EigenLayer in-depth research report Ethereum’s middleware protocol leading the narrative of re-staking
EigenLayer research report on Ethereum's middleware protocol leading re-staking narrative.Project Introduction
EigenLayer is an Ethereum-based middleware protocol that introduces the concept of re-staking, allowing Ethereum nodes to re-stake their staked ETH or LSD tokens into other protocols or services that require security and trust, thereby gaining double benefits and governance rights. It also extends the utility of the Ethereum consensus layer to various middleware, data availability layers, sidechains, and other protocols, allowing them to enjoy Ethereum-level security at a lower cost.
1. Research Focus
1.1. Core Investment Logic
EigenLayer is an innovative and promising blockchain infrastructure service project that can provide security, scalability, and interoperability to various software modules in the Ethereum ecosystem, thereby promoting innovation and diversity in blockchain applications.
Team: EigenLayer has a blockchain team focused on technological innovation, with more than 30 members, of which more than 80% are engineers. Although the team is young, they have rich backgrounds and research experience in blockchain technology. It is a vibrant and promising blockchain team worth paying attention to. Looking at the history of blockchain projects, projects built by purely technical teams have mostly been successful.
Fundraising: EigenLayer has received high recognition and support from the capital market at an early stage. EigenLayer has completed three rounds of fundraising, totaling more than $64 million, with the latest Series A funding reaching a valuation of $500 million. These data fully demonstrate EigenLayer’s leading position and huge potential in blockchain security and scalability. At the same time, sufficient funding provides strong guarantees for its subsequent development, allowing it to better serve the Ethereum ecosystem and other protocols.
- LianGuai Observation | All In Imports Elements of the Coin Circle, Coin with the Same Name Rides on the Heat
- The Success Story Behind the Explosion of TG Bots A Successful Tale of On-Chain Marketing and Grassroots Counterattack
- Will going online mean the end? BALD plummets a thousand times, what is the future of Base public chain?
Technology: EigenLayer is a disruptive technological innovation protocol that addresses a strong real demand for technological pain points. It reduces the development threshold for other project parties and brings higher security and scalability to the Ethereum ecosystem. It also enhances the trust network of Ethereum, allowing any system to utilize the security of the Ethereum pool, thereby increasing the value and influence of Ethereum.
Market: EigenLayer is the first project to propose Restaking. Currently, there are no obvious competitors in the Restaking market track. As an innovative concept, it has not been completely copied or imitated by other protocols, and the market is still in its early stages with few participants.
Backed by the largest Staking market in DeFi ($20 billion TVL), the Restaking market will have numerous growth opportunities. Contributions made by Staking and Restaking to the expansion of the DeFi market will also pave the way for the growth of other DeFi segments, such as AMM, Lending, and Farming. The market and ecosystem will form a strong positive feedback mechanism. Meanwhile, approximately six months after the birth of the Restaking concept, by the end of 2022, the LSD market has rapidly expanded and become a trend. Restaking will not be a quickly disappearing narrative but one of the most important and promising areas in DeFi.
As of now, EigenLayer does not have any obvious weaknesses. The project faces risks mainly in terms of technology and tokens. In terms of technology, EigenLayer needs to ensure the feasibility and security of the restaking protocol, and avoid situations where validators are penalized or the network is attacked. In terms of tokens, the main concerns are the utility and value of the tokens to be issued, as well as how to balance the reward distribution among validators, protocols, and users. However, these risks can be overcome as long as the EigenLayer team continues to innovate in technology and community development.
EigenLayer is undoubtedly a leader in the Restaking field with tremendous potential and prospects, worthy of attention.
1.2. Valuation
On March 28, 2023, EigenLayer completed a Series A financing of $50 million, led by Blockchain Capital, with participation from Coinbase Ventures, Polychain Capital, Bixin Ventures, Hack VC, Electric Capital, IOSG Ventures, and others. The valuation of this financing round is $500 million.
2. Project Overview
2.1. Basic Information
EigenLayer is a restaking protocol based on the ETH staking market, developed by EigenLabs in 2021. The team is mainly located in the United States. The project has not yet issued tokens, but may do so in the future. EigenLayer is currently in the first phase of mainnet, and has attracted the participation of many validators and protocols.
EigenLayer’s business scope covers two aspects: first, it allows ETH stakers to restake ETH to provide security and a trusted layer for other protocols; second, it allows new software modules in the ETH ecosystem to utilize stakers as validation nodes to enhance security and efficiency. EigenLayer supports various modules, such as consensus protocols, data availability layers, virtual machines, guardian networks, oracle networks, cross-chain bridges, threshold encryption schemes (a cryptographic technique that splits a key or data into multiple parts and distributes these parts among multiple participants. The original key or data can only be recovered when a certain number or proportion of participants cooperate.) and trusted execution environments, etc.
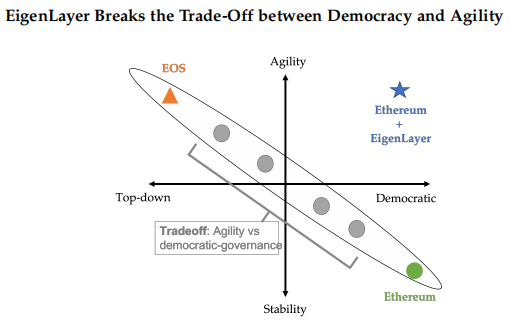
The updates to Ethereum are currently progressing slowly through robust off-chain governance. EigenLayer can enable innovations to be quickly deployed on the trusted layer of Ethereum, providing testing and experience for Ethereum’s mainnet innovations, similar to a testnet, thus avoiding the trade-off between rapid innovation and democratic governance in Ethereum.
2.2. Team Information
2.2.1. Overall Situation
EigenLayer is a restaking protocol developed by EigenLabs. EigenLabs is a laboratory focused on blockchain innovation and research, headquartered in Seattle, Washington, USA. Sreeram Kannan, the founder of EigenLabs, is an associate professor in the Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering at the University of Washington and also the head of the UW Blockchain Lab. The EigenLabs team consists of 30 experts and enthusiasts from different fields and backgrounds, mainly engineers, as well as product managers, strategic directors, and legal advisors, among others.
2.2.2. Core Members

Sreeram Kannan is the CEO of EigenLayer. He is an associate professor in the Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering at the University of Washington. His research focuses on information theory and its applications in communication networks, machine learning, and blockchain systems. He holds a Ph.D. in Electrical Engineering and a master’s degree in Mathematics from the University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign. He has also worked as a postdoctoral researcher at the University of California, Berkeley, and Stanford University. He has received several awards and honors, such as the 2019 UW ECE Outstanding Teaching Award, the 2017 NSF CAREER Award, and the first prize in the 2013 Qualcomm Cognitive Radio Contest. He is also the head of the UW Blockchain Laboratory.

Robert Raynor is an engineer at EigenLayer. He is a Ph.D. student in the Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering at the University of Washington. He is a former Air Force officer with a background in applied physics. His current research focuses on data-driven artificial intelligence, data economics, and causal reasoning. He is also a member of the UW Blockchain Laboratory.

Soubhik Deb is an engineer at EigenLayer. He is a junior Ph.D. student in the Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering at the University of Washington. He is also a member of the UW Blockchain Laboratory. His goal is to design, develop, and deploy Web3.0-based systems to promote the democratization of trust, data, and control in digital platforms. He has previously worked as an industrial researcher at NEC Corporation in Japan, focusing on 5G technology. He graduated from the Indian Institute of Technology Bombay with a dual degree in Electrical Engineering (Bachelor’s and Master’s).

Calvin Liu is the Chief Strategy Officer. He previously served as the Head of Strategy at Compound and is also an investment partner and angel investor. He has invested in multiple blockchain projects, such as Argus Labs, Catalyst, and Liquity. He graduated from Cornell University with a major in Philosophy and Economics.
2.3. Financing
According to data from Crunchbase and PitchBook, EigenLayer has completed three rounds of financing, as follows:
On May 24, 2022, EigenLayer completed an angel round of financing with an undisclosed amount, with investments from dao5, cFund, Coinbase Ventures, and others;
On August 1, 2022, EigenLayer completed a $14.5 million seed round of financing, led by Polychain Capital and Ethereal Ventures.
On March 28, 2023, EigenLayer completed a Series A financing of $50 million, led by Blockchain Capital, with participation from Coinbase Ventures, Polychain Capital, Bixin Ventures, Hack VC, Electric Capital, IOSG Ventures, and others. The valuation of this financing round was $500 million.

2.4. Development History and Roadmap
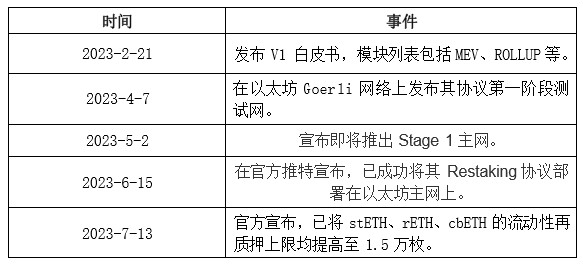
2.4.1. Development History
2.4.2. Development Plan and Roadmap
EigenLayer plans to launch its Phase 2 protocol in the fourth quarter of 2023, introducing a free market governance mechanism that allows stakers and the protocol to negotiate and reach consensus on re-staking terms, such as fees, rewards, forfeiture conditions, etc.
Meanwhile, the Operator testnet will go live in the third quarter of 2023, and the Active Validation Service (AVS) testnet will go live in the fourth quarter. The AVS mainnet is expected to go live in the first quarter of 2024.
3. Project Analysis
3.1. Project Background
In 2009, the Bitcoin network introduced the concept of decentralized trust. The Bitcoin network was designed as a peer-to-peer digital currency system that uses UTXO and script language, but it is limited in its ability to build various programs on the network.
In 2015, the Ethereum network emerged, allowing the construction of various decentralized applications (dApps). However, its performance and programmability are limited, relying on Layer 2 and other middleware to scale and innovate.

Layer 2, other middleware, and dApps cannot utilize the security of the Ethereum trusted layer and need to build their own independent Active Validation Service (AVS) to be responsible for the security of their systems. This mainly brings two problems:
1) Increase in project barriers:
① Building a new AVS requires a lot of time, cost, and resources, making it difficult to achieve.
② A new AVS requires additional fees, leading to value loss and a decrease in user experience.
③ Middleware validators need to invest funds to guard the network, which incurs certain marginal costs. Due to the consideration of token value capture, validators are often required to stake middleware native tokens, and the fluctuation in price leads to uncertainty in their risk exposure.
2) Security issues:
① For middleware: Since it exists independently of Ethereum itself and relies on staking native tokens to run the validator network, the security of the middleware depends on the overall value of the staked tokens. If the tokens plummet, the cost of attacking the network also decreases.
② For dApps: For some dApps that rely on middleware (such as derivatives that require oracle price feeds), their security actually depends on the trust assumptions of both Ethereum and the middleware. The trust assumption of the middleware essentially stems from the trust in the distributed validator network. And as we can see, due to erroneous oracle price feeds, the security of the dApps is compromised.
There have been numerous incidents of asset losses.
This can lead to a serious domino effect, as the security of the system depends on its weakest link. What may seem insignificant could trigger systemic risks.
3.2. Project Principles
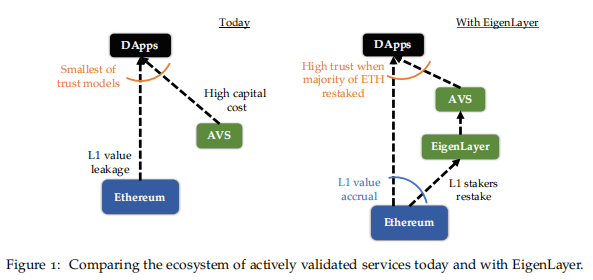
The idea behind EigenLayer is relatively simple, similar to shared security, attempting to elevate the security of middleware to the level of Ethereum.
This is accomplished through “Restaking”.
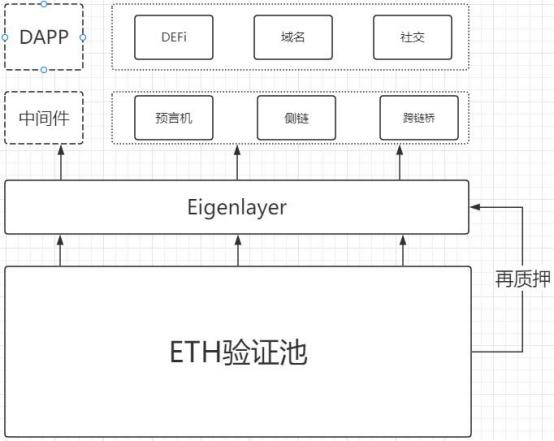
By extending the trust layer of Ethereum through “Restaking”, developers can build their own consensus protocols and execution layers on EigenLayer without the need for a separate trust layer. Through “trust computation” on EigenLayer, DApps can rely on Ethereum’s powerful trust layer without depending on middleware.
3.2.1. Slashing Mechanism Design
The security of a cryptographic network depends on the cost of attacking it, also known as “Cost-of-Corruption”. If the cost of corruption exceeds the attacker’s profit, or “Profit-from-Corruption”, then the network is secure.
The security of the ETH network consensus layer is guaranteed by the potential risk of slashing collateral, which is commonly referred to as violent means to maintain security.
L2 feeds transaction data back to the main network for inspection in order to inherit security, while EigenLayer becomes a validating node by staking “ETH-like value assets” and borrows the violent means of slashing from the main network to ensure security.
3.2.2. Restaking
Originally, validators stake assets on the Ethereum network to earn rewards, but if they behave maliciously, their staked assets will be slashed. Similarly, after Restaking, staked assets on the middleware network can earn rewards, but if malicious behavior occurs, the original ETH collateral will be slashed. In simple terms, if validators on the Ethereum network engage in malicious activity, they may have half of their staked 32 ETH tokens confiscated, while EigenLayer allows for the confiscation of the remaining 50% according to the slashing protocol.
The implementation method of Restaking is as follows: when an Ethereum validator participates in validation through EigenLayer, their fund redemption address will be set as the smart contract of EigenLayer, granting it the power of slashing. If the node violates the rules of the application layer, EigenLayer can confiscate the redeemed ETH through the slashing contract.
This slashing mechanism allows the application layer to confirm the rights and obligations of Ethereum trust layer nodes through smart contracts, providing possibilities for other applications or middleware to utilize Ethereum’s trust layer. Therefore, EigenLayer’s Restaking mechanism enhances security by significantly increasing the cost of malicious attacks.
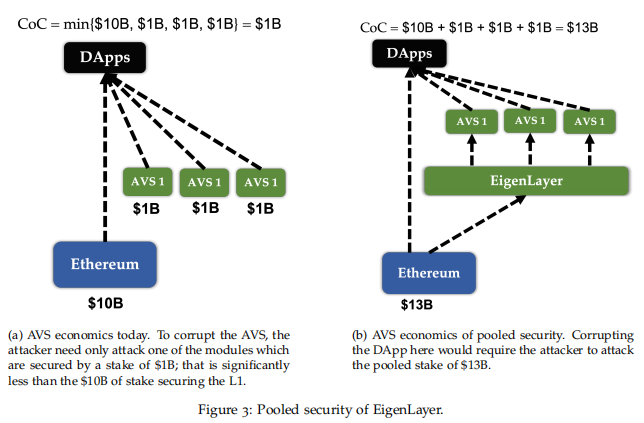
3.2.3. Trusted Transaction Market
EigenLayer will establish a public trusted transaction market, allowing Ethereum trust layer nodes and application layer protocols to determine transaction content through free market mechanisms. Nodes can decide whether to participate in the validation work of an application to gain additional income based on their preferred risk-reward ratio and forfeiture conditions, avoiding rigid governance structures. Application layer protocols can conveniently purchase “trust” through market-based prices, enabling them to focus on protocol innovation and operation at the application layer and achieve a balance between security and performance.
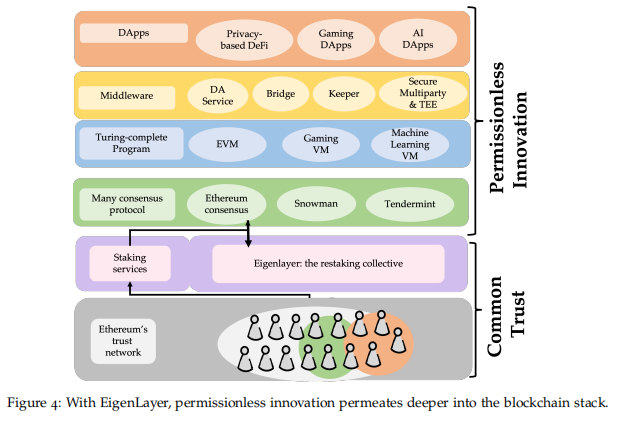
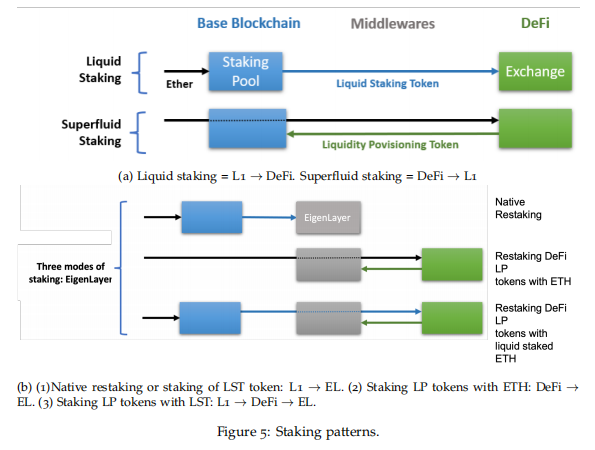
3.2.4. Support for Multiple Staking Modes
EigenLayer provides multiple staking modes similar to Liquid Staking and Superfluid Staking, where Superfluid Staking allows LP token staking. Specifically:
1) Direct staking, staking ETH directly on EigenLayer;
2) LSD staking, staking assets already staked on Lido or Rocket Pool on EigenLayer;
3) ETH LP staking, staking LP tokens from DeFi protocols on EigenLayer;
4) LSD LP staking, such as stETH-ETH from Curve, staking LPTokens on EigenLayer;
Middleware can choose to retain the staking requirement for its native tokens while introducing EigenLayer to continue to obtain value from its native tokens, thereby avoiding the “death spiral” caused by a drop in the price of a single token.
3.2.5. Delegators
For those interested in EigenLayer but do not want to operate as a node operator, they can delegate their rights to other node operators, who will then stake tokens in Ethereum and distribute a portion of the earnings to these delegators. EigenLayer provides two modes:
1) Individual staking mode: The staker provides validation services and can directly join the AVS or delegate operations to other operators while continuing to validate on Ethereum.
2) Trust mode: Choose trusted operators to operate. If the chosen operator fails to execute according to the agreed terms, the interests of the delegator will be penalized. In addition, delegators need to consider the fee ratio with the delegators, which is expected to form a new market. Each EigenLayer operator will establish a delegation contract on Ethereum, which specifies how fees will be distributed to delegators.
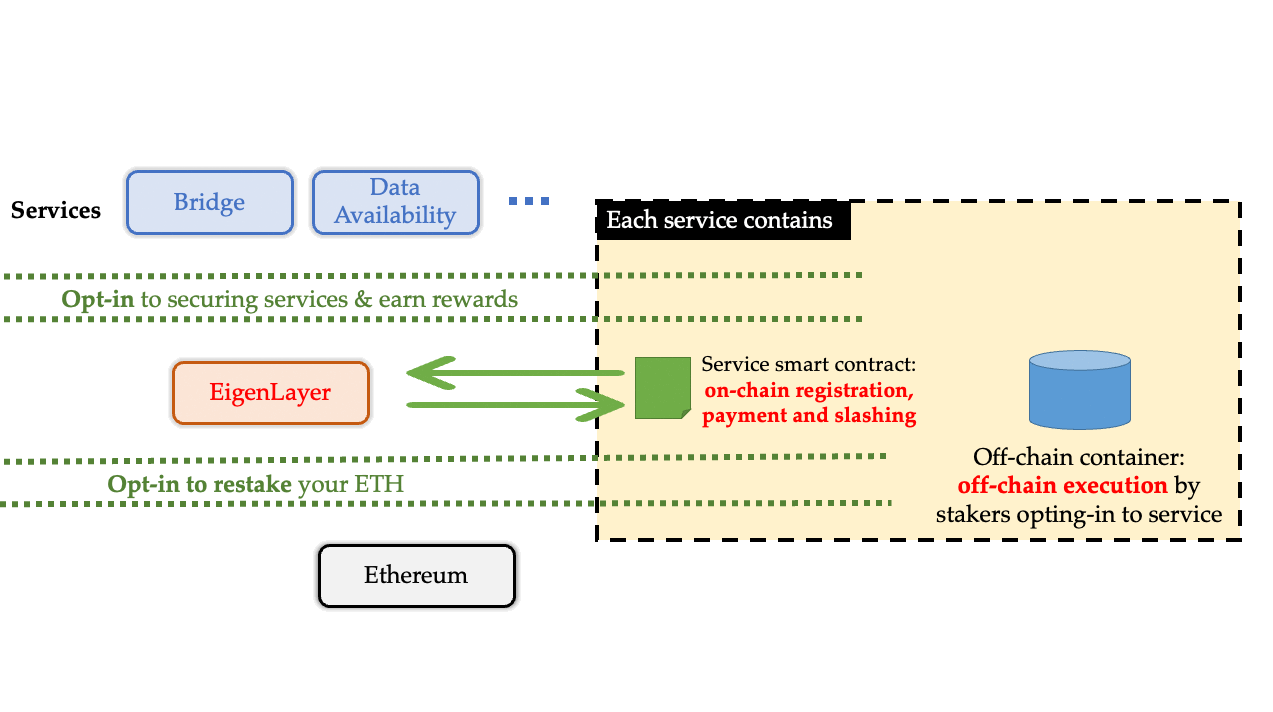
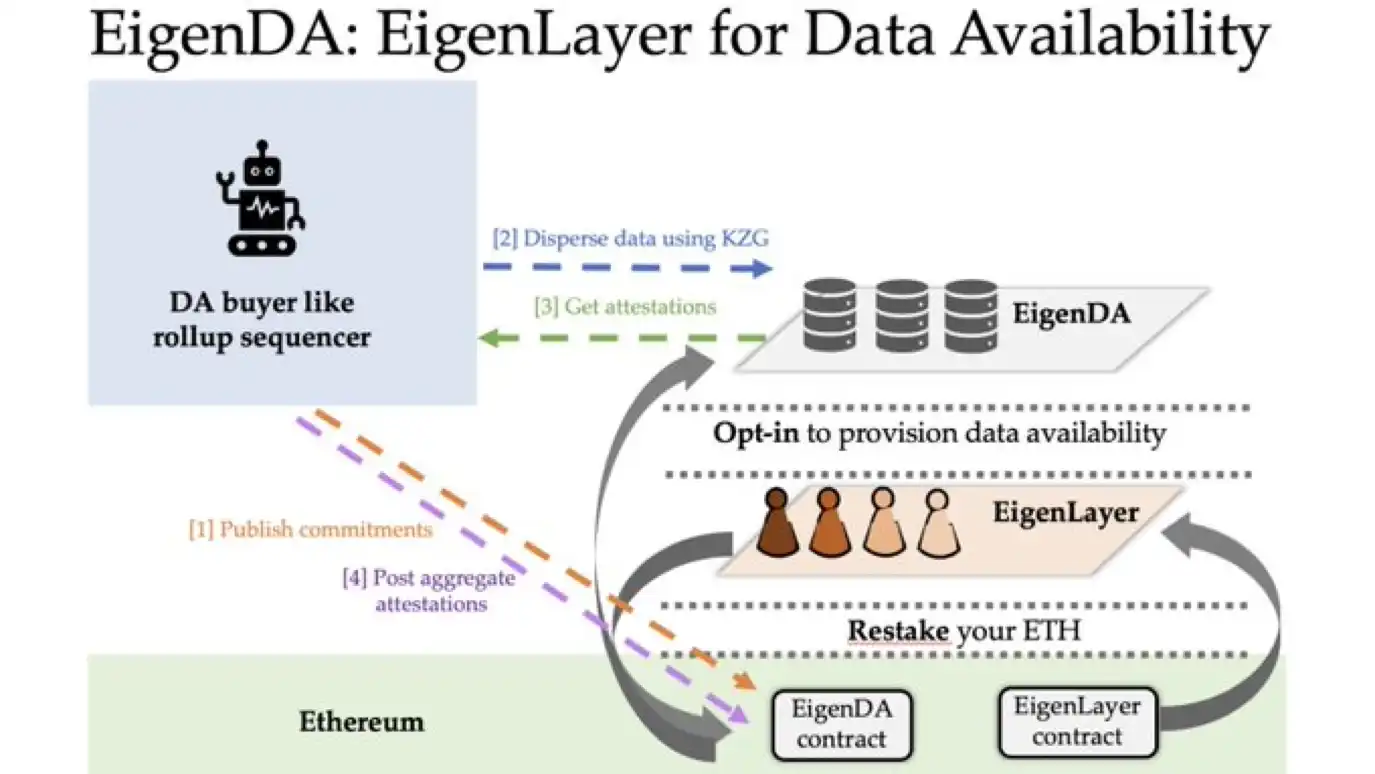
3.3. Flagship Product EigenDA of EigenLayer
EigenDA is the data availability layer developed by the EigenLayer team. The data availability layer is a layer that focuses only on data storage and verification, which is crucial for network security and scalability. Other data availability layers include Celestia and Polygon Avail, which maintain security through their own token staking mechanisms. However, EigenDA has the advantage of maintaining security through the already valuable ETH tokens in the market.
The data availability of the Ethereum network is currently the biggest limiting factor for scaling rollup networks, although the introduction of EIP-4844 and sharding is expected to improve the data availability of Ethereum and the scalability of rollup networks.
The advantages of EigenDA are:
① Allows EigenLayer to provide cheaper and higher bandwidth than the Ethereum mainnet;
② Its introduction is expected to increase the interoperability of the Ethereum protocol, thereby improving innovation speed;
③ More funds will flow into the Ethereum ecosystem to gain additional returns;
④ It enhances the security of utilizing the mainnet protocol by using EigenLayer;
⑤ It is cheaper than other modular blockchain solutions such as Celestia;
3.4. Project Ecological Applications
There are many use cases for EigenLayer, mainly those that require AVS services, including:
1) Cross-Chain Bridges: These protocols are used to connect different blockchains and can leverage the security of EigenLayer to protect cross-chain asset transfers. Cross-chain bridges like Hyperlane have a small likelihood of being penalized due to their flexibility and lack of requirements on nodes. This provides a favorable environment for EigenLayer. Other protocols include Succinct, Axelar Network, and Squid.
2) Rollup Sequencers: These are protocols used to sequence Layer 2 transactions and can leverage the security of EigenLayer to achieve decentralization and fairness. This will decentralize and secure L2 rollup sequencers, such as Optimism and Arbitrum. Currently used centralized sequencers can review and reorder transactions, while decentralized sequencers can create transaction priority auctions like Flashbots or use fair/random order (like Shutter Network).
3) RPC Nodes: These protocols are used to provide access to the Ethereum network and can leverage the security of EigenLayer to achieve truly decentralized RPC nodes. Existing solutions such as Pocket Network, as well as some centralized providers like Infura, can migrate to EigenLayer. Decentralized RPC is crucial for avoiding client-level censorship.
4) Application Chains: These are independent modular blockchains created for specific applications, which can leverage EigenLayer’s security to achieve fast and flexible innovation. Recently, the theory of application chains has sparked a lot of discussion among web2 thought leaders. It seems that certain use cases (such as games, where applications can be isolated for scalability) would benefit from running on independent modular application chains. Application chain deployment protocols like Atlas and Stackr Labs will be able to use EigenLayer behind the scenes to enable security for new application chains, with value accumulation returning to Ethereum as the underlying security collateral.
5) Oracles: These are protocols used to provide off-chain data, which can enhance oracle networks using EigenLayer’s security. Oracles are well-suited for EigenLayer because they are backed by the value of tokens like LINK. By ensuring the security of oracle networks through more collateral, oracles can achieve 10 times the security, reducing the probability of attacks on DeFi.
6) Data Availability: These are protocols used to provide efficient and reliable data storage and retrieval, which can leverage EigenLayer’s security to achieve higher data bandwidth and lower costs. One of EigenLayer’s flagship products is EigenDA, which can increase Ethereum’s data bandwidth from 80 KB per second to 15 MB, nearly 200 times more. This is particularly useful for applications like rollups that require a high level of data availability (DA).
7) Settlement Layer: These are protocols used for settlement between different execution environments, which can leverage EigenLayer’s security to achieve interoperability and shared liquidity in a modular blockchain ecosystem. Among other benefits, they allow different execution environments to settle on the same layer. The resulting interoperability and shared liquidity effects are crucial to avoid fragmentation of the modular ecosystem. This is another component of achieving fully decentralized rollup sequencers, as the settlement layer is where disputes are resolved.
3.5. Project Operation Process
Current users who want to experience and interact with EigenLayer can do so through two methods: liquidity re-staking and native re-staking. The difference between the two lies in the latter being applicable to staking users with self-operated validating nodes.
3.5.1. Liquidity Re-staking
In the current stage, EigenLayer supports three types of liquidity staking derivatives: Lido stETH (stETH), Rocket Pool ETH (rETH), and Coinbase Wrapped Stakingd ETH (cbETH). For stability reasons, EigenLayer temporarily imposes limits on the protocol’s TVL (Total Value Locked) and the amount of single deposits. In terms of TVL, the limits for the three assets stETH, rETH, and cbETH are all 15,000 tokens (approximately 45,000 ETH) in total. As for the amount of single deposits, users are required to deposit only 32 tokens each time.
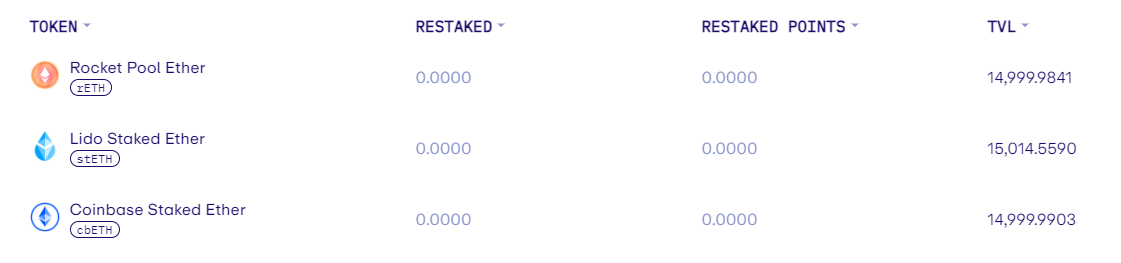
Before performing any operations, users need to prepare a certain amount of stETH, rETH, or cbETH.
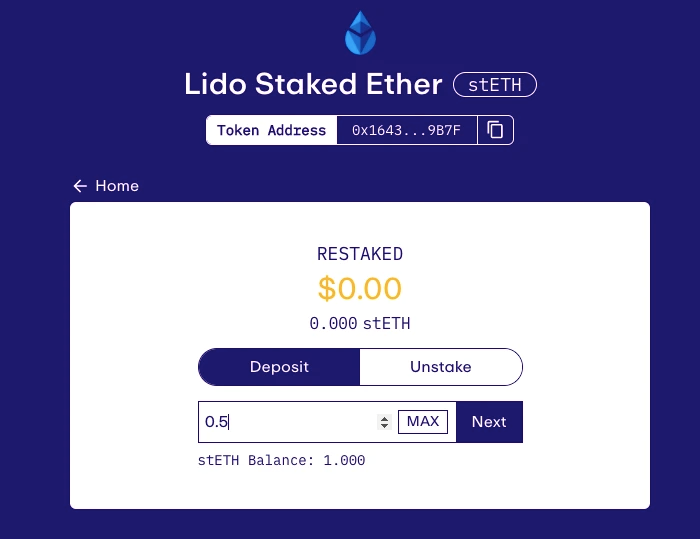
Take stETH as an example, after clicking on the stETH section on the project’s official website, you will be redirected to the corresponding re-staking page. Next, users need to input the amount of stETH they want to re-stake, click “Next,” complete the authorization (there will be a prompt for “Customize Max Spend,” just select the maximum), and confirm two transactions. When you see “Deposit Successful,” it means the re-staking is successful.
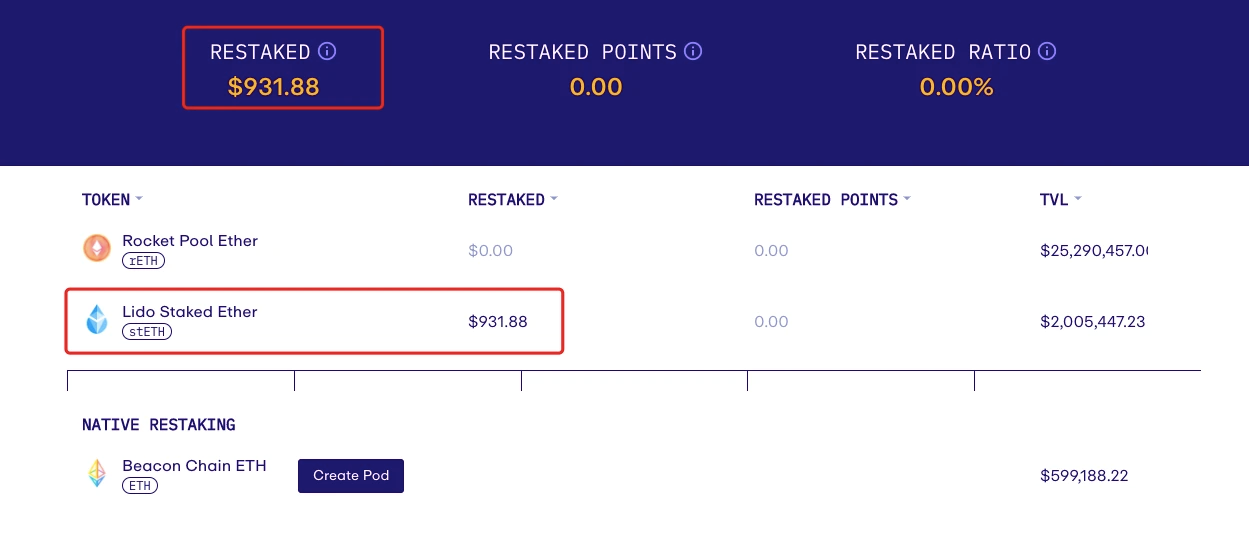
After returning to the homepage, you can directly track the changes in the rewards of your re-staked stETH.
After completing the re-staking, we can also withdraw our assets through unstaking. The specific method is to select “UnStaking” on the re-staking page of the specific token. Regarding unstaking, it is important to note that it takes 7 days of the safety period to withdraw funds from EigenLayer. Therefore, you must wait at least 7 days before withdrawing assets.
3.5.2. Native Re-staking
Unlike liquidity re-staking, native re-staking requires users to independently operate validation nodes, so there are relatively higher technical and financial thresholds for users (also 32 ETH, but the restrictions on liquidity re-staking will be relaxed in the future, while this is a mandatory requirement for staking on the Ethereum mainnet, and it is unlikely to change in the future).
For this method, EigenLayer has also set a TVL limit of 9600 ETH, but currently only 8832 ETH has been deposited (which translates to 276 addresses making deposits), leaving some space.

For users who are independently operating validation nodes and want to re-stake through this method, they can refer to the tutorial provided in the official documentation to allocate the withdrawal credentials of the validator to the EigenPods address. The specific deposit operation consists of four steps.
First, go to the project’s official website and connect your wallet.
Then, click “Create EigenPod” to create an EigenPods. After successful creation, click “Pod Details” to obtain the specific address of the EigenPods.
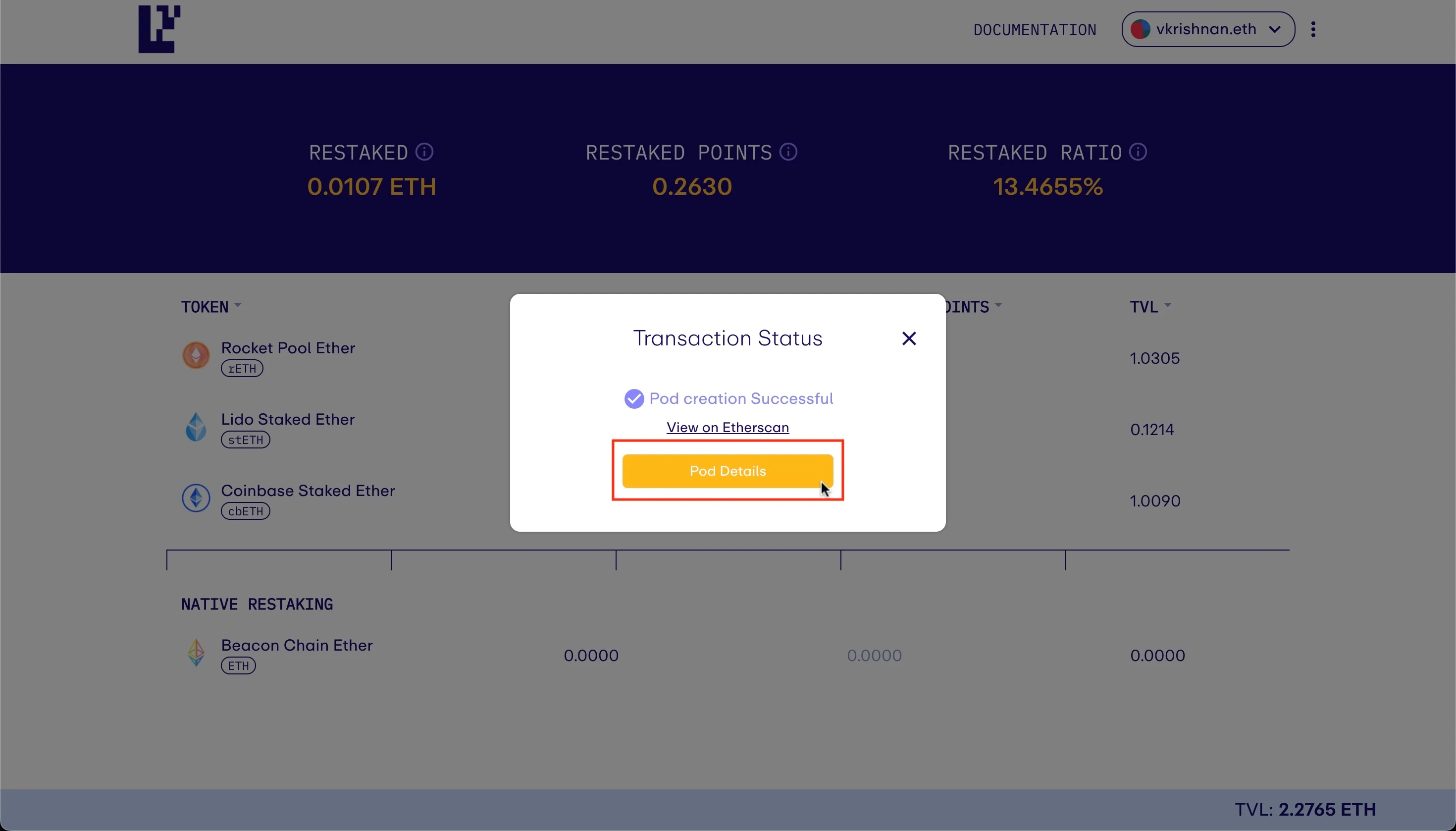
Next, the user needs to configure the withdrawal credentials on the Beacon chain to the EigenPods address (to complete this step, you need to run an Ethereum validation node).
Finally, you can also return to the homepage to monitor the changes in your re-staking rewards in real-time.
3.6. Project Data
3.6.1. Re-staking Data
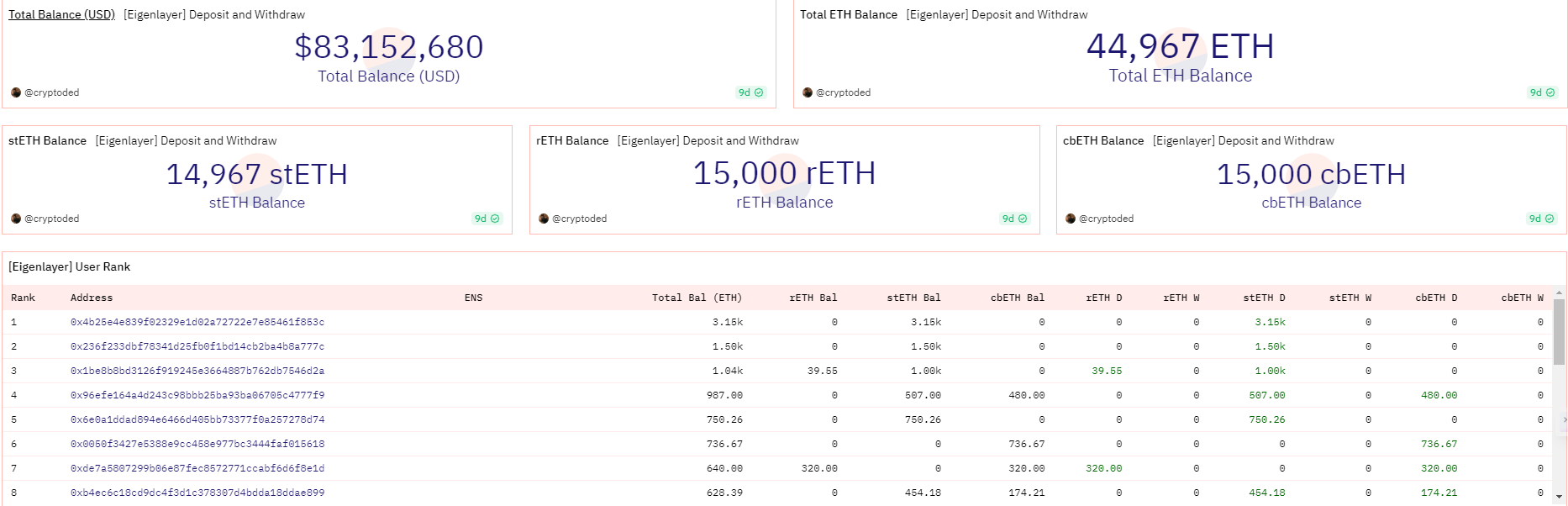
According to the data from the EigenLayer official website, as of August 1, 2023, EigenLayer has 10 supported modules and 55670.57 ETH has been re-staked. These modules include EigenDA, The Graph, Chainlink, tBTC, API3, Gravity Bridge, Threshold ECDSA, iExec, etc. These modules cover various types such as data availability layer, oracle networks, bridges, threshold encryption schemes, trusted execution environments, etc., demonstrating EigenLayer’s wide applicability and compatibility. These modules are also among the most excellent and well-known projects in the blockchain field, demonstrating EigenLayer’s high quality and standards. These data indicate that EigenLayer has achieved certain achievements and influence, and also indicate that EigenLayer still has great development space and potential.
3.6.2. Social Media Data
As of August 1, 2023, EigenLayer has performed well on social media platforms, indicating high project popularity. Currently, EigenLayer’s Discord account has attracted over 126,000 followers, with a daily online population of over 7,300 people, making it one of the most popular channels. Additionally, there is frequent interaction on Twitter. Below are the specific data for each platform:
4. Industry Space and Potential
4.1. Track Analysis
4.1.1. Project Classification
EigenLayer is a blockchain infrastructure platform that focuses on the liquidity staking field of ETH, specifically in the ETH re-staking track.
4.1.2. Market Size
According to Staking Rewards data, as of August 1, 2023, the total value locked (TVL) in the global staking market is $12.2 trillion, with Ethereum occupying the largest share at $403 billion. Other major staking networks include Solana, Cardano, Polkadot, Avalanche, Cosmos, etc.
According to DeFi Llama data, as of August 1, 2023, the total value locked (TVL) in the global staking market is $20.14 billion, with Lido occupying the largest share at $14.74 billion. Lido is a liquidity staking protocol that allows users to stake ETH on the Ethereum 2.0 network and receive equivalent stETH tokens, which can be used in the DeFi market or staked again. Other major re-staking protocols include EigenLayer, Tenet, etc.
4.1.3. Core Competitive Factors
1) Staking Size
Asset size refers to the total amount staked in the staking pool. We believe that an excellent staking platform should have a high asset size to reflect its stability and credibility.
2) Security
Protecting user assets is the most important goal of staking projects. Re-staking projects need to ensure that users’ assets are not lost due to smart contract vulnerabilities, improper validator behavior, or hacker attacks. Therefore, high-level security measures and risk management mechanisms such as multi-signature, firewall, insurance, and penalties are required.
3) Yield
Re-staking projects need to provide higher yields than single staking to attract user participation. Therefore, optimizing staking strategies, income and reward distribution, utilizing compounding effects, etc., are necessary to increase user capital efficiency and returns.
4) Liquidity
Re-staking projects need to address the liquidity issue of staked assets, allowing users to join or exit staking at any time or transfer staked assets to other protocols or platforms. Therefore, services such as liquidity staking tokens, liquidity mining, and lending markets are needed to enhance user liquidity and freedom.
5) Ecosystem
Re-staking projects need to establish a strong ecosystem to support validation services for multiple PoS networks and protocols, thereby enhancing network security and decentralization. At the same time, it also provides users with more choices and opportunities, so it is necessary to collaborate and integrate with other blockchain platforms, DeFi applications, Layer 2 protocols, etc.
4.1.4. Competing Projects
EigenLayer is a pioneer and innovator in the re-staking field. Currently, there are no obvious competitors in its re-staking track. As an innovative concept, it has not been fully replicated or imitated by other protocols, and the market is still in its early stages with few participants.
However, EigenLayer’s re-staking track may face some potential competition or challenges, such as:
1) Other LSD protocols may develop their own re-staking features, such as Lido Finance, Rocket Pool, etc.
2) Other data availability and governance services protocols may develop their own LSD functions, such as The Graph, Aragon, etc.
3) Other Layer 2 or cross-chain protocols may develop their own security and trust networks, such as Polygon, Cosmos, etc.
Meanwhile, as EigenLayer mainly adopts LSD as collateral, LSDFi projects in the market will also compete for LSD market share. We currently consider projects in this track as competitors.
1) Introduction to LSDFI
LSDFi refers to a DeFi protocol built on the basis of liquidity staking derivatives (LSD). By providing additional income opportunities, the LSDFi protocol allows LSD holders to utilize their assets and maximize profits. The LSDFi protocol has experienced rapid growth in the past few months, benefiting from the popularity of liquidity staking. The total locked value (TVL) of the most popular LSDFi protocol has exceeded 400 million USD, and the growth momentum of LSDFi includes the increase in ETH staking and the current low penetration rate of LSDFi. Currently, the TVL of the LSDFi protocol accounts for less than 3% of the reachable market.
Some typical LSDFi protocols include Lybra Finance, Gravita Protocol, Curve Finance, Alchemix, Unsheth, Origin DeFi, Asymetrix, Pendle, and FlashStaking.
2) Asset Scale Comparison
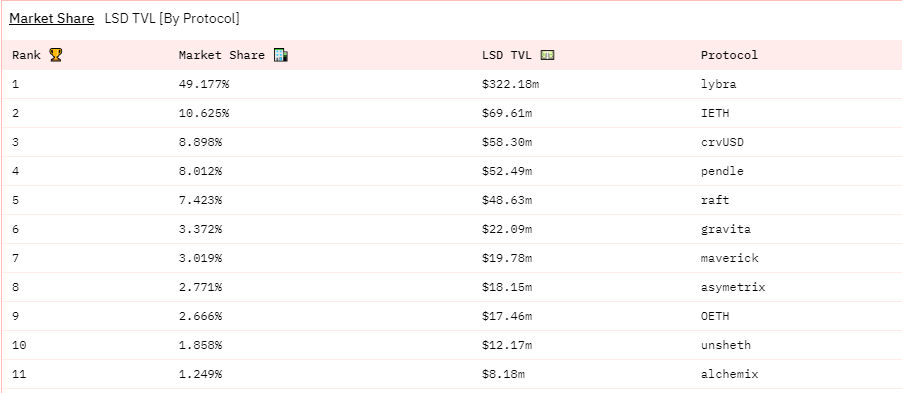
Currently, the staked blue-chip collateral of LSDFi includes stETH, wstETH, rETH, and cbETH, which are all derivatives of LSD and represent different LSD protocols. The total locked value (TVL) of LSDFi has exceeded 400 million USD, demonstrating the strong liquidity demand for LSD.
EigenLayer currently supports stETH, rETH, and cbETH as re-staking assets. The TVL of EigenLayer is 103 million USD (55709 ETH), accounting for approximately 25.75% of the LSDFi TVL. EigenLayer still has great growth potential.
3) Similarities and differences between EigenLayer’s re-staking and LSDFI
Both EigenLayer and LSDFi are innovative protocols based on LSD, which allow LSD holders to gain additional income and governance rights. The differences mainly come from the aspect of security: EigenLayer allows LSD to share the trust layer of ETH, improving the security and availability of the LSD project. At the same time, it matches LSD holders with protocols or services that require security and trust through an open market, and allows LSD holders to customize their re-staking conditions and risk preferences.
On the other hand, LSDFi’s LSD project relies on its own security rather than sharing the trust layer of ETH.
4.2 Token Economics Analysis
4.2.1 Total Token Supply and Distribution
Currently, EigenLayer does not have its own token, but it may be issued in the future. Stay tuned.
4.2.2 Token Value Capture
Based on the analysis of the EigenLayer project, if EigenLayer issues tokens, the token value may be captured through the following aspects:
① Governance: Token holders can participate in the decision-making of EigenLayer’s protocol parameters and direction.
② Income: Token holders can share the protocol revenue and rewards of EigenLayer, such as fees and rewards from re-staking protocols or services.
③ Collateral: Token holders can use EigenLayer tokens as collateral to participate in the security and trust of other protocols or services.
4.2.3 Core Demand for Tokens
Based on the analysis of the EigenLayer project, the core demand for EigenLayer tokens may include the following:
- LSD holders: They can re-stake their LSD in other protocols or services through EigenLayer, thereby gaining dual income and governance rights.
- Protocols or services that require security and trust: They can utilize the trust layer of ETH through EigenLayer, thereby reducing their security costs and risks.
5. Preliminary Value Assessment
5.1. Core Question
Which stage of the business cycle is the project in? Is it in the mature stage or the early to middle stage of development?
EigenLayer is a relatively new project. It was established in 2021 and completed its seed round financing in May 2022, followed by Series A financing in February 2023. EigenLayer has currently launched its Phase 1 mainnet. The next phase of EigenLayer will introduce Operators who will be responsible for executing validation tasks for AVS (Active Verification Services) built on the EigenLayer protocol. Currently, 10 modules are supported. EigenLayer has a large market size and potential, but it also faces challenges and risks such as technical difficulties, ecosystem compatibility, and market competitiveness. EigenLayer needs to continuously innovate, build the ecosystem, and promote the market to achieve its vision and goals. Therefore, EigenLayer is still in the early stage of development with great potential for growth.
Does the project have a reliable competitive advantage? Where does this competitive advantage come from?
- Innovation: EigenLayer introduces the novel cryptographic economic security primitive of re-staking, allowing Ethereum consensus layer stakers to choose to validate other modules and earn additional income and influence. This mechanism is unprecedented in the blockchain field and is also a trend and direction for future development.
- Technological advantage: EigenLayer utilizes Ethereum consensus layer stakers as validators, providing a high degree of decentralization and security, avoiding trust risks associated with centralized service providers or proprietary tokens.
- EigenLayer provides a free market mechanism for stakers and modules to choose and pay based on risk and return, thereby improving efficiency and flexibility and avoiding rigid governance structures.
- Scalability: EigenLayer supports various types and levels of blockchain technologies, including consensus protocols, data availability layers, virtual machines, guardian networks, oracle networks, bridges, threshold encryption schemes, trusted execution environments, etc. These technologies are among the most important and active in the blockchain field and have the most potential and prospects for future development. EigenLayer can provide fundamental services such as security, scalability, and interoperability for these technologies, promoting innovation and diversity in blockchain applications.
- Influence: EigenLayer expands Ethereum’s trust network, allowing any system to absorb Ethereum pool security, thereby increasing the value and influence of Ethereum. EigenLayer has also attracted some of the best and most well-known projects in the blockchain field as supported modules, such as The Graph, Chainlink, tBTC, API3, Gravity Bridge, etc. EigenLayer has also gained support and recognition from some of the most authoritative and influential investment institutions and individuals in the blockchain industry, such as Blockchain Capital, Coinbase Ventures, Spencer Bogart, etc.
What are the main variables in the project’s operation? Are these factors easy to quantify and measure?
- Re-staking amount: The re-staking amount refers to the quantity of ETH or liquid tokens re-staked through EigenLayer. It reflects the trust and participation of stakers in EigenLayer, as well as the market share and revenue scale of EigenLayer. The higher the re-staking amount, the more popular and supported EigenLayer is by stakers, and the more competitive and influential EigenLayer becomes. The re-staking amount is an easily quantifiable and measurable factor, which can be obtained through the EigenLayer official website or other data platforms.
- Number of supported modules: The number of supported modules refers to the quantity of software modules that can be obtained and interfaces for obtaining validating nodes through EigenLayer. It reflects the demand and level of selection of modules for EigenLayer, as well as the ecological compatibility and service scope of EigenLayer. The more supported modules, the better EigenLayer can meet the needs and expectations of modules, and the more scalable and diverse EigenLayer becomes. The number of supported modules is an easily quantifiable and measurable factor, which can be obtained through the EigenLayer official website or other data platforms.
- Verification service quality: Verification service quality refers to the effectiveness and level of the verification services provided by EigenLayer for modules. It reflects the technical capabilities and user experience of EigenLayer, as well as the value capture and creation of EigenLayer. The higher the quality of the verification service, the better EigenLayer can guarantee the security, scalability, and interoperability of modules, and the better services and experiences EigenLayer can provide. Verification service quality is a factor that is not easily quantifiable and measurable, but can be evaluated through indicators or standards such as the number and distribution of validating nodes, stability, response speed, accuracy, fee rate, reward rate, penalty rate, etc.
What are the project’s management and governance methods?
EigenLayer adopts a reputation-based committee for governance, consisting of well-known individuals from the Ethereum and EigenLayer communities. This committee will be responsible for upgrading, reviewing, and vetoing confiscation events of the EigenLayer contract, as well as allowing new AVS to enter the confiscation review process.
AVS can utilize this committee to guarantee re-delegators in EigenLayer that they will not be subjected to malicious confiscation or erroneous confiscation. At the same time, AVS developers can conduct actual testing on code libraries related to AVS. Once mature and gaining the trust of re-delegators, AVS can stop using the committee as a backup. AVS may require the committee to conduct security audits and other due diligence, including checking the system requirements for validators serving AVS, when being created on EigenLayer.
6. SWOT Analysis
6.1. Project Advantages (Strengths)
Trinity of benefits: Through the re-delegation scheme proposed by EigenLayer, in addition to capturing benefits in the Ethereum system, liquidity tokens can also receive benefits in other cross-chain bridges, oracles, etc. If LP staking of lsdETH is launched in the future, it can achieve a trinity of benefits: staking Ethereum, rewards for constructing and validating nodes, rewards for liquidity token staking in DeFi LP.
For users, this is also an additional opportunity for value-added. Combined with liquidity staking derivatives, it can significantly improve the capital efficiency of the network.
Increasing market efficiency: Unlocking the liquidity of LSD and LP tokens provides more asset choices and combinations for the DeFi industry. By renting the security of Ethereum on the public market of EigenLayer, the new protocol can save costs in internal guidance and maintenance.
Enhancing network security: Increasing the security of networks using liquidity staking allows more assets to be staked, thereby increasing the value and resistance to attacks of the network, promoting the economic security of Ethereum, and providing security for application protocols, forming a positive feedback loop.
Reducing project entry barriers: New blockchain projects need to establish their own trust layer to ensure the security of data and funds. This requires a lot of time and money, and also increases the difficulty of launching. If the staking of Ethereum on the Ethereum beacon chain can be used as a trust layer, it can reduce costs and entry barriers, improve core functionality, and enhance user experience.
6.2. Project Disadvantages (Weaknesses)
Asset loss risk: If nodes or networks are attacked, forked, or subjected to improper behavior, the assets of re-delegators may be confiscated, resulting in partial or permanent loss.
Asset bubble risk: If there are too many tokens or stablecoins in the market, it may lead to the inflation or deviation of asset values from their true values, increasing market instability and investor confusion.
Value Capture Risk: If the security and incentives provided by EigenLayer are not sufficient to attract protocols and validators, it may result in the loss of protocol sovereignty, decreased value of collaborative projects, or slow development of the ecosystem.
Unstaking Lock-up Risk: If there is a waiting period for unlocking the staked ETH when unstaking, users may face liquidity and price volatility risks.
Trust Leveraging Risk from Restaking: In a public trust trading market, trust layer nodes can provide verification services for different protocols through restaking to earn additional income. When trust layer funds provide verification services for highly valued applications/middleware layers to earn more profits, it may lead to extreme leverage of trust, where the cost of disruption is higher than the benefits, thus reducing the economic security of the trust layer.
6.3. Project Opportunities
Leadership and Innovation: Restaking is a unique concept with no direct competitors in the field, and it has not been completely copied or imitated by other protocols. Additionally, the market is still in its early stages with few participants.
Market Share: Currently, the largest market in the DeFi industry is Staking, with a total value of approximately $20 billion (TVL). Especially now, as many blockchain platforms are still under development, the scale of the cryptocurrency market is constantly expanding. Therefore, the ReStaking market will have numerous growth opportunities.
6.4. Project Threats
Tokenomics Issues: If users can earn profits by restaking ETH without using the native tokens of other protocols, EigenLayer’s native token may lack value and demand.
Reward Distribution Issues: If the protocol cannot balance the incentives for existing participants and restaking participants when adopting EigenLayer, it may result in unfair token distribution and low user engagement.
Security Event Risk: If a significant portion of staked ETH in the Ethereum network is restaked, any security vulnerability in a protocol may lead to a significant amount of ETH being confiscated, thereby affecting the security of the Ethereum network.
Technical Risk: EigenLayer involves multiple types and levels of blockchain technology, which may have technical defects or vulnerabilities that could cause system crashes or attacks. These technical risks may result in asset losses or trust losses for stakers and modules, affecting the reputation and development of the project. EigenLayer needs to mitigate technical risks through rigorous code audits, testnet deployments, and security incentives.
7. References
https://www.eigenlayer.xyz/about#mission EigenLayer Project Official Website
https://docs.eigenlayer.xyz/overview/readme/protocol-features
EigenLayer Project DOC
https://twitter.com/eigenlayer EigenLayer Official Twitter
https://forum.eigenlayer.xyz/c/new-lst-token-on-eigenlayer/21
EigenLayer Official Forum
https://www.blog.eigenlayer.xyz/ EigenLayer Official Blog
https://2039955362-files.gitbook.io/~/files/v0/b/gitbook-x-prod.appsp ot.com/o/sLianGuaices%2FPy2Kmkwju3mPSo9jrKKt%2Fuploads%2F9tExk4U2OdiRKGEsUW qW%2FEigenLayer_WhiteLianGuaiper.pdf?alt=media&token=c20ac4bd-badd-4826-9fb 6-492923741c9e EigenLayer Whitepaper
https://www.odaily.news/post/5185244 In-depth interpretation of the EigenLayer whitepaper: scaling of the consensus layer, LSD important development direction
– Investment Risks and Disclaimers –
The content analysis provided in this report is for reference information only and does not constitute any form of investment advice or decision-making basis. We strongly recommend that you do not engage in any investment activities based on this report to avoid potential risks. WJB and the report author are not responsible for any investment results made by users based on this report.
The preparation time of this report is the date shown, and subsequent changes in the market or economic conditions may cause the content to change, so the report may not fully reflect these changes. The graphics, charts, and other visual aids in the report are for reference only and cannot be used as a basis for making investment decisions. Any graphics, charts, or other visual aids in the report cannot cover all the factors and variables required to make such decisions. Please note that WJB does not assist anyone in making specific investment decisions.
Some of the discussions mentioned in this report may be WJB’s assumptions about future expectations and other forward-looking views. However, these assumptions and views are subject to known and unknown risks and uncertainties, which may result in significant differences between actual results, performance, or events and the stated views and assumptions.
All speculations, forecasts, and estimates contained in this report are based on certain assumptions and are speculative in nature. These forward-looking statements may prove to be incorrect and may be affected by incorrect assumptions or known or unknown risks, uncertainties, and other factors, most of which are beyond control. It is expected that some or all of these forward-looking assumptions will not be realized or will differ significantly from actual results.
– Copyright Information –
This report is the copyright of WJB only. Without written permission, any organization or individual may not infringe WJB’s copyright by means of reproduction, copying, quotation, or redistribution to others.
We will continue to update Blocking; if you have any questions or suggestions, please contact us!
Was this article helpful?
93 out of 132 found this helpful
Related articles
- The hype of room-temperature superconductor triggers the meme token craze of LK-99 Innovation or cutting-edge?
- AlterVerse Research Report Web3 Sandbox Game Based on Binance Chain
- LianGuai Daily | Hackers have returned all stolen funds to Alchemix Curve pool; US SEC provides over $104 million in rewards to 7 whistleblowers
- Decoding Decentralized Order Book The Best Combination of Pricing Quality and Fund Security
- LianGuai Daily | Coinbase, Block, and Apple release quarterly reports; X Company is seeking data partners to establish a trading platform.
- Ether Futures ETF Applications Pile Up, Is the Gear of Crypto ETF’s Fate Starting to Turn?
- Developer’s Guide How to Build Products on the Base Mainnet?





