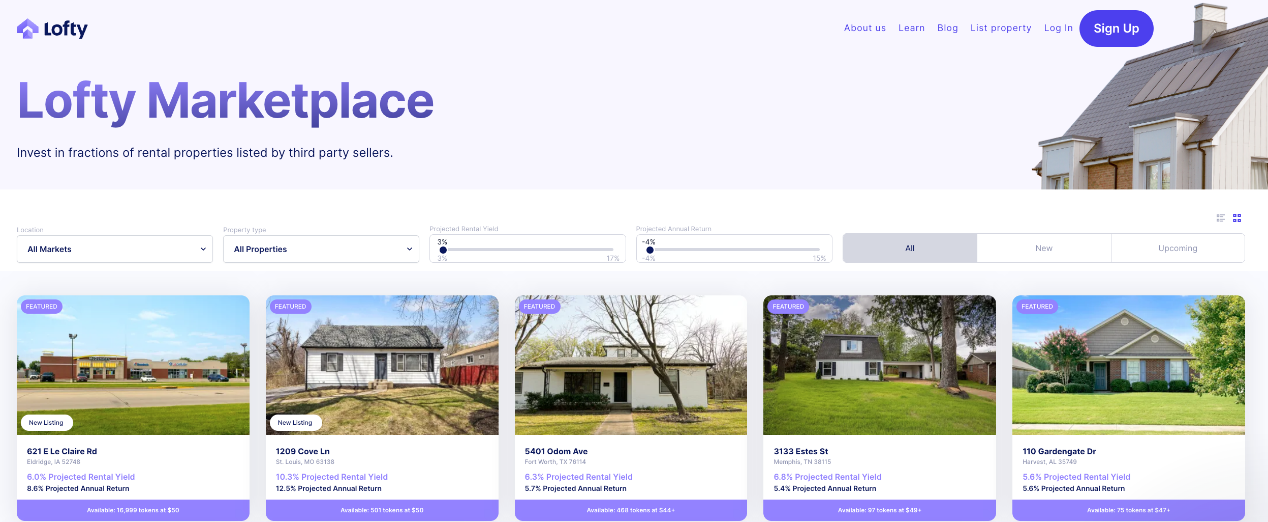
Lofty AI is a real estate investment platform based on the Algorand blockchain and headquartered in the United States. As a DeFi platform based on physical assets, Lofty AI allows users to make small investments in real estate that have been audited by proprietary algorithms and on-site teams. In 2019, Lofty AI received investment from the well-known Silicon Valley accelerator Y-Combinator. Despite the lack of DeFi projects based on real assets, Lofty AI has still achieved a TVL of $26 million.
6. Conclusion
This article has delved into various aspects of Algorand, covering its advantages, challenges, coping measures, and promising dApps in its ecosystem. In summary, Algorand is a blockchain with strong technical capabilities. Its decentralization feature allows blocks to be confirmed in 3.3 seconds with the support of a dual-node structure. The platform also promotes user-friendly experiences for individuals, institutions, and nations through the implementation of participation keys and key updates. Despite these technological advantages, Algorand still faces some obstacles, especially in maintaining continuous cooperation with institutions and nations, and the Web3 ecosystem is still in its early stages.
However, Algorand is not without opportunities. The company is strategically shifting its target market to Asia and adopting proactive marketing strategies. The launch of AlgoKit aims to assist Web2 developers and further demonstrate its commitment to accessibility. As the platform develops, it will be interesting to see if Algorand can seize these opportunities and become a significant player in the third-generation blockchain.
We will continue to update Blocking; if you have any questions or suggestions, please contact us!
Was this article helpful?
93 out of 132 found this helpful
Related articles
- The Success Story Behind the Explosion of TG Bots A Successful Tale of On-Chain Marketing and Grassroots Counterattack
- Will going online mean the end? BALD plummets a thousand times, what is the future of Base public chain?
- The hype of room-temperature superconductor triggers the meme token craze of LK-99 Innovation or cutting-edge?
- AlterVerse Research Report Web3 Sandbox Game Based on Binance Chain
- LianGuai Daily | Hackers have returned all stolen funds to Alchemix Curve pool; US SEC provides over $104 million in rewards to 7 whistleblowers
- Decoding Decentralized Order Book The Best Combination of Pricing Quality and Fund Security
- LianGuai Daily | Coinbase, Block, and Apple release quarterly reports; X Company is seeking data partners to establish a trading platform.




