Understanding Cascade: The First Rollup to Support IBC
Cascade: First Rollup Supporting IBCAuthor: Eclipse; Translator: Blockingxiaozou
As blockchain technology evolves, the need for seamless communication between different chains becomes crucial. IBC (Inter-Blockchain Communication Protocol) is a breakthrough protocol that enables data transfer between any two blockchains. In this article, we will delve into the main components of IBC, explore how IBC works, focus on its unique advantages compared to other communication solutions, and examine its recent implementation on the first cross-chain SVM (Solana Virtual Machinerollup) Rollup Cascad.
1 The Main Components of IBC
The core of IBC is defining a set of standards for managing identity verification and data transfer between two chains. To successfully communicate using IBC, the following components are needed:
- Be wary of the eth_sign blind signature scam: introduction, methods, and prevention
- WOO X responded that all accusations of misappropriation of assets and insolvency are false information that can be verified through public data.
- Decoding a16z Fundraising Deck: Why is the gaming industry worth doubling down on?
(1) Deploying IBC core communication protocols on each chain;
(2) For each chain, a light client on the other chain can verify block integrity and consensus information;
(3) A chain-side program called a relayer is responsible for querying IBC messages on each chain and delivering the corresponding IBC messages to the other chain when necessary.
2 How IBC Works
To initiate communication between two chains using IBC, a connection and a channel need to be established. The process is similar to the TLS handshake protocol and consists of four steps: open-init (A), open-try (B), open-ack (A), and open-confirm (B), where A and B represent the involved chains.
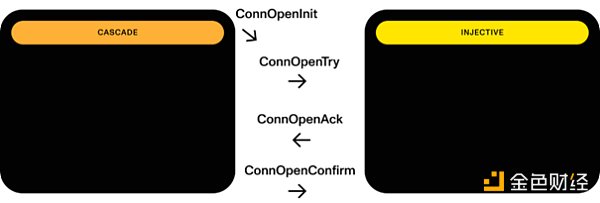
Once the channel is open, an application on one chain can begin sending messages to the other chain in the form of data packets through a two-step process: send (A) and ack (B).
Homogeneous token transfer (e.g., ERC-20 or SPL tokens) is implemented as an additional protocol on top of the generic data packet send interface and is specified in ICS 20. The token transfer applications on both sides will verify the validity of the token transfer, then burn the tokens at the sending end to have the receiving end receive them.
3 How IBC Differs from Other Communication Solutions
The difference between IBC and other communication solutions lies in its security model. IBC’s trust is entirely dependent on the correct implementation of the core protocol on each chain and the accurate verification of data by light clients. No additional trust assumptions are required, even for relayers responsible for transmitting messages between chains.
This is different from the trust model of Hyperlane or Wormhole, which rely on a guardian network of bridge operators to properly protect them from hacker attacks. However, security in IBC comes at a cost: implementing IBC communication between two chains is more time-consuming, as each chain requires the writing of two corresponding light clients, which must be validated for correctness and security.
In other words, IBC is to Hyperlane what Uniswap is to Coinbase: IBC is more decentralized, requires no trust assumptions beyond its own implementation, but correct implementation may be difficult, much like ordinary smart contracts.
4 How does IBC work on Cascade?
Cascade is the first cross-chain SVM rollup developed by Injective and Eclipse, which elevates the integration of IBC to a new level. By allowing Solana developers to seamlessly deploy their contracts and dApps to Injective, Cascade expands the possibilities of cross-chain communication. Although Eclipse is not built with the Cosmos SDK, it has added support for IBC to unlock the full potential of this cross-chain rollup.
Cascade is now running on the Injective testnet and is planned to be migrated to the mainnet in the near future. Developers who want to delve deeper into the features of Cascade can check out the comprehensive Cascade developer documentation:
https://docs.cascadehq.xyz/cascade-docs/cascade-developer-documentation
We will continue to update Blocking; if you have any questions or suggestions, please contact us!
Was this article helpful?
93 out of 132 found this helpful
Related articles
- Hotbit suddenly announced its closure. Is it a reshuffle in the industry or a trend?
- How will the Ethereum Cancun upgrade change the Layer2 landscape?
- Founder of EigenLayer Responds to Vitalik’s New Article: Consistent with the Staking Philosophy
- How has the ecosystem of Polygon zkEVM developed in the past 2 months?
- Ethereum Singapore 2023 will build a communication bridge between over 2000 Web3 developers, talents, and the local ecosystem.
- Tornado Cash is hit by a malicious governance attack, and the latest recovery proposal may be an attempt by the attacker to inflate the coin price and sell off.
- Over $76 billion in funds have been stolen, taking stock of six major tools for securing cryptocurrency assets






